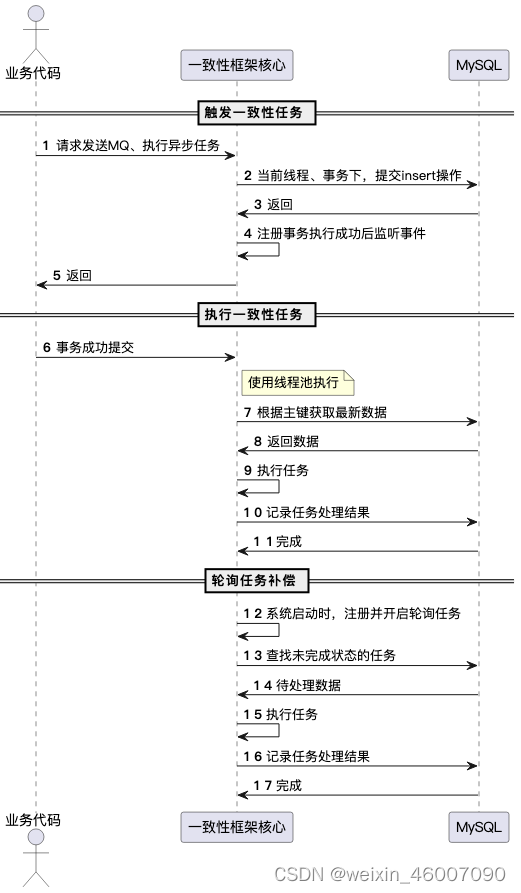
想要解决上面那个版本存在的问题:服务器重启,数据不丢失。
最好的办法:将数据存储到硬盘上。
存储的方式:1、直接使用 流对象 写入文本文件
2、借助数据库
我们采取的方式:是 MySQL 数据库的方式 来实现 持久化存储。
首先,既然我们要使用数据库来实现持久化存储。
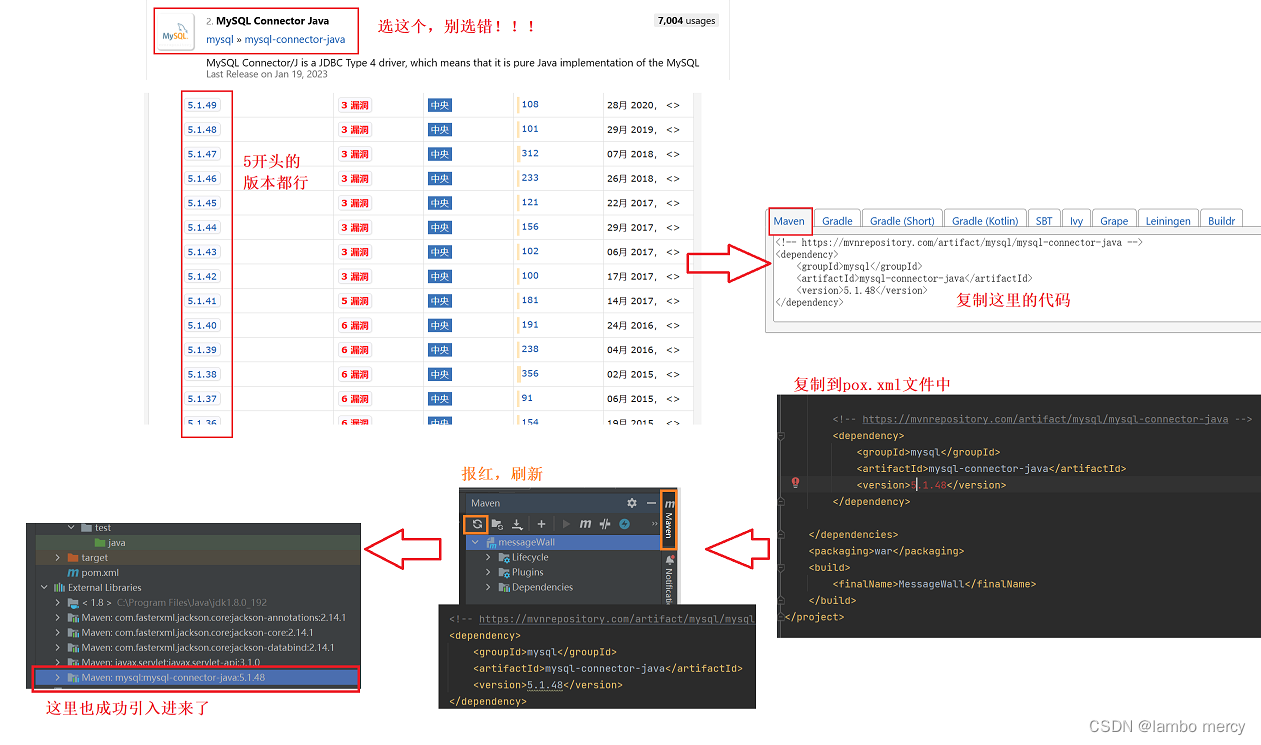
那么,我们在服务器代码中,需要引入依赖(MySQL)。Maven Repository: mysql » mysql-connector-java (mvnrepository.com)
既然我们使用MySQL 作为存储数据的手段。
那么原先的代码有些东西,就不在需要了!
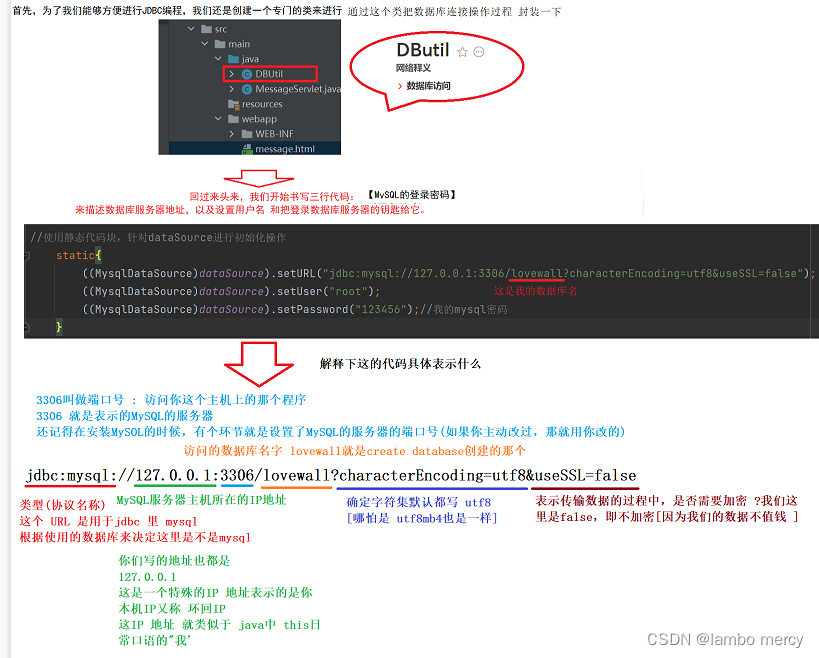
为了“嵌入”MySQL,我们需要添加一些方法去辅助我们。
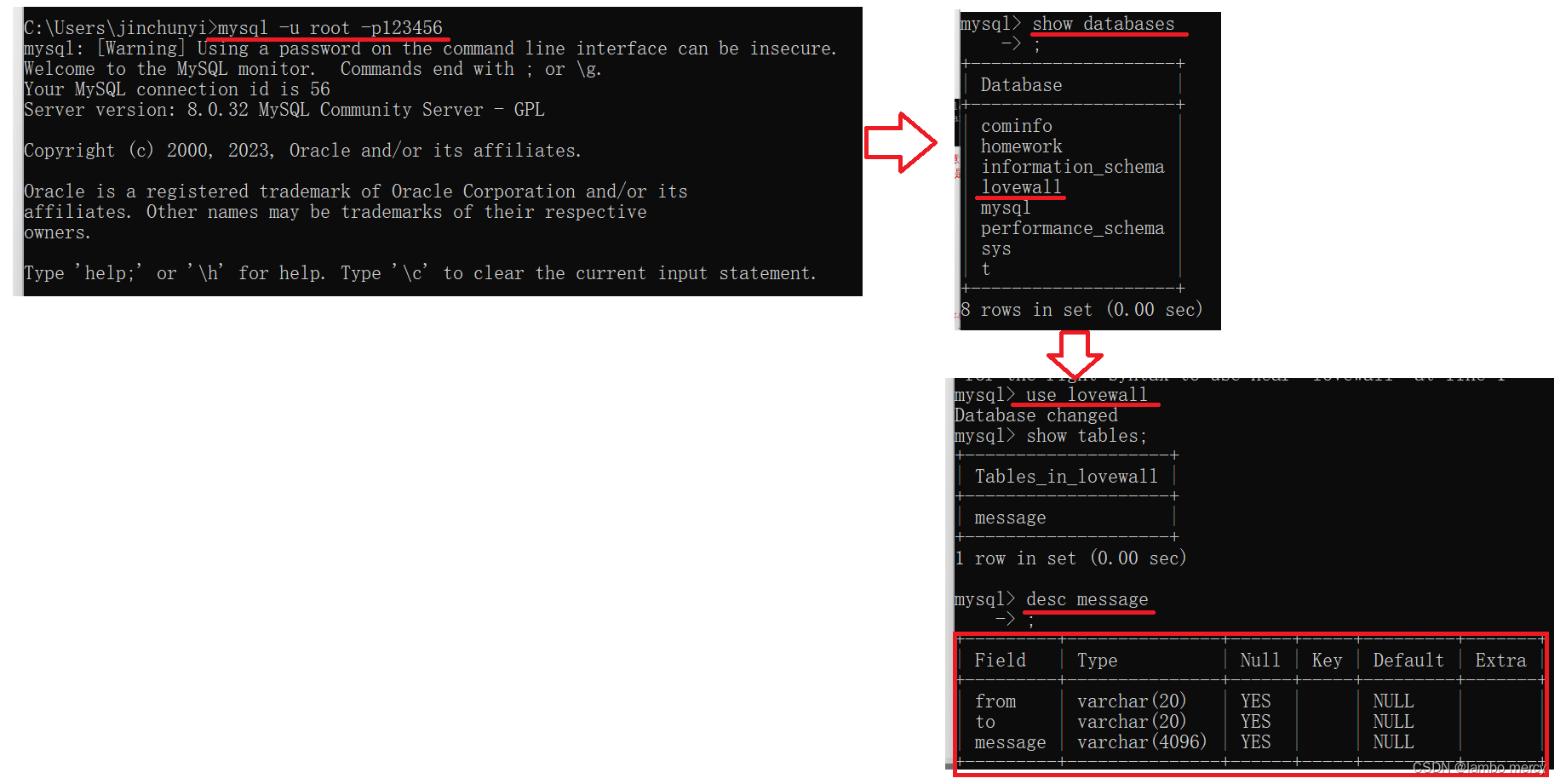
在实现 save 和 load 方法之前,我们先来在 MySQL上创建一个数据表来存储告白墙的信息。
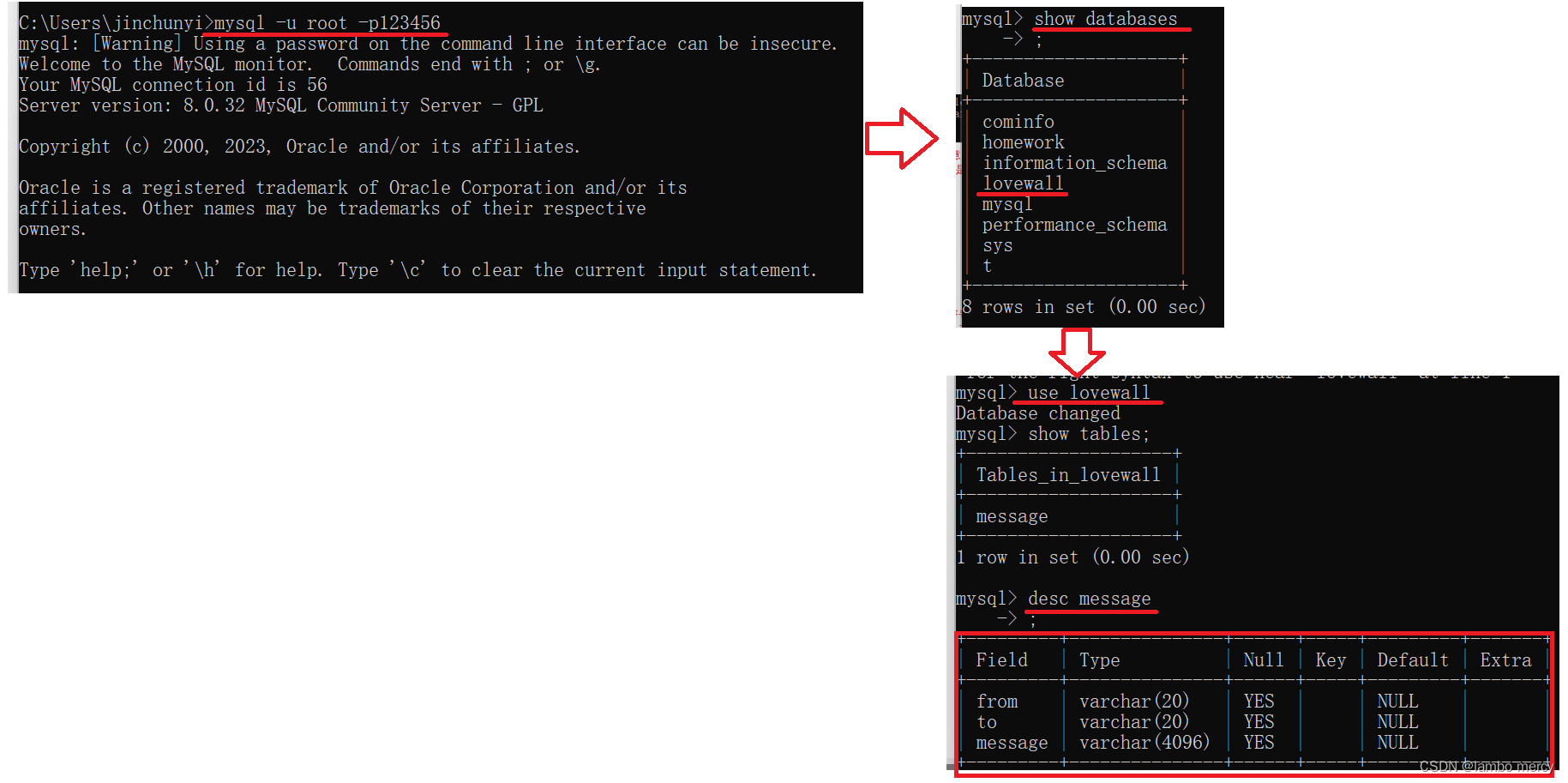
在实现 save 和 load 方法之前,我们先来在 MySQL上创建一个数据表来存储告白墙的信息。表结构为:message(from,to,message)
这下就有了数据库和表了,接下来就需要和数据库建立起连接。
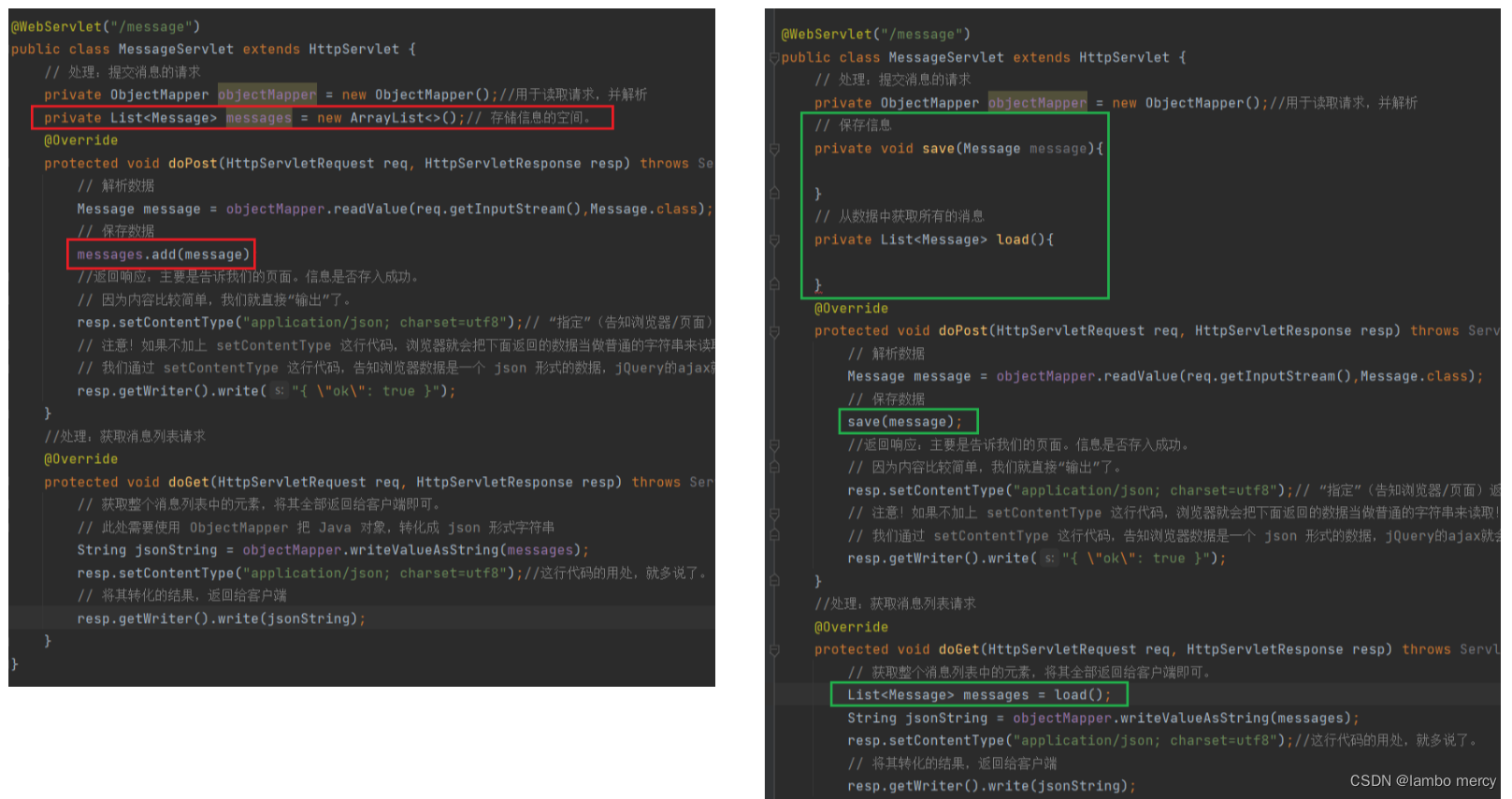
下面,我们就来为完善 save 和 load 方法做准备。
下面,我们可以来完善 MessageServlet 当中的 save 和 load 方法。
save 方法
load 方法
DButil - 数据库访问程序
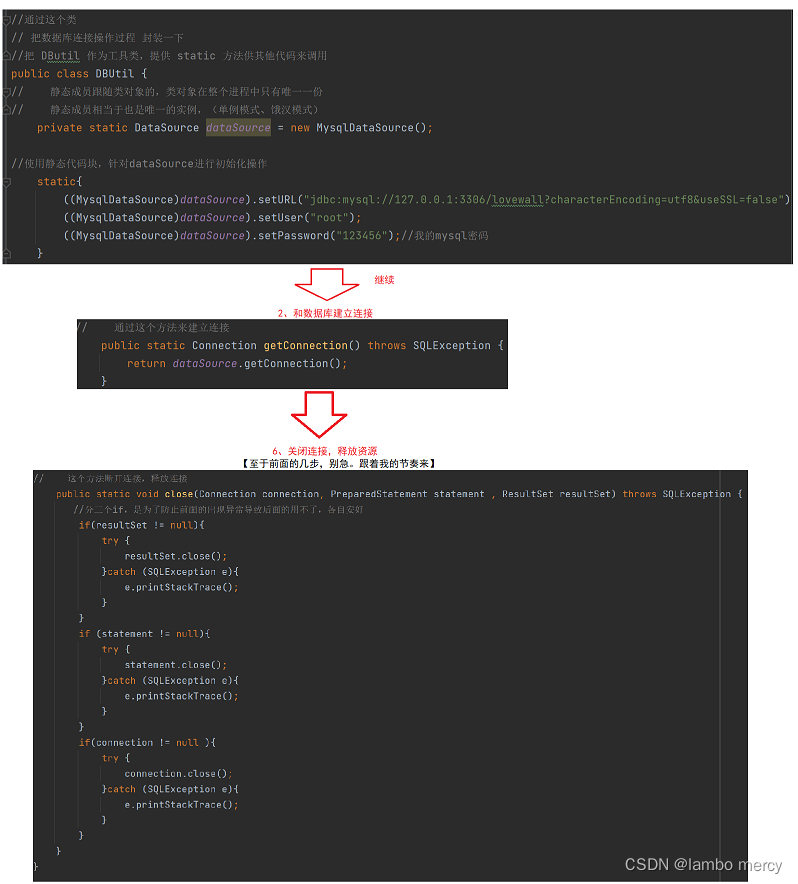
主要是简化 MessageServlet 中的程序。将 数据库连接,创建数据源,资源释放,具体实现细节给封装成一个类,来供 MessageServlet 中的程序使用。
//封装数据库连接过程
//作为工具类
public class DBUtil {
//单例饿汉模式
private static DataSource dataSource = new MysqlDataSource();
static{
//使用静态代码块初始化
((MysqlDataSource)dataSource).setUrl("jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/lovewall?characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=false");
((MysqlDataSource)dataSource).setUser("root");
((MysqlDataSource)dataSource).setPassword("123456");
}
//建立连接
public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
return dataSource.getConnection();
}
//释放资源
public static void close(Connection connection, PreparedStatement statement, ResultSet resultSet){
//此处的异常分开捕捉比较好,否则会影响后面的代码不能执行
if(resultSet!=null){
try {
resultSet.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
if(statement!=null){
try {
statement.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
if(connection!=null){
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}MessageServlet 服务器总程序
class Message{
public String from;
public String to;
public String message;
}
@WebServlet("/message")
public class MessageServlet extends HttpServlet {
// 使用这个List变量保存所有消息
private List<Message> messageList = new ArrayList<>();//有 mysql 了就不需要把 message 存在内存中了,注释掉了
private ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
// 提供一对方法
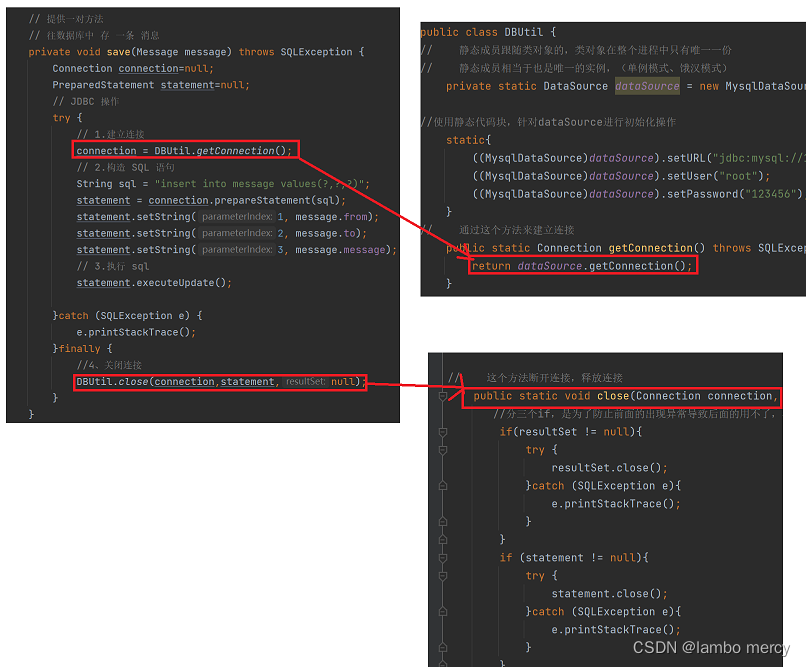
// 往数据库中 存 一条 消息
private void save(Message message) throws SQLException {
Connection connection=null;
PreparedStatement statement=null;
// JDBC 操作
try {
// 1.建立连接
connection = DBUtil.getConnection();
// 2.构造 SQL 语句
String sql = "insert into message values(?,?,?)";
statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
statement.setString(1, message.from);
statement.setString(2, message.to);
statement.setString(3, message.message);
// 3.执行 sql
statement.executeUpdate();
}catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
//4、关闭连接
DBUtil.close(connection,statement,null);
}
}
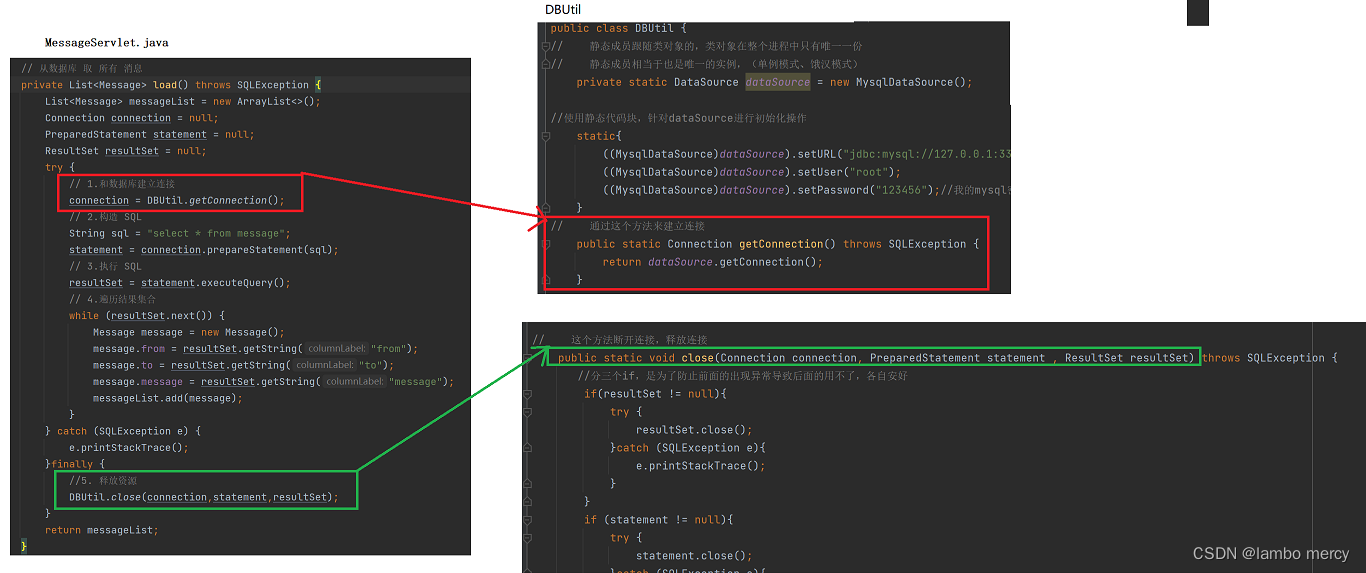
// 从数据库 取 所有 消息
private List<Message> load() throws SQLException {
List<Message> messageList = new ArrayList<>();
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement statement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
// 1.和数据库建立连接
connection = DBUtil.getConnection();
// 2.构造 SQL
String sql = "select * from message";
statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
// 3.执行 SQL
resultSet = statement.executeQuery();
// 4.遍历结果集合
while (resultSet.next()) {
Message message = new Message();
message.from = resultSet.getString("from");
message.to = resultSet.getString("to");
message.message = resultSet.getString("message");
messageList.add(message);
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
//5. 释放资源
DBUtil.close(connection,statement,resultSet);
}
return messageList;
}
// 向服务器提交数据
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
resp.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf-8");
//把body中的内容读取出来了,解析成了一个Message对象
Message message = objectMapper.readValue(req.getInputStream(), Message.class);
//1、内存方式:此处通过简单粗暴的方式保存
// messageList.add(message);//有 mysql 了就不需要了
//2、mysql方式存一条数据:调用save方法
try {
save(message);
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
//此处的设定状态码可以省略,不设置也是200
resp.setStatus(200);
}
// 服务器获取数据
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
resp.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf-8");
//1、内存方法:messageList
// objectMapper.writeValue(resp.getWriter(),messageList);//有 mysql 了就不需要了
//2、mysql方法取数据:调用 load 方法
try {
List<Message> messageList = load();
String jsonResp = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(messageList);
System.out.println("jsonResp"+jsonResp);
resp.getWriter().write(jsonResp);
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}前端代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>表白墙</title>
<style>
/* *是通配符选择器,会选中页面所有的元素 */
/* 消除浏览器的默认显示模式 */
*{
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
.container{
width: 600px;
margin: 0 auto;
}
h1{
margin-top: 100px;
text-align: center;
}
p{
text-align: center;
color: #666;
margin: 20px auto;
}
.row{
/* 开启弹性布局 */
display: flex;
height: 40px;
/* 水平方向居中 */
justify-content: center;
/* 垂直方向居中 */
align-items: center;
}
.row span{
width: 50px;
}
.row input{
width: 200px;
height: 30px;
}
.row button{
width: 250px;
height: 30px;
color: aliceblue;
background-color: orange;
/* 去掉边框 */
border: none;
border-radius: 3px;
}
/* 点击反馈 */
.row button:active{
background-color: grey;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<h1>表白墙</h1>
<p>输入信息后提交,信息会显示到表格中</p>
<div class="row">
<span>谁:</span>
<input type="text">
</div>
<div class="row">
<span>对谁:</span>
<input type="text">
</div>
<div class="row">
<span>说:</span>
<input type="text">
</div>
<div class="row">
<button>提交</button>
</div>
</div>
<script src="https://cdn.bootcdn.net/ajax/libs/jquery/3.6.4/jquery.min.js"></script>
<script>
//实现提交操作,点击提交按钮,将用户输入的内容提交到页面上
//点击的时候获取输入框内容,然后创建一个新的div.row,将内容构造进去
let containerDiv = document.querySelector('.container');
let inputs = document.querySelectorAll('input');
let button = document.querySelector('button');
button.onclick = function(){
//1.获取输入框的内容
let from = inputs[0].value;
let to = inputs[1].value;
let msg = inputs[2].value;
if(from =='' || to == '' || msg == ''){
return;
}
//2.构造新的div
let rowDiv = document.createElement('div');
rowDiv.className = 'row';
rowDiv.innerHTML = from + ' 对 ' + to + ' 说: ' + msg;
containerDiv.appendChild(rowDiv)
//3.清空之前的输入
for(let input of inputs){
input.value = '';
}
//4.新增代码,将数据提交给服务器,构造post请求
//定义js对象,key是字符串,value是js中的变量常量
let body = {
"from":from,
"to":to,
"message":msg
};
//转换
strBody = JSON.stringify(body);
console.log("strBody = "+strBody);
$.ajax({
type:'post',
url:'message',
data:strBody,
contentType:"application/json;charset = utf8",
success :function(body){
console.log("发布成功");
}
});
}
//新增:浏览器在页面加载的时候发送get请求,从服务器获取数据并添加到页面中
$.ajax({
type:'get',
url:'message',
success:function(body){
//此处拿到的body是一个js数组
//本来服务器返回的是一个json字符串,但是jquery的ajax能够自动识别并转换成js对象数组
//遍历数组,取出元素,构造到页面
for(let message of body){
//2.构造新的div
let rowDiv = document.createElement('div');
rowDiv.className = 'row message';
rowDiv.innerHTML = message.from + ' 对 ' + message.to + ' 说: ' + message.message;
containerDiv.appendChild(rowDiv);
}
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
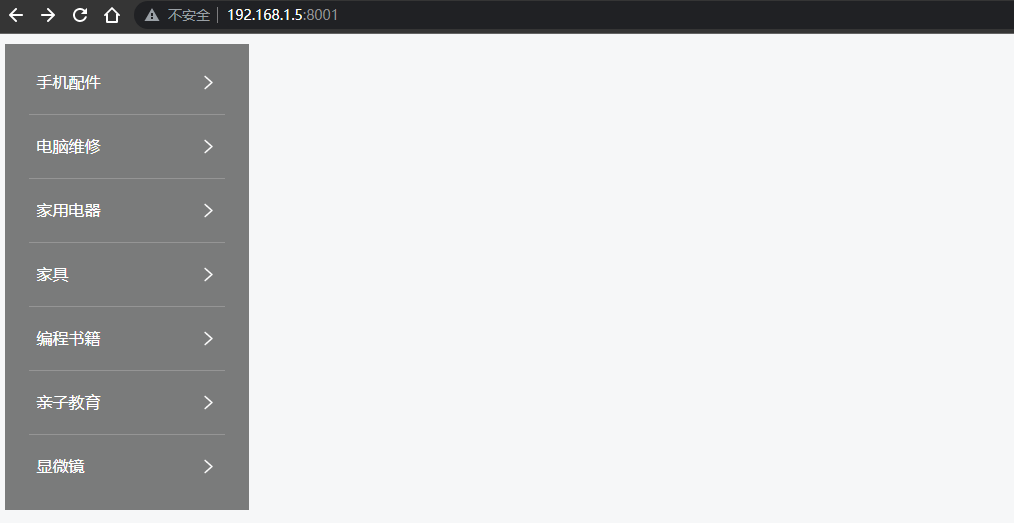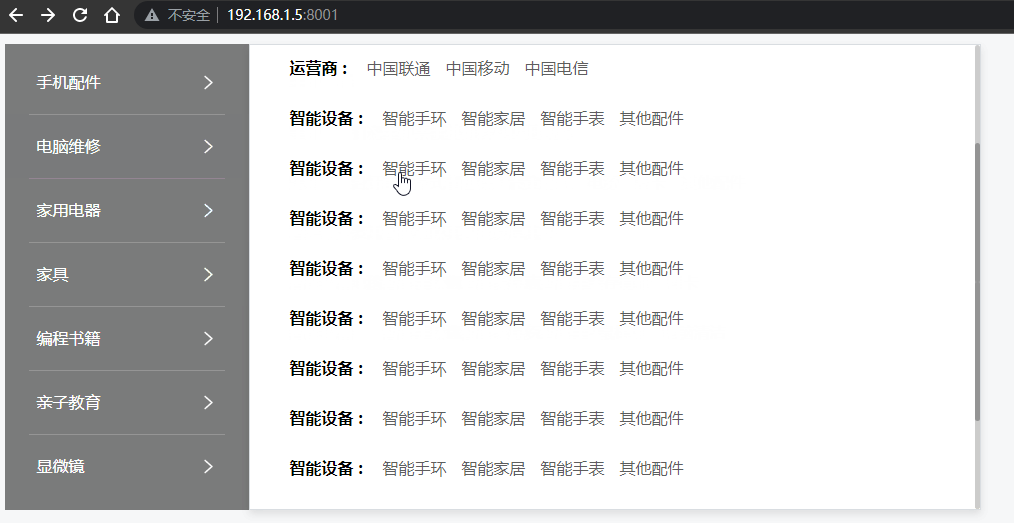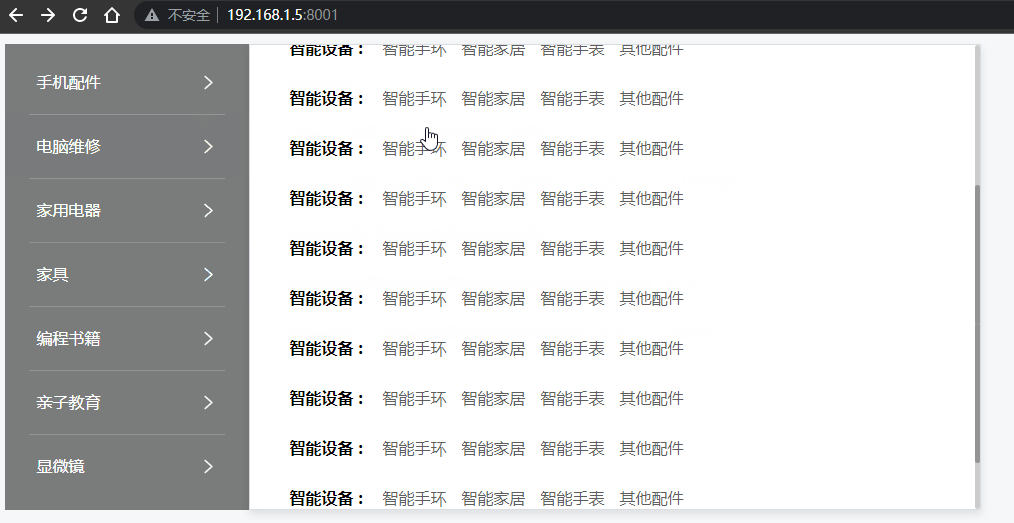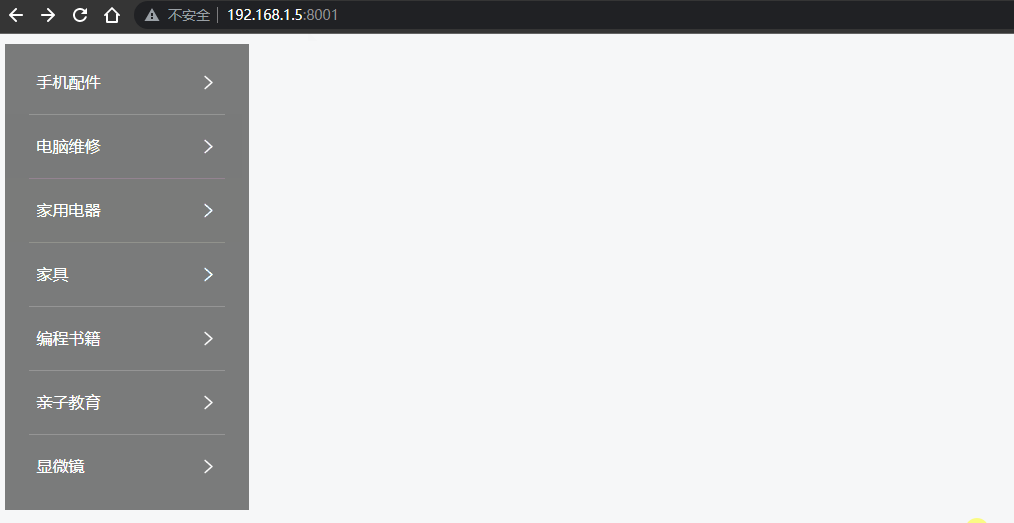
效果图
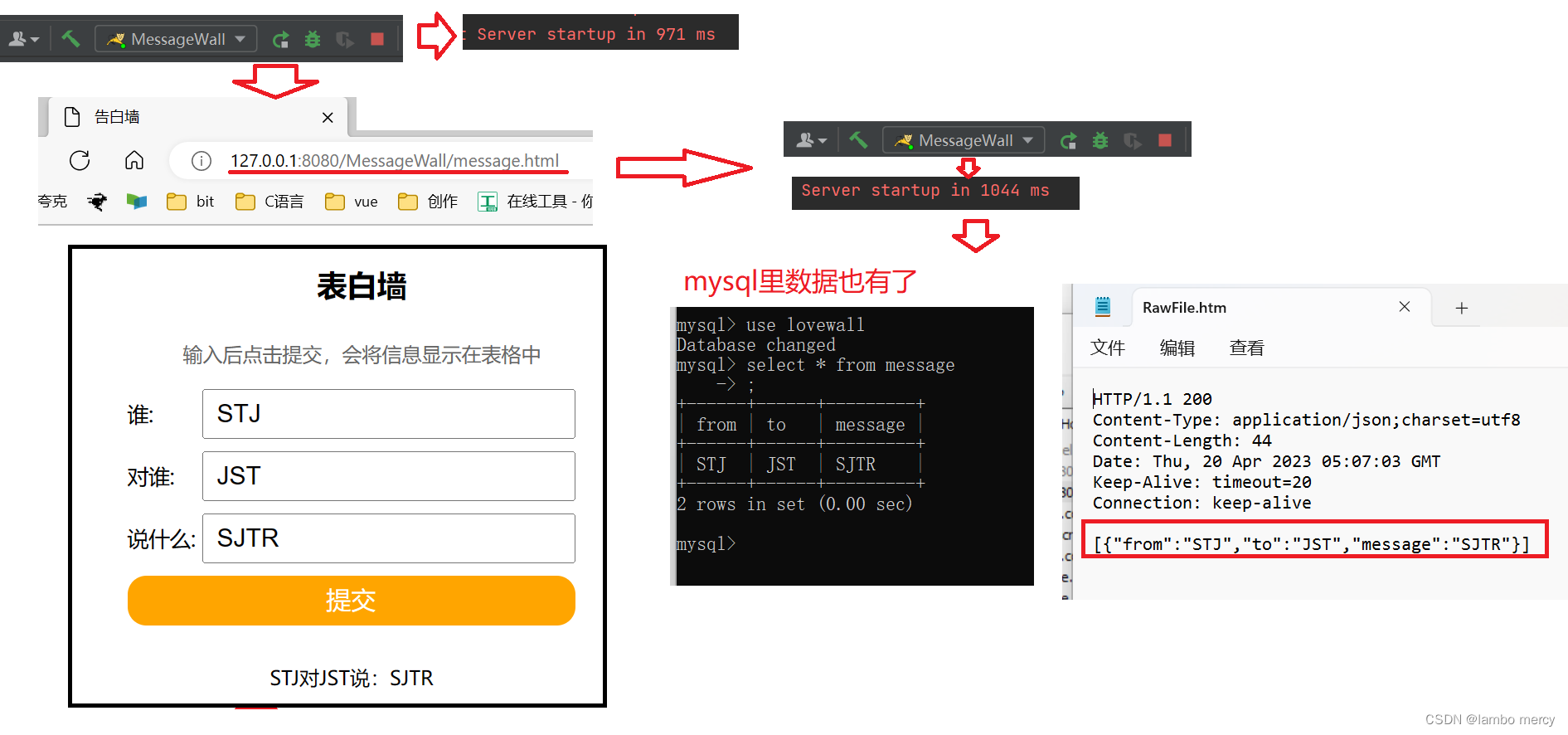
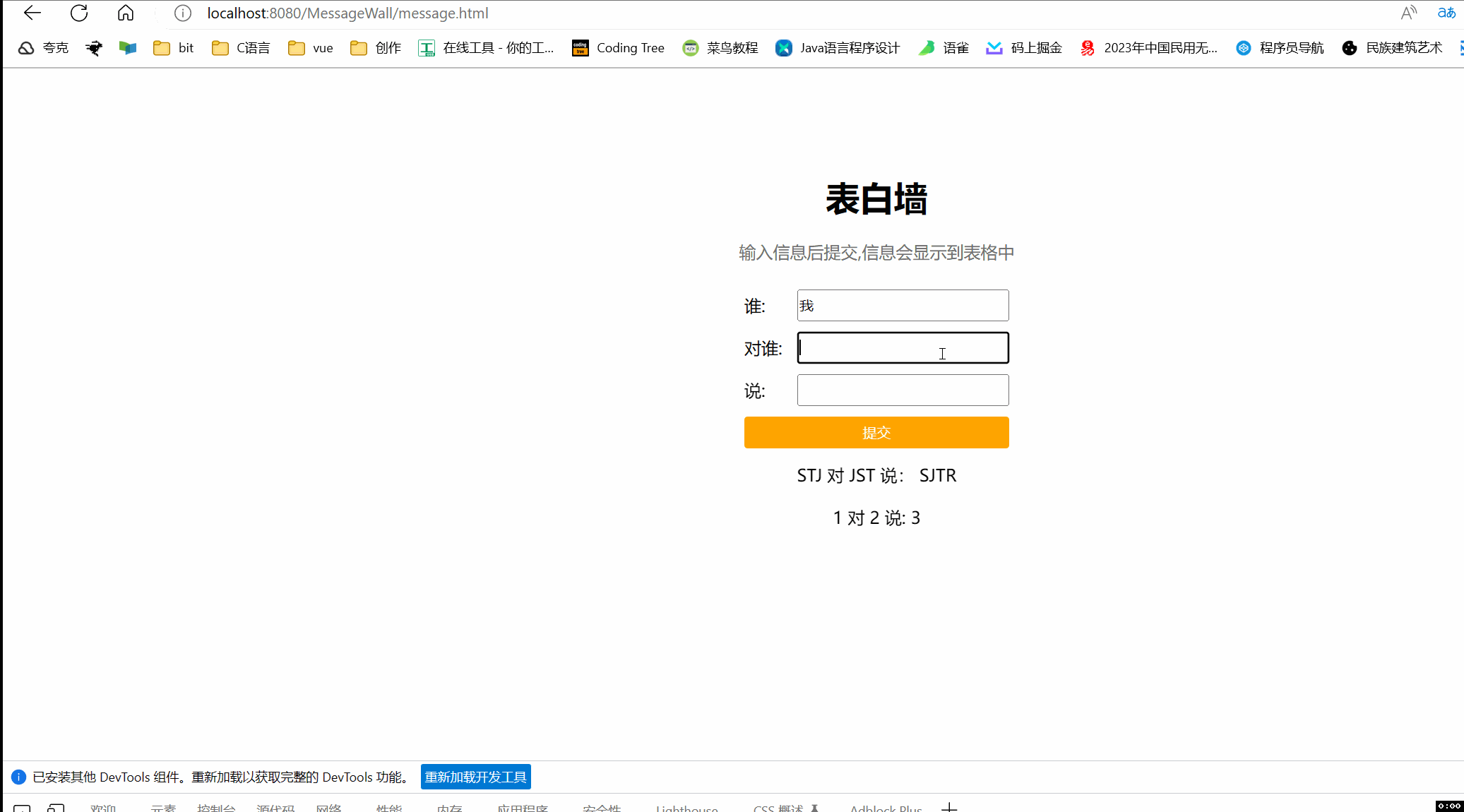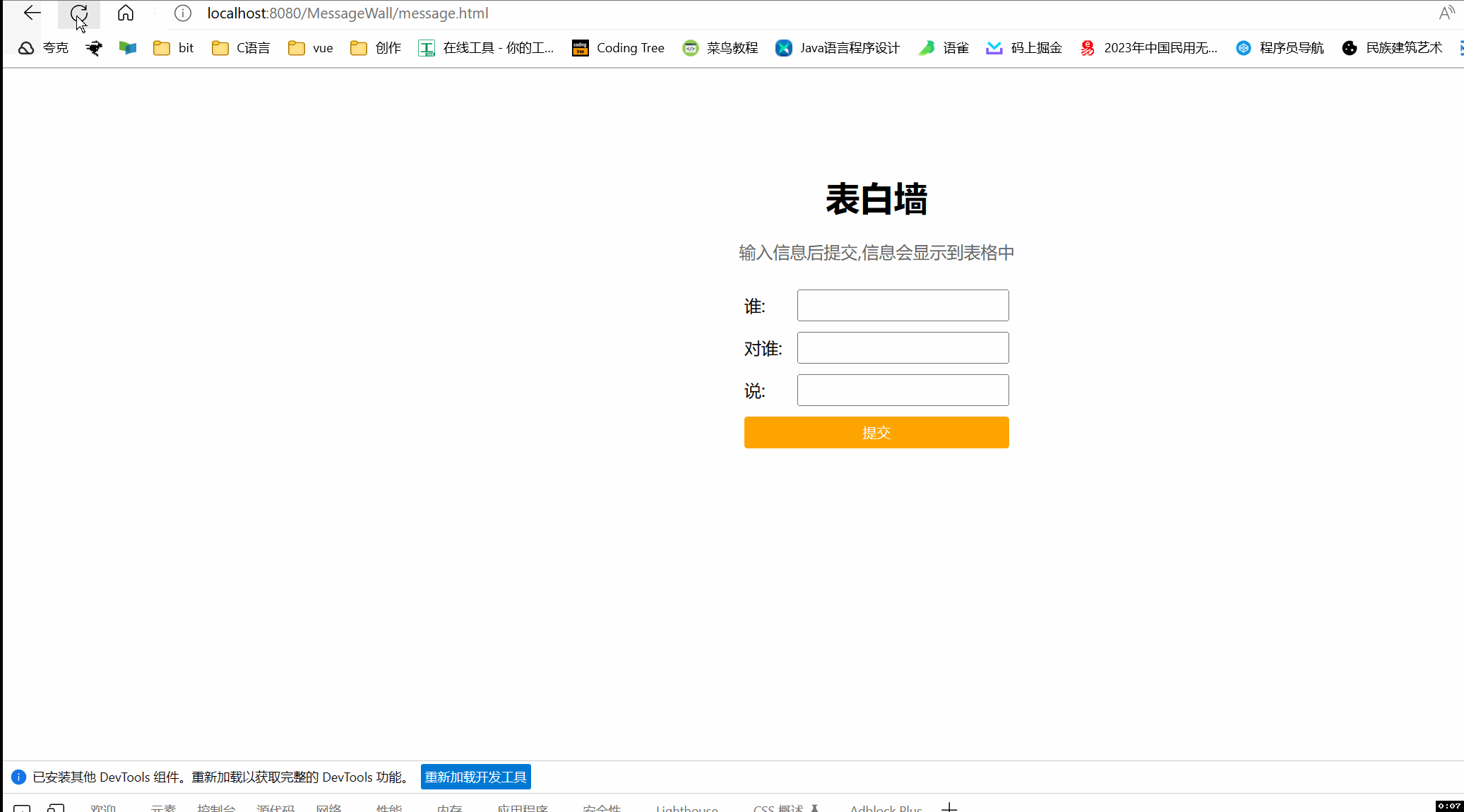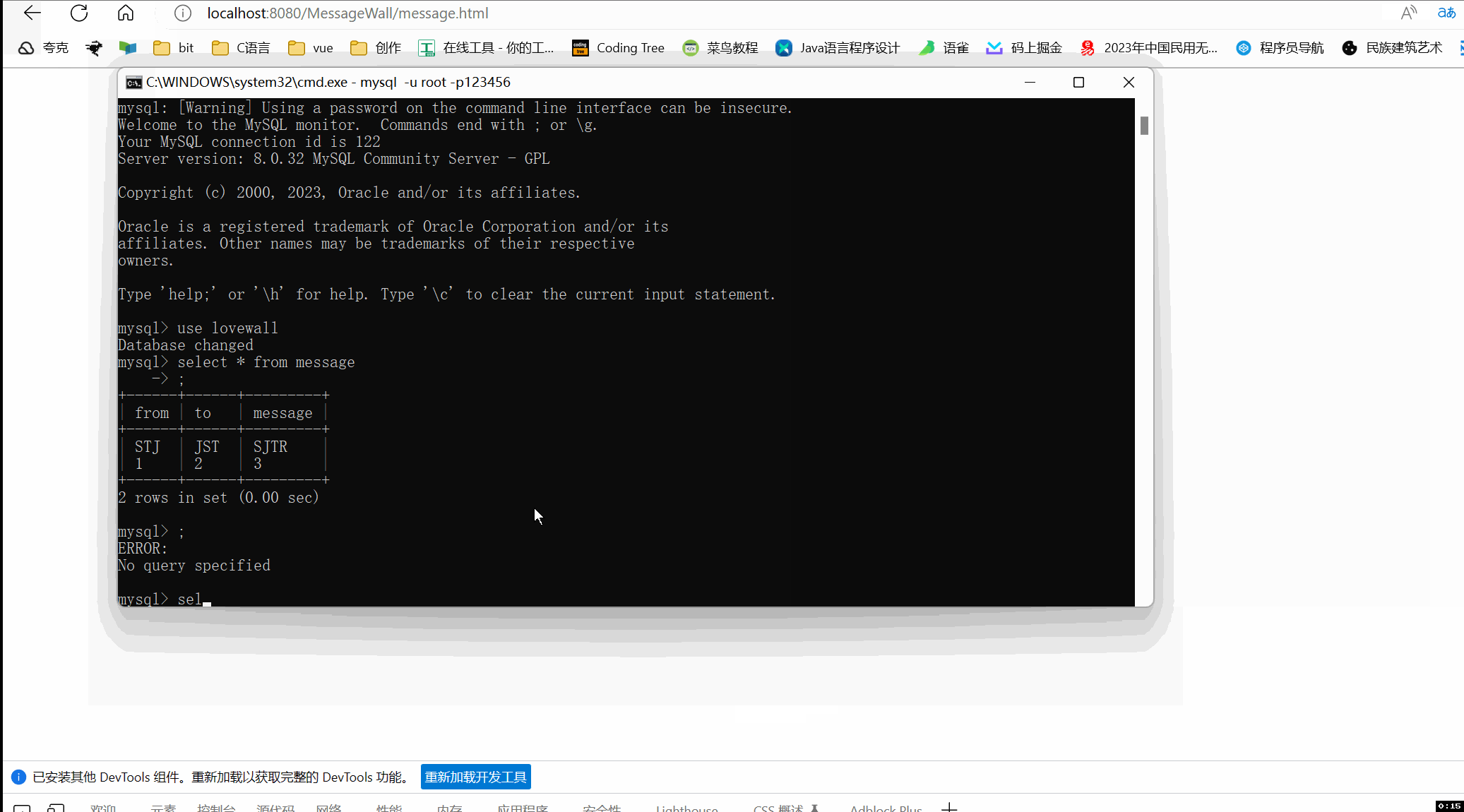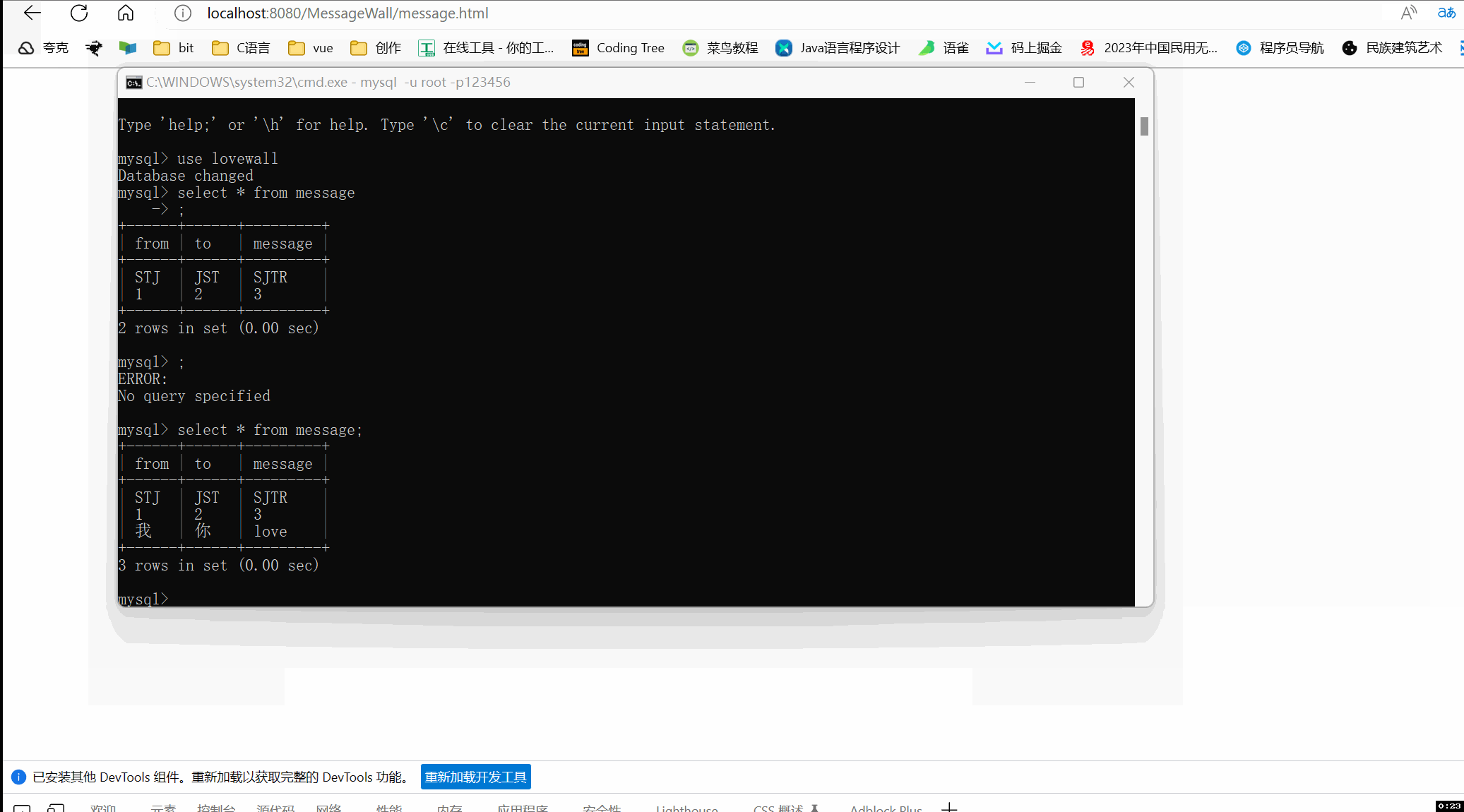
控制台打印日志

数据库的表中增加了数据

小结
开发一个表白墙(一个简单网站)基本步骤:
1、约定前后端交互的接口
请求是什么格式?响应是什么格式?
2、开发服务器代码
2.1、先编写 Servlet 能够处理的前端请求
2.2、编写数据库代码,来 存储 / 获取 关键数据
3、开发客户端代码
3.1、基于 ajax 能够构造请求以及解析响应
3.2、能够响应用户的操作。
比如:我们在点击按钮之后,触发给服务器发送请求的行为。
以后遇到像这种“网站”类的程序,实现过程都是类似的!
可以说,这就是一个模板。
说到这里,我们就需要拓展一下了。
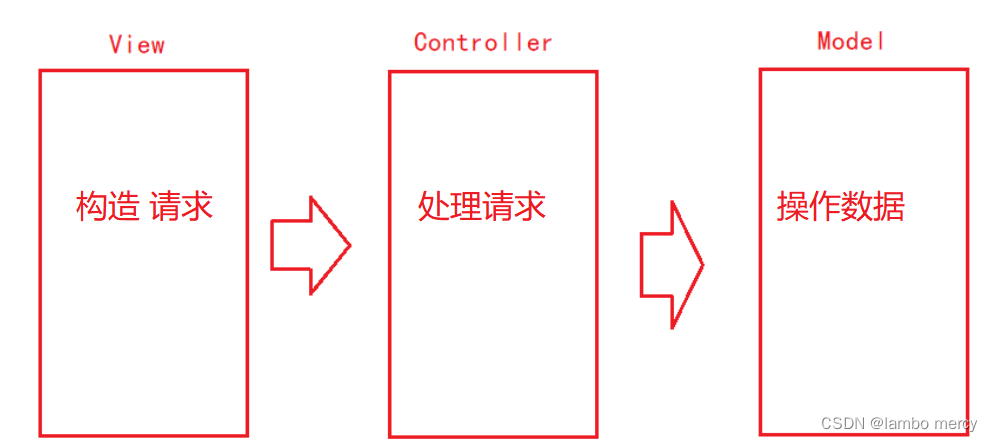
MVC
M:Model(模式) - 操作数据存取的逻辑
V:View(视图)- 页面的显示
C:Controller(控制器) - 处理请求之后的关键逻辑
View 是和用户进行交互的,View 再和 Controller 进行交互。
相当于是 View 构造 请求,Controller 在进行处理。
Controller 再和 Model 进行交互,Model 开始操作数据