Node.js 模块化
介绍
什么是模块化与模块 ?
将一个复杂的程序文件依据一定规则(规范)拆分成多个文件的过程称之为
模块化
其中拆分出的 每个文件就是一个模块,模块的内部数据是私有的,不过模块可以暴露内部数据以便其他模块使用
什么是模块化项目 ?
编码时是按照模块一个一个编码的, 整个项目就是一个模块化的项目
模块化好处
下面是模块化的一些好处:
- 防止命名冲突
- 高复用性
- 高维护性
模块暴露数据
模块初体验
可以通过下面的操作步骤,快速体验模块化
-
创建 me.js
//声明函数 function tiemo(){ console.log('贴膜....'); } //暴露数据 module.exports = tiemo; -
创建 index.js
//导入模块 const tiemo = require('./me.js'); //调用函数 tiemo(); //=> 贴膜....
暴露数据
模块暴露数据的方式有两种:
module.exports= valueexports.name= value
使用时有几点注意:
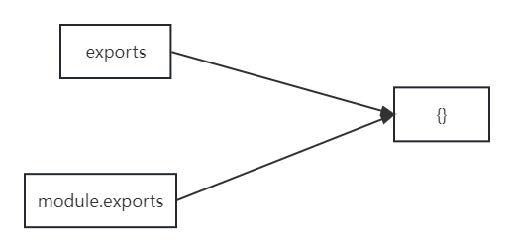
module.exports可以暴露 任意 数据- 不能使用
exports = value的形式暴露数据,模块内部 module 与 exports 的隐式关系
exports = module.exports = {},require 返回的是目标模块中module.exports的值
导入(引入)模块
在模块中使用 require 传入文件路径即可引入文件
const test = require('./me.js')
require 使用的一些注意事项:
-
对于自己创建的模块,导入时路径建议写 相对路径,且不能省略
./和../ -
js和json文件导入时可以不用写后缀,c/c++编写的node扩展文件也可以不写后缀,但是一般用不到,直接使用 node 的require()方法即可将 JSON 文件转换成 JS 对象 -
如果导入其他类型的文件,会以
js文件进行处理 -
如果导入的路径是个文件夹,则会 首先 检测该文件夹下
package.json文件中main属性对应的文件,如果存在则导入,反之如果文件不存在会报错。
如果 main 属性不存在,或者 package.json 不存在,则会尝试导入文件夹下的
index.js和
index.json,如果还是没找到,就会报错
-
导入 node.js 内置模块时,直接 require 模块的名字即可,无需加
./和../
导入模块的基本流程
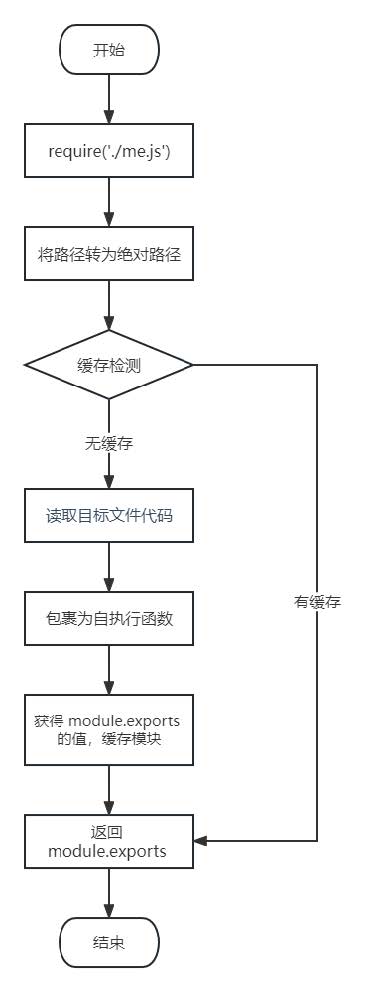
这里我们介绍一下 require 导入 自定义模块 的基本流程
- 将相对路径转为绝对路径,定位目标文件
- 缓存检测
- 读取目标文件代码
- 包裹为一个函数并执行(自执行函数)。通过
arguments.callee.toString()查看自执行函数 - 缓存模块的值
- 返回
module.exports的值
/**
* 伪代码
*/
function require(file){
//1. 将相对路径转为绝对路径,定位目标文件
let absolutePath = path.resolve(__dirname, file);
//2. 缓存检测
if(caches[absolutePath]){
return caches[absolutePath];
}
//3. 读取文件的代码
let code = fs.readFileSync(absolutePath).toString();
//4. 包裹为一个函数 然后执行
let module = {};
let exports = module.exports = {};
(function (exports, require, module, __filename, __dirname) {
const test = {
name: '尚硅谷'
}
module.exports = test;
//输出
console.log(arguments.callee.toString());
})(exports, require, module, __filename, __dirname)
//5. 缓存结果
caches[absolutePath] = module.exports;
//6. 返回 module.exports 的值
return module.exports;
}
CommonJS 规范
module.exports 、exports 以及 require 这些都是 CommonJS 模块化规范中的内容。
而 Node.js 是实现了 CommonJS 模块化规范,二者关系有点像 JavaScript 与 ECMAScript



![【洛谷 P1003】[NOIP2011 提高组] 铺地毯 题解(数组+贪心算法)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/823ec298bd31c29535b292affc8edf1f.png)