文章目录
- 1、响应JSON
- 1.1、引入开发场景
- 1.2 、jackson.jar + @ResponseBody
- 1、装填返回值处理器
- 2、返回值初步处理
- 3、获取并使用返回值处理器
- 4、观察如何获取返回值处理器
- 5、返回值处理器接口内部
- 6、返回值处理器支持的类型
- 7、返回值解析器原理
- 1.3、HTTPMessageConverter 原理
- 1、MessageConverter接口
- 2、系统中默认的 messageConverters
- 2、内容协商
- 2.1、引入xml依赖
- 2.2、postman分别测试返回json和xml
- 2.3、开启浏览器参数方式内容协商功能
- 2.4、内容协商原理
- 2.5、系统底层自动添加 converter
- 2.6、判断Converters包的方式
- 2.7、自定义 MessageConverter(消息转换器)
- 1、需求
- 2、实现逻辑
- 3、自动配置类
- 4、自定义内容协商策略
【尚硅谷】SpringBoot2零基础入门教程-讲师:雷丰阳
笔记
路还在继续,梦还在期许
1、响应JSON
1.1、引入开发场景
引入WEB场景
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
WEB场景自动引入了JSON场景
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-json</artifactId>
<version>2.3.4.RELEASE</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
JSON场景引入了JSON处理的相关依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
<version>2.11.2</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.datatype</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-datatype-jdk8</artifactId>
<version>2.11.2</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.datatype</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-datatype-jsr310</artifactId>
<version>2.11.2</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.module</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-module-parameter-names</artifactId>
<version>2.11.2</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
1.2 、jackson.jar + @ResponseBody
@Controller
public class ResponseTestController {
@ResponseBody
@GetMapping("/test/person")
public Person getPerson() {
Person person = new Person();
person.setAge(28);
person.setBirth(new Date());
person.setUserName("zhangsan");
return person;
}
}
给前端自动返回JSON数据
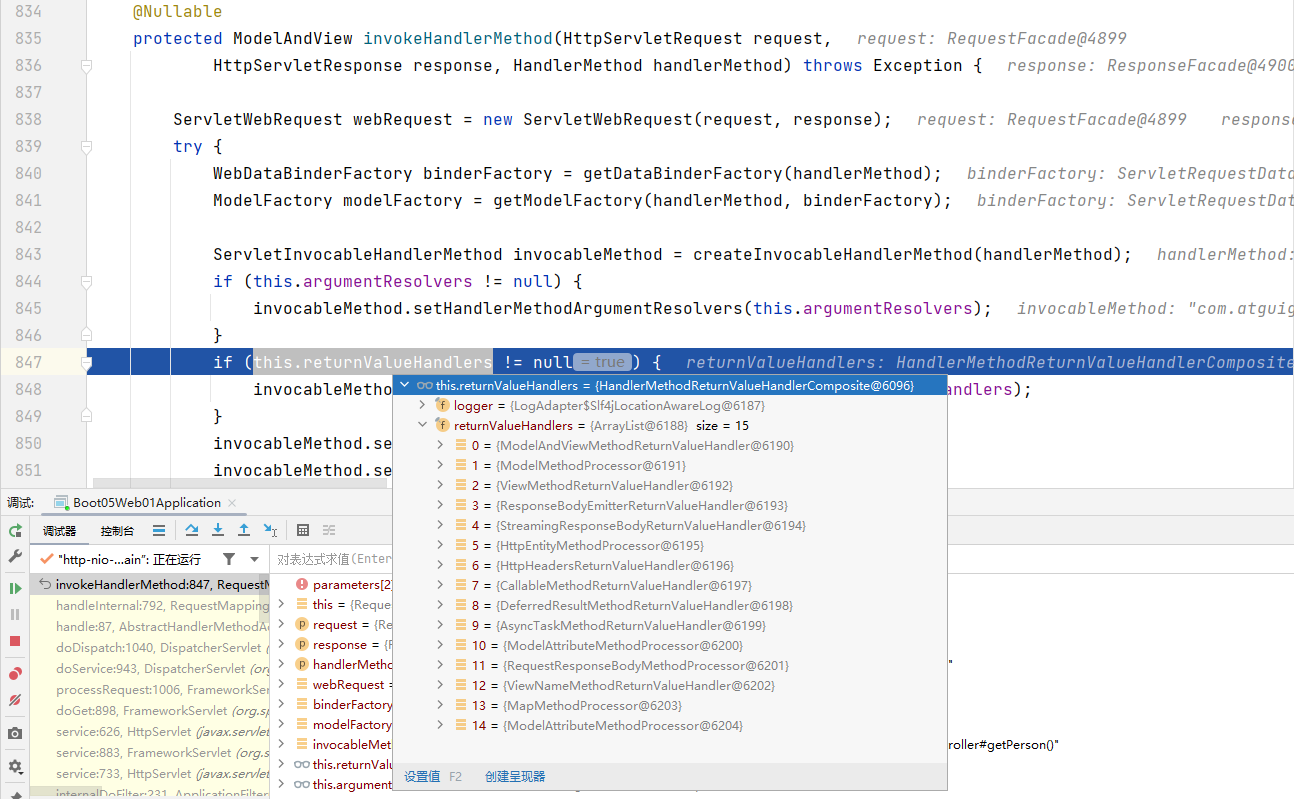
1、装填返回值处理器
位置:org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerAdapter
invokeHandlerMethod 方法
if (this.returnValueHandlers != null) {
invocableMethod.setHandlerMethodReturnValueHandlers(this.returnValueHandlers);
}
2、返回值初步处理
位置:org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.ServletInvocableHandlerMethod
invokeAndHandle 方法
/**
* Invoke the method and handle the return value through one of the
* configured {@link HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler HandlerMethodReturnValueHandlers}.
* @param webRequest the current request
* @param mavContainer the ModelAndViewContainer for this request
* @param providedArgs "given" arguments matched by type (not resolved)
*/
public void invokeAndHandle(ServletWebRequest webRequest, ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer,
Object... providedArgs) throws Exception {
// 请求执行后,返回一个返回值对象
Object returnValue = invokeForRequest(webRequest, mavContainer, providedArgs);
// 返回浏览器状态码
setResponseStatus(webRequest);
// 如果返回一个null对象,方法直接返回
if (returnValue == null) {
if (isRequestNotModified(webRequest) || getResponseStatus() != null || mavContainer.isRequestHandled()) {
disableContentCachingIfNecessary(webRequest);
mavContainer.setRequestHandled(true);
return;
}
}
// 如果返回一些失败原因
else if (StringUtils.hasText(getResponseStatusReason())) {
mavContainer.setRequestHandled(true);
return;
}
// 返回值不为空,且不是一个字符串
mavContainer.setRequestHandled(false);
Assert.state(this.returnValueHandlers != null, "No return value handlers");
try {
// 处理返回值
this.returnValueHandlers.handleReturnValue(
// 获取返回值类型,并且传入返回值处理器
returnValue, getReturnValueType(returnValue), mavContainer, webRequest);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(formatErrorForReturnValue(returnValue), ex);
}
throw ex;
}
}
3、获取并使用返回值处理器
位置:org.springframework.web.method.support.HandlerMethodReturnValueHandlerComposite
handleReturnValue 方法
/**
* Iterate over registered {@link HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler HandlerMethodReturnValueHandlers} and invoke the one that supports it.
* @throws IllegalStateException if no suitable {@link HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler} is found.
*/
@Override // 处理返回值
public void handleReturnValue(@Nullable Object returnValue, MethodParameter returnType,
ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer, NativeWebRequest webRequest) throws Exception {
// 获取returnValue(返回值)与returnType(返回值类型),寻找哪个handler (返回值处理器)可以处理
HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler handler = selectHandler(returnValue, returnType);
if (handler == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unknown return value type: " + returnType.getParameterType().getName());
}
// 使用返回值处理器处理
handler.handleReturnValue(returnValue, returnType, mavContainer, webRequest);
}
4、观察如何获取返回值处理器
位置:org.springframework.web.method.support.HandlerMethodReturnValueHandlerComposite
selectHandler 方法
@Nullable
private HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler selectHandler(@Nullable Object value, MethodParameter returnType) {
// 是不是一个异步返回值(遍历循环所有返回值处理器),都不是会返回false
boolean isAsyncValue = isAsyncReturnValue(value, returnType);
// 遍历循环所有返回值处理器
for (HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler handler : this.returnValueHandlers) {
if (isAsyncValue && !(handler instanceof AsyncHandlerMethodReturnValueHandler)) {
continue;
}
// 判断哪个返回值处理器可以处理
if (handler.supportsReturnType(returnType)) {
return handler;
}
}
return null;
}
5、返回值处理器接口内部
位置:org.springframework.web.method.support.HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler
public interface HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler {
/**
* Whether the given {@linkplain MethodParameter method return type} is
* supported by this handler.
* @param returnType the method return type to check
* @return {@code true} if this handler supports the supplied return type;
* {@code false} otherwise
*/
// 判断支持的返回值类型
boolean supportsReturnType(MethodParameter returnType);
/**
* Handle the given return value by adding attributes to the model and
* setting a view or setting the
* {@link ModelAndViewContainer#setRequestHandled} flag to {@code true}
* to indicate the response has been handled directly.
* @param returnValue the value returned from the handler method
* @param returnType the type of the return value. This type must have
* previously been passed to {@link #supportsReturnType} which must
* have returned {@code true}.
* @param mavContainer the ModelAndViewContainer for the current request
* @param webRequest the current request
* @throws Exception if the return value handling results in an error
*/
// 真正处理返回值的程序
void handleReturnValue(@Nullable Object returnValue, MethodParameter returnType,
ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer, NativeWebRequest webRequest) throws Exception;
}
6、返回值处理器支持的类型
ModelAndView
Model
View
ResponseEntity
ResponseBodyEmitter
StreamingResponseBody
HttpEntity
HttpHeaders
Callable
DeferredResult
ListenableFuture
CompletionStage
WebAsyncTask
有 @ModelAttribute 且为对象类型的
@ResponseBody 注解 —> RequestResponseBodyMethodProcessor;
位置:org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestResponseBodyMethodProcessor
supportsReturnType方法
@Override
public boolean supportsReturnType(MethodParameter returnType) {
// 使用工具类判断当前方法是否标注 ResponseBody 注解
return (AnnotatedElementUtils.hasAnnotation(returnType.getContainingClass(), ResponseBody.class) ||
returnType.hasMethodAnnotation(ResponseBody.class));
}
7、返回值解析器原理
位置:org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestResponseBodyMethodProcessor
handleReturnValue 方法
@Override
public void handleReturnValue(@Nullable Object returnValue, MethodParameter returnType,
ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer, NativeWebRequest webRequest)
throws IOException, HttpMediaTypeNotAcceptableException, HttpMessageNotWritableException {
mavContainer.setRequestHandled(true);
ServletServerHttpRequest inputMessage = createInputMessage(webRequest);
ServletServerHttpResponse outputMessage = createOutputMessage(webRequest);
// Try even with null return value. ResponseBodyAdvice could get involved.
// 使用消息转换器进行写出操作(利用MessageConverters将数据写为json)
writeWithMessageConverters(returnValue, returnType, inputMessage, outputMessage);
}
位置:org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.AbstractMessageConverterMethodProcessor
writeWithMessageConverters 方法
/**
* Writes the given return type to the given output message.
* @param value the value to write to the output message
* @param returnType the type of the value
* @param inputMessage the input messages. Used to inspect the {@code Accept} header.
* @param outputMessage the output message to write to
* @throws IOException thrown in case of I/O errors
* @throws HttpMediaTypeNotAcceptableException thrown when the conditions indicated
* by the {@code Accept} header on the request cannot be met by the message converters
* @throws HttpMessageNotWritableException thrown if a given message cannot
* be written by a converter, or if the content-type chosen by the server
* has no compatible converter.
*/
@SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes", "unchecked"})
protected <T> void writeWithMessageConverters(@Nullable T value, MethodParameter returnType,
ServletServerHttpRequest inputMessage, ServletServerHttpResponse outputMessage)
throws IOException, HttpMediaTypeNotAcceptableException, HttpMessageNotWritableException {
Object body;
Class<?> valueType;
Type targetType;
// 判断值是不是字符串类型
if (value instanceof CharSequence) {
body = value.toString();
valueType = String.class;
targetType = String.class;
}
else {
// 获取值
body = value;
// 获取值类型
valueType = getReturnValueType(body, returnType);
// 要转换的目标类型
targetType = GenericTypeResolver.resolveType(getGenericType(returnType), returnType.getContainingClass());
}
// 是不是资源类型(流数据)
if (isResourceType(value, returnType)) {
outputMessage.getHeaders().set(HttpHeaders.ACCEPT_RANGES, "bytes");
if (value != null && inputMessage.getHeaders().getFirst(HttpHeaders.RANGE) != null &&
outputMessage.getServletResponse().getStatus() == 200) {
Resource resource = (Resource) value;
try {
List<HttpRange> httpRanges = inputMessage.getHeaders().getRange();
outputMessage.getServletResponse().setStatus(HttpStatus.PARTIAL_CONTENT.value());
body = HttpRange.toResourceRegions(httpRanges, resource);
valueType = body.getClass();
targetType = RESOURCE_REGION_LIST_TYPE;
}
catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {
outputMessage.getHeaders().set(HttpHeaders.CONTENT_RANGE, "bytes */" + resource.contentLength());
outputMessage.getServletResponse().setStatus(HttpStatus.REQUESTED_RANGE_NOT_SATISFIABLE.value());
}
}
}
// MediaType 媒体类型(也成为:内容协商)
// 内容协商(浏览器默认会以请求头的方式告诉服务器他能接受什么样的内容类型)
MediaType selectedMediaType = null;
// 获取响应头中的内容类型
MediaType contentType = outputMessage.getHeaders().getContentType();
boolean isContentTypePreset = contentType != null && contentType.isConcrete();
if (isContentTypePreset) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Found 'Content-Type:" + contentType + "' in response");
}
// 使用响应头中的内容类型
selectedMediaType = contentType;
}
else {
// 获取原生的request对象
HttpServletRequest request = inputMessage.getServletRequest();
// 通过原生的request对象获取我们能接受的内容类型
List<MediaType> acceptableTypes = getAcceptableMediaTypes(request);
// 服务器可以响应的内容类型
List<MediaType> producibleTypes = getProducibleMediaTypes(request, valueType, targetType);
if (body != null && producibleTypes.isEmpty()) {
throw new HttpMessageNotWritableException(
"No converter found for return value of type: " + valueType);
}
List<MediaType> mediaTypesToUse = new ArrayList<>();
// (浏览器可接受数据类型)匹配(服务器能生产的数据类型)
for (MediaType requestedType : acceptableTypes) {
for (MediaType producibleType : producibleTypes) {
if (requestedType.isCompatibleWith(producibleType)) {
// 放入(匹配成功的数据类型)
mediaTypesToUse.add(getMostSpecificMediaType(requestedType, producibleType));
}
}
}
if (mediaTypesToUse.isEmpty()) {
if (body != null) {
throw new HttpMediaTypeNotAcceptableException(producibleTypes);
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("No match for " + acceptableTypes + ", supported: " + producibleTypes);
}
return;
}
MediaType.sortBySpecificityAndQuality(mediaTypesToUse);
for (MediaType mediaType : mediaTypesToUse) {
if (mediaType.isConcrete()) {
// 等到服务器写出的内容类型
selectedMediaType = mediaType;
break;
}
else if (mediaType.isPresentIn(ALL_APPLICATION_MEDIA_TYPES)) {
selectedMediaType = MediaType.APPLICATION_OCTET_STREAM;
break;
}
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Using '" + selectedMediaType + "', given " +
acceptableTypes + " and supported " + producibleTypes);
}
}
if (selectedMediaType != null) {
selectedMediaType = selectedMediaType.removeQualityValue();
// 遍历判断所有的 messageConverters(消息转换器),看哪个消息转换器可以将对象转换成json
for (HttpMessageConverter<?> converter : this.messageConverters) {
GenericHttpMessageConverter genericConverter = (converter instanceof GenericHttpMessageConverter ?
(GenericHttpMessageConverter<?>) converter : null);
// canWrite 判断能不能支持写操作
if (genericConverter != null ?
((GenericHttpMessageConverter) converter).canWrite(targetType, valueType, selectedMediaType) :
converter.canWrite(valueType, selectedMediaType)) {
// 需要响应的内容
body = getAdvice().beforeBodyWrite(body, returnType, selectedMediaType,
(Class<? extends HttpMessageConverter<?>>) converter.getClass(),
inputMessage, outputMessage);
if (body != null) {
Object theBody = body;
LogFormatUtils.traceDebug(logger, traceOn ->
"Writing [" + LogFormatUtils.formatValue(theBody, !traceOn) + "]");
addContentDispositionHeader(inputMessage, outputMessage);
if (genericConverter != null) {
// 写出取
genericConverter.write(body, targetType, selectedMediaType, outputMessage);
}
else {
((HttpMessageConverter) converter).write(body, selectedMediaType, outputMessage);
}
}
else {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Nothing to write: null body");
}
}
return;
}
}
}
if (body != null) {
Set<MediaType> producibleMediaTypes =
(Set<MediaType>) inputMessage.getServletRequest()
.getAttribute(HandlerMapping.PRODUCIBLE_MEDIA_TYPES_ATTRIBUTE);
if (isContentTypePreset || !CollectionUtils.isEmpty(producibleMediaTypes)) {
throw new HttpMessageNotWritableException(
"No converter for [" + valueType + "] with preset Content-Type '" + contentType + "'");
}
throw new HttpMediaTypeNotAcceptableException(this.allSupportedMediaTypes);
}
}
- 1、返回值处理器判断是否支持这种类型返回值 supportsReturnType
- 2、返回值处理器调用 handleReturnValue 进行处理
- 3、RequestResponseBodyMethodProcessor 可以处理返回值标了@ResponseBody 注解的。
-
- 利用 MessageConverters 进行处理 将数据写为json
- 1、内容协商(浏览器默认会以请求头的方式告诉服务器他能接受什么样的内容类型)
- 2、服务器最终根据自己自身的能力,决定服务器能生产出什么样内容类型的数据,
- 3、SpringMVC会挨个遍历所有容器底层的 HttpMessageConverter ,看谁能处理?
- 1、得到MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter可以将对象写为json
- 2、利用MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter将对象转为json再写出去。
-
1.3、HTTPMessageConverter 原理
1、MessageConverter接口
位置:org.springframework.http.converter.HttpMessageConverter
public interface HttpMessageConverter<T> {
/**
* Indicates whether the given class can be read by this converter.
* @param clazz the class to test for readability
* @param mediaType the media type to read (can be {@code null} if not specified);
* typically the value of a {@code Content-Type} header.
* @return {@code true} if readable; {@code false} otherwise
*/
boolean canRead(Class<?> clazz, @Nullable MediaType mediaType);
/**
* Indicates whether the given class can be written by this converter.
* @param clazz the class to test for writability
* @param mediaType the media type to write (can be {@code null} if not specified);
* typically the value of an {@code Accept} header.
* @return {@code true} if writable; {@code false} otherwise
*/
boolean canWrite(Class<?> clazz, @Nullable MediaType mediaType);
/**
* Return the list of {@link MediaType} objects supported by this converter.
* @return the list of supported media types, potentially an immutable copy
*/
List<MediaType> getSupportedMediaTypes();
/**
* Read an object of the given type from the given input message, and returns it.
* @param clazz the type of object to return. This type must have previously been passed to the
* {@link #canRead canRead} method of this interface, which must have returned {@code true}.
* @param inputMessage the HTTP input message to read from
* @return the converted object
* @throws IOException in case of I/O errors
* @throws HttpMessageNotReadableException in case of conversion errors
*/
T read(Class<? extends T> clazz, HttpInputMessage inputMessage)
throws IOException, HttpMessageNotReadableException;
/**
* Write an given object to the given output message.
* @param t the object to write to the output message. The type of this object must have previously been
* passed to the {@link #canWrite canWrite} method of this interface, which must have returned {@code true}.
* @param contentType the content type to use when writing. May be {@code null} to indicate that the
* default content type of the converter must be used. If not {@code null}, this media type must have
* previously been passed to the {@link #canWrite canWrite} method of this interface, which must have
* returned {@code true}.
* @param outputMessage the message to write to
* @throws IOException in case of I/O errors
* @throws HttpMessageNotWritableException in case of conversion errors
*/
void write(T t, @Nullable MediaType contentType, HttpOutputMessage outputMessage)
throws IOException, HttpMessageNotWritableException;
}
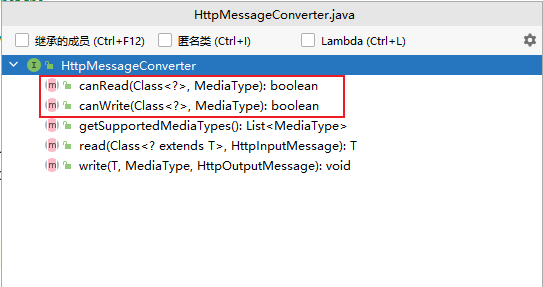
HttpMessageConverter: 看是否支持将 此 Class类型的对象,转为MediaType类型的数据。
例子:Person对象转为JSON。或者 JSON转为Person
2、系统中默认的 messageConverters
系统中默认的 messageConverters
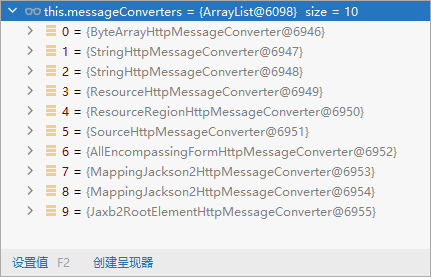
0 - 只支持Byte类型的
1 - String
2 - String
3 - Resource
4 - ResourceRegion
5 - DOMSource.class \ SAXSource.class) \ StAXSource.class \StreamSource.class \Source.class
6 - MultiValueMap
7 - true
8 - true
9 - 支持注解方式xml处理的。
最终 MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter 把对象转为JSON(利用底层的jackson的objectMapper转换的)
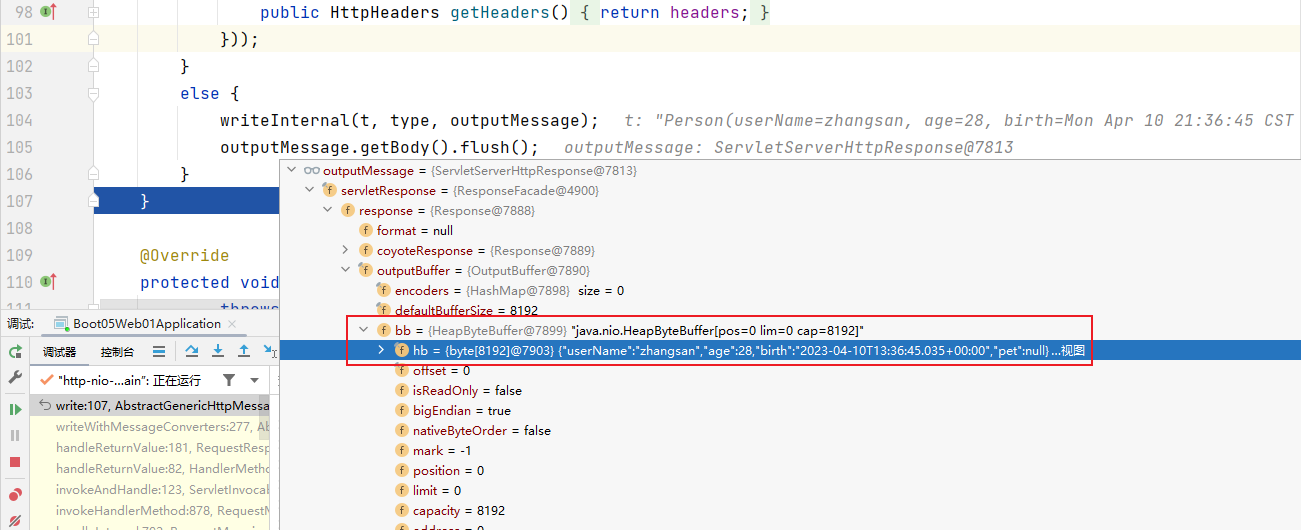
位置:org.springframework.http.converter.AbstractGenericHttpMessageConverter
write 方法
/**
* This implementation sets the default headers by calling {@link #addDefaultHeaders},
* and then calls {@link #writeInternal}.
*/
@Override
public final void write(final T t, @Nullable final Type type, @Nullable MediaType contentType,
HttpOutputMessage outputMessage) throws IOException, HttpMessageNotWritableException {
final HttpHeaders headers = outputMessage.getHeaders();
addDefaultHeaders(headers, t, contentType);
if (outputMessage instanceof StreamingHttpOutputMessage) {
StreamingHttpOutputMessage streamingOutputMessage = (StreamingHttpOutputMessage) outputMessage;
streamingOutputMessage.setBody(outputStream -> writeInternal(t, type, new HttpOutputMessage() {
@Override
public OutputStream getBody() {
return outputStream;
}
@Override
public HttpHeaders getHeaders() {
return headers;
}
}));
}
else {
writeInternal(t, type, outputMessage);
outputMessage.getBody().flush();
}
}
2、内容协商
通过遍历所有的MessageConverter,最终找到一个合适处理媒体类型数据的MessageConverter。
完整的内容协商功能:
根据客户端接收能力不同,返回不同媒体类型的数据。
安卓:返回XML
前端项目:返回JSON
2.1、引入xml依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.dataformat</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-dataformat-xml</artifactId>
</dependency>
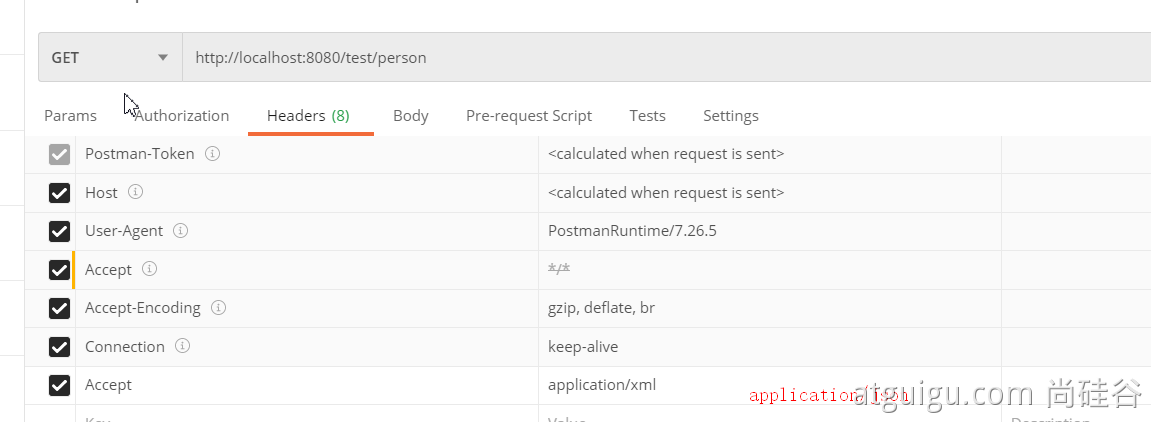
2.2、postman分别测试返回json和xml
只需要改变请求头中Accept字段。Http协议中规定的,告诉服务器本客户端可以接收的数据类型。
2.3、开启浏览器参数方式内容协商功能
为了方便内容协商,开启基于请求参数的内容协商功能。
spring:
mvc:
contentnegotiation:
favor-parameter: true #开启请求参数内容协商模式
发请求:
http://localhost:8080/test/person?format=json
http://localhost:8080/test/person?format=xml
确定客户端接收什么样的内容类型;
1、Parameter策略优先确定是要返回json数据(获取请求头中的format的值)
位置:org.springframework.web.accept.ParameterContentNegotiationStrategy
getMediaTypeKey 方法
@Override
@Nullable
// 获取请求头中的 format 的值
protected String getMediaTypeKey(NativeWebRequest request) {
return request.getParameter(getParameterName());
}
2、最终进行内容协商返回给客户端json即可。
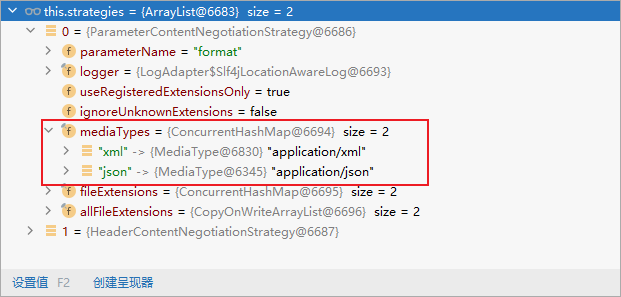
2.4、内容协商原理
- 1、判断当前响应头中是否已经有确定的媒体类型。MediaType
- 2、获取客户端(PostMan、浏览器)支持接收的内容类型。(获取客户端Accept请求头字段,值为:application/xml)
- contentNegotiationManager(内容协商管理器)默认使用基于请求头的策略,获取客户端支持接受的内容类型
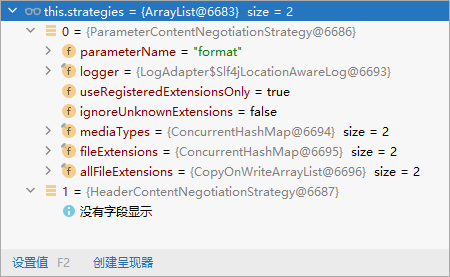
- HeaderContentNegotiationStrategy 确定客户端可以接收的内容类型
- 3、遍历循环所有当前系统的 MessageConverter,看谁支持操作这个对象(Person)
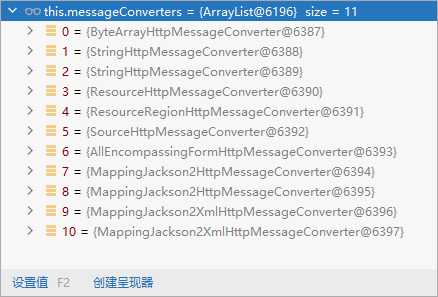
- 4、找到支持操作Person的converter,把converter支持的媒体类型统计出来。
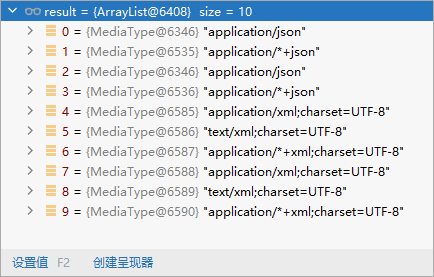
- 5、客户端需要【application/xml】。服务端能力有 10种,既能返回 json 又能 xml。
- 6、进行内容协商的最佳匹配媒体类型
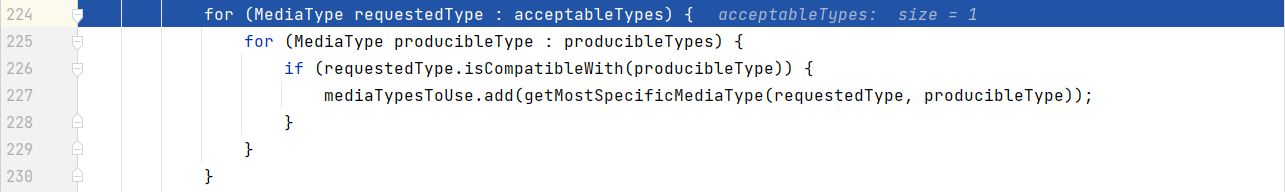
- 7、用 支持 将对象转为 最佳匹配媒体类型 的converter。调用它进行转化 。
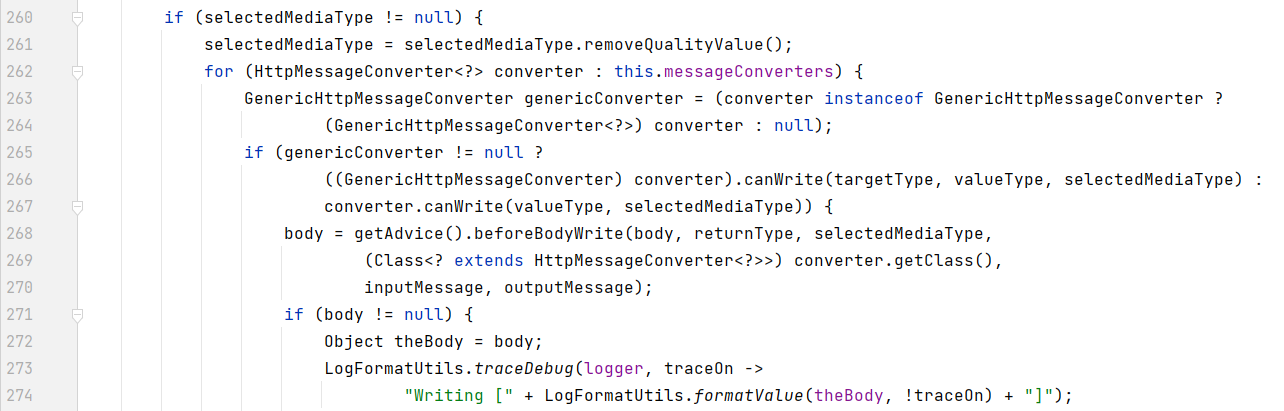
2.5、系统底层自动添加 converter
位置:org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurationSupport
addDefaultHttpMessageConverters 方法
/**
* Adds a set of default HttpMessageConverter instances to the given list.
* Subclasses can call this method from {@link #configureMessageConverters}.
* @param messageConverters the list to add the default message converters to
*/
protected final void addDefaultHttpMessageConverters(List<HttpMessageConverter<?>> messageConverters) {
// 自动添加 converter
messageConverters.add(new ByteArrayHttpMessageConverter());
messageConverters.add(new StringHttpMessageConverter());
messageConverters.add(new ResourceHttpMessageConverter());
messageConverters.add(new ResourceRegionHttpMessageConverter());
try {
messageConverters.add(new SourceHttpMessageConverter<>());
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// Ignore when no TransformerFactory implementation is available...
}
messageConverters.add(new AllEncompassingFormHttpMessageConverter());
if (romePresent) {
messageConverters.add(new AtomFeedHttpMessageConverter());
messageConverters.add(new RssChannelHttpMessageConverter());
}
// 导入了jackson处理xml的包,xml的converter就会自动进来
if (jackson2XmlPresent) {
Jackson2ObjectMapperBuilder builder = Jackson2ObjectMapperBuilder.xml();
if (this.applicationContext != null) {
builder.applicationContext(this.applicationContext);
}
// 添加 jackson 处理 xml 的Converter
messageConverters.add(new MappingJackson2XmlHttpMessageConverter(builder.build()));
}
else if (jaxb2Present) {
messageConverters.add(new Jaxb2RootElementHttpMessageConverter());
}
if (jackson2Present) {
Jackson2ObjectMapperBuilder builder = Jackson2ObjectMapperBuilder.json();
if (this.applicationContext != null) {
builder.applicationContext(this.applicationContext);
}
messageConverters.add(new MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter(builder.build()));
}
else if (gsonPresent) {
messageConverters.add(new GsonHttpMessageConverter());
}
else if (jsonbPresent) {
messageConverters.add(new JsonbHttpMessageConverter());
}
if (jackson2SmilePresent) {
Jackson2ObjectMapperBuilder builder = Jackson2ObjectMapperBuilder.smile();
if (this.applicationContext != null) {
builder.applicationContext(this.applicationContext);
}
messageConverters.add(new MappingJackson2SmileHttpMessageConverter(builder.build()));
}
if (jackson2CborPresent) {
Jackson2ObjectMapperBuilder builder = Jackson2ObjectMapperBuilder.cbor();
if (this.applicationContext != null) {
builder.applicationContext(this.applicationContext);
}
messageConverters.add(new MappingJackson2CborHttpMessageConverter(builder.build()));
}
}
2.6、判断Converters包的方式
使用类工具,判断系统中是否有一下类。
解释了,当导入了jackson处理xml的包,xml的converter就会自动进来的原理。
位置:org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurationSupport
//
static {
ClassLoader classLoader = WebMvcConfigurationSupport.class.getClassLoader();
romePresent = ClassUtils.isPresent("com.rometools.rome.feed.WireFeed", classLoader);
jaxb2Present = ClassUtils.isPresent("javax.xml.bind.Binder", classLoader);
jackson2Present = ClassUtils.isPresent("com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper", classLoader) &&
ClassUtils.isPresent("com.fasterxml.jackson.core.JsonGenerator", classLoader);
jackson2XmlPresent = ClassUtils.isPresent("com.fasterxml.jackson.dataformat.xml.XmlMapper", classLoader);
jackson2SmilePresent = ClassUtils.isPresent("com.fasterxml.jackson.dataformat.smile.SmileFactory", classLoader);
jackson2CborPresent = ClassUtils.isPresent("com.fasterxml.jackson.dataformat.cbor.CBORFactory", classLoader);
gsonPresent = ClassUtils.isPresent("com.google.gson.Gson", classLoader);
jsonbPresent = ClassUtils.isPresent("javax.json.bind.Jsonb", classLoader);
}
2.7、自定义 MessageConverter(消息转换器)
1、需求
一个控制器方法,利用内容协商实现多协议数据兼容。
浏览器 发请求,返回 xml [application/xml] jacksonXmlConverter。
ajax 发请求,返回 json [application/json] jacksonXmlConverter。
app 发请求,返回自定义协议数据 [application/x-guigu] xxxxConverter。
2、实现逻辑
1、添加自定义的 MessageConverter 进系统底层。
2、系统底层就会统计出所有 MessageConverter 能操作哪些类型数据。
3、客户端内容协商需要 [application/x-guigu] 类型数据,自定义的 MessageConverter 就会起作用。
0、@ResponseBody 响应数据出去 调用 RequestResponseBodyMethodProcessor 处理
1、Processor 处理方法返回值。通过 MessageConverter 处理
2、所有 MessageConverter 合起来可以支持各种媒体类型数据的操作(读、写)
3、内容协商找到最终的 messageConverter;
3、自动配置类
SpringMVC 的自动配置类,WebMvcAutoConfiguration 中有一个类实现了 WebMvcConfigurer 配置类,内部配置了 MessageConverters。
在 spring boot 中,定制 springmvc 的功能,需要给容器中放入一个 WebMvcConfigurer 组件,在这个组件中,重写哪些方法,就是定制 springmvc 的哪些功能。
自动配置类
@Bean
public WebMvcConfigurer webMvcConfigurer(){
return new WebMvcConfigurer() {
// 扩展消息转换器
@Override
public void extendMessageConverters(List<HttpMessageConverter<?>> converters) {
// 添加自定义Converters
converters.add(new GuiguMessageconverter());
}
}
}
自定义MessageConverter
// 自定义Converter
public class GuiguMessageconverter implements HttpMessageConverter<Person> {
@Override
public boolean canRead(Class<?> clazz, MediaType mediaType) {
return false;
}
@Override
public boolean canWrite(Class<?> clazz, MediaType mediaType) {
return clazz.isAssignableFrom(Person.class);
}
// 服务器要统计所有MessageConverter都能写出哪些内容类型
@Override
public List<MediaType> getSupportedMediaTypes() {
return MediaType.parseMediaTypes("application/x-guigu");
}
@Override
public Person read(Class<? extends Person> clazz, HttpInputMessage inputMessage) throws IOException, HttpMessageNotReadableException {
return null;
}
@Override
public void write(Person person, MediaType contentType, HttpOutputMessage outputMessage) throws IOException, HttpMessageNotWritableException {
// 自定义协议数据的写出
String data = person.getUserName() + ";" + person.getAge() + ";" + person.getBirth();
// 写出去
OutputStream body = outputMessage.getBody();
body.write(data.getBytes());
}
}
4、自定义内容协商策略
在 WebMvcConfigurer 中自定义内容协商策略
// 自定义内容协商策略
@Override
public void configureContentNegotiation(ContentNegotiationConfigurer configurer) {
// 传入参数策略支持的媒体类型
Map<String, MediaType> mediaTypes = new HashMap<>();
// 指定支持解析参数对应的媒体类型
mediaTypes.put("json",MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON);
mediaTypes.put("xml",MediaType.APPLICATION_XML);
mediaTypes.put("gg",MediaType.parseMediaType("application/x-guigu"));
// 参数的内容协商策略
ParameterContentNegotiationStrategy strategy = new ParameterContentNegotiationStrategy(mediaTypes);
// 将策略传入
configurer.strategies(Arrays.asList(strategy));
}
内容协商管理器
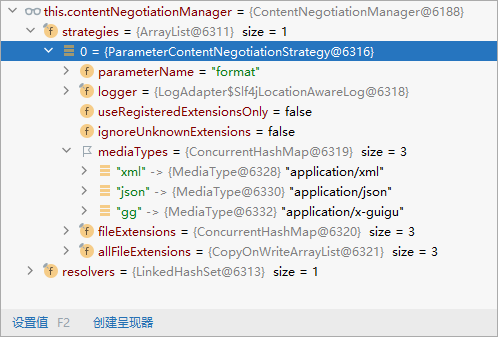
有可能我们添加的自定义的功能会覆盖默认很多功能,导致一些默认的功能失效,在配置的时候,将默认的也添加上。
// 自定义内容协商策略
@Override
public void configureContentNegotiation(ContentNegotiationConfigurer configurer) {
// 传入参数策略支持的媒体类型
Map<String, MediaType> mediaTypes = new HashMap<>();
// 指定支持解析参数对应的媒体类型
mediaTypes.put("json",MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON);
mediaTypes.put("xml",MediaType.APPLICATION_XML);
mediaTypes.put("gg",MediaType.parseMediaType("application/x-guigu"));
// 参数的内容协商策略
ParameterContentNegotiationStrategy strategy = new ParameterContentNegotiationStrategy(mediaTypes);
// 基于请求头的任容协商策略
HeaderContentNegotiationStrategy headerContentNegotiationStrategy = new HeaderContentNegotiationStrategy();
// 将策略传入
configurer.strategies(Arrays.asList(strategy,headerContentNegotiationStrategy));
}
大家考虑,上述功能除了我们完全自定义外?SpringBoot有没有为我们提供基于配置文件的快速修改媒体类型功能?怎么配置呢?【提示:参照SpringBoot官方文档web开发内容协商章节】