文章目录
- 写在前面
- 关于这个项目的收获
- 简单的项目介绍
- 整体逻辑与第三方库
- 每一步的具体细节
- util.hpp
- parser.cc
- index.hpp
- searcher.hpp
- http_server.hpp
- 其他模块
项目地址:boost_searcher: 项目:boost站内搜索 (gitee.com)
写在前面
这个项目是用C++写的,做完它后第一个反应是:用其他语言也可以写。也不能这么说,只是说这个项目没有体现C++的优势。但博主没有学习过其他语言,只是学过C++,所以这个观点只是我感性认识,没错,这是片面的。
至于我为什么这么说,因为我认为C++的优势是:可以直接操作内存,从而优化程序运行效率,总的来说就是快(当然这个观点也有些片面)。这个项目很关键的一步是:分词所有文档以构建索引。关于这部分,该项目原创者的演示视频中,他的机器用了半分钟就完成了索引构建,而我的机器却用了十分钟。使我一度怀疑是我的代码问题,在我不断思考对代码进行优化后(当然优化可能不够彻底),构建索引的时间依旧漫长。我分别在腾讯云和阿里云的服务器上进行了测试,时间没有差别,这两台服务器的配置都是2核2G,其中阿里云的内存还小一些,每次构建索引时,程序占用的cpu资源都超过了95%。
当我排除了服务器问题,想着继续优化代码时,我直接clone项目原创者的代码到服务器,运行他的构建索引程序。得到的结果是:运行时间依然很慢,从而得出结论:问题出在服务器的配置上,要解决很简单,用钱就行了。我排查了每个模块的具体用时,发现是jieba的CutForSearch运行了太久,一遇到大文件就顶不住。所以针对自己的项目优化CutForSearch算法或者自己造轮子也能解决这个问题,至于说效果就不得而知了。这个解决方法耗时久,难度大,一头栽进去可能就偏离了原项目的方向,所以我就把它抛在一边了。
在出现这个问题之前,项目的进度按着节奏在有序的推进,问题出现后,推进的节奏就被彻底打乱。处理一个不超过20MB的网站html资源就需要超过十分钟的时间,这导致项目的调试变得困难。并且自己也逐渐对这个项目失去了兴趣,好在构建索引是整个项目的最后的核心模块,我只要再写一些简单的模块,这个项目就完成了。
关于前端代码:由于我没有系统学习过这部分知识,知识量为0,为了方便也为了快点结束这个项目,我就copy原项目作者的代码了。
关于这个项目的收获
这是博主做的第一个项目,虽然对我来说它的难度不大,并且我也没有通过它感受到C++的魅力,只能说是一个中规中矩的项目吧。但是从中也获得了
- 一些工程经验:比如一个项目整体的架构,每个模块之间的逻辑关系,阅读项目源码时的方法论
- 好的命名风格:自己在这个项目中的命名风格不够同一,甚至存在一些陷阱,之后会更加注意命名这块的规范
- 缺乏关于单例模式的经验:编写单例类时,明显不够熟练,这块需要系统性的复习下
- 一些Linux指令:ln -s / nohup / & / jobs / fg / top / netstat nltp…
总的来说,这个中规中矩的项目开了个好头,用适中的成本获得上面的收获还是值得的,唯一的瑕疵就是:服务器配置太低(大概率)。在这个项目的整理完成后,复习一段时间就开始做下一个项目:高并发内存池。两个项目完成后,就开始深入学习高性能服务器的知识。
简单的项目介绍
由于boost官网(boost.org)没有站内搜索功能,使得查找某一函数与深入学习boost库的成本变高。于是就有了这么一个项目:搜索引擎_线上分享: 搜索引擎_线上分享 (gitee.com),在看完项目源码后,我试着按照它的逻辑仿照着写了一个出来
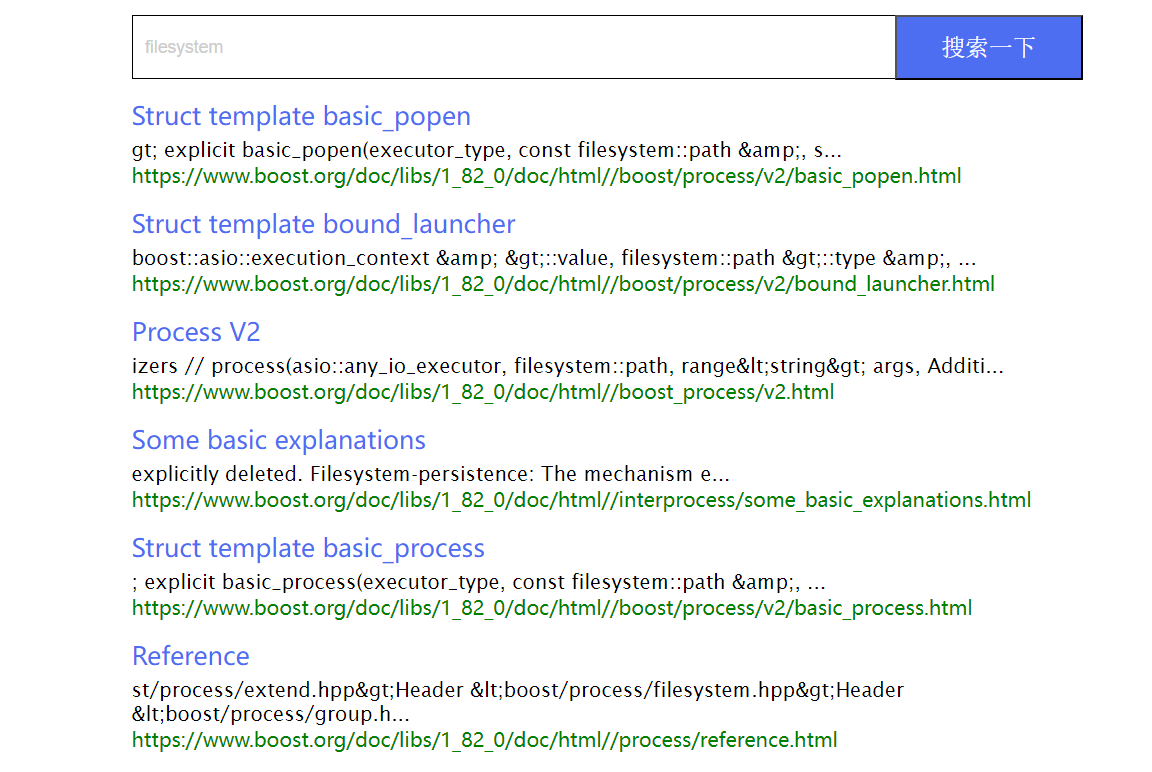
- 初始网页只有一个搜索框与搜索按钮
- 输入关键字搜索后,网页会返回相关搜索结果,其中包含了标题、内容摘要与url
- 点击标题就会重新打开一个网页,该网页则是boost官网的相关资源
整体逻辑与第三方库
- 首先对用来搜索的html文件进行parser操作,清洗得到我们需要的文档标题、内容与url
- 接着是构建索引,包括了正排与倒排两种索引
- 最后是用用户输入的关键字查找索引,将其转换成json格式进行返回
关于第三方库:
- 由于需要遍历某一路径下的html文件,需要使用boost库
- 由于构建索引需要进行分词,需要使用jiebacpp库
- 由于需要进行json转换,需要使用jsoncpp库
- 由于该服务需要需要部署到网络中,需要使用cpp-httplib库
每一步的具体细节
boost官网提供了关于boost的所有资源的下载链接,其中就包括了boost.org的html网页资源
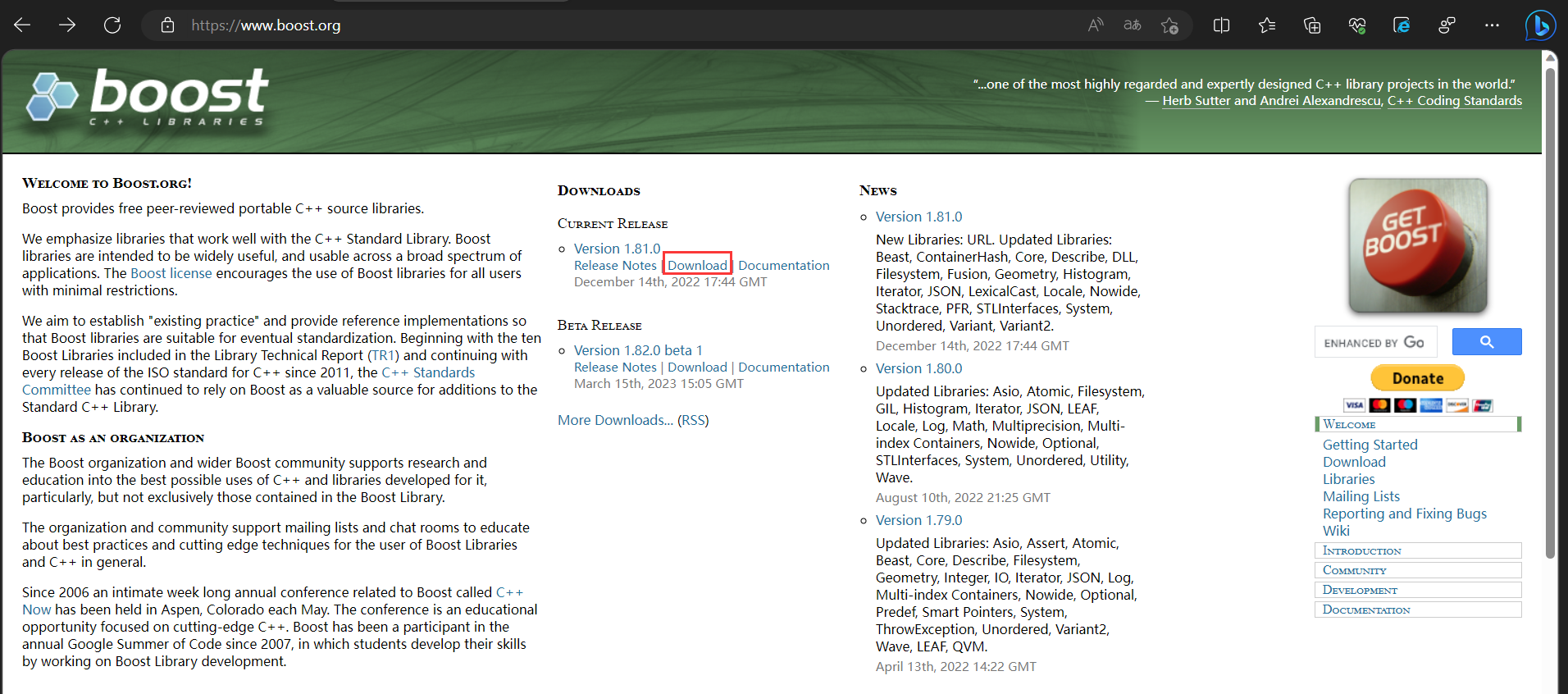
解压文件后(tar xzf [原文件名]),搜索需要使用的网页资源在boost_xxx_0/doc/html这个目录下,将该目录下的所有文件拷贝到项目路径下
(ps:下载后的压缩包可以使用rz命令上传到远端,centos环境下按照rz命令的指令是sudo yum install -y lrzsz)
util.hpp
关于工具类的头文件,其他模块会用到一些工具函数:如文件操作与字符串处理,这些操作会被封装到util.hpp头文件中
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <fstream>
#include <mutex>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <boost/algorithm/string.hpp>
#include "cppjieba/Jieba.hpp"
#include "log.hpp"
namespace ns_util
{
class FileUtil
{
public:
static bool ReadFile(const std::string& file_path, std::string* out_buffer)
{
std::ifstream file(file_path, std::ios::in);
if (!file.is_open())
{
LOG(NORMAL, "util::ReadFile fail");
return false;
}
std::string tmp;
while (std::getline(file, tmp))
{
*out_buffer += tmp;
}
file.close();
return true;
}
};
class StringUtil
{
public:
static void SplitString(std::vector<std::string>* out, const std::string& src, const std::string& sep)
{
boost::split(*out, src, boost::is_any_of(sep), boost::token_compress_on);
}
};
const char* const DICT_PATH = "./dict/jieba.dict.utf8";
const char* const HMM_PATH = "./dict/hmm_model.utf8";
const char* const USER_DICT_PATH = "./dict/user.dict.utf8";
const char* const IDF_PATH = "./dict/idf.utf8";
const char* const STOP_WORD_PATH = "./dict/stop_words.utf8";
// 该类设计成单例
class JiebaUtil
{
public:
static JiebaUtil* GetInstance()
{
if (_instance == nullptr)
{
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(_mtx);
if (_instance == nullptr)
{
_instance = new JiebaUtil();
_instance->InitJiebaUtil();
}
}
return _instance;
}
static void CutString(const std::string& src, std::vector<std::string>* out)
{
ns_util::JiebaUtil::GetInstance()->CutStringHelper(src, out);
}
private:
cppjieba::Jieba _jieba;
std::unordered_set<std::string> _stop_words;
// for singleton
static JiebaUtil* _instance;
static std::mutex _mtx;
// member function
JiebaUtil():_jieba(DICT_PATH, HMM_PATH, USER_DICT_PATH, IDF_PATH, STOP_WORD_PATH)
{}
JiebaUtil(const JiebaUtil& x) = delete;
const JiebaUtil& operator==(const JiebaUtil& x) = delete;
void InitJiebaUtil()
{
std::ifstream in(STOP_WORD_PATH, std::ios::in);
if (!in.is_open())
{
LOG(FATAL, "load stop word file error");
return;
}
std::string line;
while (std::getline(in, line))
{
_stop_words.insert(line);
}
in.close();
}
void CutStringHelper(const std::string src, std::vector<std::string>* out)
{
_jieba.CutForSearch(src, *out);
for (auto it = out->begin(); it != out->end(); )
{
if (_stop_words.count(*it))
it = out->erase(it);
else
++it;
}
}
};
// 静态成员的初始化
JiebaUtil* JiebaUtil::_instance = nullptr;
std::mutex JiebaUtil::_mtx;
}
其中封装了三个工具类:
- FileUtil:封装文件操作,打开文件
- StringUtil:封装字符串处理函数,boost库的split(以指定分隔符分割字符串)
- JiebaUtil:封装jieba分词的操作,主要函数是CutForSearch。该类被封装为单例,因为分词只需要一个进程进行
parser.cc
该模块主要功能是:清洗html文件,得到每份文件的title、content与url。
主要分为三个部分:
bool EnumFile(const std::string& src_path, std::vector<std::string>* pfiles_list);
bool ParserHtml(const std::vector<std::string>& files_list, std::vector<DocInfo>* presults);
bool SaveHtml(const std::vector<DocInfo>& results, const std::string& output_path);
- EnumFile:将指定目录下的所有文件名加载到vector<string>中
- ParserHtml:打开EnumFile加载的文件名,并进行清理,title、content与url这个三元组用DocInfo结构体保存。所以清洗的结果将保存到vector<DocInfo*>中
- SaveHtml:将ParserHtml清洗得到的所有DocInfo保存到指定目录下,三元组中的元素以’\3’分隔,三元组之间以’\n’分隔
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <boost/filesystem.hpp>
#include "util.hpp"
const std::string src_path = "data/input";
const std::string output_path = "data/orig/orig.txt";
struct DocInfo
{
std::string _title; // 标题
std::string _content; // 内容
std::string _url; // 文档在官网中的url
};
bool EnumFile(const std::string& src_path, std::vector<std::string>* pfiles_list);
bool ParserHtml(const std::vector<std::string>& files_list, std::vector<DocInfo>* presults);
bool SaveHtml(const std::vector<DocInfo>& results, const std::string& output_path);
int main()
{
std::vector<std::string> files_list;
// 1.将带路径的html文件的文件名加载到files_list中
if (!EnumFile(src_path, &files_list))
{
std::cerr << "parser::EnumFile fail" << std::endl;
return 1;
}
std::vector<DocInfo> results;
// 2.读取files_list中的文件,解析这些文件信息到results中
if (!ParserHtml(files_list, &results))
{
std::cerr << "parser::ParserHtml fail" << std::endl;
return 1;
}
// 3.将results中的所有html文件信息保存到目标文件中
if (!SaveHtml(results, output_path));
return 0;
}
bool EnumFile(const std::string& src_path, std::vector<std::string>* pfiles_list)
{
namespace fs = boost::filesystem;
fs::path root_path(src_path);
if (!fs::exists(root_path))
{
std::cerr << "parser::exist fail" << std::endl;
return false;
}
fs::recursive_directory_iterator end;
for (fs::recursive_directory_iterator it(root_path); it != end; ++it)
{
if (!fs::is_regular(*it)) continue;
if (it->path().extension() != ".html") continue;
pfiles_list->push_back(it->path().string());
}
return true;
}
bool ParserTitle(const std::string& file_content, std::string* ptitle)
{
size_t front = file_content.find("<title>");
if (front == std::string::npos) return false;
size_t back = file_content.find("</title>");
if (back == std::string::npos) return false;
front += std::string("<title>").size();
if (front > back) return false;
*ptitle = file_content.substr(front, back - front);
return true;
}
bool ParserContent(const std::string& file_content, std::string* pcontent)
{
enum STATE
{
LABLE,
CONTENT
};
STATE s = LABLE;
for (char c : file_content)
{
switch(s)
{
case LABLE:
if (c == '>')
s = CONTENT;
break;
case CONTENT:
if (c == '<')
s = LABLE;
else
{
if (c == '\n')
c = ' ';
pcontent->push_back(c);
}
break;
default:
break;
}
}
return true;
}
bool ParserUrl(const std::string& file_path, std::string* purl)
{
std::string head = "https://www.boost.org/doc/libs/1_82_0/doc/html/";
std::string tail = file_path.substr(src_path.size());
*purl = (head + tail);
return true;
}
bool ParserHtml(const std::vector<std::string>& files_list, std::vector<DocInfo>* presults)
{
for (const std::string& file_path : files_list)
{
// 读取文件信息到字符串中
std::string file_content;
DocInfo doc;
ns_util::FileUtil::ReadFile(file_path, &file_content);
if (!ParserTitle(file_content, &doc._title)) continue;
if (!ParserContent(file_content, &doc._content)) continue;
if (!ParserUrl(file_path, &doc._url)) continue;
presults->push_back(std::move(doc));
}
return true;
}
bool SaveHtml(const std::vector<DocInfo>& results, const std::string& output_path)
{
#define SEP '\3'
std::ofstream out(output_path, std::ios::out | std::ios::binary | std::ios::trunc);
if (!out.is_open())
{
std::cerr << "parser::SaveHtml fail" << std::endl;
return 1;
}
for (DocInfo result : results)
{
std::string str;
str += result._title;
str += SEP;
str += result._content;
str += SEP;
str += result._url;
str += '\n';
out.write(str.c_str(), str.size());
}
out.close();
return true;
}
关于这个模块的重点:
- 首先是boost库的filesystem模块的使用,包括了path类和recursive_directory_iterator迭代器的递归遍历。当然这些都是封装好了,明白接口的含义会调用就行
- 其次是清洗content时,由于要去除html中的标签,所以这里用到了一个简单的状态机
- 最后是要熟悉文件的相关操作以及move的资源掠夺要谨慎使用
index.hpp
该hpp封装构建索引的类:index,该类也被设计为单例,因为内存中需要存储的索引只需要一份。该类含有两个对象:正排索引和倒排索引
- 正排索引是文档id和文档内容(id、title、content和url)的映射,vector的下标可以天然作为文档的id,所以正排索引用vector进行存储。用id值获取文档内容
- 倒排索引是关键词和倒排拉链(多个倒排节点,倒排节点存储了word、id与word在文档中的权重)的映射。用关键词获取倒排拉链,得到所有出现过该word的文档以及word在文档中的权重
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <fstream>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <mutex>
#include <string>
#include "util.hpp"
#include "log.hpp"
namespace ns_index
{
// 文档信息
struct DocInfo
{
std::string _title;
std::string _content;
std::string _url;
uint64_t _id; // 文档id
};
// 倒排中,word映射的信息
struct InventedElem
{
std::string _word; // 表示映射该InventElem的word
uint64_t _id;
int _weight = 0;
};
typedef std::vector<InventedElem> InventedElems_t;
class index
{
private:
std::vector<DocInfo> _forward_index;
std::unordered_map<std::string, InventedElems_t> _invented_index;
// for singleton
private:
static index* _instance;
static std::mutex _mtx;
// member function
index(){}
index(const index& x) = delete;
index& operator==(const index& x) = delete;
public:
// 单例的获取
static index* GetInstance();
// 建立索引
bool BuildIndex(const std::string& input);
DocInfo* BuildForwardIndex_once(const std::string& file);
bool BuildInventedIndex_once(const DocInfo& doc);
// 获取索引
DocInfo* GetForwardItem(uint64_t id);
InventedElems_t* GetInvetedItem(const std::string& word);
};
// static member initialize
index* index::_instance = nullptr;
std::mutex index::_mtx;
index* index::GetInstance()
{
if (_instance == nullptr)
{
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(_mtx);
if (_instance == nullptr)
{
_instance = new index();
}
}
return _instance;
}
bool index::BuildIndex(const std::string& input)
{
const std::string& orig_path = "./data/orig/orig.txt";
std::ifstream in(orig_path, std::ios::in | std::ios::binary);
if (!in.is_open())
{
LOG(FATAL, "open orig.txt fail");
return false;
}
std::string file;
int count = 0;
while (std::getline(in, file))
{
DocInfo* pdoc = BuildForwardIndex_once(file);
if (pdoc == nullptr)
{
LOG(NORMAL, "BuildForwardIndex fail");
continue;
}
if (!BuildInventedIndex_once(*pdoc))
{
LOG(NORMAL, "BuildinventedIndex fail");
}
count++;
LOG(NORMAL, "已建立索引数: " + std::to_string(count));
}
in.close();
return true;
}
DocInfo* index::BuildForwardIndex_once(const std::string& file)
{
std::vector<std::string> worked_file;
const std::string sep = "\3";
ns_util::StringUtil::SplitString(&worked_file, file, sep);
if (worked_file.size() != 3)
{
LOG(NORFMAL, "文档未被正确处理");
return nullptr;
}
DocInfo doc;
doc._title = worked_file[0];
doc._content = worked_file[1];
doc._url = worked_file[2];
doc._id = _forward_index.size();
_forward_index.push_back(std::move(doc));
// because of move(doc),so is wrong to return &doc
return &_forward_index.back();
}
bool index::BuildInventedIndex_once(const DocInfo& doc)
{
struct cnt
{
uint64_t _title_cnt = 0;
uint64_t _content_cnt = 0;
};
// 词频映射表
std::unordered_map<std::string, cnt> word_cnt;
// 前两个for是在统计doc文档中的词频
std::vector<std::string> title_words;
ns_util::JiebaUtil::CutString(doc._title, &title_words);
for (std::string& word : title_words)
{
boost::to_lower(word);
word_cnt[word]._title_cnt++;
}
std::vector<std::string> content_words;
ns_util::JiebaUtil::CutString(doc._content, &content_words);
for (std::string& word : content_words)
{
boost::to_lower(word);
word_cnt[word]._content_cnt++;
}
#define TWEIGHT 10
#define CWEIGHT 1
for (auto& word_cnt_part : word_cnt)
{
InventedElem inventedElem;
inventedElem._word = word_cnt_part.first;
inventedElem._id = doc._id;
inventedElem._weight = TWEIGHT * word_cnt_part.second._title_cnt + \
CWEIGHT * word_cnt_part.second._content_cnt;
// 注意&
InventedElems_t& inventedElems = _invented_index[inventedElem._word];
inventedElems.push_back(std::move(inventedElem));
}
return true;
}
DocInfo* index::GetForwardItem(uint64_t id)
{
if (id >= _forward_index.size())
{
LOG(NORMAL, "获取正排索引时: " + std::to_string(id) + "不存在");
return nullptr;
}
return &_forward_index[id];
}
InventedElems_t* index::GetInvetedItem(const std::string& word)
{
auto it = _invented_index.find(word);
if (it == _invented_index.end())
{
LOG(NORMAL, "获取倒排索引时: " + word + "不存在");
return nullptr;
}
return &(it->second);
}
}
关于这个模块的重点:索引的构建。这个逻辑很重要,是这个项目的核心部分。
- 索引的构建分为构建正排和倒排两个索引
- 正排索引的构建:parser.cc将清洗后html文件放到了指定路径下,所有html文档被清洗到一起,以’\n’分割,文档中的元素以’\3’分割
- 读取清洗后的文档(getline直接读一组三元组,这是用’\n’分割三元组的原因),用StringUtil的Split分割三元组得到每个元素
- 将得到的元素存储到结构体中,之后push_back进行正排索引的vector中
- 倒排索引的构建:对一组三元组建立的正排索引,紧接着就要对其建立倒排索引
- 将三元组的title和content用JiebaUtil的CurString进行分词,用一个词频表记录每个单词出现的次数
- 对分词后的每一个关键词:根据其词频计算权重,构建倒排节点
- 获取该关键词在倒排索引中的倒排拉链,将刚才构建好的倒排节点push_back到拉链中
- 重复以上步骤,对每一组三元组进行正排和倒排索引的构建,正排索引比较好理解,关于倒排:
- 重新理解下:倒排索引映射了word与倒排拉链,为什么要映射一组倒排节点,而不映射一个倒排节点?
- 倒排节点存储的是word在文档中的权重,boost肯定不止一个文档,所以word可能在多个文档中出现,因此我们要把word在这些文档中的权重都存储起来,也就是要存储多个倒排节点,一组倒排节点构成了倒排拉链
- 构建倒排节点后,要做的操作是查找映射表中是否有以word为值的key,如果没有则创建key。如果有则获取该key的倒排拉链,将倒排节点push_back到倒排拉链中。这里用映射表的operator[]实现该操作
最后要注意是:计算词频要忽略大小写
searcher.hpp
该hpp封装用来搜索的类:search,该类也被设计成单例。
搜索的逻辑:
- 将用户输入的字符串进行分词,得到关键字
- 用关键字进行倒排索引,得到每个关键字的权值,将位于同一文档的不同关键字的权值相加,根据这些用文档进行降序排序
- 最后根据文档的id进行正排索引,对文档的信息进行json序列化后返回
#pragma once
#include <algorithm>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <jsoncpp/json/json.h>
#include "index.hpp"
#include "util.hpp"
namespace ns_search
{
// search返回的结构,当然这只是一个中间结构,需要将文档转换成string
struct SearchResult
{
std::vector<std::string> _words;
uint64_t _id;
int _weight;
};
class search
{
public:
// 获取index单例并进行初始化
void InitSearch(const std::string& input_path);
void Search(const std::string& query, std::string* retString);
std::string GetPartContent(const std::string& content, const std::string& word);
private:
ns_index::index* _index;
};
void search::InitSearch(const std::string& input_path)
{
_index = ns_index::index::GetInstance();
_index->BuildIndex(input_path);
}
void search::Search(const std::string& query, std::string* retString)
{
// 1.query的分词
std::vector<std::string> query_words;
ns_util::JiebaUtil::CutString(query, &query_words);
std::vector<SearchResult> searchResults;
std::unordered_map<uint64_t, SearchResult> mapIdResult;
// 2.根据分词结果进行倒排索引
for (std::string query_word : query_words)
{
boost::to_lower(query_word);
ns_index::InventedElems_t* inventedElems = _index->GetInvetedItem(query_word);
if (inventedElems == nullptr) continue;
// 根据倒排索引的结果构建mapIdResult
for (ns_index::InventedElem item : *inventedElems)
{
SearchResult& srh_item = mapIdResult[item._id];
srh_item._id = item._id;
srh_item._words.push_back(item._word);
srh_item._weight += item._weight;
}
}
// 将mapIdResult映射表映射的内容存储到searchResults中
for (auto& map_pair : mapIdResult)
{
searchResults.push_back(std::move(map_pair.second));
}
// 3.根据权重将searchResults中的元素进行排序
std::sort(searchResults.begin(), searchResults.end(), \
[](const SearchResult& x1, const SearchResult& x2){
return x1._weight > x2._weight;
});
// 4.根据排序后的结果进行正排索引,构建Json对象
Json::Value root;
for (SearchResult srh_item : searchResults)
{
ns_index::DocInfo* docInfo = _index->GetForwardItem(srh_item._id);
if (docInfo == nullptr) continue;
Json::Value elem;
elem["title"] = docInfo->_title;
elem["part_content"] = GetPartContent(docInfo->_content, srh_item._words[0]);
elem["url"] = docInfo->_url;
elem["id"] = (long)srh_item._id;
elem["weight"] = srh_item._weight;
root.append(elem);
}
// JsonString的构建
// Json::StyledWriter writer;
Json::FastWriter writer;
*retString = writer.write(root);
}
std::string search::GetPartContent(const std::string& content, const std::string& word)
{
// 这个仿函数的参数是int,编译器会报错吗?char->int,但tolower的参数也是int
auto iter = std::search(content.begin(), content.end(), word.begin(), word.end(),\
[](int x, int y) {
return std::tolower(x) == std::tolower(y);
});
if (iter == content.end()) return "not fine word in the content";
int start = 0;
int end = content.size() - 1;
int pos = std::distance(content.begin(), iter);
if (pos - start > 50) start = pos - 50;
if (end - pos > 50) end = pos + 50;
if (start > end) return "start > end";
return content.substr(start, end - start) + "...";
}
}
关于这个模块的重点:去重与结果的构建。先说结果的构建
- 根据用户输入的关键字进行倒排索引,我们将得到word对应的倒排拉链。其含有多个倒排节点,分别表明了含有word的文档id以及word在其中的权重
- 我们需要根据权重对文档进行降序排序,以找出用户最有可能需要的文档。但是用户可能输入了多个关键字,不同关键字可能在同一文档中出现,此时该文档的权重就需要增加
- 可以看到,在倒排拉链的节点中,权重针对的是文档中的word。而对于结果,权重针对的是文档。如果一个文档含有用户搜索的多个word,那么就需要把权值进行累加,以便进行后续的降序排序
- 因此我们需要一个保存搜索结果的结构——vector<SearchResult> searchResults。它含有id、weight与words,id用来标识文档,用户搜索的关键字若出现在文档中,这些关键字会被保存到words中。并且这些关键字在该文档的权值会被累加,保存到weight中
- 对用户搜索的所有关键字进行倒排索引后,我们需要根据权值将searchResults进行降序排序
- 排序完成,我们需要根据根据排好序的searchResults的id值进行正排索引,获取文档的title、content与url,保存这些信息的json序列化,返回结果
有了以上的铺垫,去重就很好理解了
- 因为用户可能搜索多个关键字,一个关键字映射多个倒排节点,也就是多个文档,多个关键字映射的文档可能相同
- 使用unordered_map就可以实现去重,通过opeartor[]将文档的id作为key值插入pair对象(或者获取其引用)
- 并且使用SearchResult结构存储文档的权值
关于其他细节:
- 正排索引获取的文档内容,我们不需要全部使用,只需要使用含有关键字的部分
- 由于第一次接触Json,关于Json的相关操作需要熟悉
- 构建Json的kv对象时,key值是前端获取其value的依据
http_server.hpp
cpp-httplib库的使用:
- httplib::Server类的set_base_dir方法:设置默认html资源,当用户访问网站时,将该html资源呈现
- httplib::Server类的Get方法:设置指定路径与处理函数。当用户访问该路径下的资源时,将触发处理函数并进行调用。注意该函数有两个参数:httplib::Request和httplib::Response,分别含有get_param_value和set_content方法,用来进行字符串的获取与设置
#include <time.h>
#include <string>
#include "log.hpp"
#include "searcher.hpp"
#include "cpp-httplib/httplib.h"
const std::string input_path = "./data/orig/orig.txt";
const std::string html_root_path = "./wwwroot";
int main()
{
clock_t begin = clock();
ns_search::search* psearch = new ns_search::search();
psearch->InitSearch(input_path);
clock_t end = clock();
LOG(NORMAL, "构建索引消耗的总时间: " + std::to_string(end - begin));
httplib::Server svr;
svr.set_base_dir(html_root_path.c_str());
svr.Get("/s", [psearch](const httplib::Request& req, httplib::Response& res){
if (!req.has_param("word"))
{
res.set_content("请输入搜索关键字", "text/plain; charset=utf-8");
return;
}
std::string word = req.get_param_value("word");
LOG(NORMAL, "用户搜索的: " + word);
std::string retString;
psearch->Search(word, &retString);
res.set_content(retString, "application/json");
});
svr.listen("0.0.0.0", 8080);
return 0;
}
关于这个模块的逻辑:
- 创建Search类对象并进行初始化,也就是进行索引的构建
- 设置默认html资源,也就是搜索页的设置
- 绑定指定资源的处理方法
- 最后监听服务器所有IP的8080号端口,等待TCP连接
其他模块
// html资源
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-2.1.1.min.js"></script>
<title>boost 搜索引擎</title>
<style>
/* 去掉网页中的所有的默认内外边距,html的盒子模型 */
* {
/* 设置外边距 */
margin: 0;
/* 设置内边距 */
padding: 0;
}
/* 将我们的body内的内容100%和html的呈现吻合 */
html,
body {
height: 100%;
}
/* 类选择器.container */
.container {
/* 设置div的宽度 */
width: 800px;
/* 通过设置外边距达到居中对齐的目的 */
margin: 0px auto;
/* 设置外边距的上边距,保持元素和网页的上部距离 */
margin-top: 15px;
}
/* 复合选择器,选中container 下的 search */
.container .search {
/* 宽度与父标签保持一致 */
width: 100%;
/* 高度设置为52px */
height: 52px;
}
/* 先选中input标签, 直接设置标签的属性,先要选中, input:标签选择器*/
/* input在进行高度设置的时候,没有考虑边框的问题 */
.container .search input {
/* 设置left浮动 */
float: left;
width: 600px;
height: 50px;
/* 设置边框属性:边框的宽度,样式,颜色 */
border: 1px solid black;
/* 去掉input输入框的有边框 */
border-right: none;
/* 设置内边距,默认文字不要和左侧边框紧挨着 */
padding-left: 10px;
/* 设置input内部的字体的颜色和样式 */
color: #CCC;
font-size: 14px;
}
/* 先选中button标签, 直接设置标签的属性,先要选中, button:标签选择器*/
.container .search button {
/* 设置left浮动 */
float: left;
width: 150px;
height: 52px;
/* 设置button的背景颜色,#4e6ef2 */
background-color: #4e6ef2;
/* 设置button中的字体颜色 */
color: #FFF;
/* 设置字体的大小 */
font-size: 19px;
font-family:Georgia, 'Times New Roman', Times, serif;
}
.container .result {
width: 100%;
}
.container .result .item {
margin-top: 15px;
}
.container .result .item a {
/* 设置为块级元素,单独站一行 */
display: block;
/* a标签的下划线去掉 */
text-decoration: none;
/* 设置a标签中的文字的字体大小 */
font-size: 20px;
/* 设置字体的颜色 */
color: #4e6ef2;
}
.container .result .item a:hover {
text-decoration: underline;
}
.container .result .item p {
margin-top: 5px;
font-size: 16px;
font-family:'Lucida Sans', 'Lucida Sans Regular', 'Lucida Grande', 'Lucida Sans Unicode', Geneva, Verdana, sans-serif;
}
.container .result .item i{
/* 设置为块级元素,单独站一行 */
display: block;
/* 取消斜体风格 */
font-style: normal;
color: green;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<div class="search">
<input type="text" value="请输入搜索关键字">
<button onclick="Search()">搜索一下</button>
</div>
<div class="result">
</div>
</div>
<script>
function Search(){
// 是浏览器的一个弹出框
// alert("hello js!");
// 1. 提取数据, $可以理解成就是JQuery的别称
let query = $(".container .search input").val();
console.log("query = " + query); //console是浏览器的对话框,可以用来进行查看js数据
//2. 发起http请求,ajax: 属于一个和后端进行数据交互的函数,JQuery中的
$.ajax({
type: "GET",
url: "/s?word=" + query,
success: function(data){
// console.log(data);
BuildHtml(data);
}
});
}
function BuildHtml(data){
// 获取html中的result标签
let result_lable = $(".container .result");
// 清空历史搜索结果
result_lable.empty();
for( let elem of data){
console.log(elem.title);
console.log(elem.url);
let a_lable = $("<a>", {
text: elem.title,
href: elem.url,
// 跳转到新的页面
target: "_blank"
});
let p_lable = $("<p>", {
text: elem.part_content
});
let i_lable = $("<i>", {
text: elem.url
});
let div_lable = $("<div>", {
class: "item"
});
a_lable.appendTo(div_lable);
p_lable.appendTo(div_lable);
i_lable.appendTo(div_lable);
div_lable.appendTo(result_lable);
}
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
// log.hpp
#pragma once
#include <ctime>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#define LOG(LEVEL, MESSAGE) log(#LEVEL, MESSAGE, __FILE__, __LINE__)
void log(std::string level, std::string message, std::string filename, int line)
{
std::cout << "[" << level << "]" << "[" << time(nullptr) << "]" << "[" << message << "]"\
<< "[" << filename << ":" << line << "]" << std::endl;
}
// makefile
cc=g++
PARSER=parser
DEBUG=debug
SVR=server
.PHONY:all
all:$(PARSER) $(DEBUG) $(SVR)
$(PARSER):parser.cc
$(cc) -o $@ $^ -std=c++11 -l boost_system -l boost_filesystem
$(DEBUG):debug.cc
$(cc) -o $@ $^ -std=c++11 -l jsoncpp -l boost_system -l boost_filesystem
$(SVR):http_server.cc
$(cc) -o $@ $^ -std=c++11 -l pthread -l jsoncpp
.PHONY:clean
clean:
rm -f $(PARSER) $(DEBUG) $(SVR)