在AB3MOT模型中有一个步骤为计算IOU时,需要先计算两个立体在地面的投影2D形状,然后计算两个投影的重叠部分,实际上为多边形的裁剪算法。
AB3MOT
@classmethod
def box2corners3d_camcoord(cls, bbox):
Takes an object's 3D box with the representation of [x,y,z,theta,l,w,h] and
convert it to the 8 corners of the 3D box, the box is in the camera coordinate
with right x, down y, front z
Returns:
corners_3d: (8,3) array in in rect camera coord
box corner order is like follows
1 -------- 0 top is bottom because y direction is negative
/| /|
2 -------- 3 .
| | | |
. 5 -------- 4
|/ |/
6 -------- 7
rect/ref camera coord:
right x, down y, front z
x -> w, z -> l, y -> h
上面为作者定义了立方体的坐标系
def iou(box_a, box_b, metric='giou_3d'):
''' Compute 3D/2D bounding box IoU, only working for object parallel to ground
Input:
Box3D instances
Output:
iou_3d: 3D bounding box IoU
iou_2d: bird's eye view 2D bounding box IoU
box corner order is like follows
1 -------- 0 top is bottom because y direction is negative
/| /|
2 -------- 3 .
| | | |
. 5 -------- 4
|/ |/
6 -------- 7
rect/ref camera coord:
right x, down y, front z
'''
# compute 2D related measures
boxa_bot, boxb_bot = compute_bottom(box_a, box_b)
I_2D = compute_inter_2D(boxa_bot, boxb_bot)
# only needed for GIoU
if 'giou' in metric:
C_2D = convex_area(boxa_bot, boxb_bot)
if '2d' in metric: # return 2D IoU/GIoU
U_2D = box_a.w * box_a.l + box_b.w * box_b.l - I_2D
if metric == 'iou_2d': return I_2D / U_2D
if metric == 'giou_2d': return I_2D / U_2D - (C_2D - U_2D) / C_2D
elif '3d' in metric: # return 3D IoU/GIoU
overlap_height = compute_height(box_a, box_b)
I_3D = I_2D * overlap_height
U_3D = box_a.w * box_a.l * box_a.h + box_b.w * box_b.l * box_b.h - I_3D
if metric == 'iou_3d': return I_3D / U_3D
if metric == 'giou_3d':
union_height = compute_height(box_a, box_b, inter=False)
C_3D = C_2D * union_height
return I_3D / U_3D - (C_3D - U_3D) / C_3D
else:
assert False, '%s is not supported' % space
其中
I_2D = compute_inter_2D(boxa_bot, boxb_bot)
def compute_inter_2D(boxa_bottom, boxb_bottom):
# computer intersection over union of two sets of bottom corner points
_, I_2D = convex_hull_intersection(boxa_bottom, boxb_bottom)
# a slower version
# from shapely.geometry import Polygon
# reca, recb = Polygon(boxa_bottom), Polygon(boxb_bottom)
# I_2D = reca.intersection(recb).area
return I_2D
其中
_, I_2D = convex_hull_intersection(boxa_bottom, boxb_bottom)
def convex_hull_intersection(p1, p2):
""" Compute area of two convex hull's intersection area.
p1,p2 are a list of (x,y) tuples of hull vertices.
return a list of (x,y) for the intersection and its volume
"""
inter_p = polygon_clip(p1,p2)
if inter_p is not None:
hull_inter = ConvexHull(inter_p)
return inter_p, hull_inter.volume
else:
return None, 0.0
其中
inter_p = polygon_clip(p1,p2)
def polygon_clip(subjectPolygon, clipPolygon):
""" Clip a polygon with another polygon.
Ref: https://rosettacode.org/wiki/Sutherland-Hodgman_polygon_clipping#Python
Args:
subjectPolygon: a list of (x,y) 2d points, any polygon.
clipPolygon: a list of (x,y) 2d points, has to be *convex*
Note:
**points have to be counter-clockwise ordered**
Return:
a list of (x,y) vertex point for the intersection polygon.
"""
def inside(p):
return (cp2[0] - cp1[0]) * (p[1] - cp1[1]) > (cp2[1] - cp1[1]) * (p[0] - cp1[0])
def computeIntersection():
dc = [cp1[0] - cp2[0], cp1[1] - cp2[1]]
dp = [s[0] - e[0], s[1] - e[1]]
n1 = cp1[0] * cp2[1] - cp1[1] * cp2[0]
n2 = s[0] * e[1] - s[1] * e[0]
n3 = 1.0 / (dc[0] * dp[1] - dc[1] * dp[0])
return [(n1 * dp[0] - n2 * dc[0]) * n3, (n1 * dp[1] - n2 * dc[1]) * n3]
outputList = subjectPolygon
cp1 = clipPolygon[-1]
for clipVertex in clipPolygon:
cp2 = clipVertex
inputList = outputList
outputList = []
s = inputList[-1]
for subjectVertex in inputList:
e = subjectVertex
if inside(e):
if not inside(s): outputList.append(computeIntersection())
outputList.append(e)
elif inside(s): outputList.append(computeIntersection())
s = e
cp1 = cp2
if len(outputList) == 0: return None
return (outputList)
可以看到作者给了参考链接,Ref: https://rosettacode.org/wiki/Sutherland-Hodgman_polygon_clipping#Python我发现代码一模一样,也就是作者ctrl+c ctrl+v cv大法过来的,那么多边形的裁剪的原理是什么呢?
1.前言
多边形裁剪
Sutherland Hodgman算法
凸边形与凹边形的区别
相交点暴力求解(官方版)
相交点github优雅版
2.代码
根据参考链接官方提示,我用Python对代码进行了可视化如下:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from pylab import mpl
mpl.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['STZhongsong'] # 指定默认字体:解决plot不能显示中文问题
mpl.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False # 解决保存图像是负号'-'显示为方块的问题
def clip(subjectPolygon, clipPolygon):
def inside(p):
return(cp2[0]-cp1[0])*(p[1]-cp1[1]) > (cp2[1]-cp1[1])*(p[0]-cp1[0])
def computeIntersection():
dc = [ cp1[0] - cp2[0], cp1[1] - cp2[1] ]
dp = [ s[0] - e[0], s[1] - e[1] ]
n1 = cp1[0] * cp2[1] - cp1[1] * cp2[0]
n2 = s[0] * e[1] - s[1] * e[0]
n3 = 1.0 / (dc[0] * dp[1] - dc[1] * dp[0])
return [(n1*dp[0] - n2*dc[0]) * n3, (n1*dp[1] - n2*dc[1]) * n3]
outputList = subjectPolygon
cp1 = clipPolygon[-1]
for clipVertex in clipPolygon:
cp2 = clipVertex
inputList = outputList
outputList = []
s = inputList[-1]
for subjectVertex in inputList:
e = subjectVertex
if inside(e):
if not inside(s):
outputList.append(computeIntersection())
outputList.append(e)
elif inside(s):
outputList.append(computeIntersection())
s = e
cp1 = cp2
return(outputList)
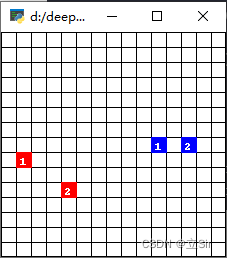
coord = [(50, 150), (200, 50), (350, 150), (350, 300), (250, 300), (200, 250), (150, 350), (100, 250), (100, 200)]
coord1 = [(100, 100), (300, 100), (300, 300), (100, 300)]
out = clip(coord, coord1)
out.append(out[0]) #repeat the first point to create a 'closed loop'
xs2, ys2 = zip(*out) #create lists of x and y values
coord.append(coord[0]) #repeat the first point to create a 'closed loop'
coord1.append(coord1[0]) #repeat the first point to create a 'closed loop'
xs, ys = zip(*coord) #create lists of x and y values
xs1, ys1 = zip(*coord1) #create lists of x and y values
plt.figure()
plt.plot(xs, ys, label = "被裁剪凸边形", color = 'r')
plt.plot(xs1, ys1, label = "裁剪凸边形", color = 'g', linestyle='--')
plt.plot(xs2, ys2, label = "结果", color = 'b')
plt.legend()
plt.show() # if you need...

图中我采用RGB顺序显示,其中红色代表被裁减多边形,绿色代表使用的裁剪框,蓝色代表最终裁剪结果。very amazing!发现结果确实这样,那么原理可以参考链接,就是一个迭代的过程。这里记录在学习原理几个难点。
判断是否在裁剪多边形内
主要是利用两个向量的叉乘:由于叉乘采用的是右手坐标系,而代码中又采用逆时针裁剪,所以只要叉乘大于0.就说明在向量的右边也就是裁剪边向量的右边,注意是向量的右边是指符合右手定则,不是真的指右边。

左图 v 1 ⃗ \vec{v_1} v1 x v 2 ⃗ \vec{v_2} v2 = ∣ v 1 ∣ ∣ v 2 ∣ s i n ( θ ) |v_1||v_2|sin(\theta) ∣v1∣∣v2∣sin(θ)符合右手定则,右图因为按照右手定则夹角为大的角,所以叉乘是负数
计算交点
源代码为
def computeIntersection():
dc = [ cp1[0] - cp2[0], cp1[1] - cp2[1] ]
dp = [ s[0] - e[0], s[1] - e[1] ]
n1 = cp1[0] * cp2[1] - cp1[1] * cp2[0]
n2 = s[0] * e[1] - s[1] * e[0]
n3 = 1.0 / (dc[0] * dp[1] - dc[1] * dp[0])
return [(n1*dp[0] - n2*dc[0]) * n3, (n1*dp[1] - n2*dc[1]) * n3]
看了半天没看懂,不如优雅版清晰
后来发现源代码采用了最暴力的求解方式,就是两条直线求交点,列一个等式,只不过斜率k与截距b是用点表示的。知乎暴力版,推导过程就是因式分解,合并同类项的过程,思路不难,难得是简,正好对应起来了。



![[Gitops--1]GitOps环境准备](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/92ab2f02fad146948d9e0eda8a2675c2.png)