Redis-cli Go代码
安装
go get github.com/redis/go-redis/v9
建立连接
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"github.com/redis/go-redis/v9"
)
client := redis.NewClient(&redis.Options{
Addr: "localhost:6379",
Password: "", // no password set
DB: 0, // use default DB
})
Options 配置
// Options keeps the settings to set up redis connection.
type Options struct {
// The network type, either tcp or unix.
// Default is tcp.
Network string
// host:port address.
Addr string
// ClientName will execute the `CLIENT SETNAME ClientName` command for each conn.
ClientName string
// Dialer creates new network connection and has priority over
// Network and Addr options.
Dialer func(ctx context.Context, network, addr string) (net.Conn, error)
// Hook that is called when new connection is established.
OnConnect func(ctx context.Context, cn *Conn) error
// Use the specified Username to authenticate the current connection
// with one of the connections defined in the ACL list when connecting
// to a Redis 6.0 instance, or greater, that is using the Redis ACL system.
Username string
// Optional password. Must match the password specified in the
// requirepass server configuration option (if connecting to a Redis 5.0 instance, or lower),
// or the User Password when connecting to a Redis 6.0 instance, or greater,
// that is using the Redis ACL system.
Password string
// CredentialsProvider allows the username and password to be updated
// before reconnecting. It should return the current username and password.
CredentialsProvider func() (username string, password string)
// Database to be selected after connecting to the server.
DB int
// Maximum number of retries before giving up.
// Default is 3 retries; -1 (not 0) disables retries.
MaxRetries int
// Minimum backoff between each retry.
// Default is 8 milliseconds; -1 disables backoff.
MinRetryBackoff time.Duration
// Maximum backoff between each retry.
// Default is 512 milliseconds; -1 disables backoff.
MaxRetryBackoff time.Duration
// Dial timeout for establishing new connections.
// Default is 5 seconds.
DialTimeout time.Duration
// Timeout for socket reads. If reached, commands will fail
// with a timeout instead of blocking. Supported values:
// - `0` - default timeout (3 seconds).
// - `-1` - no timeout (block indefinitely).
// - `-2` - disables SetReadDeadline calls completely.
ReadTimeout time.Duration
// Timeout for socket writes. If reached, commands will fail
// with a timeout instead of blocking. Supported values:
// - `0` - default timeout (3 seconds).
// - `-1` - no timeout (block indefinitely).
// - `-2` - disables SetWriteDeadline calls completely.
WriteTimeout time.Duration
// ContextTimeoutEnabled controls whether the client respects context timeouts and deadlines.
// See https://redis.uptrace.dev/guide/go-redis-debugging.html#timeouts
ContextTimeoutEnabled bool
// Type of connection pool.
// true for FIFO pool, false for LIFO pool.
// Note that FIFO has slightly higher overhead compared to LIFO,
// but it helps closing idle connections faster reducing the pool size.
PoolFIFO bool
// Maximum number of socket connections.
// Default is 10 connections per every available CPU as reported by runtime.GOMAXPROCS.
PoolSize int
// Amount of time client waits for connection if all connections
// are busy before returning an error.
// Default is ReadTimeout + 1 second.
PoolTimeout time.Duration
// Minimum number of idle connections which is useful when establishing
// new connection is slow.
MinIdleConns int
// Maximum number of idle connections.
MaxIdleConns int
// ConnMaxIdleTime is the maximum amount of time a connection may be idle.
// Should be less than server's timeout.
//
// Expired connections may be closed lazily before reuse.
// If d <= 0, connections are not closed due to a connection's idle time.
//
// Default is 30 minutes. -1 disables idle timeout check.
ConnMaxIdleTime time.Duration
// ConnMaxLifetime is the maximum amount of time a connection may be reused.
//
// Expired connections may be closed lazily before reuse.
// If <= 0, connections are not closed due to a connection's age.
//
// Default is to not close idle connections.
ConnMaxLifetime time.Duration
// TLS Config to use. When set, TLS will be negotiated.
TLSConfig *tls.Config
// Limiter interface used to implement circuit breaker or rate limiter.
Limiter Limiter
// Enables read only queries on slave/follower nodes.
readOnly bool
}
初始化连接
var Client *redis.Client
// 建立新连接时的回调
func OnConnect(ctx context.Context, cn *redis.Conn) error {
if cn != nil {
fmt.Println("connect ok")
}
return nil
}
//初始化redis
func InitRedis() {
if Client == nil {
fmt.Println("init client")
Client = redis.NewClient(&redis.Options{
Addr: "localhost:6379",
Password: "", // no password set
DB: 0, // use default DB
OnConnect: OnConnect,
})
}
}
// Set
func Set(ctx context.Context, key string, val interface{}, duration time.Duration) error {
return Client.Set(ctx, key, val, duration).Err()
}
// Get
func Get(ctx context.Context, key string) string {
val, err := Client.Get(ctx, key).Result()
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
return val
}
string 测试Get Set 方法
func TestRedis(t *testing.T) {
InitRedis()
ctx := context.Background()
err := Set(ctx, "zdm", "赵德满", 1*time.Hour)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err.Error())
}
fmt.Println(Get(ctx, "zdm"))
}

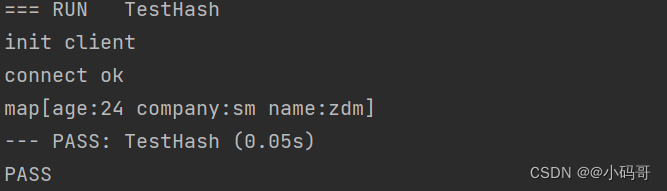
存储hash
func TestHash(t *testing.T) {
InitRedis()
session := map[string]string{"name":"zdm","company":"sm","age":"24"}
ctx := context.Background()
for k,v := range session {
err := HSet(ctx,"user:session",k,v)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err.Error())
}
}
res,err := HGetAll(ctx,"user:session")
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err.Error())
}
fmt.Println(res)
}
连接到Redis群集
var ReCluster *redis.ClusterClient
func InitRedisCluster() {
if ReCluster == nil {
ReCluster = redis.NewClusterClient(&redis.ClusterOptions{
Addrs: []string{":16379", ":16380", ":16381", ":16382", ":16383", ":16384"},
// To route commands by latency or randomly, enable one of the following.
//RouteByLatency: true,
//RouteRandomly: true,
})
}
}
使用Redis 集群扩展
Redis使用称为Redis Cluster的部署拓扑进行水平扩展。本主题将教您如何在生产中设置、测试和操作Redis集群。您将从最终用户的角度了解Redis Cluster的可用性和一致性特征。
如果您计划运行生产Redis Cluster部署,或者想更好地了解Redis Cluster如何在内部工作,请参阅Redis Cluster规范(https://redis.io/docs/reference/cluster-spec/)。要了解Redis Enterprise如何处理缩放,请参阅Redis Enterprise的线性缩放(https://redis.com/redis-enterprise/technology/linear-scaling-redis-enterprise)。
创建和使用一个Redis 集群
包含以下几个步骤
- Create a Redis Cluster (创建一个Redis 集群)
- Interact with the cluster (与集群交互)
- Write an example app with redis-rb-cluster (编写一个带有redis-rb集群的示例应用程序)
- Reshard the cluster
- A more interesting example application
- Test the failover (测试故障切换)
- Manual failover (手动故障转移)
- Add a new node (添加一个新节点)
- Remove a node (移除一个新节点)
- Replica migration (复制副本迁移)
- Upgrade nodes in a Redis Cluster (升级redis 中集群的节点)
- 迁移到Redis群集 (迁移到redis 集群)
首先我们要熟悉创建集群的要求
Requirements to create a Redis Cluster (创建集群的要求)
To create a cluster, the first thing you need is to have a few empty Redis instances running in cluster mode.
At minimum, set the following directives in the redis.conf file:
要创建一个集群,首先需要有几个空的Redis实例在集群模式下运行。
至少在redis.conf文件中设置以下指令:
port 7000
cluster-enabled yes
cluster-config-file nodes.conf
cluster-node-timeout 5000
appendonly yes
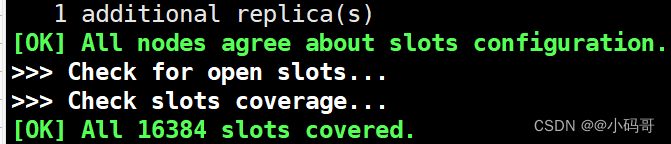
要启用群集模式,请将启用群集的指令设置为yes。每个实例还包含存储该节点配置的文件的路径,默认情况下为nodes.conf。人类永远不会接触该文件;它只是在启动时由Redis Cluster实例生成,并在每次需要时更新。
请注意,按预期工作的最小集群必须至少包含三个主节点。对于部署,我们强烈建议使用六节点集群,其中包含三个主节点和三个副本。
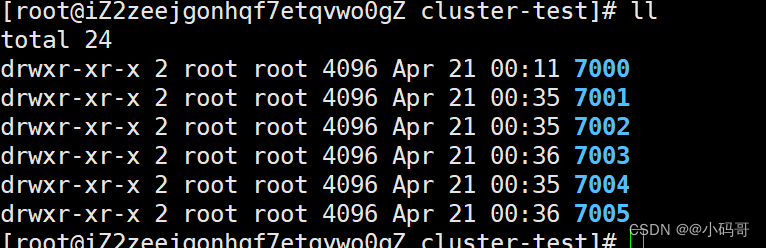
您可以通过创建以下目录来本地测试这一点,这些目录以您将在任何给定目录中运行的实例的端口号命名。
mkdir cluster-test
cd cluster-test
mkdir 7000 7001 7002 7003 7004 7005
每个文件夹下放的redis-conf 文件,port 改为对应的7001 7002…
daemonize no # 改为yes 支持后台进程启动
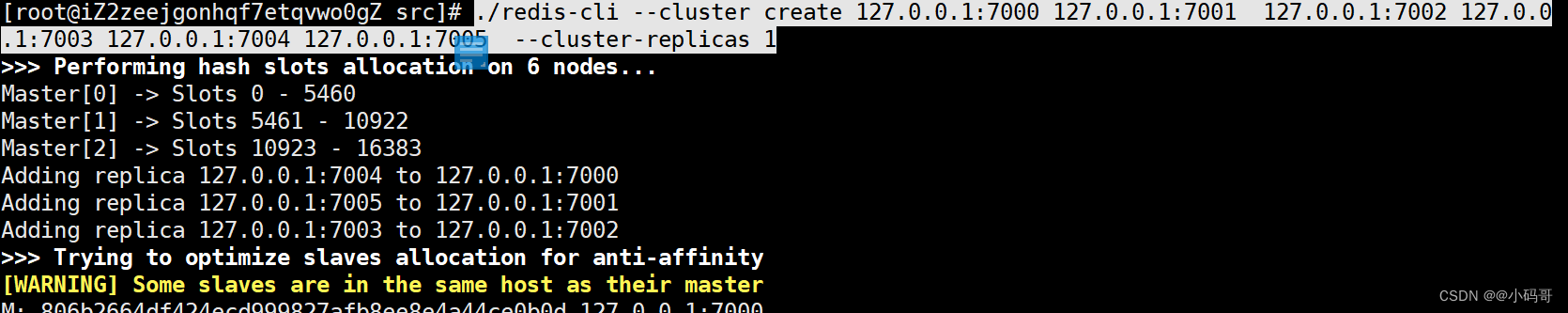
./redis-cli --cluster create 127.0.0.1:7000 127.0.0.1:7001 127.0.0.1:7002 127.0.0.1:7003 127.0.0.1:7004 127.0.0.1:7005 --cluster-replicas 1







![[架构之路-174]-《软考-系统分析师》-5-数据库系统-7-数据仓库技术与数据挖掘技术](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/06763829bfcd4264be4d1f0adc547eb3.png)