一、Spring @Transactional 声明式事务执行原理
@Transactional 是 Spring 框架中用于声明事务的注解,可以标注在方法或类上。当标注在类上时,表示该类的所有public方法都将支持事务。当标注在方法上时,表示该方法将在一个事务内执行。
@Transactional 的执行原理依赖于 AOP ,因此在看本篇文章时,最好对 AOP 的原理有所了解,如果不了解,可以看下下面两篇文章:
SpringAop 源码解析 (一) - Aspect 切面方法的查找匹配过程
SpringAop 源码解析 (二) - 代理对象的创建以及执行过程
下面一起开始源码的分析。
二、@EnableTransactionManagement
在普通的 Spring 项目中,开启声明式事务的支持需要使用 @EnableTransactionManagement 注解,该注解在 SpringBoot 中会自动调用,可以从该注解入手,看到底做了啥事情:
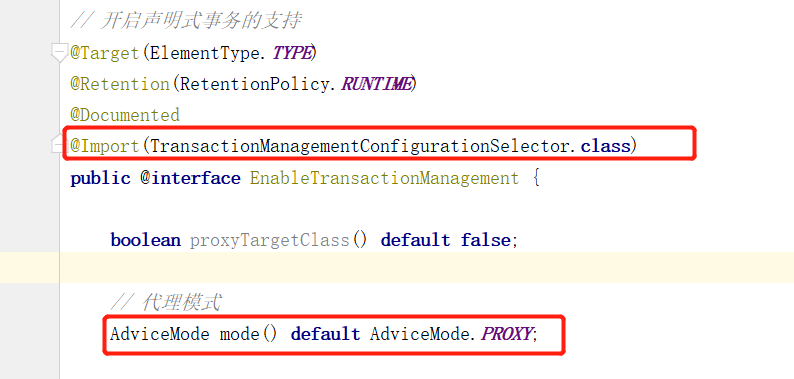
注意注解中代理模式默认为 PROXY ,同时还使用 @Import 引入了 TransactionManagementConfigurationSelector 类,看下该类的继承关系:
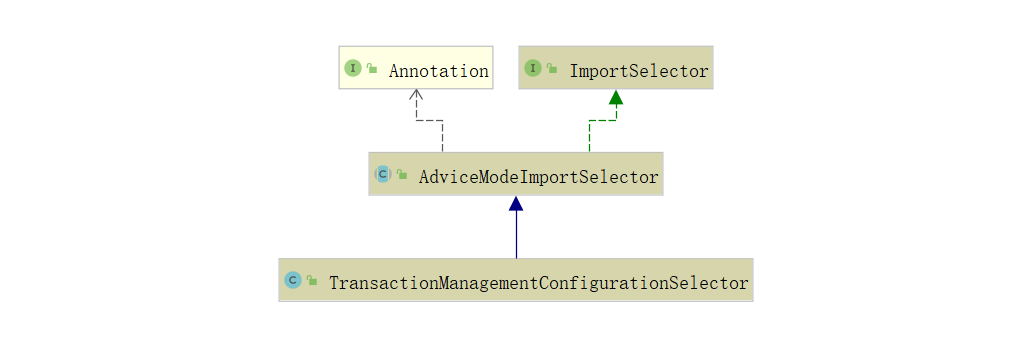
有实现 ImportSelector 选择注入器,因此先找到 selectImports(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata) 方法,在 AdviceModeImportSelector 类下:
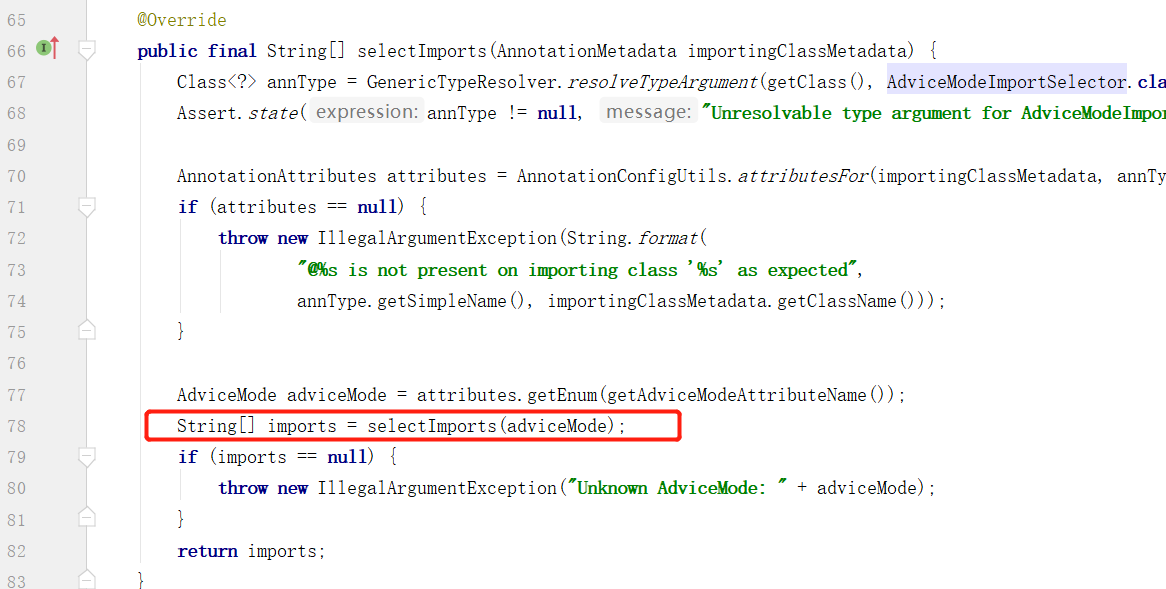
这里又使用了子类的selectImports方法的结果注入了 Spring 容器,就是TransactionManagementConfigurationSelector 类下的 selectImports 方法:
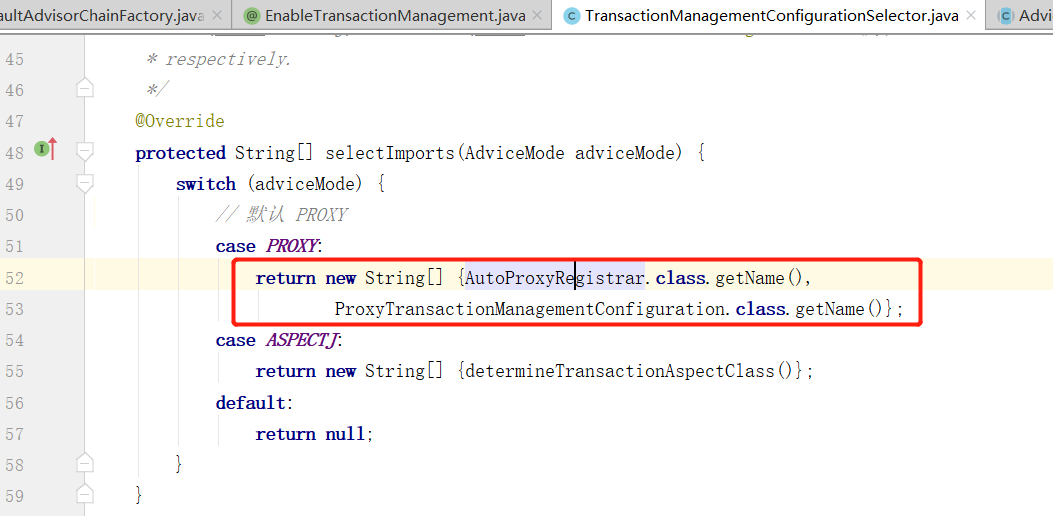
从上面注解中可以得到默认为 PROXY 模式,因此会注入AutoProxyRegistrar 和 ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration 这里主要分析下 ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration 配置类:
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
// 事务代理配置
public class ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration extends AbstractTransactionManagementConfiguration {
@Bean(name = TransactionManagementConfigUtils.TRANSACTION_ADVISOR_BEAN_NAME)
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
// 事务切面
public BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor transactionAdvisor(
TransactionAttributeSource transactionAttributeSource, TransactionInterceptor transactionInterceptor) {
// 创建事务切面增强器
BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor advisor = new BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor();
// 设置事务属性解析器
advisor.setTransactionAttributeSource(transactionAttributeSource);
// 设置
advisor.setAdvice(transactionInterceptor);
if (this.enableTx != null) {
advisor.setOrder(this.enableTx.<Integer>getNumber("order"));
}
return advisor;
}
@Bean
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
// 事务属性解析器
public TransactionAttributeSource transactionAttributeSource() {
// 创建一个注解事务属性解析器
return new AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource();
}
@Bean
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
// 事务拦截器
public TransactionInterceptor transactionInterceptor(TransactionAttributeSource transactionAttributeSource) {
// 创建事务拦截器
TransactionInterceptor interceptor = new TransactionInterceptor();
// 设置事务属性拦截器
interceptor.setTransactionAttributeSource(transactionAttributeSource);
if (this.txManager != null) {
// 设置事务管理器
interceptor.setTransactionManager(this.txManager);
}
return interceptor;
}
}
该配置类中声明了三个非常重要的对象:
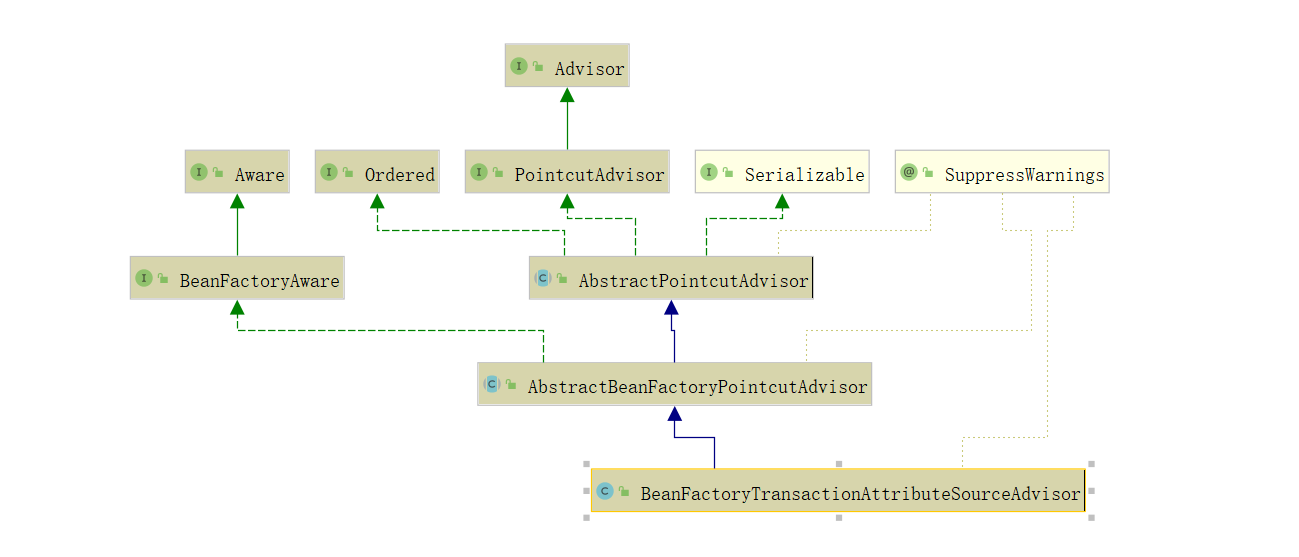
BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor :是Advisor 的子类,该类也是源码分析的关键点,由于其属于 Advisor 的子类,因此在 AOP 扫描 Advisor 增强器时会被扫描到,执行后续 AOP 的逻辑。
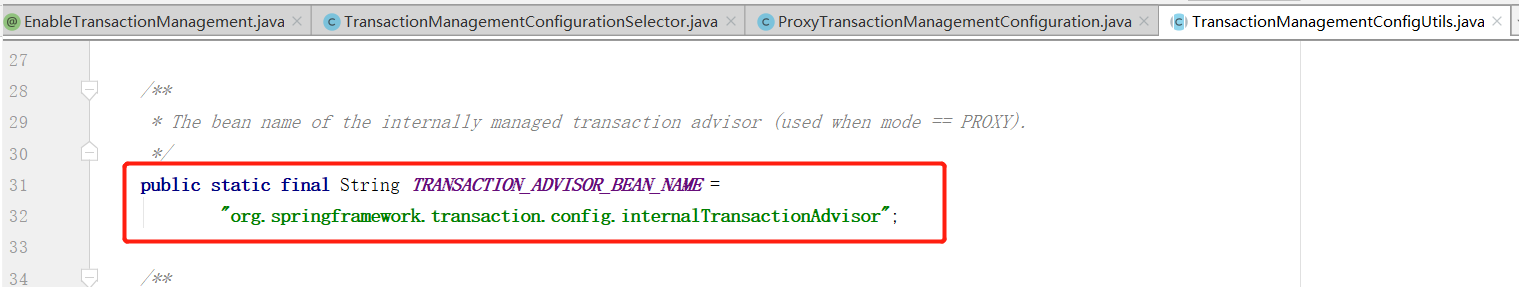
注意该类在Spring 中注册的名称为:org.springframework.transaction.config.internalTransactionAdvisor
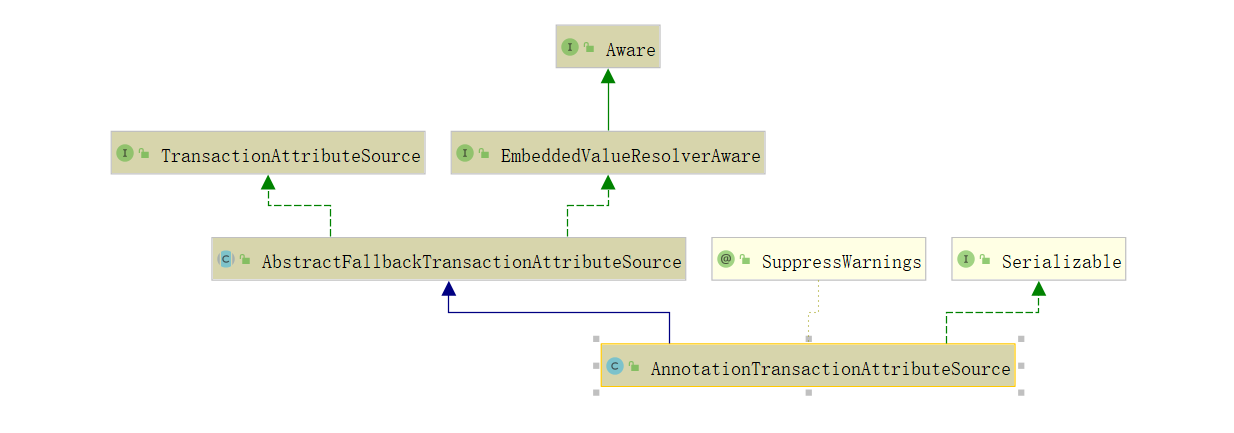
TransactionAttributeSource :事务属性解析器,这里实例为 AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource ,主要在 AOP 中匹配Advisor 增强器时用到,一方面判断是否带有 @Transactional 注解,另一方面对注解中的参数进行解析包装。
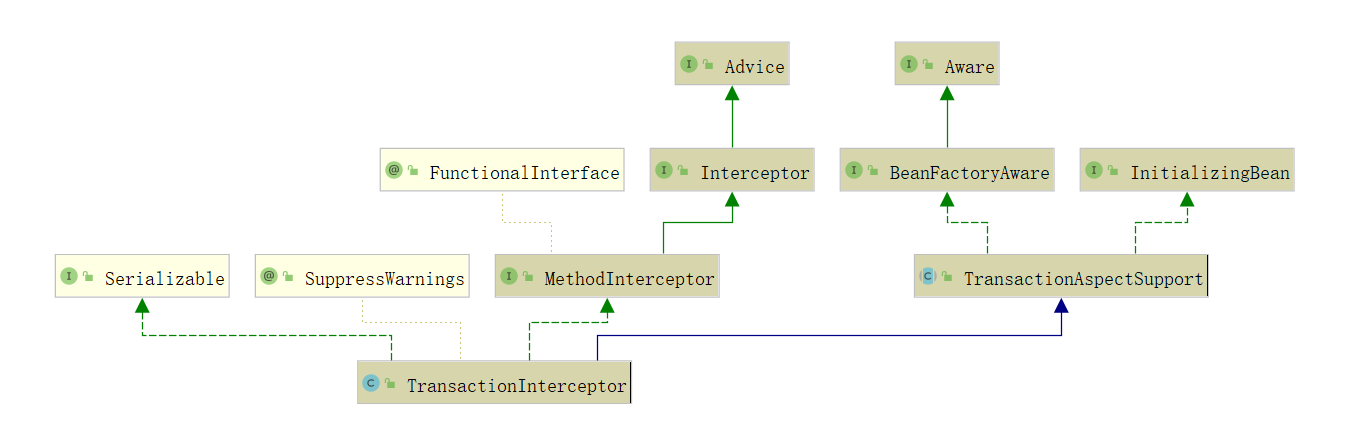
TransactionInterceptor: 事务拦截器,是 MethodInterceptor 的子类,因此在AOP中也是最终触发执行逻辑的类,其中包含了事务的开启、提交、回滚等。
三、事务切面增强器的扫描过程
下面我们从 AOP 的执行逻辑中 AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator 类下的 getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean 方法进行分析,主要实现了Advices 切面增强方法的扫描和匹配过程。
这里的处理过程在上篇 AOP 的文章中有分析过,因此这里主要对BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor 的扫描和匹配过程进行分析,如果对这块不了解的话,建议看下前面的 AOP 分析的文章:
下面看到该方法中:
protected Object[] getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(
Class<?> beanClass, String beanName, @Nullable TargetSource targetSource) {
//获取增强方法
List<Advisor> advisors = findEligibleAdvisors(beanClass, beanName);
//判断是否为空
if (advisors.isEmpty()) {
//如果为空,返回一个空数组
return DO_NOT_PROXY;
}
//如果不为空,转化为数组然后返回
return advisors.toArray();
}
使用 findEligibleAdvisors 方法获取到匹配的增强方法,也就是切面方法,看到该方法中:
protected List<Advisor> findEligibleAdvisors(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) {
//获取所有的增强方法
List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors = findCandidateAdvisors();
//从所有的增强方法中匹配适合该 bean 的增强方法
List<Advisor> eligibleAdvisors = findAdvisorsThatCanApply(candidateAdvisors, beanClass, beanName);
//对匹配后的增强方法进行扩展
extendAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors);
//判断是否为空
if (!eligibleAdvisors.isEmpty()) {
//如果不为空,进行排序
eligibleAdvisors = sortAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors);
}
//返回处理后的增强方法
return eligibleAdvisors;
}
这里通过 findCandidateAdvisors 方法获取到所有的切面方法,然后使用 findAdvisorsThatCanApply 方法匹配出符合该 beanName 的切面方法,首先看到 findCandidateAdvisors 方法,在 AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator 类下:
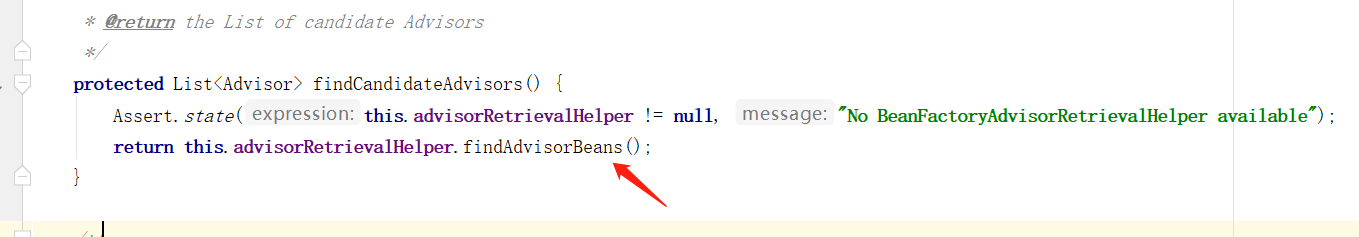
这里又调用了 BeanFactoryAdvisorRetrievalHelper 类下的 findAdvisorBeans 方法:
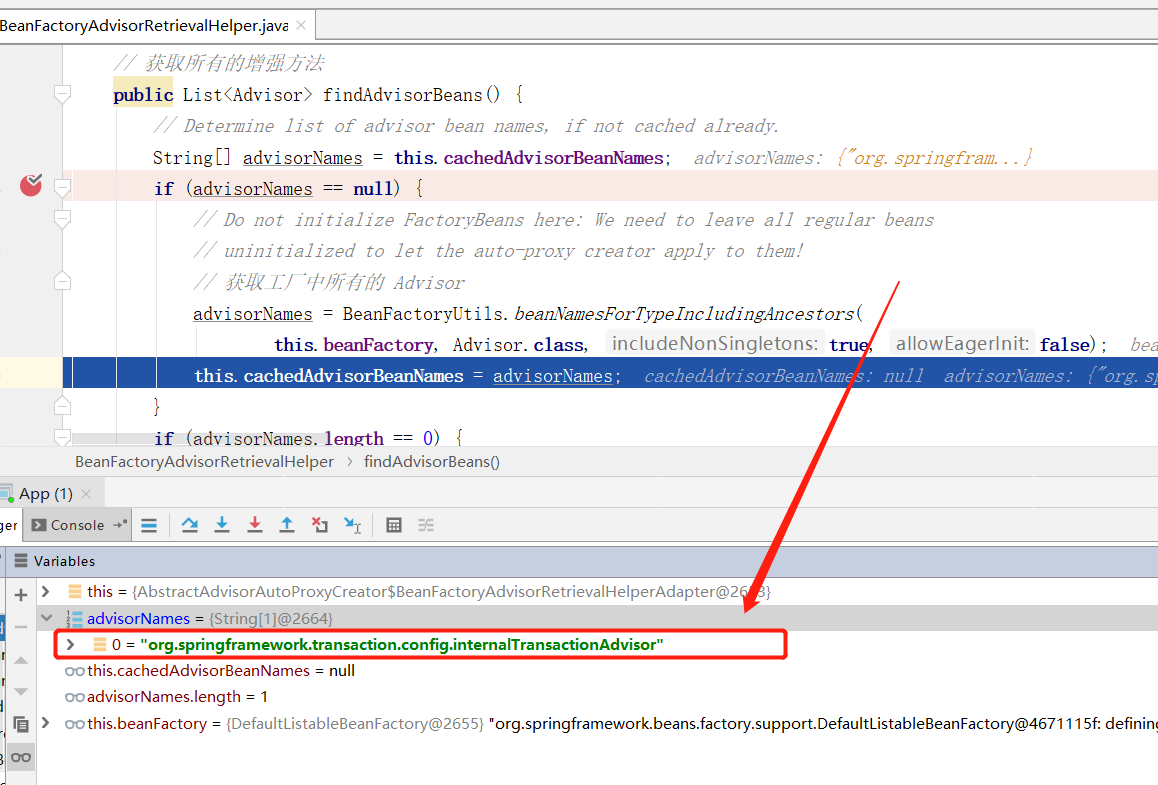
public List<Advisor> findAdvisorBeans() {
// Determine list of advisor bean names, if not cached already.
String[] advisorNames = this.cachedAdvisorBeanNames;
if (advisorNames == null) {
// Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans
// uninitialized to let the auto-proxy creator apply to them!
// 获取工厂中所有的 Advisor
advisorNames = BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(
this.beanFactory, Advisor.class, true, false);
this.cachedAdvisorBeanNames = advisorNames;
}
if (advisorNames.length == 0) {
return new ArrayList<>();
}
List<Advisor> advisors = new ArrayList<>();
for (String name : advisorNames) {
if (isEligibleBean(name)) {
if (this.beanFactory.isCurrentlyInCreation(name)) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Skipping currently created advisor '" + name + "'");
}
}
else {
try {
// 从工厂中获取对象实例
advisors.add(this.beanFactory.getBean(name, Advisor.class));
}
catch (BeanCreationException ex) {
Throwable rootCause = ex.getMostSpecificCause();
if (rootCause instanceof BeanCurrentlyInCreationException) {
BeanCreationException bce = (BeanCreationException) rootCause;
String bceBeanName = bce.getBeanName();
if (bceBeanName != null && this.beanFactory.isCurrentlyInCreation(bceBeanName)) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Skipping advisor '" + name +
"' with dependency on currently created bean: " + ex.getMessage());
}
// Ignore: indicates a reference back to the bean we're trying to advise.
// We want to find advisors other than the currently created bean itself.
continue;
}
}
throw ex;
}
}
}
}
return advisors;
}
这里从工厂中获取到了所有的 Advisor 类型的 beanName ,后面直接从工厂中获取到了对应的实例对象。
前面说 BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor 实现了 Advisor ,因此这里 advisors 列表中也带有 BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor 类型的实例对象。
四、事务切面增强器的匹配过程
下面再回到 findEligibleAdvisors 方法中,已经通过 findCandidateAdvisors 方法获取到 Advisor 切面增强方法了,下面通过 findAdvisorsThatCanApply 匹配出符合当前 beanName 的 Advisor,看到该方法中:
这里又调用了 AopUtils.findAdvisorsThatCanApply 方法,继续看到该方法下:
public static List<Advisor> findAdvisorsThatCanApply(List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors, Class<?> clazz) {
if (candidateAdvisors.isEmpty()) {
return candidateAdvisors;
}
// 创建一个合适的 Advisor 的集合 eligibleAdvisors
List<Advisor> eligibleAdvisors = new ArrayList<>();
//循环所有的Advisor
for (Advisor candidate : candidateAdvisors) {
// 判断切面是否匹配
//如果Advisor是 IntroductionAdvisor 引介增强 可以为目标类 通过AOP的方式添加一些接口实现
if (candidate instanceof IntroductionAdvisor && canApply(candidate, clazz)) {
eligibleAdvisors.add(candidate);
}
}
//是否有引介增强
boolean hasIntroductions = !eligibleAdvisors.isEmpty();
for (Advisor candidate : candidateAdvisors) {
//如果是IntroductionAdvisor类型的话 则直接跳过
if (candidate instanceof IntroductionAdvisor) {
// already processed
continue;
}
// 判断切面是否匹配
if (canApply(candidate, clazz, hasIntroductions)) {
eligibleAdvisors.add(candidate);
}
}
return eligibleAdvisors;
}
这里对 Advisor 判断是否为 IntroductionAdvisor 引介增强类型,前面看到 BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor 的继承树关系,并没有实现 IntroductionAdvisor接口 ,因此最后会使用 canApply 方法进行匹配,再看到 canApply 方法中:
public static boolean canApply(Advisor advisor, Class<?> targetClass, boolean hasIntroductions) {
if (advisor instanceof IntroductionAdvisor) {
// IntroductionAdvisor,根据类过滤器,进行匹配
//如果是 IntroductionAdvisor 的话,则调用IntroductionAdvisor类型的实例进行类的过滤
//这里是直接调用的ClassFilter的matches方法
return ((IntroductionAdvisor) advisor).getClassFilter().matches(targetClass);
}
// 通常情况下 Advisor 都是 PointcutAdvisor 类型
else if (advisor instanceof PointcutAdvisor) {
PointcutAdvisor pca = (PointcutAdvisor) advisor;
// 从Advisor中获取Pointcut的实现类 就是是AspectJExpressionPointcut
return canApply(pca.getPointcut(), targetClass, hasIntroductions);
}
else {
// It doesn't have a pointcut so we assume it applies.
return true;
}
}
这里根据不同的类型走不同的匹配方式,再看下 BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor 的继承树关系,其中有实现 PointcutAdvisor 接口,因此会进入到 canApply(Pointcut pc, Class<?> targetClass, boolean hasIntroductions) 方法中,注意这里第一个 Pointcut 参数是通过 pca.getPointcut() 获取到的,在 BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor 中就是 TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut 对象:

下面看到 canApply(Pointcut pc, Class<?> targetClass, boolean hasIntroductions) 方法中:
public static boolean canApply(Pointcut pc, Class<?> targetClass, boolean hasIntroductions) {
Assert.notNull(pc, "Pointcut must not be null");
//进行切点表达式的匹配最重要的就是 ClassFilter 和 MethodMatcher这两个方法的实现。
//首先进行ClassFilter的matches方法校验
//首先这个类要在所匹配的规则下
if (!pc.getClassFilter().matches(targetClass)) {
return false;
}
MethodMatcher methodMatcher = pc.getMethodMatcher();
// 通过切点的方法匹配策略 进行匹配
if (methodMatcher == MethodMatcher.TRUE) {
// No need to iterate the methods if we're matching any method anyway...
return true;
}
// 如果当前 MethodMatcher 也是IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher类型,则转为该类型
IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher introductionAwareMethodMatcher = null;
if (methodMatcher instanceof IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher) {
introductionAwareMethodMatcher = (IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher) methodMatcher;
}
Set<Class<?>> classes = new LinkedHashSet<>();
if (!Proxy.isProxyClass(targetClass)) {
// 目标对象没有采用jdk动态代理,则要么是cglib代理,要么没有代理,获取到没有代理的原始类
classes.add(ClassUtils.getUserClass(targetClass));
}
// 获取到目标类的所有的超类接口
classes.addAll(ClassUtils.getAllInterfacesForClassAsSet(targetClass));
for (Class<?> clazz : classes) {
// 获取目标类即接口的方法,只要有一个方法满足切点条件,即视为切点可以匹配
Method[] methods = ReflectionUtils.getAllDeclaredMethods(clazz);
// 只要有一个方法能匹配到就返回true
//MethodMatcher 中有两个 matches 方法。
// boolean matches(Method method, Class<?> targetClass) 用于静态的方法匹配
// boolean matches(Method method, Class<?> targetClass, Object... args) 用于运行期动态的进行方法匹配
for (Method method : methods) {
// 如果 MethodMatcher 是IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher类型,则使用该类型的方法进行匹配
// 否则使用 MethodMatcher.matches() 方法进行匹配
if (introductionAwareMethodMatcher != null ?
introductionAwareMethodMatcher.matches(method, targetClass, hasIntroductions) :
methodMatcher.matches(method, targetClass)) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
该方法首先使用 ClassFilter 对类进行匹配是否符合,如果不符合直接跳过,这里先看下 TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut 中 getClassFilter 获取的是哪个对象:
从 TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut 的构造函数中可以看出具体对象为 TransactionAttributeSourceClassFilter 类型,下面看到 TransactionAttributeSourceClassFilter 类下的 matches(Class<?> clazz) 方法:
public boolean matches(Class<?> clazz) {
// 判断是否属于 TransactionalProxy 或 TransactionManager 或 PersistenceExceptionTranslator
if (TransactionalProxy.class.isAssignableFrom(clazz) ||
TransactionManager.class.isAssignableFrom(clazz) ||
PersistenceExceptionTranslator.class.isAssignableFrom(clazz)) {
// 如果是返回 false 不尽兴匹配
return false;
}
// 匹配判断
TransactionAttributeSource tas = getTransactionAttributeSource();
return (tas == null || tas.isCandidateClass(clazz));
}
这里如果是 TransactionalProxy 或 TransactionManager 或 PersistenceExceptionTranslator 类直接返回 false 不进行后面的匹配,再接着获取到一个 TransactionAttributeSource 对象,从前面 ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration 类中可以看出,主要为AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource类型实例,因此进到该类下的 isCandidateClass 方法中:
public boolean isCandidateClass(Class<?> targetClass) {
// 遍历事务注解析器
for (TransactionAnnotationParser parser : this.annotationParsers) {
// 是否可解析
if (parser.isCandidateClass(targetClass)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
这里遍历了所有的事务解析器,这些解析器怎么来的呢,看到 AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource 的构造方法中:
public AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource(boolean publicMethodsOnly) {
this.publicMethodsOnly = publicMethodsOnly;
if (jta12Present || ejb3Present) {
this.annotationParsers = new LinkedHashSet<>(4);
this.annotationParsers.add(new SpringTransactionAnnotationParser());
if (jta12Present) {
this.annotationParsers.add(new JtaTransactionAnnotationParser());
}
if (ejb3Present) {
this.annotationParsers.add(new Ejb3TransactionAnnotationParser());
}
}
else {
this.annotationParsers = Collections.singleton(new SpringTransactionAnnotationParser());
}
}
这里主要对 SpringTransactionAnnotationParser 类进行分析,下面可以看到 SpringTransactionAnnotationParser 类下的 isCandidateClass 方法中:
public boolean isCandidateClass(Class<?> targetClass) {
// 检查类是否带有 @Transactional 注解
return AnnotationUtils.isCandidateClass(targetClass, Transactional.class);
}
主要就是检查类是否带有 @Transactional 注解。
下面再回到 canApply(Pointcut pc, Class<?> targetClass, boolean hasIntroductions) 方法中,继续向下看会通过 pc.getMethodMatcher() 获取到一个 MethodMatcher 对象,这里看下 TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut 的继承关系图:
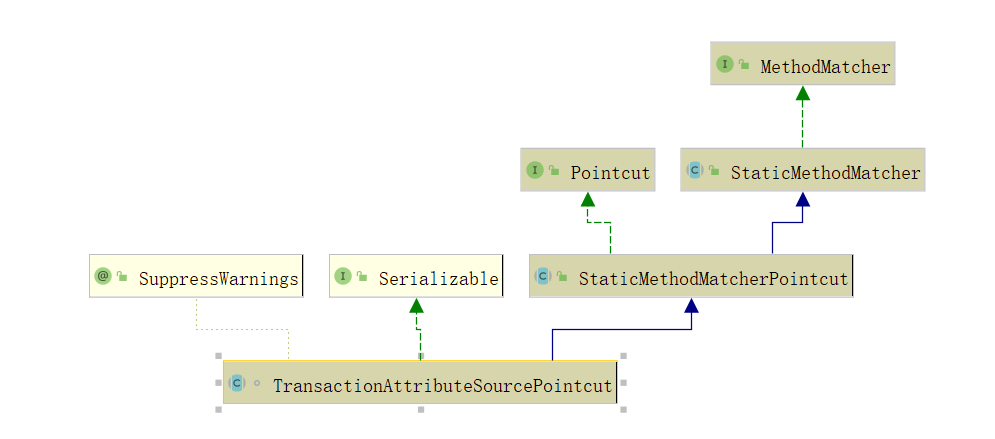
可以看到 TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut 就是 MethodMatcher 类型, 但 TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut 没有重写 getMethodMatcher() 方法,实现触发的StaticMethodMatcherPointcut 类下的 getMethodMatcher() 方法:
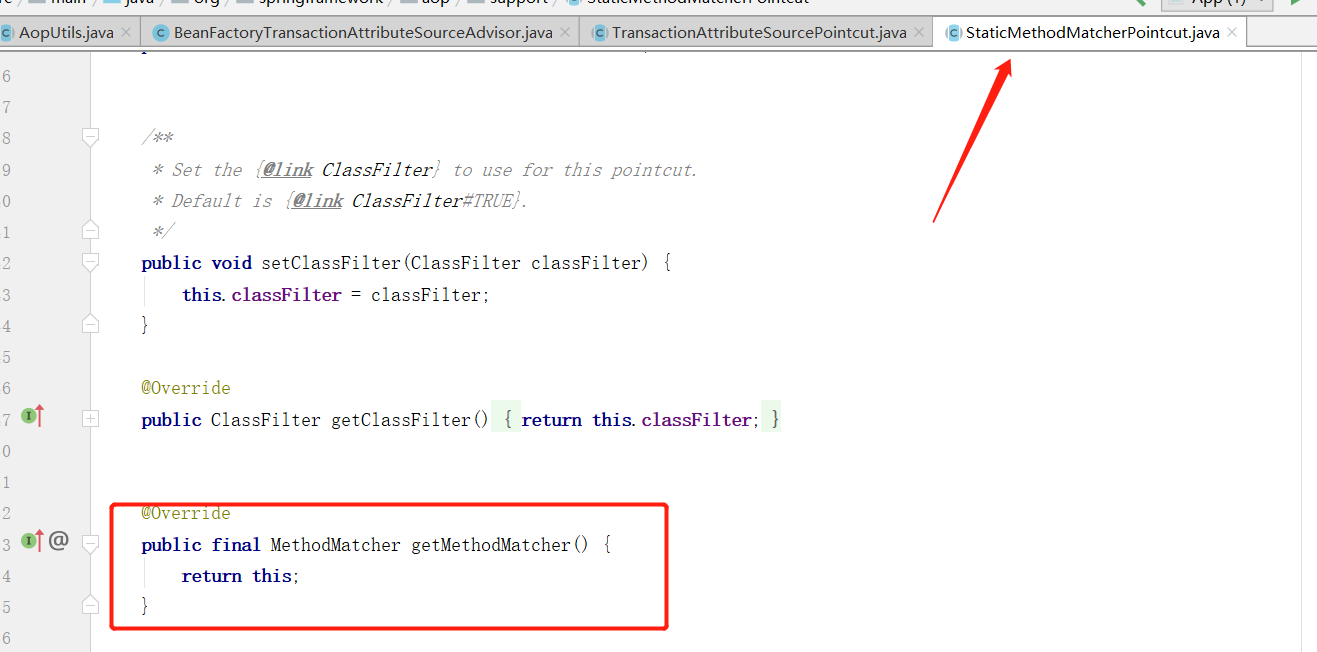
这里直接返回的自身,因此这里MethodMatcher 对象就是自身 TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut 。
下面再回到 canApply(Pointcut pc, Class<?> targetClass, boolean hasIntroductions) 方法中,最后通过反射获取到类下的方法,由于这里不属于introductionAwareMethodMatcher类型,会通过 methodMatcher.matches 判断是否符合,下面看到 TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut 类下的 matches(Method method, Class<?> targetClass) 方法中:
public boolean matches(Method method, Class<?> targetClass) {
TransactionAttributeSource tas = getTransactionAttributeSource();
// 如果存在事务信息则返回true
return (tas == null || tas.getTransactionAttribute(method, targetClass) != null);
}
上面已经分析过了 TransactionAttributeSource 主要为 AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource类型实例,因此看到该类下的 getTransactionAttribute 方法中:
主要实现在父类的 AbstractFallbackTransactionAttributeSource 类中:
public TransactionAttribute getTransactionAttribute(Method method, @Nullable Class<?> targetClass) {
// 如果是 Object 类型,直接返回 null
if (method.getDeclaringClass() == Object.class) {
return null;
}
// First, see if we have a cached value.
// 生成缓存 key
Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(method, targetClass);
// 从缓存中获取
TransactionAttribute cached = this.attributeCache.get(cacheKey);
// 缓存中存在
if (cached != null) {
// Value will either be canonical value indicating there is no transaction attribute,
// or an actual transaction attribute.
if (cached == NULL_TRANSACTION_ATTRIBUTE) {
return null;
}
else {
return cached;
}
}
else {
//缓存中不存在
// We need to work it out.
// 判断是否为事务方法,是的话获取事务属性
TransactionAttribute txAttr = computeTransactionAttribute(method, targetClass);
// Put it in the cache.
// 不存在事务
if (txAttr == null) {
this.attributeCache.put(cacheKey, NULL_TRANSACTION_ATTRIBUTE);
}
else {
// 存在事务的话
// 获取方法名称
String methodIdentification = ClassUtils.getQualifiedMethodName(method, targetClass);
if (txAttr instanceof DefaultTransactionAttribute) {
DefaultTransactionAttribute dta = (DefaultTransactionAttribute) txAttr;
dta.setDescriptor(methodIdentification);
dta.resolveAttributeStrings(this.embeddedValueResolver);
}
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Adding transactional method '" + methodIdentification + "' with attribute: " + txAttr);
}
this.attributeCache.put(cacheKey, txAttr);
}
return txAttr;
}
}
这里对事物属性进行了缓存,看下缓存中不存在的情况,通过 computeTransactionAttribute 方法,尝试解析事物属性,也就是解析 @Transactional 中的属性,下面看到该方法中:
protected TransactionAttribute computeTransactionAttribute(Method method, @Nullable Class<?> targetClass) {
// Don't allow no-public methods as required.
if (allowPublicMethodsOnly() && !Modifier.isPublic(method.getModifiers())) {
return null;
}
// The method may be on an interface, but we need attributes from the target class.
// If the target class is null, the method will be unchanged.
Method specificMethod = AopUtils.getMostSpecificMethod(method, targetClass);
// First try is the method in the target class.
// 首先尝试检测方法是否符合
TransactionAttribute txAttr = findTransactionAttribute(specificMethod);
// 如果存在则返回
if (txAttr != null) {
return txAttr;
}
// Second try is the transaction attribute on the target class.
// 检测方法所在类上是否符合
txAttr = findTransactionAttribute(specificMethod.getDeclaringClass());
if (txAttr != null && ClassUtils.isUserLevelMethod(method)) {
return txAttr;
}
if (specificMethod != method) {
// Fallback is to look at the original method.
txAttr = findTransactionAttribute(method);
if (txAttr != null) {
return txAttr;
}
// Last fallback is the class of the original method.
txAttr = findTransactionAttribute(method.getDeclaringClass());
if (txAttr != null && ClassUtils.isUserLevelMethod(method)) {
return txAttr;
}
}
return null;
}
这里会先尝试从方法上取获取 @Transactional 注解,不存在的话再去检测方法所在类上是否符合,这里主要看下方法层面的 findTransactionAttribute(Method method) 方法:
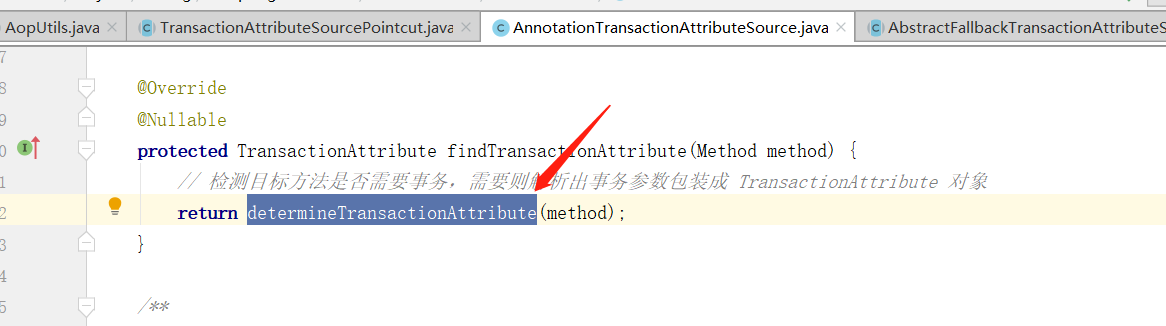
这里又触发了 determineTransactionAttribute 方法,继续看到该方法中:
protected TransactionAttribute determineTransactionAttribute(AnnotatedElement element) {
// 遍历事务解析器
for (TransactionAnnotationParser parser : this.annotationParsers) {
// 使用解析器解析事务信息
TransactionAttribute attr = parser.parseTransactionAnnotation(element);
if (attr != null) {
return attr;
}
}
return null;
}
这里又使用了前面提到的 TransactionAnnotationParser 解析器,还是主要看 SpringTransactionAnnotationParser,进到 SpringTransactionAnnotationParser 类下的 parseTransactionAnnotation 方法中:
public TransactionAttribute parseTransactionAnnotation(AnnotatedElement element) {
// 寻找目标上的 @Transactional 注解信息
AnnotationAttributes attributes = AnnotatedElementUtils.findMergedAnnotationAttributes(
element, Transactional.class, false, false);
if (attributes != null) {
// 解析注解中的参数属性,包装到 TransactionAttribute 对象中
return parseTransactionAnnotation(attributes);
}
else {
return null;
}
}
这里首先尝试获取方法上的 @Transactional 注解,如果存在的话则使用 parseTransactionAnnotation 方法解析参数,进到 parseTransactionAnnotation 方法中:
protected TransactionAttribute parseTransactionAnnotation(AnnotationAttributes attributes) {
RuleBasedTransactionAttribute rbta = new RuleBasedTransactionAttribute();
// 事务的传播方式
Propagation propagation = attributes.getEnum("propagation");
rbta.setPropagationBehavior(propagation.value());
// 事务隔离级别
Isolation isolation = attributes.getEnum("isolation");
rbta.setIsolationLevel(isolation.value());
// 超时时间
rbta.setTimeout(attributes.getNumber("timeout").intValue());
String timeoutString = attributes.getString("timeoutString");
Assert.isTrue(!StringUtils.hasText(timeoutString) || rbta.getTimeout() < 0,
"Specify 'timeout' or 'timeoutString', not both");
rbta.setTimeoutString(timeoutString);
// 事务读写性
rbta.setReadOnly(attributes.getBoolean("readOnly"));
// 可选的限定描述符,指定使用的事务管理器
rbta.setQualifier(attributes.getString("value"));
rbta.setLabels(Arrays.asList(attributes.getStringArray("label")));
// 回滚的类型
List<RollbackRuleAttribute> rollbackRules = new ArrayList<>();
for (Class<?> rbRule : attributes.getClassArray("rollbackFor")) {
rollbackRules.add(new RollbackRuleAttribute(rbRule));
}
// 回滚的类名称
for (String rbRule : attributes.getStringArray("rollbackForClassName")) {
rollbackRules.add(new RollbackRuleAttribute(rbRule));
}
// 不回滚的类型
for (Class<?> rbRule : attributes.getClassArray("noRollbackFor")) {
rollbackRules.add(new NoRollbackRuleAttribute(rbRule));
}
// 不回滚的类名称
for (String rbRule : attributes.getStringArray("noRollbackForClassName")) {
rollbackRules.add(new NoRollbackRuleAttribute(rbRule));
}
rbta.setRollbackRules(rollbackRules);
return rbta;
}
分别解析出注解中的属性信息,并包装为 TransactionAttribute 类型对象。
下面再回到 getTransactionAttribute 方法中,通过 computeTransactionAttribute 方法获取到事务的属性信息后,如果结果不为空的话进行属性的补充后直接将属性信息返回给了 TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut 中的 matches 方法,这里如果结果不为空返回就是为 true ,也就是匹配符合条件了。
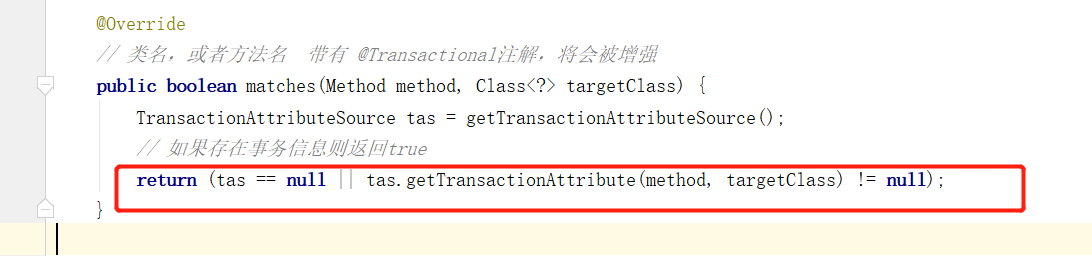
五、事务拦截器的触发过程
在 AOP 中查找完匹配的增强方法后,如果存在会创建一个代理对象放入 Spring 容器中,在代理对象执行时,先根据 Advisor 生成一个 Advice 类型的增强器链,这里以 JDK 动态代理为例,在 JdkDynamicAopProxy 类中 invoke 方法下触发的 this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice :
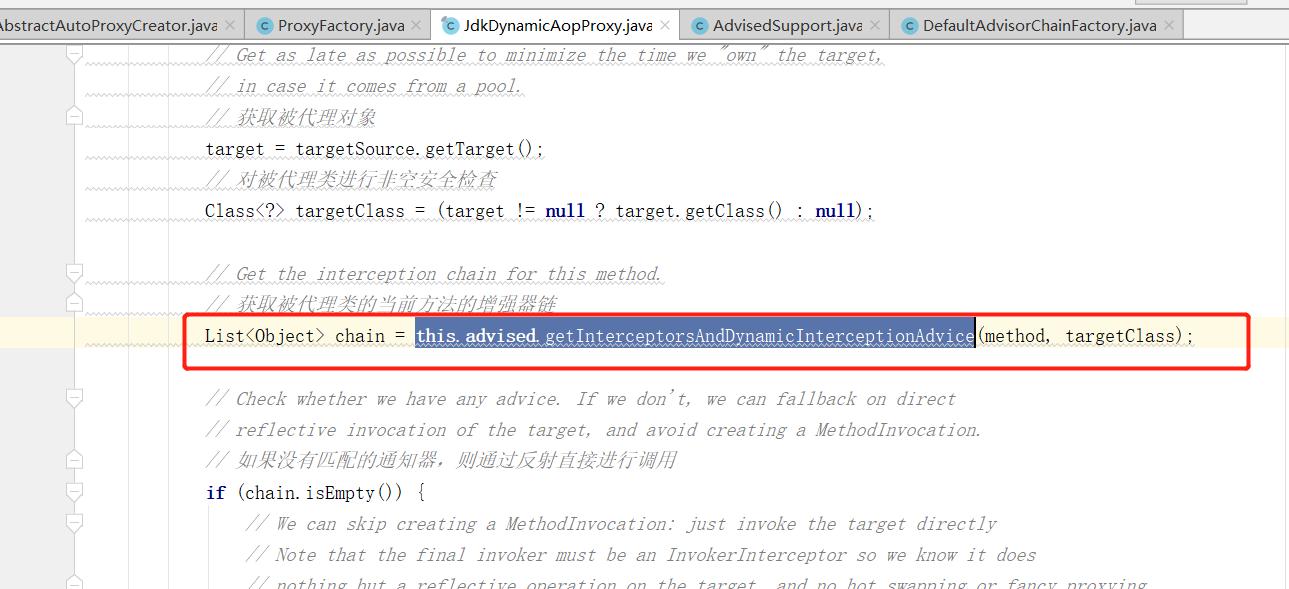
其中从 Advisor 中获取 Advice 对象的逻辑在DefaultAdvisorAdapterRegistry类下的 getInterceptors 方法中:
public MethodInterceptor[] getInterceptors(Advisor advisor) throws UnknownAdviceTypeException {
List<MethodInterceptor> interceptors = new ArrayList<>(3);
Advice advice = advisor.getAdvice();
if (advice instanceof MethodInterceptor) {
interceptors.add((MethodInterceptor) advice);
}
for (AdvisorAdapter adapter : this.adapters) {
if (adapter.supportsAdvice(advice)) {
interceptors.add(adapter.getInterceptor(advisor));
}
}
if (interceptors.isEmpty()) {
throw new UnknownAdviceTypeException(advisor.getAdvice());
}
return interceptors.toArray(new MethodInterceptor[0]);
}
增强切面方法的执行主要在 ReflectiveMethodInvocation 类下的 proceed() 中:
public Object proceed() throws Throwable {
// 该方法为 jdk的AOP实现的核心
// We start with an index of -1 and increment early.
// 从拦截器链条的尾部向头部进行递归执行
if (this.currentInterceptorIndex == this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.size() - 1) {
return invokeJoinpoint();
}
// 获取下一个要执行的拦截器
Object interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice =
this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.get(++this.currentInterceptorIndex);
// 如果通知器为 动态方法匹配拦截器,则还需要方法是否匹配的验证
if (interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice instanceof InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) {
// Evaluate dynamic method matcher here: static part will already have
// been evaluated and found to match.
InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher dm =
(InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice;
//获取被代理的对象类型
Class<?> targetClass = (this.targetClass != null ? this.targetClass : this.method.getDeclaringClass());
//进行动态匹配
if (dm.methodMatcher.matches(this.method, targetClass, this.arguments)) {
return dm.interceptor.invoke(this);
}
//如果动态匹配失败,递归进行proceed
//不匹配就不执行当前的拦截器
else {
// Dynamic matching failed.
// Skip this interceptor and invoke the next in the chain.
return proceed();
}
}
//如果不是增强器,只是一般的拦截器
else {
// It's an interceptor, so we just invoke it: The pointcut will have
// been evaluated statically before this object was constructed.
// 获取通知,并进行执行
return ((MethodInterceptor) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice).invoke(this);
}
}
这里会顺序执行 MethodInterceptor 类型的 invoke 方法 ,从前面的分析可以知道 BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor 中的 Advice 为 TransactionInterceptor,而 TransactionInterceptor 又实现了MethodInterceptor ,因此这里看到 TransactionInterceptor 类的 invoke 方法下:
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable {
// Work out the target class: may be {@code null}.
// The TransactionAttributeSource should be passed the target class
// as well as the method, which may be from an interface.
Class<?> targetClass = (invocation.getThis() != null ? AopUtils.getTargetClass(invocation.getThis()) : null);
// Adapt to TransactionAspectSupport's invokeWithinTransaction...
// 调用父类的 方法
return invokeWithinTransaction(invocation.getMethod(), targetClass, invocation::proceed);
}
这里又调用了父类 TransactionAspectSupport 下的 invokeWithinTransaction 方法,下面主要看到该方法中:
protected Object invokeWithinTransaction(Method method, @Nullable Class<?> targetClass,
final InvocationCallback invocation) throws Throwable {
// If the transaction attribute is null, the method is non-transactional.
// 获取事务属性源,如果为空则表示不存在事物
TransactionAttributeSource tas = getTransactionAttributeSource();
// 获取前面解析出来 @Transactional 注解的属性
final TransactionAttribute txAttr = (tas != null ? tas.getTransactionAttribute(method, targetClass) : null);
// 根据事物属性获取对应的事物管理器,一般为 DataSourceTransactionManager
final TransactionManager tm = determineTransactionManager(txAttr);
// 是否存在 反应式事务
if (this.reactiveAdapterRegistry != null && tm instanceof ReactiveTransactionManager) {
....省略...
}
PlatformTransactionManager ptm = asPlatformTransactionManager(tm);
// 获取目标方法唯一标识,如 com.xx.XX.xx
final String joinpointIdentification = methodIdentification(method, targetClass, txAttr);
// 根据条件执行目标增强
if (txAttr == null || !(ptm instanceof CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager)) {
// Standard transaction demarcation with getTransaction and commit/rollback calls.
// 判断是否有必要创建一个事物,根据事物传播行为决定,如果需要则新建事务信息,还会保存至 ThreadLocal 中
TransactionInfo txInfo = createTransactionIfNecessary(ptm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification);
// 返回值
Object retVal;
try {
// This is an around advice: Invoke the next interceptor in the chain.
// This will normally result in a target object being invoked.
// 切面向下执行,如果没有事务切面了,就执行业务方法
retVal = invocation.proceedWithInvocation();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// target invocation exception
// 业务方法执行报错,回滚
completeTransactionAfterThrowing(txInfo, ex);
throw ex;
}
finally {
// 清除当前事务
cleanupTransactionInfo(txInfo);
}
if (retVal != null && vavrPresent && VavrDelegate.isVavrTry(retVal)) {
// Set rollback-only in case of Vavr failure matching our rollback rules...
TransactionStatus status = txInfo.getTransactionStatus();
if (status != null && txAttr != null) {
retVal = VavrDelegate.evaluateTryFailure(retVal, txAttr, status);
}
}
// 提交事务
commitTransactionAfterReturning(txInfo);
// 如果方法正常执行,则必提交事务成功
return retVal;
}
else {
....省略...
}
}
这里会获取到前面拿到前面解析出来 @Transactional 注解的属性,并获取到事物管理器,一般为 DataSourceTransactionManager ,后面我们也主要看该类型的事务操作过程。
其中里面几个重要的方法: createTransactionIfNecessary 方法主要开启事务,completeTransactionAfterThrowing 方法回滚事务,commitTransactionAfterReturning 方法提交事务。
五、开启事务的过程
看到 TransactionAspectSupport 类下的 createTransactionIfNecessary 方法:
protected TransactionInfo createTransactionIfNecessary(@Nullable PlatformTransactionManager tm,
@Nullable TransactionAttribute txAttr, final String joinpointIdentification) {
// If no name specified, apply method identification as transaction name.
if (txAttr != null && txAttr.getName() == null) {
txAttr = new DelegatingTransactionAttribute(txAttr) {
@Override
public String getName() {
return joinpointIdentification;
}
};
}
TransactionStatus status = null;
if (txAttr != null) {
if (tm != null) {
// 从事务管理器里面,获取事务状态,此处会开启事务,整个流程的重点
status = tm.getTransaction(txAttr);
}
else {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Skipping transactional joinpoint [" + joinpointIdentification +
"] because no transaction manager has been configured");
}
}
}
// 创建事务信息对象,记录新老事务信息
return prepareTransactionInfo(tm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification, status);
}
再看到 tm.getTransaction 方法中,如果事务不存在就开启一个事务:
public final TransactionStatus getTransaction(@Nullable TransactionDefinition definition)
throws TransactionException {
// Use defaults if no transaction definition given.
TransactionDefinition def = (definition != null ? definition : TransactionDefinition.withDefaults());
// 获取事务对象,本质上,是将当前线程的数据库连接对象,与事务相关联
Object transaction = doGetTransaction();
boolean debugEnabled = logger.isDebugEnabled();
// 首次进入,connectionHolder为空,不存在事务
// 如果事务已经存在
if (isExistingTransaction(transaction)) {
// Existing transaction found -> check propagation behavior to find out how to behave.
// 处理已经存在的事务
return handleExistingTransaction(def, transaction, debugEnabled);
}
// Check definition settings for new transaction.
// 默认事务无超时设置
if (def.getTimeout() < TransactionDefinition.TIMEOUT_DEFAULT) {
throw new InvalidTimeoutException("Invalid transaction timeout", def.getTimeout());
}
// No existing transaction found -> check propagation behavior to find out how to proceed.
// 不存在事务,且事务传播属性为 强制时,抛错
if (def.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_MANDATORY) {
throw new IllegalTransactionStateException(
"No existing transaction found for transaction marked with propagation 'mandatory'");
}
// 如果事务隔离级别为 requered,requires_new,nested, 则加入事务
else if (def.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRED ||
def.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW ||
def.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_NESTED) {
// 挂起
SuspendedResourcesHolder suspendedResources = suspend(null);
if (debugEnabled) {
logger.debug("Creating new transaction with name [" + def.getName() + "]: " + def);
}
try {
// 创建新事务
return startTransaction(def, transaction, debugEnabled, suspendedResources);
}
catch (RuntimeException | Error ex) {
resume(null, suspendedResources);
throw ex;
}
}
else {
// Create "empty" transaction: no actual transaction, but potentially synchronization.
if (def.getIsolationLevel() != TransactionDefinition.ISOLATION_DEFAULT && logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Custom isolation level specified but no actual transaction initiated; " +
"isolation level will effectively be ignored: " + def);
}
boolean newSynchronization = (getTransactionSynchronization() == SYNCHRONIZATION_ALWAYS);
return prepareTransactionStatus(def, null, true, newSynchronization, debugEnabled, null);
}
}
这里首先通过 doGetTransaction 方法获取事务对象,前提有事务的话,本质就是去 ThreadLocal 中获取连接句柄,看到 DataSourceTransactionManager 类下 doGetTransaction 方法:
protected Object doGetTransaction() {
DataSourceTransactionObject txObject = new DataSourceTransactionObject();
txObject.setSavepointAllowed(isNestedTransactionAllowed());
//当前数据源,在当前线程 的 连接对象
ConnectionHolder conHolder =
(ConnectionHolder) TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource(obtainDataSource());
// 将该连接对象,设置进事务中
txObject.setConnectionHolder(conHolder, false);
return txObject;
}
其中 TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource 就是去 ThreadLocal 中获取:
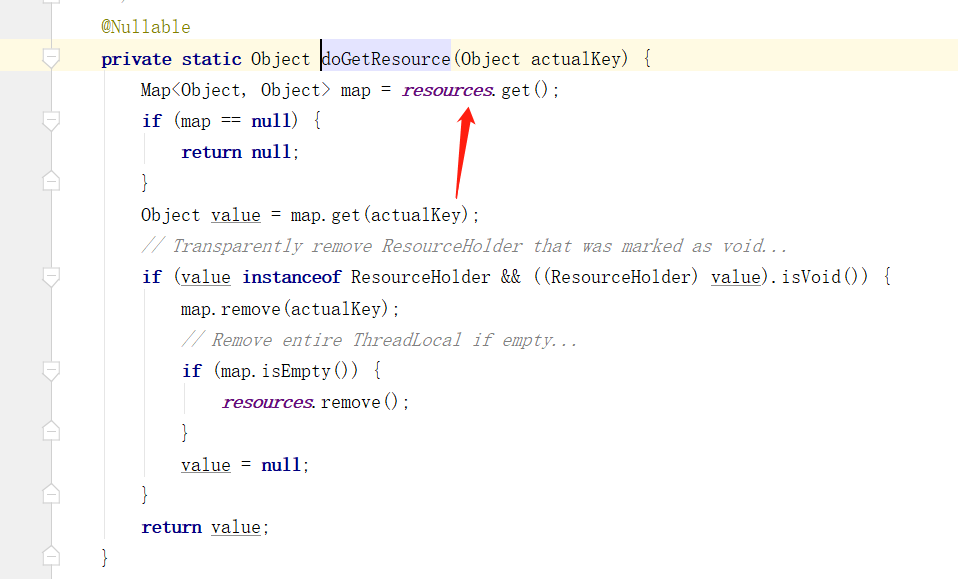
下面回到 getTransaction 方法中,如果不存在事务的话,下面通过 startTransaction 方法开启事务,看到该方法中:
private TransactionStatus startTransaction(TransactionDefinition definition, Object transaction,
boolean debugEnabled, @Nullable SuspendedResourcesHolder suspendedResources) {
boolean newSynchronization = (getTransactionSynchronization() != SYNCHRONIZATION_NEVER);
// 创建事务状态信息,封装一些事务对象的信息,记录事务状态
// 该事务标志为 新事务
DefaultTransactionStatus status = newTransactionStatus(
definition, transaction, true, newSynchronization, debugEnabled, suspendedResources);
// 开启事务,
// jdbc: transaction -> DataSourceTransactionObject jta: JtaTransactionObject
// jms: transaction-> JmsTransactionObject jca: CciLocalTransactionObject
doBegin(transaction, definition);
// 开启事务后,改变事务状态
prepareSynchronization(status, definition);
return status;
}
再看到 doBegin 方法中,来到 DataSourceTransactionManager 类下的方法:
protected void doBegin(Object transaction, TransactionDefinition definition) {
DataSourceTransactionObject txObject = (DataSourceTransactionObject) transaction;
Connection con = null;
try {
// 如果之前没有连接,则新建连接
if (!txObject.hasConnectionHolder() ||
txObject.getConnectionHolder().isSynchronizedWithTransaction()) {
// 此处是 从连接池获取连接,算是应用层底层与上层的交界处
Connection newCon = obtainDataSource().getConnection();
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Acquired Connection [" + newCon + "] for JDBC transaction");
}
// 将首次创建的连接,保存至 connectionHolder,connectionHolder 由 ThreadLocal实现
txObject.setConnectionHolder(new ConnectionHolder(newCon), true);
}
txObject.getConnectionHolder().setSynchronizedWithTransaction(true);
// 从当前事务,获取连接,一个事务下,用的同一个连接
con = txObject.getConnectionHolder().getConnection();
Integer previousIsolationLevel = DataSourceUtils.prepareConnectionForTransaction(con, definition);
txObject.setPreviousIsolationLevel(previousIsolationLevel);
// 设置事务的可读状态
txObject.setReadOnly(definition.isReadOnly());
// Switch to manual commit if necessary. This is very expensive in some JDBC drivers,
// so we don't want to do it unnecessarily (for example if we've explicitly
// configured the connection pool to set it already).
// 有事务的环境,如果设置了自动提交,则会自动切换到 手动提交
if (con.getAutoCommit()) {
txObject.setMustRestoreAutoCommit(true);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Switching JDBC Connection [" + con + "] to manual commit");
}
// 关闭连接得自动提交,这一步实际上就开启了事务
con.setAutoCommit(false);
}
// 设置事务只读状态
prepareTransactionalConnection(con, definition);
txObject.getConnectionHolder().setTransactionActive(true);
int timeout = determineTimeout(definition);
if (timeout != TransactionDefinition.TIMEOUT_DEFAULT) {
txObject.getConnectionHolder().setTimeoutInSeconds(timeout);
}
// Bind the connection holder to the thread.
// 如果是新创建的事务
if (txObject.isNewConnectionHolder()) {
// 就 建立 当前线程,和 数据库连接的绑定关系
TransactionSynchronizationManager.bindResource(obtainDataSource(), txObject.getConnectionHolder());
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (txObject.isNewConnectionHolder()) {
DataSourceUtils.releaseConnection(con, obtainDataSource());
txObject.setConnectionHolder(null, false);
}
throw new CannotCreateTransactionException("Could not open JDBC Connection for transaction", ex);
}
}
获取到数据库连接后,通过 con.setAutoCommit(false) 将自动提交关闭,实际上就已经开启了事务。
在最后 TransactionSynchronizationManager.bindResource 就是将当前连接句柄存放发到前面提到的 resources ThreadLocal 中:
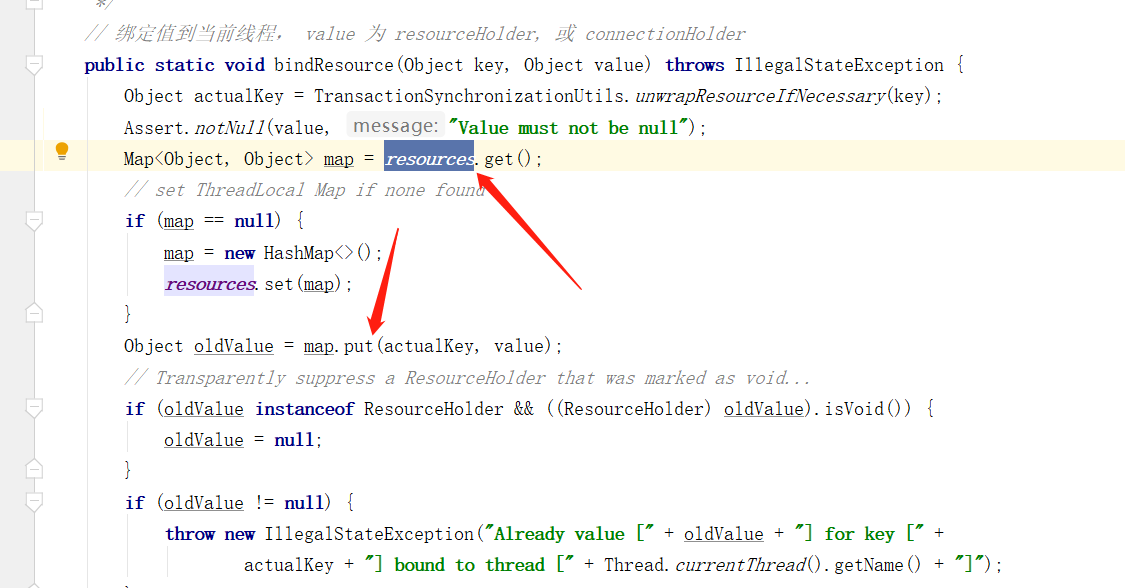
六、回滚事务过程
看到 TransactionAspectSupport 类下的 completeTransactionAfterThrowing 方法:
protected void completeTransactionAfterThrowing(@Nullable TransactionInfo txInfo, Throwable ex) {
if (txInfo != null && txInfo.getTransactionStatus() != null) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Completing transaction for [" + txInfo.getJoinpointIdentification() +
"] after exception: " + ex);
}
// 异常回滚
if (txInfo.transactionAttribute != null && txInfo.transactionAttribute.rollbackOn(ex)) {
try {
//调用 事务管理器进行 回滚操作
txInfo.getTransactionManager().rollback(txInfo.getTransactionStatus());
}
catch (TransactionSystemException ex2) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by rollback exception", ex);
ex2.initApplicationException(ex);
throw ex2;
}
catch (RuntimeException | Error ex2) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by rollback exception", ex);
throw ex2;
}
}
// 否则提交该事务
else {
// We don't roll back on this exception.
// Will still roll back if TransactionStatus.isRollbackOnly() is true.
try {
txInfo.getTransactionManager().commit(txInfo.getTransactionStatus());
}
catch (TransactionSystemException ex2) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by commit exception", ex);
ex2.initApplicationException(ex);
throw ex2;
}
catch (RuntimeException | Error ex2) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by commit exception", ex);
throw ex2;
}
}
}
}
如果设置了 rollbackOn 参数,会异常类型判断是否符合,不符合直接提交事务。
如果符合则获取到事务管理器进行 回滚操作,看到 rollback 方法中:
public final void rollback(TransactionStatus status) throws TransactionException {
if (status.isCompleted()) {
throw new IllegalTransactionStateException(
"Transaction is already completed - do not call commit or rollback more than once per transaction");
}
DefaultTransactionStatus defStatus = (DefaultTransactionStatus) status;
// 回滚
processRollback(defStatus, false);
}
再看到 processRollback 方法中:
private void processRollback(DefaultTransactionStatus status, boolean unexpected) {
try {
boolean unexpectedRollback = unexpected;
try {
triggerBeforeCompletion(status);
// 内嵌事务,则去除回滚点
if (status.hasSavepoint()) {
if (status.isDebug()) {
logger.debug("Rolling back transaction to savepoint");
}
status.rollbackToHeldSavepoint();
}
// 当前事务为新事务
else if (status.isNewTransaction()) {
if (status.isDebug()) {
logger.debug("Initiating transaction rollback");
}
// 则执行回滚
doRollback(status);
}
else {
...省略...
}
}
catch (RuntimeException | Error ex) {
triggerAfterCompletion(status, TransactionSynchronization.STATUS_UNKNOWN);
throw ex;
}
// 触发后置通知
triggerAfterCompletion(status, TransactionSynchronization.STATUS_ROLLED_BACK);
// Raise UnexpectedRollbackException if we had a global rollback-only marker
if (unexpectedRollback) {
throw new UnexpectedRollbackException(
"Transaction rolled back because it has been marked as rollback-only");
}
}
finally {
cleanupAfterCompletion(status);
}
}
主要回滚逻辑在 doRollback 方法中,看到DataSourceTransactionManager 类下的该方法:
protected void doRollback(DefaultTransactionStatus status) {
DataSourceTransactionObject txObject = (DataSourceTransactionObject) status.getTransaction();
Connection con = txObject.getConnectionHolder().getConnection();
if (status.isDebug()) {
logger.debug("Rolling back JDBC transaction on Connection [" + con + "]");
}
try {
// 通过数据库实现回滚
con.rollback();
}
catch (SQLException ex) {
throw translateException("JDBC rollback", ex);
}
}
获取到数据库连接后,通过 con.rollback() 进行事务的回滚。
七、提交事务的过程
看到TransactionAspectSupport 类下的 commitTransactionAfterReturning 方法中:
protected void commitTransactionAfterReturning(@Nullable TransactionInfo txInfo) {
if (txInfo != null && txInfo.getTransactionStatus() != null) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Completing transaction for [" + txInfo.getJoinpointIdentification() + "]");
}
// 调用事务管理器提交该事务
txInfo.getTransactionManager().commit(txInfo.getTransactionStatus());
}
}
这里使用了事务管理器的 commit 方法,看到该方法下:
public final void commit(TransactionStatus status) throws TransactionException {
if (status.isCompleted()) {
throw new IllegalTransactionStateException(
"Transaction is already completed - do not call commit or rollback more than once per transaction");
}
DefaultTransactionStatus defStatus = (DefaultTransactionStatus) status;
if (defStatus.isLocalRollbackOnly()) {
if (defStatus.isDebug()) {
logger.debug("Transactional code has requested rollback");
}
processRollback(defStatus, false);
return;
}
if (!shouldCommitOnGlobalRollbackOnly() && defStatus.isGlobalRollbackOnly()) {
if (defStatus.isDebug()) {
logger.debug("Global transaction is marked as rollback-only but transactional code requested commit");
}
processRollback(defStatus, true);
return;
}
// 处理事务提交操作
processCommit(defStatus);
}
再看到 processCommit 方法下:
private void processCommit(DefaultTransactionStatus status) throws TransactionException {
try {
boolean beforeCompletionInvoked = false;
try {
boolean unexpectedRollback = false;
prepareForCommit(status);
triggerBeforeCommit(status);
triggerBeforeCompletion(status);
beforeCompletionInvoked = true;
// 内嵌事务
if (status.hasSavepoint()) {
if (status.isDebug()) {
logger.debug("Releasing transaction savepoint");
}
// 不提交,只是将 savepoint 清除
unexpectedRollback = status.isGlobalRollbackOnly();
status.releaseHeldSavepoint();
}
// 当前事务为新事务
else if (status.isNewTransaction()) {
if (status.isDebug()) {
logger.debug("Initiating transaction commit");
}
unexpectedRollback = status.isGlobalRollbackOnly();
// 提交事务
doCommit(status);
}
else if (isFailEarlyOnGlobalRollbackOnly()) {
unexpectedRollback = status.isGlobalRollbackOnly();
}
// Throw UnexpectedRollbackException if we have a global rollback-only
// marker but still didn't get a corresponding exception from commit.
if (unexpectedRollback) {
throw new UnexpectedRollbackException(
"Transaction silently rolled back because it has been marked as rollback-only");
}
}
catch (UnexpectedRollbackException ex) {
// can only be caused by doCommit
triggerAfterCompletion(status, TransactionSynchronization.STATUS_ROLLED_BACK);
throw ex;
}
catch (TransactionException ex) {
// can only be caused by doCommit
if (isRollbackOnCommitFailure()) {
doRollbackOnCommitException(status, ex);
}
else {
triggerAfterCompletion(status, TransactionSynchronization.STATUS_UNKNOWN);
}
throw ex;
}
catch (RuntimeException | Error ex) {
if (!beforeCompletionInvoked) {
triggerBeforeCompletion(status);
}
doRollbackOnCommitException(status, ex);
throw ex;
}
// Trigger afterCommit callbacks, with an exception thrown there
// propagated to callers but the transaction still considered as committed.
try {
triggerAfterCommit(status);
}
finally {
triggerAfterCompletion(status, TransactionSynchronization.STATUS_COMMITTED);
}
}
finally {
cleanupAfterCompletion(status);
}
}
这里的判断逻辑和回滚的逻辑差不多,主要提交逻辑在 doCommit 方法中,看到 DataSourceTransactionManager 类下该方法:
protected void doCommit(DefaultTransactionStatus status) {
DataSourceTransactionObject txObject = (DataSourceTransactionObject) status.getTransaction();
Connection con = txObject.getConnectionHolder().getConnection();
if (status.isDebug()) {
logger.debug("Committing JDBC transaction on Connection [" + con + "]");
}
try {
// 通过数据库连接,实现事务提交
con.commit();
}
catch (SQLException ex) {
throw translateException("JDBC commit", ex);
}
}
获取到数据库连接后,通过 con.commit() 进行事务的提交。