netty源码学习之-HashedWheelTimer
- 概述
- 使用
- 相关概念解析
- 时间轮 运行时序图
- 源码
- worker
- HashedWheelTimeout
- HashedWheelBucket
概述
该部分源码是netty的时间轮,netty的时间轮是单轮,其他时间轮是多轮设计,今天先了解下netty的时间轮设计
使用
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(1);
HashedWheelTimer timer = new HashedWheelTimer(1, TimeUnit.SECONDS, 16);
System.out.println("current timestamp="+System.currentTimeMillis());
timer.newTimeout((timeout) -> {
System.out.println("task execute,current timestamp="+System.currentTimeMillis());
countDownLatch.countDown();
}, 2000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
timer.newTimeout((timeout) -> {
System.out.println("task execute,current timestamp="+System.currentTimeMillis());
countDownLatch.countDown();
}, 2000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
timer.newTimeout((timeout) -> {
System.out.println("task execute,current timestamp="+System.currentTimeMillis());
countDownLatch.countDown();
}, 2000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
countDownLatch.await();
timer.stop();
}
关键部分就
创建时间轮
HashedWheelTimer timer = new HashedWheelTimer(1, TimeUnit.SECONDS, 16);
时间轮添加任务
timer.newTimeout()
相关概念解析
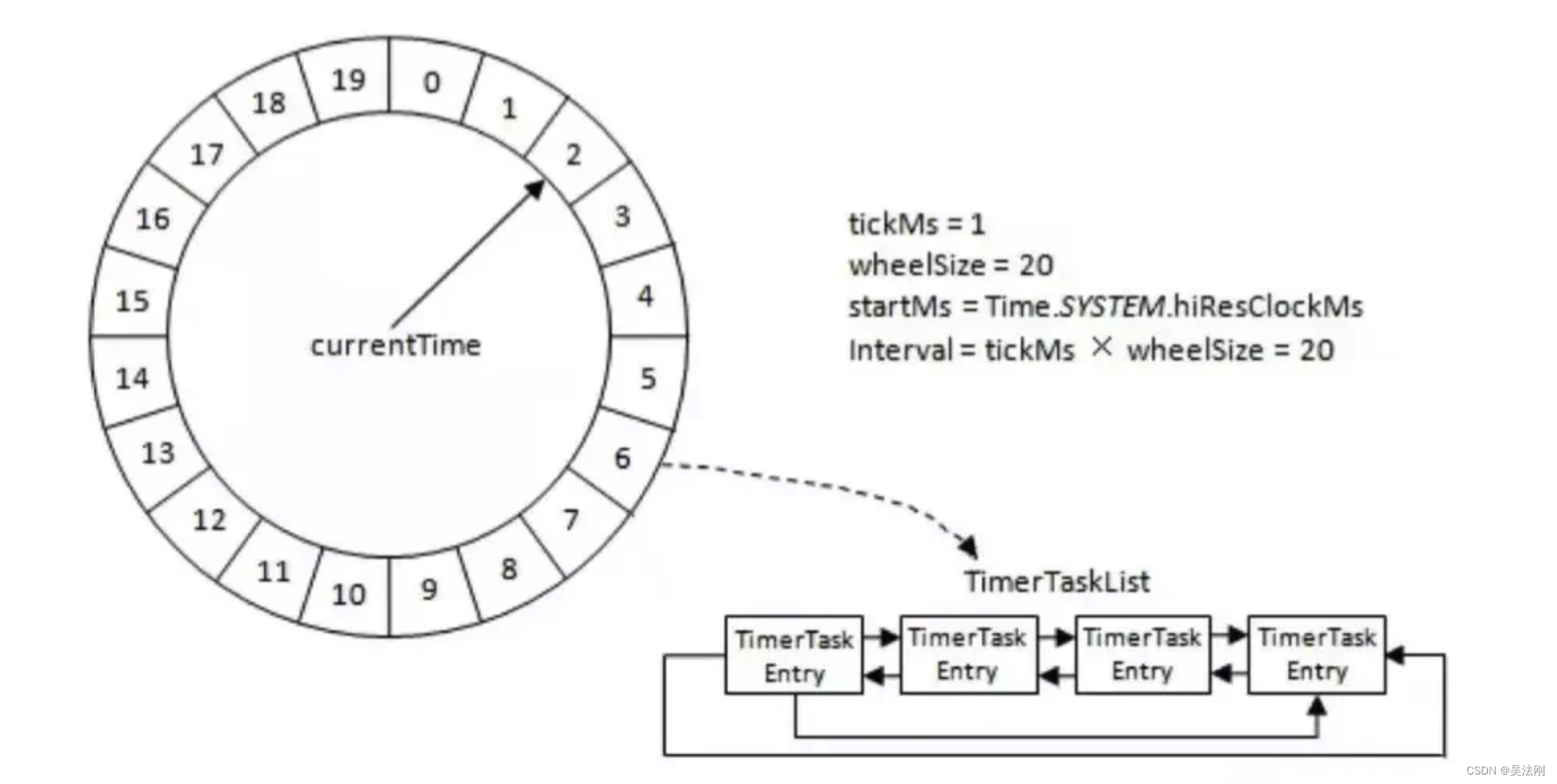
HashedWheelTimer 时间轮中包含了那些信息
一个时间轮主要包含了这么多信息
wheel 是一个数组,和时间轮的曹数一样大的一个数组,即存放每个时间刻度的任务
timeout 就是任务的包装类
Queue timeouts
Queue cancelledTimeouts
两个对立,方便存放任务和取消任务的两个独立。由于是一个work线程访问,因此是线程安全的
时间轮 运行时序图
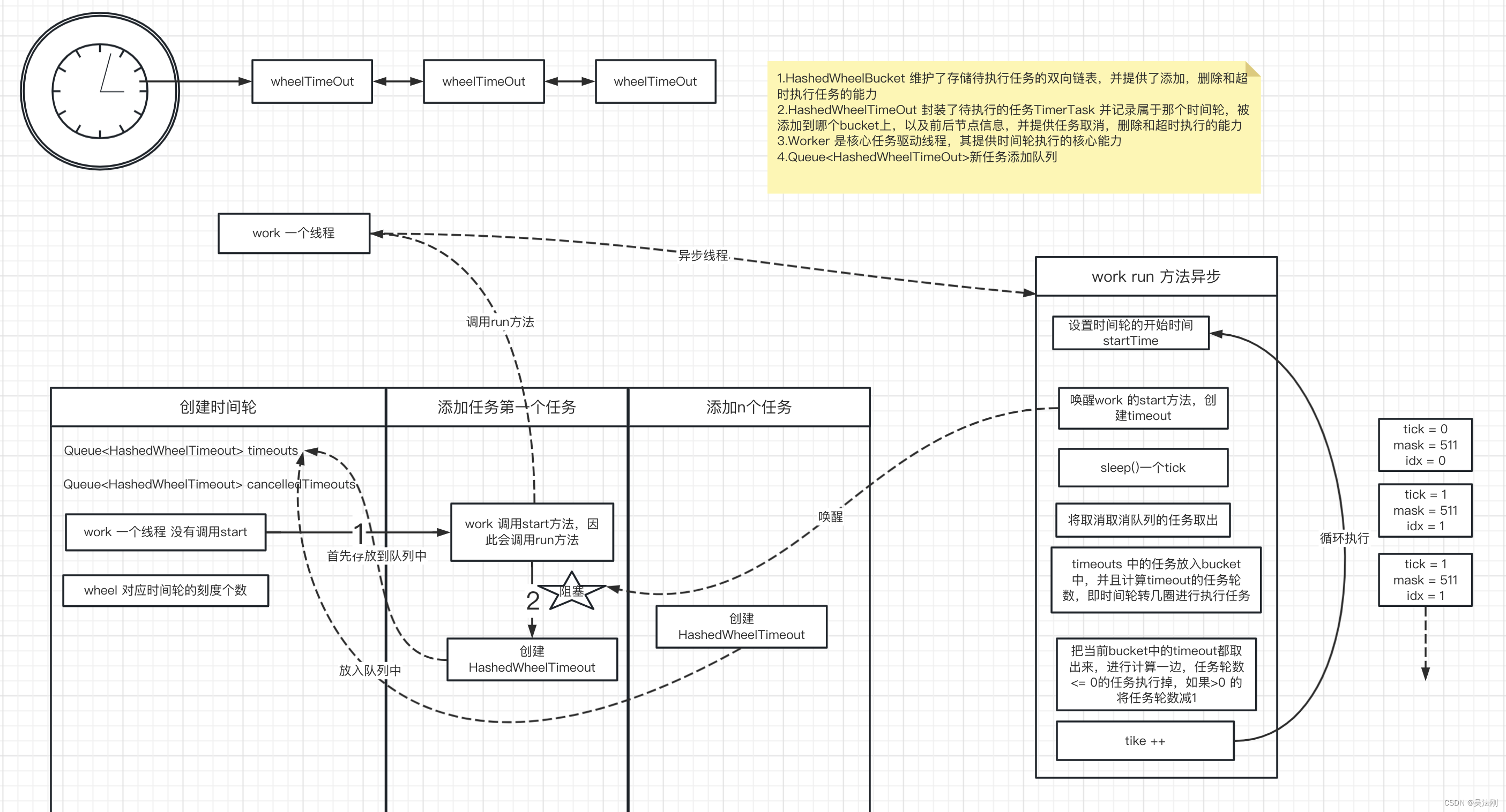
源码
package io.netty.util;
import io.netty.util.internal.PlatformDependent;
import io.netty.util.internal.logging.InternalLogger;
import io.netty.util.internal.logging.InternalLoggerFactory;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.RejectedExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadFactory;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicBoolean;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicLong;
import static io.netty.util.internal.StringUtil.simpleClassName;
public class HashedWheelTimer implements Timer {
static final InternalLogger logger =
InternalLoggerFactory.getInstance(HashedWheelTimer.class);
private static final AtomicInteger INSTANCE_COUNTER = new AtomicInteger();
private static final AtomicBoolean WARNED_TOO_MANY_INSTANCES = new AtomicBoolean();
private static final int INSTANCE_COUNT_LIMIT = 64;
private static final ResourceLeakDetector<HashedWheelTimer> leakDetector = ResourceLeakDetectorFactory.instance()
.newResourceLeakDetector(HashedWheelTimer.class, 1);
private static final AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater<HashedWheelTimer> WORKER_STATE_UPDATER =
AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater.newUpdater(HashedWheelTimer.class, "workerState");
private final ResourceLeakTracker<HashedWheelTimer> leak;
private final Worker worker = new Worker();
private final Thread workerThread;
public static final int WORKER_STATE_INIT = 0;
public static final int WORKER_STATE_STARTED = 1;
public static final int WORKER_STATE_SHUTDOWN = 2;
@SuppressWarnings({ "unused", "FieldMayBeFinal" })
private volatile int workerState; // 0 - init, 1 - started, 2 - shut down
private final long tickDuration;
private final HashedWheelBucket[] wheel;
private final int mask;
private final CountDownLatch startTimeInitialized = new CountDownLatch(1);
private final Queue<HashedWheelTimeout> timeouts = PlatformDependent.newMpscQueue();
private final Queue<HashedWheelTimeout> cancelledTimeouts = PlatformDependent.newMpscQueue();
private final AtomicLong pendingTimeouts = new AtomicLong(0);
private final long maxPendingTimeouts;
private volatile long startTime;
/**
* Creates a new timer.
*
* @param threadFactory a {@link ThreadFactory} that creates a
* background {@link Thread} which is dedicated to
* {@link TimerTask} execution.
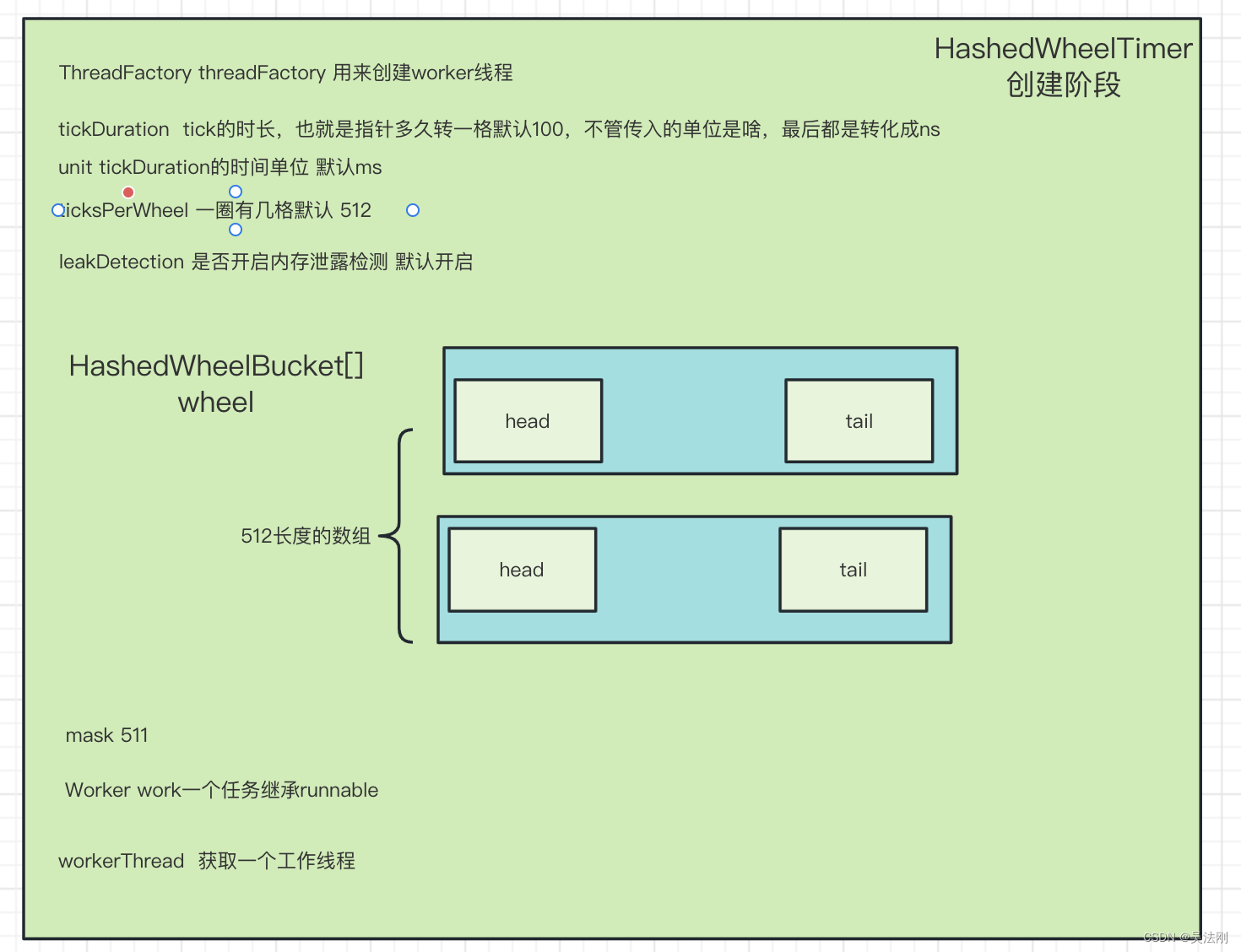
* 用来创建worker线程
* @param tickDuration the duration between tick
* tick的时长,也就是指针多久转一格
* @param unit the time unit of the {@code tickDuration}
* tickDuration的时间单位
* @param ticksPerWheel the size of the wheel
* 一圈有几格
* @param leakDetection {@code true} if leak detection should be enabled always,
* if false it will only be enabled if the worker thread is not
* a daemon thread.
* 是否开启内存泄露检测
* @param maxPendingTimeouts The maximum number of pending timeouts after which call to
* {@code newTimeout} will result in
* {@link java.util.concurrent.RejectedExecutionException}
* being thrown. No maximum pending timeouts limit is assumed if
* this value is 0 or negative.
* @throws NullPointerException if either of {@code threadFactory} and {@code unit} is {@code null}
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if either of {@code tickDuration} and {@code ticksPerWheel} is <= 0
*/
public HashedWheelTimer(
ThreadFactory threadFactory,
long tickDuration, TimeUnit unit, int ticksPerWheel, boolean leakDetection,
long maxPendingTimeouts) {
if (threadFactory == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("threadFactory");
}
if (unit == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("unit");
}
if (tickDuration <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("tickDuration must be greater than 0: " + tickDuration);
}
if (ticksPerWheel <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("ticksPerWheel must be greater than 0: " + ticksPerWheel);
}
// Normalize ticksPerWheel to power of two and initialize the wheel.
//创建时间轮基本的数据结构,一个数组。长度为不小于ticksPerWheel的最小2的n次方
wheel = createWheel(ticksPerWheel);
// 这是一个标示符,用来快速计算任务应该呆的格子。
// 我们知道,给定一个deadline的定时任务,其应该呆的格子=deadline%wheel.length.但是%操作是个相对耗时的操作,所以使用一种变通的位运算代替:
// 因为一圈的长度为2的n次方,mask = 2^n-1后低位将全部是1,然后deadline&mast == deadline%wheel.length
// java中的HashMap也是使用这种处理方法
mask = wheel.length - 1;
// Convert tickDuration to nanos.
this.tickDuration = unit.toNanos(tickDuration);
// Prevent overflow.
// 校验是否存在溢出。即指针转动的时间间隔不能太长而导致tickDuration*wheel.length>Long.MAX_VALUE
if (this.tickDuration >= Long.MAX_VALUE / wheel.length) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.format(
"tickDuration: %d (expected: 0 < tickDuration in nanos < %d",
tickDuration, Long.MAX_VALUE / wheel.length));
}
//创建worker线程
workerThread = threadFactory.newThread(worker);
//这里默认是启动内存泄露检测:当HashedWheelTimer实例超过当前cpu可用核数*4的时候,将发出警告
leak = leakDetection || !workerThread.isDaemon() ? leakDetector.track(this) : null;
this.maxPendingTimeouts = maxPendingTimeouts;
if (INSTANCE_COUNTER.incrementAndGet() > INSTANCE_COUNT_LIMIT &&
WARNED_TOO_MANY_INSTANCES.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
reportTooManyInstances();
}
}
@Override
protected void finalize() throws Throwable {
try {
super.finalize();
} finally {
// This object is going to be GCed and it is assumed the ship has sailed to do a proper shutdown. If
// we have not yet shutdown then we want to make sure we decrement the active instance count.
if (WORKER_STATE_UPDATER.getAndSet(this, WORKER_STATE_SHUTDOWN) != WORKER_STATE_SHUTDOWN) {
INSTANCE_COUNTER.decrementAndGet();
}
}
}
private static HashedWheelBucket[] createWheel(int ticksPerWheel) {
if (ticksPerWheel <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"ticksPerWheel must be greater than 0: " + ticksPerWheel);
}
if (ticksPerWheel > 1073741824) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"ticksPerWheel may not be greater than 2^30: " + ticksPerWheel);
}
// 初始化ticksPerWheel的值为不小于ticksPerWheel的最小2的n次方
ticksPerWheel = normalizeTicksPerWheel(ticksPerWheel);
// 初始化wheel数组
HashedWheelBucket[] wheel = new HashedWheelBucket[ticksPerWheel];
for (int i = 0; i < wheel.length; i ++) {
wheel[i] = new HashedWheelBucket();
}
return wheel;
}
/**
* 这里其实不建议使用这种方式,因为当ticksPerWheel的值很大的时候,
* 这个方法会循环很多次,方法执行时间不稳定,效率也不够。推荐使用java8 HashMap的做法:
*/
private static int normalizeTicksPerWheel(int ticksPerWheel) {
int normalizedTicksPerWheel = 1;
while (normalizedTicksPerWheel < ticksPerWheel) {
normalizedTicksPerWheel <<= 1;
}
return normalizedTicksPerWheel;
}
/**
* Starts the background thread explicitly. The background thread will
* start automatically on demand even if you did not call this method.
*显示的启动后台线程。即使你没有调用这个方法,后台线程也将启动
*
* 启动时间轮。这个方法其实不需要显示的主动调用,因为在添加定时任务(newTimeout()方法)的时候会自动调用此方法。
*这个是合理的设计,因为如果时间轮里根本没有定时任务,启动时间轮也是空耗资源
*
* public void start() {
* 判断当前时间轮的状态,如果是初始化,则启动worker线程,启动整个时间轮;
* 如果已经启动则略过;
* 如果是已经停止,则报错
*
* 这里是一个Lock Free(无锁)的设计。因为可能有多个线程调用启动方法,这里使用AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater原子的更新时间轮的状态
* @throws IllegalStateException if this timer has been
* {@linkplain #stop() stopped} already
*/
public void start() {
switch (WORKER_STATE_UPDATER.get(this)) {
case WORKER_STATE_INIT:
if (WORKER_STATE_UPDATER.compareAndSet(this, WORKER_STATE_INIT, WORKER_STATE_STARTED)) {
workerThread.start();
}
break;
case WORKER_STATE_STARTED:
break;
case WORKER_STATE_SHUTDOWN:
throw new IllegalStateException("cannot be started once stopped");
default:
throw new Error("Invalid WorkerState");
}
// Wait until the startTime is initialized by the worker.
//等待worker线程初始化时间轮的启动时间 startTimeInitialized.countDown();
while (startTime == 0) {
try {
startTimeInitialized.await();
} catch (InterruptedException ignore) {
// Ignore - it will be ready very soon.
}
}
}
/**
*停止时间轮
*/
@Override
public Set<Timeout> stop() {
// worker线程不能停止时间轮,也就是加入的定时任务,不能调用这个方法。
// 不然会有恶意的定时任务调用这个方法而造成大量定时任务失效
if (Thread.currentThread() == workerThread) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
HashedWheelTimer.class.getSimpleName() +
".stop() cannot be called from " +
TimerTask.class.getSimpleName());
}
// 尝试CAS替换当前状态为“停止:2”。如果失败,则当前时间轮的状态只能是“初始化:0”或者“停止:2”。直接将当前状态设置为“停止:2“
if (!WORKER_STATE_UPDATER.compareAndSet(this, WORKER_STATE_STARTED, WORKER_STATE_SHUTDOWN)) {
// workerState can be 0 or 2 at this moment - let it always be 2.
if (WORKER_STATE_UPDATER.getAndSet(this, WORKER_STATE_SHUTDOWN) != WORKER_STATE_SHUTDOWN) {
INSTANCE_COUNTER.decrementAndGet();
if (leak != null) {
boolean closed = leak.close(this);
assert closed;
}
}
return Collections.emptySet();
}
//中断worker线程
try {
boolean interrupted = false;
while (workerThread.isAlive()) {
workerThread.interrupt();
try {
workerThread.join(100);
} catch (InterruptedException ignored) {
interrupted = true;
}
}
//从中断中恢复
if (interrupted) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
} finally {
INSTANCE_COUNTER.decrementAndGet();
if (leak != null) {
boolean closed = leak.close(this);
assert closed;
}
}
return worker.unprocessedTimeouts();
}
/**
* 添加定时任务
*/
@Override
public Timeout newTimeout(TimerTask task, long delay, TimeUnit unit) {
if (task == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("task");
}
if (unit == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("unit");
}
long pendingTimeoutsCount = pendingTimeouts.incrementAndGet();
if (maxPendingTimeouts > 0 && pendingTimeoutsCount > maxPendingTimeouts) {
pendingTimeouts.decrementAndGet();
throw new RejectedExecutionException("Number of pending timeouts ("
+ pendingTimeoutsCount + ") is greater than or equal to maximum allowed pending "
+ "timeouts (" + maxPendingTimeouts + ")");
}
//如果时间轮没有启动 则启动时间轮
start();
// Add the timeout to the timeout queue which will be processed on the next tick.
// During processing all the queued HashedWheelTimeouts will be added to the correct HashedWheelBucket.
//计算任务的deadline
// 这里定时任务不是直接加到对应的格子中,而是先加入到一个队列里,
// 然后等到下一个tick的时候,会从队列里取出最多100000个任务加入到指定的格子中
long deadline = System.nanoTime() + unit.toNanos(delay) - startTime;
HashedWheelTimeout timeout = new HashedWheelTimeout(this, task, deadline);
timeouts.add(timeout);
System.out.println("wheel ============="+wheel.length+ wheel[0].head);
return timeout;
}
/**
* Returns the number of pending timeouts of this {@link Timer}.
*/
public long pendingTimeouts() {
return pendingTimeouts.get();
}
private static void reportTooManyInstances() {
String resourceType = simpleClassName(HashedWheelTimer.class);
logger.error("You are creating too many " + resourceType + " instances. " +
resourceType + " is a shared resource that must be reused across the JVM," +
"so that only a few instances are created.");
}
worker
//Worker是时间轮的核心线程类。tick的转动,过期任务的处理都是在这个线程中处理的。
private final class Worker implements Runnable {
private final Set<Timeout> unprocessedTimeouts = new HashSet<Timeout>();
private long tick;
@Override
public void run() {
// Initialize the startTime.
// 初始化startTime.只有所有任务的的deadline都是想对于这个时间点
startTime = System.nanoTime();
// 由于System.nanoTime()可能返回0,甚至负数。并且0是一个标示符,用来判断startTime是否被初始化,所以当startTime=0的时候,重新赋值为1
if (startTime == 0) {
// We use 0 as an indicator for the uninitialized value here, so make sure it's not 0 when initialized.
startTime = 1;
}
logger.info("work ==== run===startTime: {} ", startTime);
// Notify the other threads waiting for the initialization at start().
// 唤醒阻塞在start()的线程
startTimeInitialized.countDown();
//只要时间轮的状态为WORKER_STATE_STARTED,就循环的“转动”tick,循环判断响应格子中的到期任务
do {
/**
* 首先 worker 线程会通过 waitForNextTick()方法根据时间轮的时间刻度等待一轮循环的开始,
* 在默认情况下时间轮的时间刻度是 100ms,
* 那么此处 worker 线程也将在这个方法中 sleep 相应的时间等待下一轮循环的开始。
* 此处也决定了时间轮的定时任务时间精度。
*
* waitForNextTick方法主要是计算下次tick的时间, 然后sleep到下次tick
* 返回值就是System.nanoTime() - startTime, 也就是Timer启动后到这次tick, 所过去的时间
*/
final long deadline = waitForNextTick();
logger.info("work ==== deadline: {} ", deadline);
if (deadline > 0) { // 可能溢出或者被中断的时候会返回负数, 所以小于等于0不管
//获取tick对应的格子索引
int idx = (int) (tick & mask);
// 移除被取消的任务
processCancelledTasks();
HashedWheelBucket bucket =
wheel[idx];
/**
* 当 worker 线程经过相应时间间隔的 sleep 之后,也代表新的一轮调度开始。
* 此时,会通过 transferTimeoutsToBuckets()方法将之前刚刚加入到
* timeouts 队列中的定时任务放入到时间轮具体槽位上的链表中。
*
* 首先,在每一轮的调度中,最多只会从 timeouts 队列中定位到时间轮 100000 个定时任务,
* 这也是为了防止在这里耗时过久导致后面触发定时任务的延迟。
* 在这里会不断从 timeouts 队列中获取刚加入的定时任务。
*/
transferTimeoutsToBuckets();
// 过期执行格子中的任务
bucket.expireTimeouts(deadline);
tick++;
}
} while (WORKER_STATE_UPDATER.get(HashedWheelTimer.this) == WORKER_STATE_STARTED);
// Fill the unprocessedTimeouts so we can return them from stop() method.
// 这里应该是时间轮停止了,清除所有格子中的任务,并加入到未处理任务列表,以供stop()方法返回
for (HashedWheelBucket bucket: wheel) {
bucket.clearTimeouts(unprocessedTimeouts);
}
// 将还没有加入到格子中的待处理定时任务队列中的任务取出,
// 如果是未取消的任务,则加入到未处理任务队列中,以供stop()方法返回
for (;;) {
HashedWheelTimeout timeout = timeouts.poll();
logger.info("work ==== timeout{} ", timeout);
if (timeout == null) {
break;
}
if (!timeout.isCancelled()) {
unprocessedTimeouts.add(timeout);
}
}
// 处理取消的任务
processCancelledTasks();
}
// 将newTimeout()方法中加入到待处理定时任务队列中的任务加入到指定的格子中
private void transferTimeoutsToBuckets() {
// transfer only max. 100000 timeouts per tick to prevent a thread to stale the workerThread when it just
// adds new timeouts in a loop.
// 每次tick只处理10w个任务,以免阻塞worker线程
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {
HashedWheelTimeout timeout = timeouts.poll();
// 如果没有任务了,直接跳出循环
if (timeout == null) {
// all processed
break;
}
// 还没有放入到格子中就取消了,直接略过
if (timeout.state() == HashedWheelTimeout.ST_CANCELLED) {
// Was cancelled in the meantime.
continue;
}
// 计算任务需要经过多少个tick
long calculated = timeout.deadline / tickDuration;
// 计算任务的轮数
timeout.remainingRounds = (calculated - tick) / wheel.length;
//如果任务在timeouts队列里面放久了, 以至于已经过了执行时间,
// 这个时候就使用当前tick, 也就是放到当前bucket, 此方法调用完后就会被执行.
final long ticks = Math.max(calculated, tick); // Ensure we don't schedule for past.
int stopIndex = (int) (ticks & mask);
// 将任务加入到响应的格子中
HashedWheelBucket bucket = wheel[stopIndex];
bucket.addTimeout(timeout);
}
}
// 将取消的任务取出,并从格子中移除
private void processCancelledTasks() {
for (;;) {
HashedWheelTimeout timeout = cancelledTimeouts.poll();
if (timeout == null) {
// all processed
break;
}
try {
timeout.remove();
} catch (Throwable t) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("An exception was thrown while process a cancellation task", t);
}
}
}
}
/**
* calculate goal nanoTime from startTime and current tick number,
* then wait until that goal has been reached.
* @return Long.MIN_VALUE if received a shutdown request,
* current time otherwise (with Long.MIN_VALUE changed by +1)
* sleep, 直到下次tick到来, 然后返回该次tick和启动时间之间的时长
*/
private long waitForNextTick() {
//下次tick的时间点, 用于计算需要sleep的时间
long deadline = tickDuration * (tick + 1);
for (;;) {
/**
* 计算需要sleep的时间, 之所以加999999后再除10000000, 是为了保证足够的sleep时间
* 例如:当deadline - currentTime=2000002的时候,如果不加999999,则只睡了2ms,
* 而2ms其实是未到达deadline这个时间点的,所有为了使上述情况能sleep足够的时间,加上999999后,会多睡1ms
*/
final long currentTime = System.nanoTime() - startTime;
long sleepTimeMs = (deadline - currentTime + 999999) / 1000000;
//这里的意思应该是从时间轮启动到现在经过太长的时间(跨度大于292年...),以至于让long装不下,都溢出了
if (sleepTimeMs <= 0) {
if (currentTime == Long.MIN_VALUE) {
return -Long.MAX_VALUE;
} else {
return currentTime;
}
}
// Check if we run on windows, as if thats the case we will need
// to round the sleepTime as workaround for a bug that only affect
// the JVM if it runs on windows.
//
// See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/356
// 这里是因为windows平台的定时调度最小单位为10ms,如果不是10ms的倍数,可能会引起sleep时间不准确
if (PlatformDependent.isWindows()) {
sleepTimeMs = sleepTimeMs / 10 * 10;
}
try {
Thread.sleep(sleepTimeMs);
} catch (InterruptedException ignored) {
if (WORKER_STATE_UPDATER.get(HashedWheelTimer.this) == WORKER_STATE_SHUTDOWN) {
return Long.MIN_VALUE;
}
}
}
}
public Set<Timeout> unprocessedTimeouts() {
return Collections.unmodifiableSet(unprocessedTimeouts);
}
}
HashedWheelTimeout
/**
* HashedWheelTimeout是一个定时任务的内部包装类,双向链表结构。
* 会保存定时任务到期执行的任务、deadline、round等信息。
*/
private static final class HashedWheelTimeout implements Timeout {
//定义定时任务的3个状态:初始化、取消、过期
private static final int ST_INIT = 0;
private static final int ST_CANCELLED = 1;
private static final int ST_EXPIRED = 2;
//用来CAS方式更新定时任务状态
private static final AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater<HashedWheelTimeout> STATE_UPDATER =
AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater.newUpdater(HashedWheelTimeout.class, "state");
// 时间轮引用
private final HashedWheelTimer timer;
// 具体到期需要执行的任务
private final TimerTask task;
private final long deadline;
@SuppressWarnings({"unused", "FieldMayBeFinal", "RedundantFieldInitialization" })
private volatile int state = ST_INIT;
// remainingRounds will be calculated and set by Worker.transferTimeoutsToBuckets() before the
// HashedWheelTimeout will be added to the correct HashedWheelBucket.
// 离任务执行的轮数,当将次任务加入到格子中是计算该值,每过一轮,该值减一。
long remainingRounds;
// This will be used to chain timeouts in HashedWheelTimerBucket via a double-linked-list.
// As only the workerThread will act on it there is no need for synchronization / volatile.
//双向链表结构,由于只有worker线程会访问,这里不需要synchronization / volatile
HashedWheelTimeout next;
HashedWheelTimeout prev;
// The bucket to which the timeout was added
//定时任务所在的格子
HashedWheelBucket bucket;
HashedWheelTimeout(HashedWheelTimer timer, TimerTask task, long deadline) {
this.timer = timer;
this.task = task;
this.deadline = deadline;
}
@Override
public Timer timer() {
return timer;
}
@Override
public TimerTask task() {
return task;
}
@Override
public boolean cancel() {
// only update the state it will be removed from HashedWheelBucket on next tick.
//这里只是修改状态为ST_CANCELLED,会在下次tick时,在格子中移除
if (!compareAndSetState(ST_INIT, ST_CANCELLED)) {
return false;
}
// If a task should be canceled we put this to another queue which will be processed on each tick.
// So this means that we will have a GC latency of max. 1 tick duration which is good enough. This way
// we can make again use of our MpscLinkedQueue and so minimize the locking / overhead as much as possible.
// 加入到时间轮的待取消队列,并在每次tick的时候,从相应格子中移除。
timer.cancelledTimeouts.add(this);
return true;
}
//从格子中移除自身
void remove() {
HashedWheelBucket bucket = this.bucket;
if (bucket != null) {
bucket.remove(this);
} else {
timer.pendingTimeouts.decrementAndGet();
}
}
public boolean compareAndSetState(int expected, int state) {
return STATE_UPDATER.compareAndSet(this, expected, state);
}
public int state() {
return state;
}
@Override
public boolean isCancelled() {
return state() == ST_CANCELLED;
}
@Override
public boolean isExpired() {
return state() == ST_EXPIRED;
}
// 过期并执行任务
public void expire() {
if (!compareAndSetState(ST_INIT, ST_EXPIRED)) {
return;
}
try {
task.run(this);
} catch (Throwable t) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("An exception was thrown by " + TimerTask.class.getSimpleName() + '.', t);
}
}
}
@Override
public String toString() {
final long currentTime = System.nanoTime();
long remaining = deadline - currentTime + timer.startTime;
StringBuilder buf = new StringBuilder(192)
.append(simpleClassName(this))
.append('(')
.append("deadline: ");
if (remaining > 0) {
buf.append(remaining)
.append(" ns later");
} else if (remaining < 0) {
buf.append(-remaining)
.append(" ns ago");
} else {
buf.append("now");
}
if (isCancelled()) {
buf.append(", cancelled");
}
return buf.append(", task: ")
.append(task())
.append(')')
.toString();
}
}
HashedWheelBucket
/**
* Bucket that stores HashedWheelTimeouts. These are stored in a linked-list like datastructure to allow easy
* removal of HashedWheelTimeouts in the middle. Also the HashedWheelTimeout act as nodes themself and so no
* extra object creation is needed.
* HashedWheelBucket用来存放HashedWheelTimeout,结构类似于LinkedList。
* 提供了expireTimeouts(long deadline)方法来过期并执行格子中的定时任务
*/
private static final class HashedWheelBucket {
// Used for the linked-list datastructure
// 指向格子中任务的首尾
private HashedWheelTimeout head;
private HashedWheelTimeout tail;
/**
* Add {@link HashedWheelTimeout} to this bucket.
* // 基础的链表添加操作
*/
public void addTimeout(HashedWheelTimeout timeout) {
assert timeout.bucket == null;
timeout.bucket = this;
if (head == null) {
head = tail = timeout;
} else {
tail.next = timeout;
timeout.prev = tail;
tail = timeout;
}
}
/**
* Expire all {@link HashedWheelTimeout}s for the given {@code deadline}.
* 过期并执行格子中的到期任务,tick到该格子的时候,worker线程会调用这个方法,
* 根据deadline和remainingRounds判断任务是否过期
*/
public void expireTimeouts(long deadline) {
HashedWheelTimeout timeout = head;
// process all timeouts
//遍历格子中的所有定时任务
while (timeout != null) {
HashedWheelTimeout next = timeout.next;
if (timeout.remainingRounds <= 0) {
next = remove(timeout);
if (timeout.deadline <= deadline) {
timeout.expire();
} else {
// The timeout was placed into a wrong slot. This should never happen.
//如果round数已经为0,deadline却>当前格子的deadline,说放错格子了,这种情况应该不会出现
throw new IllegalStateException(String.format(
"timeout.deadline (%d) > deadline (%d)", timeout.deadline, deadline));
}
} else if (timeout.isCancelled()) {
next = remove(timeout);
} else {
//没有到期,轮数-1
timeout.remainingRounds --;
}
timeout = next;
}
}
//基础的链表移除node操作
public HashedWheelTimeout remove(HashedWheelTimeout timeout) {
HashedWheelTimeout next = timeout.next;
// remove timeout that was either processed or cancelled by updating the linked-list
if (timeout.prev != null) {
timeout.prev.next = next;
}
if (timeout.next != null) {
timeout.next.prev = timeout.prev;
}
if (timeout == head) {
// if timeout is also the tail we need to adjust the entry too
if (timeout == tail) {
tail = null;
head = null;
} else {
head = next;
}
} else if (timeout == tail) {
// if the timeout is the tail modify the tail to be the prev node.
tail = timeout.prev;
}
// null out prev, next and bucket to allow for GC.
timeout.prev = null;
timeout.next = null;
timeout.bucket = null;
timeout.timer.pendingTimeouts.decrementAndGet();
return next;
}
/**
* Clear this bucket and return all not expired / cancelled {@link Timeout}s.
*/
public void clearTimeouts(Set<Timeout> set) {
for (;;) {
HashedWheelTimeout timeout = pollTimeout();
if (timeout == null) {
return;
}
if (timeout.isExpired() || timeout.isCancelled()) {
continue;
}
set.add(timeout);
}
}
//链表的poll操作
private HashedWheelTimeout pollTimeout() {
HashedWheelTimeout head = this.head;
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
HashedWheelTimeout next = head.next;
if (next == null) {
tail = this.head = null;
} else {
this.head = next;
next.prev = null;
}
// null out prev and next to allow for GC.
head.next = null;
head.prev = null;
head.bucket = null;
return head;
}
}
}