目录
程序设计
程序设计1:根据要求设计UI,补充相应布局文件,即.xml文件
程序设计2:根据要求,补充Activity.java文件
程序填空
说明:
程序设计
程序设计1:根据要求设计UI,补充相应布局文件,即.xml文件
Design the UI using proper layouts and widgets for the House Selling App/Car Selling App. The UI should include multiple widgets such as TextView文本框, EditText输入框, Button按钮, Radiobutton单选按钮, Checkbox复选框, Menu菜单,Spinner列表,ListView列表,Seekbar进度条,preference设置。
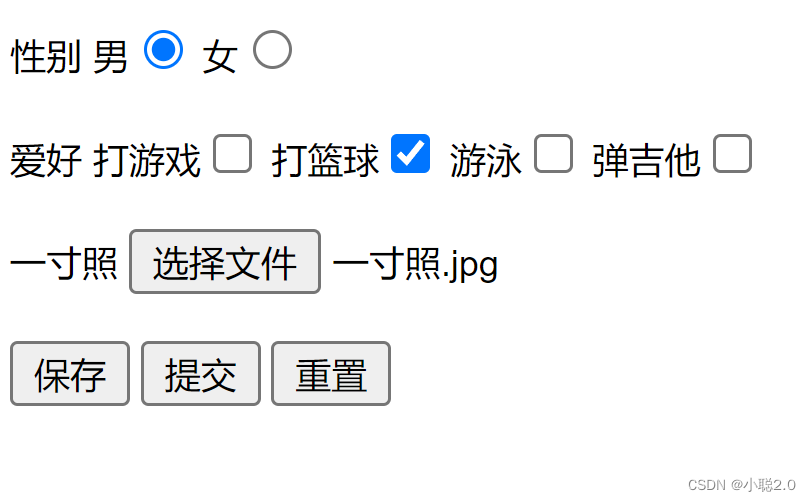
说明:我将4个实验中要求组件整合到一起来设计了UI
UI设计图如下:

(Spinner列表,写代码时我漏掉了,在这就不补充了,)
main_activity.xml文件如下
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<!--布局方式有6种,常用的有LinearLayout、TableLayout、RelativeLayout,此xml以LinearLayout布局编写-->
<!--eg:构建一个2行3列的TableLayout
<TableLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
android:layout_width=...
...
<TableRow>
<组件1.1/>
<组件1.2/>
<组件1.3/>
</TableRow>
<TableRow>
<组件2.1/>
<组件2.2/>
<组件2.3/>
</TableRow>
</TableLayout>
-->
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="...">
android:id="@+id/llt_02"
android:layout_width="match_parint"
android:layout_heigth="wrap_parint"
android:orientation="vertical">
<!--设置布局的宽为match_parint/wrap_content/具体值-->
<!--设置布局的高为match_parint/wrap_content/具体值-->
<!--orientation设置布局的方向为vertical/horizontal-->
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tvCarSale"
android:layout_width="wrap_parint"
android:layout_heigth="wrap_parint"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="汽车销售"/>
<!--TextView还有textColor,textStyle,textSize,background等属性-->
<!--TextView宽高赋值不同,会影响布局,具体问题,具体分析-->
<!--gravity设置对齐方式left/center/right默认left-->
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tvSearch"
android:layout_width="wrap_parint"
android:layout_heigth="wrap_parint"
android:text="请输入你想要搜索的汽车:"/>
<EditText
android:id="@+id/et1"
android:layout_width="wrap_parint"
android:layout_heigth="wrap_parint"
android:ems="10"
android:hint="输入关键字"/>
<!--ems设置下划线长度,hint设置未输入时下划线显示的字符-->
<Button
android:id="@+id/btmakesure"
android:layout_width="wrap_parint"
android:layout_heigth="wrap_parint"
android:text="确认"/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tvdanxuan"
android:layout_width="wrap_parint"
android:layout_heigth="wrap_parint"
android:text="变速箱类型(单选):"/>
<RadioGroup
android:id="@+id/rgp1"
android:layout_width="match_parint"
android:layout_heigth="wrap_parint"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<!--设置选项方向为水平-->
<RadioButton
android:id="@+id/rbt1"
android:layout_width="wrap_parint"
android:layout_heigth="wrap_parint"
android:text="手动"/>
<RadioButton
android:id="@+id/rbt2"
android:layout_width="wrap_parint"
android:layout_heigth="wrap_parint"
android:text="自动"/>
</RadioGroup>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tvduoxuan"
android:layout_width="wrap_parint"
android:layout_heigth="wrap_parint"
android:text=":汽车类型(多选):"/>
<CheckBox
android:id="@+id/ckbSuv"
android:layout_width="wrap_parint"
android:layout_heigth="wrap_parint"
android:text=":SUV"/>
<CheckBox
android:id="@+id/ckbSportsCar"
android:layout_width="wrap_parint"
android:layout_heigth="wrap_parint"
android:text=":跑车"/>
<CheckBox
android:id="@+id/ckbSaloonCar"
android:layout_width="wrap_parint"
android:layout_heigth="wrap_parint"
android:text=":轿车"/>
<CheckBox
android:id="@+id/ckbother"
android:layout_width="wrap_parint"
android:layout_heigth="wrap_parint"
android:text=":其他"/>
<FrameLayout
android:id="@+id/settings"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_parent"/>
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="..."><!--编写listView布局,并为其添加进度条-->
android:id="@+id/llt_02"
android:layout_width="match_parint"
android:layout_heigth="wrap_parint"
android:orientation="vertical">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tvCarlistview"
android:layout_width="match_parint"
android:layout_heigth="wrap_parint"
android:text="畅销汽车列表(ListView):"/>
<ListView
android:id="@+id/lv"
android:layout_width="match_parint"
android:layout_heigth="wrap_parint">
</ListView>
<SeekBar
android:id="@+id/sk"
android:layout_width="match_parint"
android:layout_heigth="wrap_parint"
android:max="100"
android:progress="50"/>
<!--max最大进度,progress当前进度-->
</LinearLayout>meun.xml文件如下
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<!--menu文件写在另一个xml文件中,在Activity中通过重写onCreateOptionsMenu方法,进行调用-->
<menu xmlns:android="...">
android:layout_width="match_parint"
android:layout_heigth="match_parint">
<item
android:id="@+id/m1"
android:title="收藏"/>
<item
android:id="@+id/m2"
android:title="历史记录"/>
<item
android:id="@+id/m3"
android:title="帮助与反馈"/>
<item
android:id="@+id/m4"
android:title="关于App"/>
</menu>listView.item.xml文件如下
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<!--listView的item文件写在另一个xml文件中,通过Adapter与Activity建立联系-->
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="...">
android:layout_width="match_parint"
android:layout_heigth="match_parint"
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_car1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="五菱" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_car2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="大众" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_car3"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="比亚迪" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_car4"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="特斯拉" />
</LinearLayout>setting.xml文件如下
<?xml version="l.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<PreferenceScreen>
<Preference
android:key="largeSize"
android:title="大字体"
android:summary="Setting a large font"/>
<Preference
android:key="middleSize"
android:title="中字体"
android:summary="Setting a middle font"/>
<Preference
android:key="smallSize"
android:title="小字体"
android:summary="Setting a small font"/>
<!--summary将在title以小字体解释说明title-->
<Preference
android:key="cancel"
android:title="取消"/>
</PreferenceScreen>程序设计2:根据要求,补充Activity.java文件
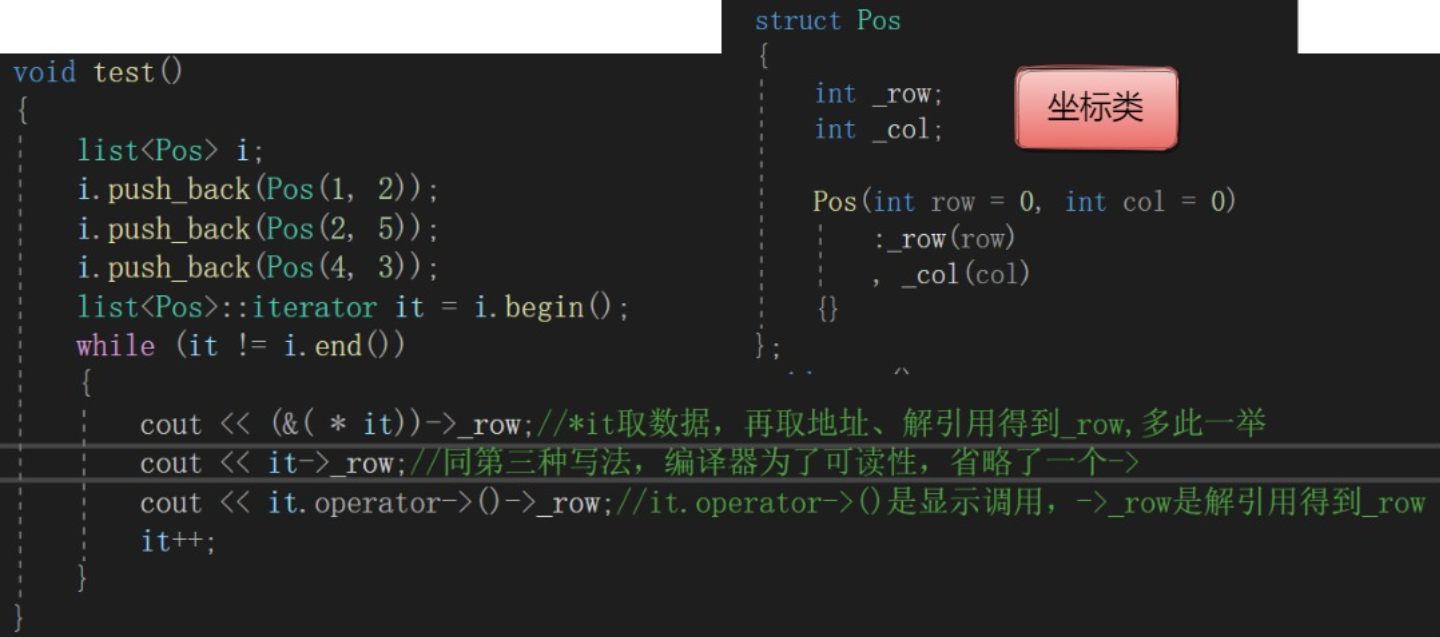
1、在Activity中获取RadioButton,为RadioGroup添加监听器,实现OnCheckedChangedListener接口,代码如下
public class MainActivity extends Activity {//继承父类
private RadioButton shoudong,zidong;//
private RadioGroup speedchange
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState){//实现onCreate方法,包含下一行
super.onCreate(savedlnstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);//调用方法,展现视图View
speedchange=(RadioGroup)findViewByld(R.id.bgp1);
shoudong=(RadioButton)findViewByld(R.id.rbt1);
zidong=(RadioButton)findViewByld(R.id.rbt2);//这里的bgp1,rbt1,rbt2与xml文件中id一致
speedchange.setOnClickedChangeListener(new zjrRadioButtonListener());
}
class zjrRadioButtonListener implements OnClickedChangeListener{
@Override
public void onCheckedChanged(RadioGroup Group,int checkedId){
switch(checkedId){
case R.id.rbt1:
Log.i("speedchange","变速箱选择了"+rbt1.getText().toString());
break;
case R.id.rbt2:
Log.i("speedchange","变速箱选择了"+rbt2.getText().toString());
break;
//这里点击事件发生后我写了log,考试时要具体分析
}
}
}
}
2、在Activity中获取Button,添加监听器,实现OnClickListener接口,并利用Intent实现两个活动状态之间的转换,代码如下
public class MainActivity extends Activity {//继承父类
private Button button;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState){//实现onCreate方法,包含下一行
super.onCreate(savedlnstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);//调用方法,展现视图View
button=(Button)findViewByld(R.id.btmakesure);
button.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener(){
@Override
public void onClick(View v){
Intent intent=new Intent(MainActivity.this,NextActivity.class);
startActivity(intent);
}
});
}
}
3、编写Menu菜单的Activity.java文件
//The Activity.java for menu
public class TipCalculatorActivity extends Activity{
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState){
super.onCreate(savedlnstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
}
@Override
public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu) {//The code that displays the menu展示菜单
getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu-activity_tip_calculator, menu);
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean onOptionsItemSelected(Menultem item) {//The code that handles the menu item events处理项目点击事件
switch(item.getItemId()) {
case R.id.menu_settings:
startActivity(new Intent(getApplicationContext( ),SettingsActivity.class));
return true;
case R.id.menu_about:
startActivity(new Intent(getApplicationContext( ),AboutActivity.class));
return true;
default:
return super.onOptionsItemSelected(item);
}
}
}程序填空
程序填空能考的实在太多了,上面的程序设计题中已经覆盖了很多填空的知识,所以要理解地选择记忆
补充一些上面没有涉及到的,如下:
1、第四章how to trace code execution跟踪代码执行的两种方法
- 利用日志Logcat
//How to use the Log class如何使用日志
//第1步:Import the Log class导入日志类
import android.util.Log;
//第2步:Declare a constant for the tag parameter为标签参数声明一个常量
private static final String TAG = "TipCalculatorActivity";
//第3步:Send messages to the log向日志发送消息
Log.d(TAG, "calculateAndDisplay method started");
Log.d(TAG, "billAmount: " + billAmount);- 利用消息提示框Toast
//How to display a toast如何展示消息框
//第1步:Import the Toast class导入消息类
import android.widget.Toast;
//第2步:Use two statements使用方法makeText()和show()
Toast t = Toast.makeText(this, "onCreate method", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT);
t.show();
//第3步:Use a single statement (method chaining)使用方法makeText()链接
Toast.makeText(this, "onCreate method ", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();2、第十章
- 考点一:how to use SAX ( Simple API for XML) to parse XML files
final String FILENAME = "news_feed.xml";
RSSFeed feed;
try {
SAXParserFactory factory = SAXParserFactory.newlnstance();// get the XML reader
SAXParser parser = factory.newSAXParser();
XMLReader xmlreader = parser.getXMLReader();
RSSFeedHandler theRssHandler = new RSSFeedHandler();// set content handler
xmlreader.setContentHandler(theRssHandler);
FilelnputStream in = openFilelnput(FILENAME); // get the input stream
InputSource is = new InputSource(in);// parse the data
xmlreader.parse(is);
feed = theRssHandler.getFeed();// get the content handler and return it
}
catch (Exception e) {
Log.e("News reader", e.toString());
}- 考点二:How to use an adapter to display data in a list view
//Code that creates and sets the adapter创建和设置适配器的代码
ArrayList <RSSItem> items = feed.getAllItems();// 获取提要项
ArrayList <HashMap<String, String>> data = new ArrayList<HashMap<String, String>>();// 创建Map<String, ?>对象列表
for (RSSItem item : items) {
HashMap<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, String>();
map.put("date", item.getPubDateFormatted());
map.put("title", item.getTitle( ));
data.add(map);
}
int resource = R.layout.listview_item;// 创建资源变量、from变量和to变量
String[] from = {"date", "title"};
int[] to = {R.id.pubDateTextView, R.id.titleTextView};
SimpleAdapter adapter =new SimpleAdapter(this, data, resource, from, to);// 创建和设置适配器
itemsListView.setAdapter(adapter);
3、第十一章
- 考点一:Service核心代码
//The NewsReaderService class with its lifecycle methods implemented
//NewsReaderService类及其实现的生命周期方法
public class NewsReaderService extends Service {
@Override
public void onCreate() {
}
@Override
public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startld) {
return START_STICKY;
}
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
return null;
}
@Override
public void onDestroyO {
}
}
- 考点二:notifications核心代码
//How to create a notification如何创建通知
//Step 1: Create the variables for the notification步骤1:为通知创建变量
int icon = R.drawable.ic_launcher;
CharSequence tickerText = "Updated news feed is available";
CharSequence contentTitle = getText(R.string.app_name);
CharSequence contentText = "Select to view updated feed.";
//Step 2: Create the Notification object步骤2:创建Notification对象
Notification notification =new Notification.Builder(this)
.setSmallIcon(icon)
.setTicker(tickerText )
.setContentTitle(contentTitle)
.setContentText(contentText )
.setContentlntent(pendingIntent )
.setAutoCancel(true)
.build();4、第十二章
- The BootReceiver class
public class BootReceiver extends BroadcastReceiver {
@Override
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
Log.d("News reader", "Boot completed");
// start service
Intent service = new Intent(context, NewsReaderService.class);
context.startService(service);
}
}
说明:
我不推荐大家看我的博文来复习
- 第一,这篇总结我并没有写完整,至少还剩1/3没写,但是我没时间写了
- 第二,我总结的只是老师划的重点以及我阅读代码后的见解,能覆盖多少咱说不准
- 我写的并不是很通俗易懂,实在没时间写那么细,如果看不懂,我建议先去图书馆找android中文书,走马观花地过一遍,我看的是以下两本,图书馆3楼东,关于android开发的书很多
|
|
|