需要源码和配置文件请点赞关注收藏后评论区留言~~~
一、基于机器学习的语音推断
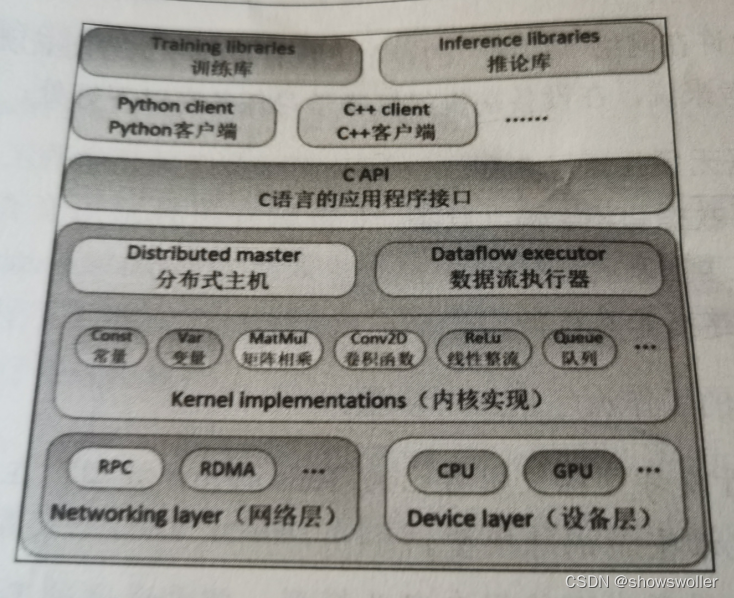
Tensorflow基于分层和模块化的设计思想,整个框架以C语言的编程接口为界,分为前端和后端两大部分 Tensorflow框架结构如下图
二、Tensorflow Lite简介
虽然Tensorflow是一款十分优秀的机器学习框架,但是它层次众多,不适合在单个设备上独立运行,为此Google推出了Tensorflow Lite,也就是Tensorflow的精简版,它可以在移动设备,嵌入式设备和物联网设备上运行Tensorflow模型
Tensorflow Lite包括下列两个主要组件
Tensorflow Lite解释器 允许在设备端的不同硬件上运行优化过的模型
Tensorflow Lite转换器 将Tensorflow模型转换为解释器使用的格式 同时通过优化提高应用性能
Tensorflow Lite允许在网络边缘的设备上执行机器学习任务,无须在设备与服务器之间来回发送数据 对开发者来说 在设备端执行机器学习任务有以下好处
缩短延迟 数组无须往返服务器
保护隐私 任何数据都不会离开设备
减少连接 不需要互联网连接
降低功耗 网络连接非常耗电
三、从语音中识别指令实战
首先给App工程手工添加Tensorflow Lite支持
implementation 'org.tensorflow:tensorflow-lite:2.5.0'同时还要引入语音识别的配置文件 请点赞关注收藏后评论区留言私信博主
然后在活动代码中初始化Tensorflow Lite 分别读取标签配置 加载模型文件
运行效果如下
语音识别支持App支持识别英文单词指令 识别到的指令会高亮显示在App界面 并且标出吻合度
需要对着手机大声朗读上述英文单词 就可观察到语音推断结果
所以此处连接真机测试效果更好 模拟机不好录制语音~~~



四、代码
部分源码如下 需要全部代码请点赞关注收藏后评论区留言~~~
package com.example.voice;
import android.content.res.AssetFileDescriptor;
import android.content.res.AssetManager;
import android.media.AudioFormat;
import android.media.AudioRecord;
import android.media.MediaRecorder;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.Handler;
import android.os.Looper;
import android.util.Log;
import android.widget.TextView;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import androidx.recyclerview.widget.GridLayoutManager;
import androidx.recyclerview.widget.RecyclerView;
import com.example.voice.adapter.WordRecyclerAdapter;
import com.example.voice.bean.WordInfo;
import com.example.voice.tensorflow.RecognizeCommands;
import org.tensorflow.lite.Interpreter;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.nio.MappedByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
public class VoiceInferenceActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private final static String TAG = "VoiceInferenceActivity";
private TextView tv_cost; // 声明一个文本视图对象
private WordRecyclerAdapter mAdapter; // 英语单词的循环适配器
private String[] mWordArray = new String[]{"Yes", "No", "Up", "Down", "Left", "Right", "On", "Off", "Stop", "Go"};
private List<WordInfo> mWordList = new ArrayList<>(); // 单词信息列表
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_voice_inference);
initView(); // 初始化视图
initTensorflow(); // 初始化Tensorflow
}
// 初始化视图
private void initView() {
TextView tv_rate = findViewById(R.id.tv_rate);
tv_rate.setText(SAMPLE_RATE + " Hz");
tv_cost = findViewById(R.id.tv_cost);
for (String word : mWordArray) {
mWordList.add(new WordInfo(word, null));
}
RecyclerView rv_word = findViewById(R.id.rv_word);
GridLayoutManager manager = new GridLayoutManager(this, 2);
rv_word.setLayoutManager(manager);
mAdapter = new WordRecyclerAdapter(this, mWordList);
rv_word.setAdapter(mAdapter);
}
private static final int SAMPLE_RATE = 16000;
private static final int SAMPLE_DURATION_MS = 1000;
private static final int RECORDING_LENGTH = (int) (SAMPLE_RATE * SAMPLE_DURATION_MS / 1000);
private static final long AVERAGE_WINDOW_DURATION_MS = 1000;
private static final float DETECTION_THRESHOLD = 0.50f;
private static final int SUPPRESSION_MS = 1500;
private static final int MINIMUM_COUNT = 3;
private static final long MINIMUM_TIME_BETWEEN_SAMPLES_MS = 30;
private static final String LABEL_FILENAME = "conv_actions_labels.txt";
private static final String MODEL_FILENAME = "conv_actions_frozen.tflite";
// Working variables.
private short[] recordBuffer = new short[RECORDING_LENGTH];
private int recordOffset = 0;
private boolean continueRecord = true;
private Thread recordThread;
private boolean continueRecognize = true;
private Thread recognizeThread;
private final ReentrantLock recordBufferLock = new ReentrantLock();
private List<String> labelList = new ArrayList<>(); // 指令标签列表
private RecognizeCommands recognizeCommands = null; // 待识别的指令
private Interpreter.Options tfLiteOptions = new Interpreter.Options(); // 解释器选项
private Interpreter tfLite; // Tensorflow Lite的解释器
private long costTime; // 每次语音识别的耗费时间
// 初始化Tensorflow
private void initTensorflow() {
Log.d(TAG, "Reading labels from: " + LABEL_FILENAME);
try (BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(getAssets().open(LABEL_FILENAME)))) {
String line;
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
labelList.add(line);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException("Problem reading label file!", e);
}
Log.d(TAG, "labelList.size()=" + labelList.size());
// 设置一个对象来平滑识别结果,以提高准确率
recognizeCommands = new RecognizeCommands(
labelList,
AVERAGE_WINDOW_DURATION_MS,
DETECTION_THRESHOLD,
SUPPRESSION_MS,
MINIMUM_COUNT,
MINIMUM_TIME_BETWEEN_SAMPLES_MS);
try {
MappedByteBuffer tfLiteModel = loadModelFile(getAssets(), MODEL_FILENAME);
tfLite = new Interpreter(tfLiteModel, tfLiteOptions);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
tfLite.resizeInput(0, new int[]{RECORDING_LENGTH, 1});
tfLite.resizeInput(1, new int[]{1});
startRecord(); // 开始录音
startRecognize(); // 开始识别
}
private MappedByteBuffer loadModelFile(AssetManager assets, String modelFilename) throws Exception {
Log.d(TAG, "modelFilename="+modelFilename);
AssetFileDescriptor descriptor = assets.openFd(modelFilename);
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(descriptor.getFileDescriptor());
FileChannel fileChannel = fis.getChannel();
long startOffset = descriptor.getStartOffset();
long declaredLength = descriptor.getDeclaredLength();
return fileChannel.map(FileChannel.MapMode.READ_ONLY, startOffset, declaredLength);
}
// 开始录音
public synchronized void startRecord() {
if (recordThread != null) {
return;
}
continueRecord = true;
recordThread = new Thread(() -> record());
recordThread.start();
}
// 停止录音
public synchronized void stopRecord() {
if (recordThread == null) {
return;
}
continueRecord = false;
recordThread = null;
}
// 录制音频
private void record() {
android.os.Process.setThreadPriority(android.os.Process.THREAD_PRIORITY_AUDIO);
// Estimate the buffer size we'll need for this device.
int bufferSize = AudioRecord.getMinBufferSize(
SAMPLE_RATE, AudioFormat.CHANNEL_IN_MONO, AudioFormat.ENCODING_PCM_16BIT);
if (bufferSize == AudioRecord.ERROR || bufferSize == AudioRecord.ERROR_BAD_VALUE) {
bufferSize = SAMPLE_RATE * 2;
}
short[] audioBuffer = new short[bufferSize / 2];
AudioRecord record = new AudioRecord(
MediaRecorder.AudioSource.DEFAULT,
SAMPLE_RATE,
AudioFormat.CHANNEL_IN_MONO,
AudioFormat.ENCODING_PCM_16BIT,
bufferSize);
if (record.getState() != AudioRecord.STATE_INITIALIZED) {
Log.e(TAG, "Audio Record can't initialize!");
return;
}
record.startRecording();
Log.d(TAG, "Start record");
// Loop, gathering audio data and copying it to a round-robin buffer.
while (continueRecord) {
int numberRead = record.read(audioBuffer, 0, audioBuffer.length);
int maxLength = recordBuffer.length;
int newRecordOffset = recordOffset + numberRead;
int secondCopyLength = Math.max(0, newRecordOffset - maxLength);
int firstCopyLength = numberRead - secondCopyLength;
// We store off all the data for the recognition thread to access. The ML
// thread will copy out of this buffer into its own, while holding the
// lock, so this should be thread safe.
recordBufferLock.lock();
try {
System.arraycopy(audioBuffer, 0, recordBuffer, recordOffset, firstCopyLength);
System.arraycopy(audioBuffer, firstCopyLength, recordBuffer, 0, secondCopyLength);
recordOffset = newRecordOffset % maxLength;
} finally {
recordBufferLock.unlock();
}
}
record.stop();
record.release();
}
// 开始识别
public synchronized void startRecognize() {
if (recognizeThread != null) {
return;
}
continueRecognize = true;
recognizeThread = new Thread(() -> recognize());
recognizeThread.start();
}
// 停止识别
public synchronized void stopRecognize() {
if (recognizeThread == null) {
return;
}
continueRecognize = false;
recognizeThread = null;
}
// 识别语音
private void recognize() {
Log.d(TAG, "Start recognition");
short[] inputBuffer = new short[RECORDING_LENGTH];
float[][] floatInputBuffer = new float[RECORDING_LENGTH][1];
float[][] outputScores = new float[1][labelList.size()];
int[] sampleRateList = new int[]{SAMPLE_RATE};
// Loop, grabbing recorded data and running the recognition model on it.
while (continueRecognize) {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
// The record thread places data in this round-robin buffer, so lock to
// make sure there's no writing happening and then copy it to our own
// local version.
recordBufferLock.lock();
try {
int maxLength = recordBuffer.length;
int firstCopyLength = maxLength - recordOffset;
int secondCopyLength = recordOffset;
System.arraycopy(recordBuffer, recordOffset, inputBuffer, 0, firstCopyLength);
System.arraycopy(recordBuffer, 0, inputBuffer, firstCopyLength, secondCopyLength);
} finally {
recordBufferLock.unlock();
}
// We need to feed in float values between -1.0f and 1.0f, so divide the
// signed 16-bit inputs.
for (int i = 0; i < RECORDING_LENGTH; ++i) {
floatInputBuffer[i][0] = inputBuffer[i] / 32767.0f;
}
Object[] inputArray = {floatInputBuffer, sampleRateList};
Map<Integer, Object> outputMap = new HashMap<>();
outputMap.put(0, outputScores);
// Run the model.
tfLite.runForMultipleInputsOutputs(inputArray, outputMap);
// Use the smoother to figure out if we've had a real recognition event.
final RecognizeCommands.RecognitionResult result =
recognizeCommands.processLatestResults(outputScores[0], System.currentTimeMillis());
costTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
runOnUiThread( () -> {
tv_cost.setText(costTime + " ms");
// If we do have a new command, highlight the right list entry.
if (!result.foundCommand.startsWith("_") && result.isNewCommand) {
int position = labelList.indexOf(result.foundCommand) - 2;
WordInfo word = mWordList.get(position);
word.percent = Math.round(result.score * 100) + "%";
mWordList.set(position, word);
mAdapter.notifyItemChanged(position);
new Handler(Looper.myLooper()).postDelayed(() -> {
word.percent = "";
mWordList.set(position, word);
mAdapter.notifyItemChanged(position);
}, 1500);
}
});
try {
// We don't need to run too frequently, so snooze for a bit.
Thread.sleep(MINIMUM_TIME_BETWEEN_SAMPLES_MS);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
}
Log.d(TAG, "End recognition");
}
}创作不易 觉得有帮助请点赞关注收藏~~~