目录
- 前言
- 实现
- application.properties
- config.RedisConfig
- MainApplication
- controller.TrafficLimitController
- aop.AccessLimiterAspect
- aop.annotation.AccessLimiter
- 项目结构
- 运行
- 限流脚本
- 计数器
- 滑动窗口
- 令牌桶
- 漏桶
- 参考资料
前言
服务的某些场景可能会出现短时间内的巨大访问流量,比如某宝在某个日子可能会有数倍于平时的高峰访问流量,导致接口超时异常,甚至服务被压垮,还可能会导致系统其它服务发生故障,造成服务雪崩。
我们如何让系统保证高并发,同时还能保证稳定性?
加机器吗?
硬件资源不是无限的。
为了避免极端情况,我们不得不在后端服务中采取保护措施:缓存、异步、降级、限流……
分布式限流是一种将限流机制分布在不同服务器或不同网络节点上的技术,它可以实现高效地限制请求流量,对高并发访问进行限速或者对一段时间内的请求进行限速,来保护系统,一旦达到限速规则,则可以采用一定的方式来处理这些请求(视具体业务而定),如:拒绝服务(友好提示或者跳转到错误页面),排队或等待(比如秒杀系统),服务降级(返回默认的兜底数据)。保证系统的稳定性和可靠性。它可以帮助系统避免过度负载,防止系统崩溃或者性能下降。
实现
application.properties
application.properties
server.port=8080
## if savebatch, could try rewriteBatchedStatements=true setting postgres/123456
spring.datasource.platform=postgres
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:postgresql://127.0.0.1:5432/postgres?stringtype=unspecified
spring.datasource.username=postgres
spring.datasource.password=weiyuzeng0827+
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=org.postgresql.Driver
#spring.jpa.database-platform=org.hibernate.dialect.PostgreSQLDialect
# mybatis-plus
mybatis-plus.configuration.log-impl=org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl
mybatis-plus.global-config.db-config.logic-delete-value=1
mybatis-plus.global-config.db-config.logic-not-delete-value=0
# redis
spring.redis.host = 10.86.9.118
spring.redis.password =
spring.redis.port = 6379
# thread pool config
#spring.threadpool.corePoolSize=14
#spring.threadpool.maxPoolSize=60
#spring.threadpool.queueCapacity=5000
#spring.threadpool.keepAliveSeconds=600
#spring.threadpool.threadNamePrefix=async-thread-pool-thread
config.RedisConfig
RedisConfig
package org.example.config;
import cn.hutool.core.util.StrUtil;
import org.redisson.Redisson;
import org.redisson.api.RedissonClient;
import org.redisson.config.Config;
import org.redisson.connection.balancer.RandomLoadBalancer;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
@Configuration
//@PropertySource({"classpath:redis.properties"})
public class RedisConfig {
@Value("${spring.redis.host}")
private String host;
@Value("${spring.redis.port}")
private String port;
@Value("${spring.redis.password}")
private String password;
@Bean
public RedissonClient getRedissionClient() {
Config config = new Config();
config.useSingleServer().setAddress("redis://" + host + ":" + port);
if (StrUtil.isNotBlank(password)) {
config.useClusterServers().setPassword(password);
}
RedissonClient redisson = Redisson.create(config);
return redisson;
}
}
MainApplication
MainApplication
package org.example;
import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableAsync;
/**
* @author z
*/
@EnableAsync
@SpringBootApplication(scanBasePackages = "org.example")
@MapperScan("org.example.dao.mapper")
public class MainApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(MainApplication.class, args);
}
}
controller.TrafficLimitController
TrafficLimitController
package org.example.controller;
import cn.hutool.core.util.ObjectUtil;
import org.example.aop.annotation.AccessLimiter;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.concurrent.CopyOnWriteArrayList;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
/**
*
* @author zengweiyu
* @since 2022-05-09
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/traffic-limit-algorithm")
public class TrafficLimitController {
private static CopyOnWriteArrayList<AtomicInteger> listCache = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>();
private static AtomicInteger queryOrderRecort = new AtomicInteger(0);
@AccessLimiter
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String hello() {
return "hello web!";
}
@PostMapping("/query")
@AccessLimiter(name = "限流测试", limit = 300, expireTime = 10)
public String trafficLimitTest() {
// 操作数递增
if (!ObjectUtil.isEmpty(queryOrderRecort)) {
queryOrderRecort.incrementAndGet();
}
listCache.add(new AtomicInteger(queryOrderRecort.get()));
System.out.println(listCache);
return listCache.toString();
}
}
RedisClientUtil
```java
package org.example.utils;
import org.apache.logging.log4j.LogManager;
import org.apache.logging.log4j.Logger;
import org.redisson.api.RScript;
import org.redisson.api.RedissonClient;
import org.redisson.client.codec.StringCodec;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
@Component
public class RedisClientUtil {
private static final Logger logger = LogManager.getLogger(RedisClientUtil.class);
@Autowired
private RedissonClient redissonClient;
private static RedisClientUtil redisClientUtil;
@PostConstruct
private void init() {
redisClientUtil = this;
redisClientUtil.redissonClient = this.redissonClient;
}
/**
* @desc 计数器,ip限流
* @param key redis key
* @param numLimit 单位时间间隔内的请求限制数
* @param expireTime 请求限制的单位时间间隔
* @author pankaixin
* @return
*/
public static Boolean isExceedIpCountLimit(String key, Integer numLimit, Integer expireTime) {
RScript rScript = redisClientUtil.redissonClient.getScript(StringCodec.INSTANCE);
List<Object> keys = new ArrayList<>(1);
keys.add(key);
// 直接获得参数key和expire_time,tonumber转为数字得到参数limit
// lua调用redis:redis.call(command, key, params),command是调用redis的命令,key是调用命令使用的key,params是给key的参数
// redis.call('EXISTS', key)是判断key在redis中是否存在(EXISTS)
// redis.call('INCR', key):对存储在指定key的数值执行原子的加1操作。
// redis.call('SET', key, 1):对存储在key的数值设为1
// redis.call('EXPIRE', key, expire_time):对存储在key的字段设定expire_time的过期时间
String strScript = "local key = KEYS[1] " +
"local limit = tonumber(ARGV[1]) " +
"local expire_time = ARGV[2] " +
"local is_exists = redis.call('EXISTS', key) " +
"if is_exists == 1 then " +
" if redis.call('INCR', key) > limit then " +
" return false " +
" else " +
" return true " +
" end " +
"else " +
" redis.call('SET', key, 1) " +
" redis.call('EXPIRE', key, expire_time) " +
" return true " +
"end ";
// 执行lua脚本
Boolean bResult = rScript.eval(RScript.Mode.READ_WRITE, strScript, RScript.ReturnType.BOOLEAN, keys, numLimit, expireTime);
return !bResult;
}
}
aop.AccessLimiterAspect
AccessLimiterAspect
package org.example.aop;
import org.apache.logging.log4j.LogManager;
import org.apache.logging.log4j.Logger;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.aspectj.lang.reflect.MethodSignature;
import org.example.aop.annotation.AccessLimiter;
import org.example.common.RedisConstants;
import org.example.utils.RedisClientUtil;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.RequestContextHolder;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.ServletRequestAttributes;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.List;
/**
* 限流切面
* @author z
*/
@Component
@Aspect
@Order(3)
public class AccessLimiterAspect {
private static final Logger logger = LogManager.getLogger(AccessLimiterAspect.class);
/**
* 请求ip
*/
private static final String IP = "ip";
/**
* 切入点,创建的注解类
*/
@Pointcut("@annotation(org.example.aop.annotation.AccessLimiter)")
public void limiterPointcut() {
}
@Before("limiterPointcut()")
public void limiter(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
// 1:获取方法的签名作为key,通过签名获取目标方法信息
MethodSignature methodSignature = (MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature();
Method method = methodSignature.getMethod();
// String classname = methodSignature.getMethod().getDeclaringClass().getName();
// 4: 读取方法的注解信息获取限流参数
AccessLimiter annotation = method.getAnnotation(AccessLimiter.class);
// 5:获取注解方法名
String methodNameKey = method.getName();
// 6:获取当前服务请求的对象
ServletRequestAttributes requestAttributes = (ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
HttpServletRequest request = requestAttributes.getRequest();
// HttpServletResponse response = requestAttributes.getResponse();
String servletPath = request.getServletPath();
String userIp = request.getHeader(IP);
// 7:通过方法反射获取注解的参数
Integer limit = annotation.limit();
Integer expireTime = annotation.expireTime();
String accessName = annotation.name();
String redisKey = RedisConstants.REDIS_CACHE_KEY_IP_URL_ACCESS_LIMIT_KEY + ":" + servletPath + ":" + userIp;
// 8: 执行lua脚本,每次访问会在redis中存储在key的数值计数加一次,过期时间设置为expireTime,一旦过期时间内超过计数器超过limit,
// 则返回False,以此达到限流的效果
Boolean isExceedIpCountLimit = RedisClientUtil.isExceedIpCountLimit(redisKey, limit, expireTime);
// 超过请求限制
if (isExceedIpCountLimit) {
logger.error(" [{}] 接口 {}: 达到限流, ip is:{}, servletPath is:{}, numLimit is:{}, expireTime is:{}", accessName, methodNameKey, userIp, servletPath, limit, expireTime);
throw new RuntimeException("exceed access traffic limit error");
}
logger.info(" [{}] 接口 {}: 未达到限流.......ip is:{}, servletPath is:{}, numLimit is:{}, expireTime is:{}", accessName, methodNameKey, userIp, servletPath, limit, expireTime);
}
}
aop.annotation.AccessLimiter
AccessLimiter
package org.example.aop.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
/**
* 限流接口
* @author z
*/
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface AccessLimiter {
/**
* 资源名称,用于描述接口功能
*/
String name() default "";
/**
* 每expireTime限制请求的个数
*/
int limit() default 300;
/**
* 时间,单位默认是秒
*/
int expireTime() default 10;
}
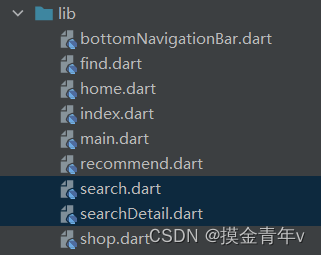
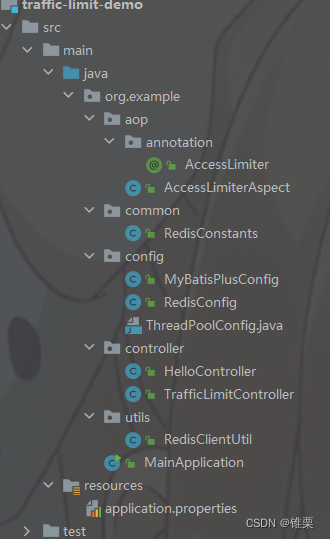
项目结构
项目结构如下:
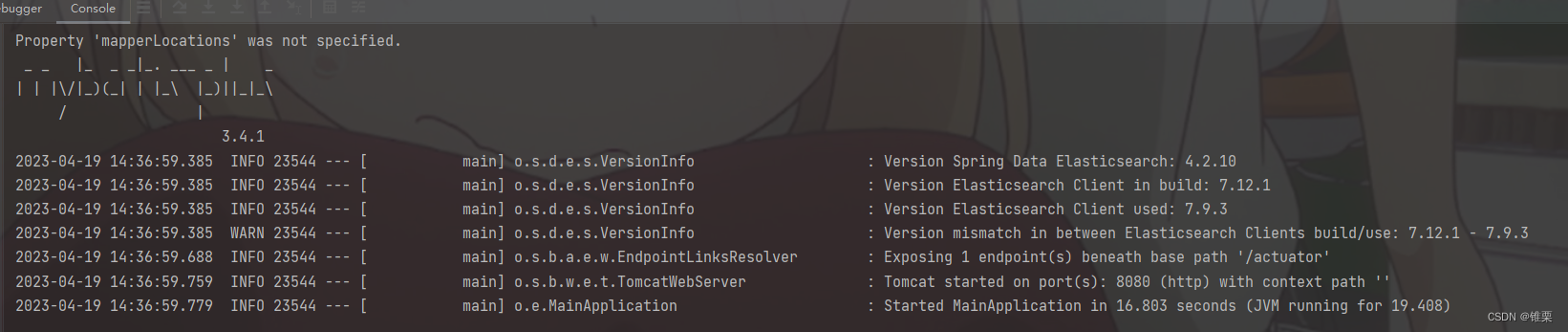
运行
运行项目
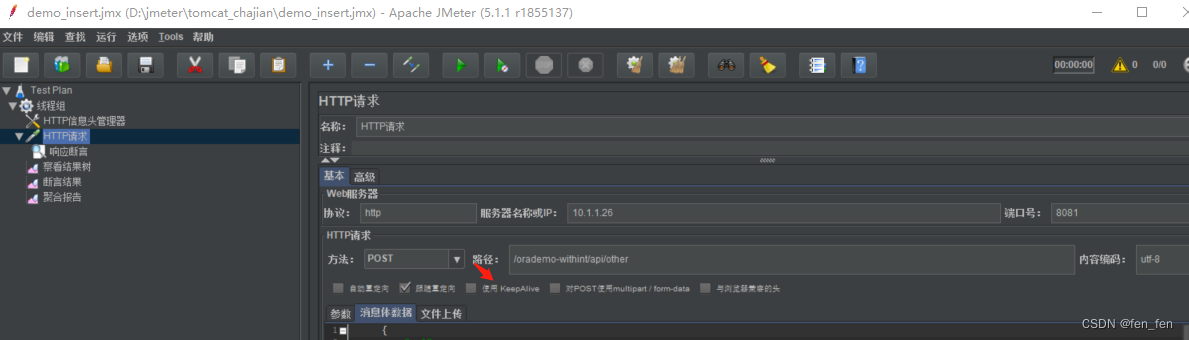
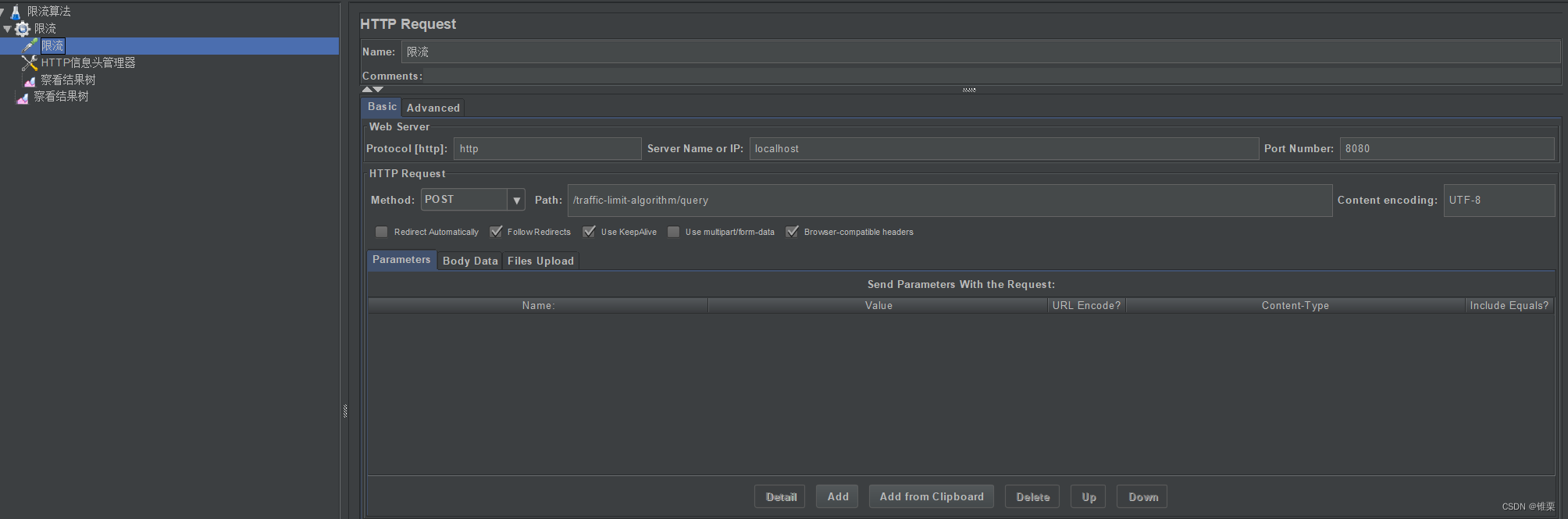
创建一个jmeter 脚本:
配置如下
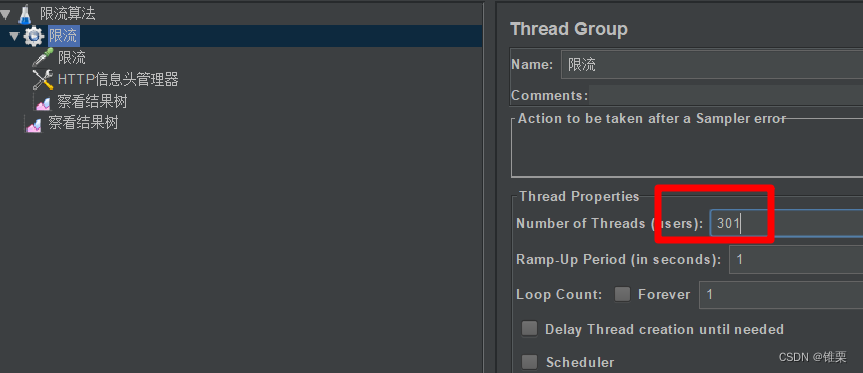
我们限制在10秒内最多允许300个请求,因此并发线程设置301个,故意超过上限。
protocol:http,IP:localhost,port:8080,POST,path:/traffic-limit-algorithm/query
运行线程组:
查看控制台:
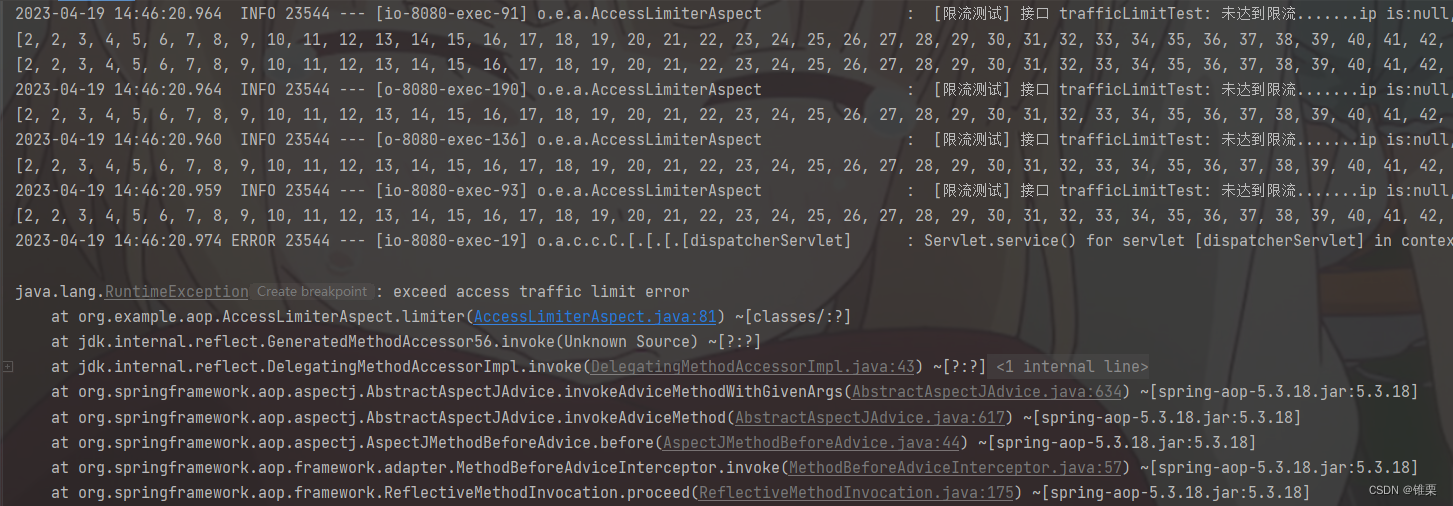
可以看到成功拦截请求。
限流脚本
记录了一些Lua限流脚本的写法,仅供参考,不能直接套用运行
计数器
-- 获取调用脚本时传入的第一个key值(用作限流的 key)
local key = KEYS[1]
-- 获取调用脚本时传入的第一个参数值(限流大小)
local limit = tonumber(ARGV[1])
-- 获取调用脚本时传入的第二个参数值(限流时长)
local time = tonumber(ARGV[2])
-- 获取当前流量大小
local curentLimit = tonumber(redis.call('get', key) or "0")
-- 是否超出限流
if curentLimit + 1 > limit then
-- 返回(拒绝)
return 0
else
-- 没有超出 value + 1
redis.call("INCRBY", key, 1)
-- 设置过期时间
redis.call("EXPIRE", key, time)
-- 返回(放行)
return 1
end
local key = KEYS[1] --限流KEY(一秒一个)
local limit = tonumber(ARGV[1]) --限流大小
local current = tonumber(redis.call('get', key) or "0")
if current + 1 > limit then --如果超出限流大小
return 0
else --请求数+1,并设置2秒过期
redis.call("INCRBY", key, "1")
redis.call("expire", key "2")
return 1
end
local key = KEYS[1]
-- 如果这个key此前不存在则返回-1
-- 关于 or 的写法参考下面图片的截图
local requests = tonumber(redis.call('GET', key) or '-1')
-- 在固定时间范围内允许的最大请求数,例如这里应该是3
local max_requests = tonumber(ARGV[1])
-- 通常是固定窗口的大小,例如60s
local expiry = tonumber(ARGV[2])
-- 当该窗口的key不存在或者未达到最大请求时
if (requests == -1) or (requests < max_requests) then
-- 自增
redis.call('INCR', key)
-- 重新设置该key的过期日期为60s后
redis.call('EXPIRE', key, expiry)
return false
else
return true
end
滑动窗口
local key = KEYS[1]
-- 当前时间戳
local current_time = tonumber(ARGV[1])
-- 窗口大小,本例中是60 * 1000
local window_size = tonumber(ARGV[3])
-- 本例中是3
local max_requests = tonumber(ARGV[4])
-- 根据当前时间毫秒数 - 超时毫秒数,得到过期时间 expired
local has_expired = current_time - window_size
-- 清除过期的数据
redis.call('ZREMRANGEBYSCORE', key, 0, has_expired)
-- 获取 zset 中的当前元素个数
local current_num = tonumber(redis.call('ZCARD', key))
local next = current_num + 1
-- 达到限流大小 返回 0
if next > max_requests then
return 0;
else
-- 往 zset 中添加一个值、得分均为当前时间戳的元素,[value,score]
redis.call("ZADD", key, current_time, current_time)
-- 每次访问均重新设置 zset 的过期时间
redis.call("PEXPIRE", key, window_size)
return next
end
String lock_stock_lua2 = "local c\n" +
"redis.call('zremrangebyscore',KEYS[1],0,ARGV[3])\n" +
"c = redis.call('zcard',KEYS[1])\n" +
"if c and tonumber(c) > tonumber(ARGV[4]) then\n" +
" return c;\n" +
"end\n" +
"redis.call('zadd',KEYS[1],ARGV[2],ARGV[1])\n" +
"return c + 1";
令牌桶
脚本1
-- 当前时间戳
local ts = tonumber(ARGV[1])
-- 设置窗口大小为1s
local min = ts -1
-- 可以为多个key设置添加令牌的速率
for i,key in pairs(KEYS) do
-- 移除过期的的令牌
redis.call('ZREMRANGEBYSCORE', key, '-inf', min)
redis.call('ZADD', key, ts, ts)
redis.call('EXPIRE', key, 10)
end
脚本2
-- 当前时间戳
local ts = tonumber(ARGV[1])
local key = KEYS[1]
local min = ts -1
-- 移除过期的的令牌
redis.call('ZREMRANGEBYSCORE', key, '-inf', min)
-- 只需要计算令牌桶的大小即可,如果令牌桶是有值的,则放行
return redis.call('ZCARD', key)
-- 令牌桶
local bucketKey = KEYS[1]
-- 上次请求的时间key
local last_request_time_key = 'lastRequestTime'
-- 令牌桶的容量
local capacity = tonumber(ARGV[1])
-- 请求令牌的数量
local permits = tonumber(ARGV[2])
-- 令牌流入的速率(按毫秒计算)
local rate = tonumber(ARGV[3])
-- 当前时间(毫秒)
local current_time = tonumber(ARGV[4])
-- 唯一标识
local unique_identifier = bucketKey
-- 恶意请求
if permits <= 0 then
return 1
end
-- 获取当前桶内令牌的数量
local current_limit = tonumber(redis.call('HGET', unique_identifier, bucketKey) or '0')
-- 获取上次请求的时间
local last_mill_request_time = tonumber(redis.call('HGET', unique_identifier, last_request_time_key) or '0')
-- 计算向桶里添加令牌的数量
local add_token_num = 0
if last_mill_request_time == 0 then
-- 如果是第一次请求,则进行初始化令牌桶,并且更新上次请求时间
add_token_num = capacity
redis.call("HSET", unique_identifier, last_request_time_key, current_time)
else
-- 令牌流入桶内
add_token_num = math.floor((current_time - last_mill_request_time) * rate)
end
-- 更新令牌的数量
if current_limit + add_token_num > capacity then
current_limit = capacity
else
current_limit = current_limit + add_token_num
end
-- 更新桶内令牌的数量
redis.pcall('HSET',unique_identifier, bucketKey, current_limit)
-- 限流判断
if current_limit - permits < 0 then
-- 达到限流大小
return 0
else
-- 没有达到限流大小
current_limit = current_limit - permits
redis.pcall('HSET', unique_identifier, bucketKey, current_limit)
-- 更新上次请求的时间
redis.call('HSET', unique_identifier, last_request_time_key, current_time)
return 1
end
漏桶
local ts = tonumber(ARGV[1])
-- calls per seconds,例如每秒4次,也就是250ms内允许发起1次请求
local cps = tonumber(ARGV[2])
local key = KEYS[1]
local min = ts -1
redis.call('ZREMRANGEBYSCORE', key, '-inf', min)
local last = redis.call('ZRANGE', key, -1, -1)
local next = ts
if type(last) == 'table' and #last > 0 then
for key,value in pairs(last) do
-- 最后一个元素 + 固定速率的时间
next = tonumber(value) + 1/cps
break
end
end
if ts > next then
-- the current ts is > than last+1/cps
-- we'll keep ts
next = ts
end
-- 如果ts < next,这里next还是现有zset的最后一个元素 + 1/cps 后的时间
redis.call('ZADD', key, next, next)
-- 必须等待的时间,
-- 如果是ts > next,则这里直接返回0,意味着不等待,直接调用
-- 如果是ts < next, 则说明下一个速率还没达到,则需要等到, next - ts这么长时间
return tostring(next - ts)
参考资料
https://bbs.huaweicloud.com/blogs/329392
https://bbs.huaweicloud.com/blogs/329586
https://juejin.cn/post/7168077279531106318
https://blog.csdn.net/dghkgjlh/article/details/128504766
https://blog.csdn.net/truelove12358/article/details/127751693
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44991304/article/details/126527087
https://blog.csdn.net/l688899886/article/details/126131180
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_43638685/article/details/121653457