原题链接
https://www.dotcpp.com/oj/problem3162.html
想直接看题解的,跳转到第三次尝试即可。
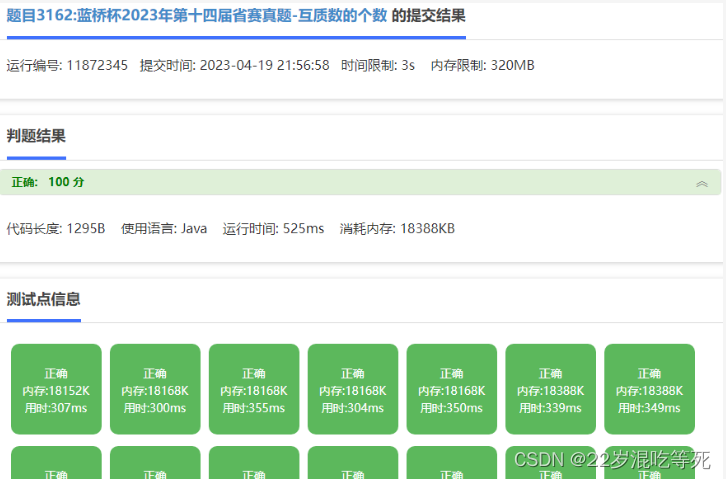
已AC。
解析:
(1)首先大家要知道什么叫互质:
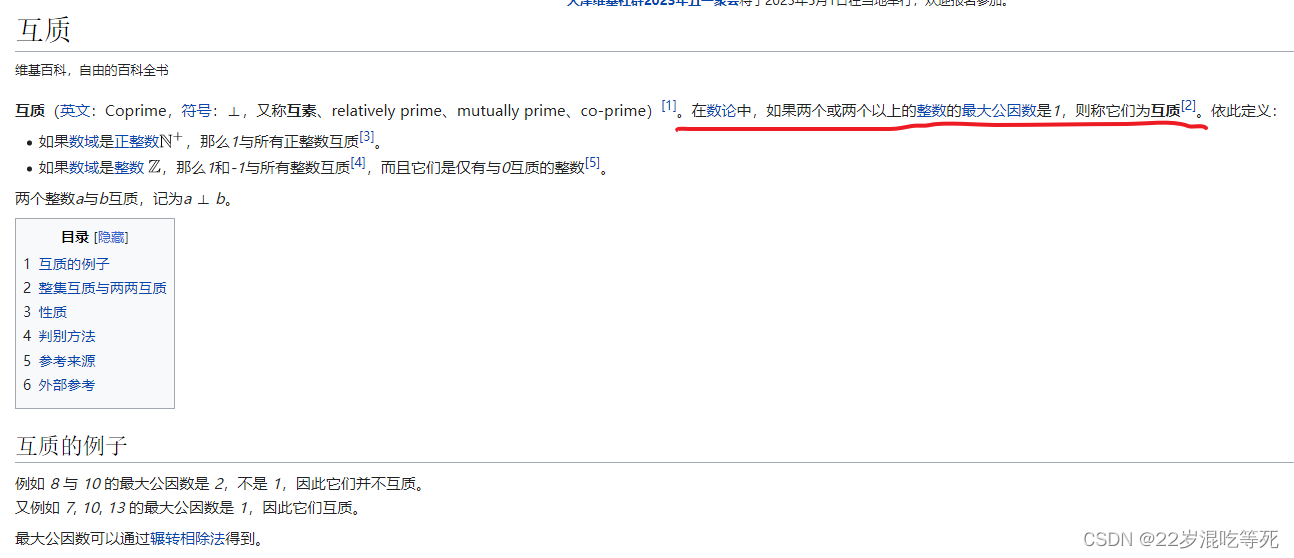
以及它们的性质:
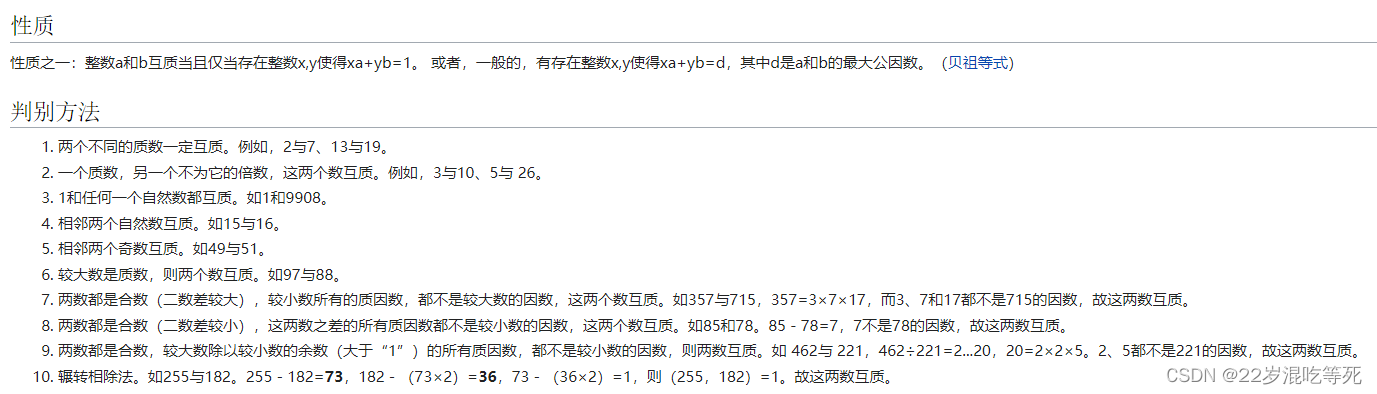
欧拉函数
在数论中,对正整数n,欧拉函数φ(n)是小于或等于n的正整数中与n互质的数的数目。此函数以其首名研究者欧拉命名,它又称为φ函数(由高斯所命名)或是欧拉总计函数(totient function,由西尔维斯特所命名)。
例如φ(8) = 4,因为1,3,5,7均和8互质。
也可以从简化剩余系的角度来解释,简化剩余系(reduced residue system)也称既约剩余系或缩系,是m的完全剩余系中与m互素的数构成的子集,如果模m的一个剩余类里所有数都与m互素,就把它叫做与模m互素的剩余类。在与模m互素的全体剩余类中,从每一个类中各任取一个数作为代表组成的集合,叫做模m的一个简化剩余系。
(1,3,5,7)就构成了8的一个简化剩余系。
参考链接: https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/151756874
第一次尝试代码:
package Dotcpp;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class 题目3180蓝桥杯2023年第十四届省赛真题_互质数的个数 {
private static long mod = 998244353L;
private static long a,b,ans;
static BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
static StreamTokenizer st = new StreamTokenizer(br);
static int nextLong() throws Exception {st.nextToken();return (int) st.nval;}
static PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
a = nextLong();
b = nextLong();
long n = Euler_pow(a,b-1);
long m = Euler(a);
System.out.println((n*m%mod)%mod);
}
private static long Euler(long n) {
long res = n;
for (long i = 2; i * i <= n; ++i) {
if (n % i == 0) {
res = res / i * (i - 1);
while (n % i == 0) {
n /= i;
}
}
}
if (n > 1) {
res -= res / n;
}
return res;
}
private static long Euler_pow(long a, long b) {
long ans = 1;
while (b != 0){
if (b % 2 ==1){
ans*=(a%mod)%mod;
}
a*=a%mod;
a=a%mod;
b /= 2;
}
return ans;
}
}
运行结果:
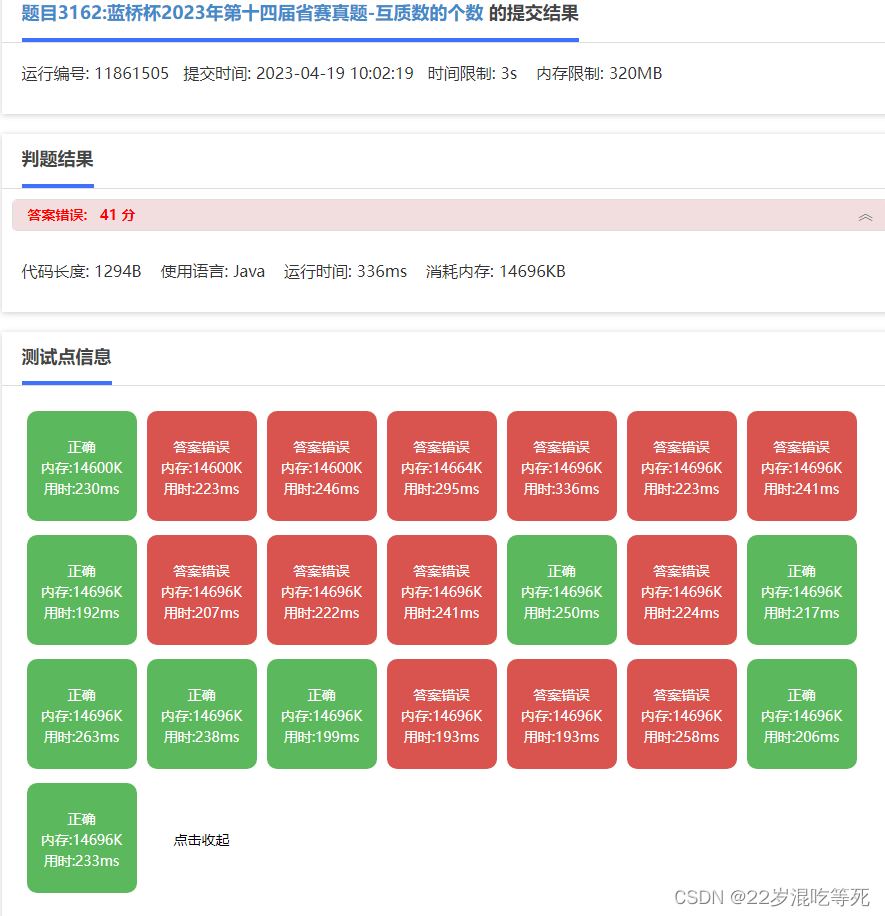
分析:
第二次尝试代码:
package Dotcpp;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class 题目3180蓝桥杯2023年第十四届省赛真题_互质数的个数__运行错误32分 {
private static long mod = 998244353L;
private static long a, b, res;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
a = scanner.nextInt();
b = scanner.nextInt();
long n = Euler_pow(a, b);
res = n;
for (int i = 2; i <= n / i; i++) {
if (n % i == 0) {
while (n % i == 0) {
n /= i;
n%=mod;
}
res = (res - res / i);
res%=mod;
}
}
if (n > 1) {
res = (res - res / n);
res%=mod;
}
System.out.println(res%=mod);
}
private static long Euler_pow(long a, long b) {
long ans = 1;
while (b > 0) {
if ((b & 1) > 0) {
ans = ((ans % mod) * (a % mod)) % mod;
}
a = ((a % mod) * (a % mod)) % mod;
b /= 2;
}
return ans;
}
}
运行结果:
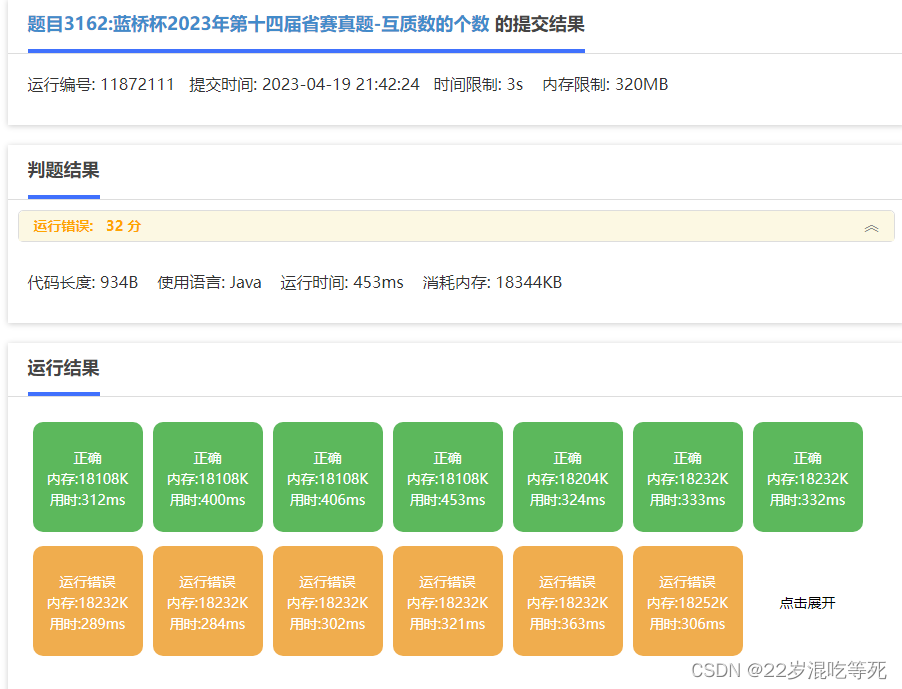
补充说明:
这第二次是我参考其他语言的代码,转化成Java来实现的。
如图可见:
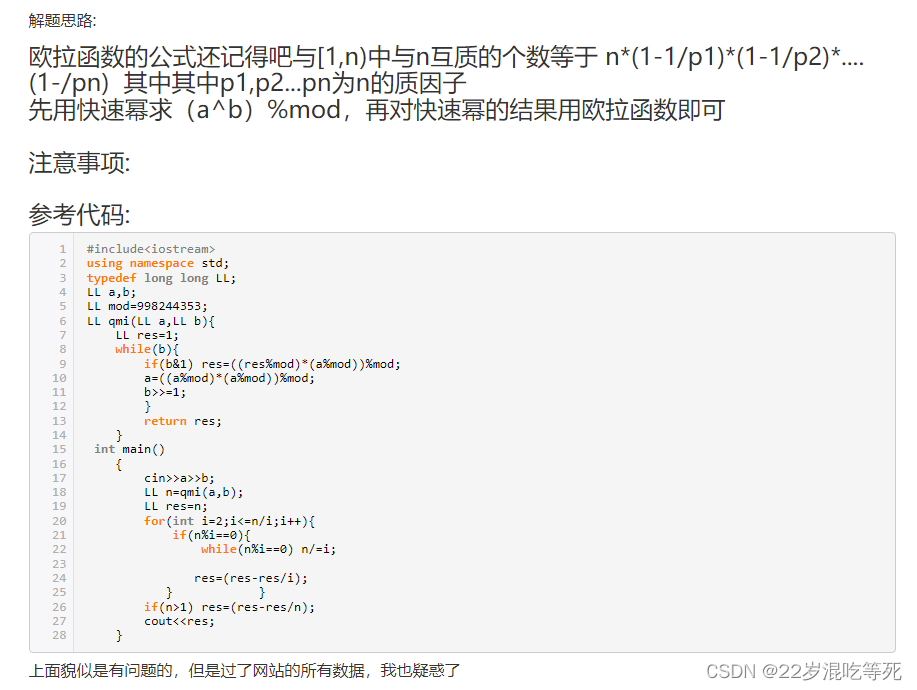
感谢大佬提供的思路: https://blog.dotcpp.com/a/95823
分析:
当时一想,一种方法超时,一种方法会导致报错,两者结合一起,是不是可行呢。?
第三次尝试:
package Dotcpp;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class 题目3180蓝桥杯2023年第十四届省赛真题_互质数的个数 {
private static long mod = 998244353L;
private static long a,b,res;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
a = scanner.nextLong();
b = scanner.nextLong();
long n = Euler_pow(a,b);
res = n;
for (int i = 2; i <= n / i; i++) {
if (n % i == 0) {
while (n % i == 0) {
n /= i;
n%=mod;
}
res = (res - res / i);
res%=mod;
}
}
if (n > 1) {
res = (res - res / n);
res%=mod;
}
scanner.close();
System.out.println(res%=mod);
}
private static long Euler(long n) {
long res = n;
for (long i = 2; i * i <= n; ++i) {
if (n % i == 0) {
res = res / i * (i - 1);
while (n % i == 0) {
n /= i;
}
}
}
if (n > 1) {
res -= res / n;
}
return res;
}
private static long Euler_pow(long a, long b) {
long ans = 1;
while (b > 0) {
if ((b & 1) > 0) {
ans = ((ans % mod) * (a % mod)) % mod;
}
a = ((a % mod) * (a % mod)) % mod;
b /= 2;
}
return ans;
}
}
结果: