一、Git仓库用法
1、linu终端输入下面命令安装
git clone https://e.coding.net/weidongshan/linux_course/linux_basic_develop.git
2、
进入到GIT仓库目录
cd /D/abc/doc_and_source_for_mcu_mpu
在doc_and_source_for_mcu_mpu目录下,执行以下命令获得资料的最新版本。
git pull origin
二、字符设备驱动开发
1、hello驱动程序步骤
- 创建
file_operations结构体(字符设备驱动的核心) - 注册字符设备设备
- 写入口函数(相当于main)
- 写退出函数
三、字符设备驱动程序源码
#include <linux/mm.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/miscdevice.h>
#include <linux/slab.h>
#include <linux/vmalloc.h>
#include <linux/mman.h>
#include <linux/random.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/raw.h>
#include <linux/tty.h>
#include <linux/capability.h>
#include <linux/ptrace.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
#include <linux/highmem.h>
#include <linux/backing-dev.h>
#include <linux/shmem_fs.h>
#include <linux/splice.h>
#include <linux/pfn.h>
#include <linux/export.h>
#include <linux/io.h>
#include <linux/uio.h>
#include <linux/uaccess.h>
static int major;
static int hello_open (struct inode *node, struct file *filp)
{
printk("%s %s %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
return 0;
}
static ssize_t hello_read (struct file *filp, char __user *buf, size_t size, loff_t *offset)
{
printk("%s %s %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
return size;
}
static ssize_t hello_write(struct file *filp, const char __user *buf, size_t size, loff_t *offset)
{
printk("%s %s %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
return size;
}
static int hello_release (struct inode *node, struct file *filp)
{
printk("%s %s %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
return 0;
}
/* 1. create file_operations */
static const struct file_operations hello_drv = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.read = hello_read,
.write = hello_write,
.open = hello_open,
.release = hello_release,
};
/* 2. register_chrdev */
/* 3. entry function */
static int hello_init(void)
{
major = register_chrdev(0, "100ask_hello", &hello_drv);
return 0;
}
/* 4. exit function */
static void hello_exit(void)
{
unregister_chrdev(major, "100ask_hello");
}
module_init(hello_init);
module_exit(hello_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
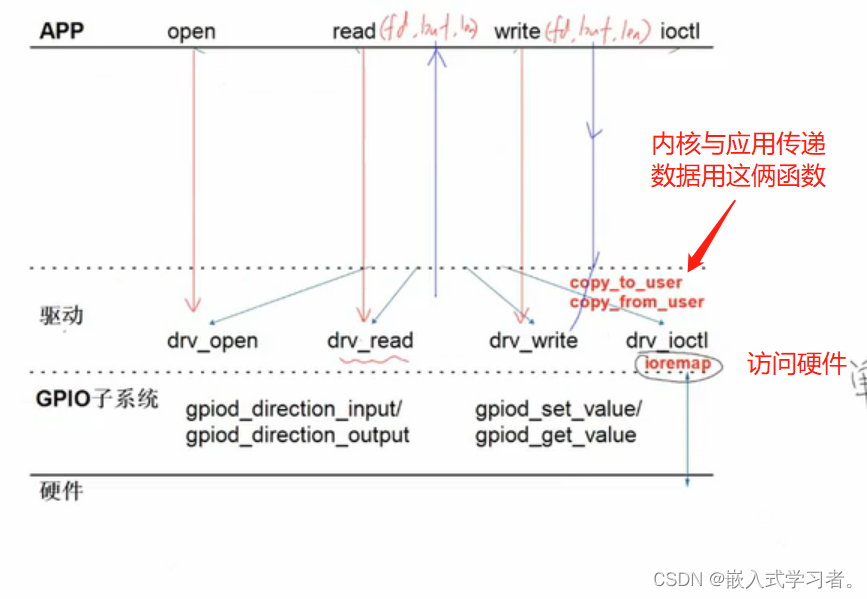
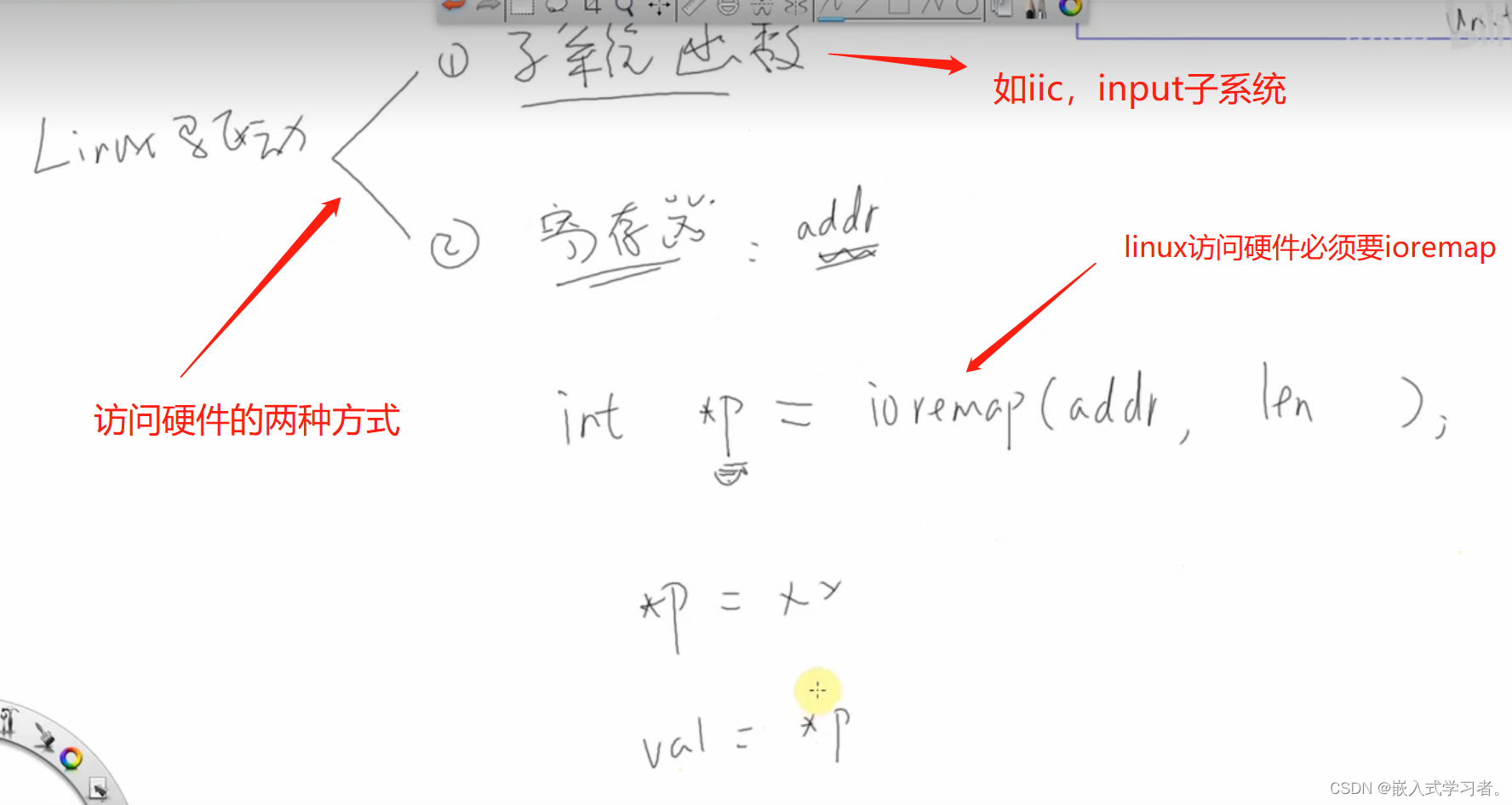
用户与内核传数据和创建设备文件驱动程序
#include "asm/cacheflush.h"
#include <linux/mm.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/miscdevice.h>
#include <linux/slab.h>
#include <linux/vmalloc.h>
#include <linux/mman.h>
#include <linux/random.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/raw.h>
#include <linux/tty.h>
#include <linux/capability.h>
#include <linux/ptrace.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
#include <linux/highmem.h>
#include <linux/backing-dev.h>
#include <linux/shmem_fs.h>
#include <linux/splice.h>
#include <linux/pfn.h>
#include <linux/export.h>
#include <linux/io.h>
#include <linux/uio.h>
#include <linux/uaccess.h>
static struct class *hello_class; //定义一个类型,用于创建设备
static int major; //主设备号
static unsigned char hello_buf[100]; //内核数据缓存
static int hello_open (struct inode *node, struct file *filp)
{
printk("%s %s %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
return 0;
}
static ssize_t hello_read (struct file *filp, char __user *buf, size_t size, loff_t *offset)
{
unsigned long len = size > 100 ? 100 : size;
printk("%s %s %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
copy_to_user(buf, hello_buf, len); //将内核数据发送给用户
return len;
}
static ssize_t hello_write(struct file *filp, const char __user *buf, size_t size, loff_t *offset)
{
unsigned long len = size > 100 ? 100 : size;
printk("%s %s %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
copy_from_user(hello_buf, buf, len);
return len;
}
static int hello_release(struct inode *node, struct file *filp)
{
printk("%s %s %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
return 0;
}
/* 1. create file_operations */
static const struct file_operations hello_drv = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.read = hello_read,
.write = hello_write,
.open = hello_open,
.release = hello_release,
};
/* 2. register_chrdev */
/* 3. entry function */
static int hello_init(void)
{ //申请设备号,只能进行注测主设备号0-255个设备,次设备号全部被占用
major = register_chrdev(0, "100ask_hello", &hello_drv); //0代表自动寻找设备号,
hello_class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "hello_class"); //创建一个类型
if (IS_ERR(hello_class)) {
printk("failed to allocate class\n");
return PTR_ERR(hello_class);
}
//创建一个名字为hello的设备
device_create(hello_class, NULL, MKDEV(major, 0), NULL, "hello"); /* /dev/hello */
return 0;
}
/* 4. exit function */
static void hello_exit(void)
{
device_destroy(hello_class, MKDEV(major, 0));
class_destroy(hello_class);
unregister_chrdev(major, "100ask_hello");
}
module_init(hello_init);
module_exit(hello_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
应用
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
/* 写: ./hello_test /dev/xxx 100ask
* 读: ./hello_test /dev/xxx
*/
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int fd;
int len;
char buf[100];
if (argc < 2)
{
printf("Usage: \n");
printf("%s <dev> [string]\n", argv[0]);
return -1;
}
// open
fd = open(argv[1], O_RDWR);
if (fd < 0)
{
printf("can not open file %s\n", argv[1]);
return -1;
}
if (argc == 3)
{
// write
len = write(fd, argv[2], strlen(argv[2])+1);
printf("write ret = %d\n", len);
}
else
{
// read
len = read(fd, buf, 100);
buf[99] = '\0';
printf("read str : %s\n", buf);
}
// close
close(fd);
return 0;
}
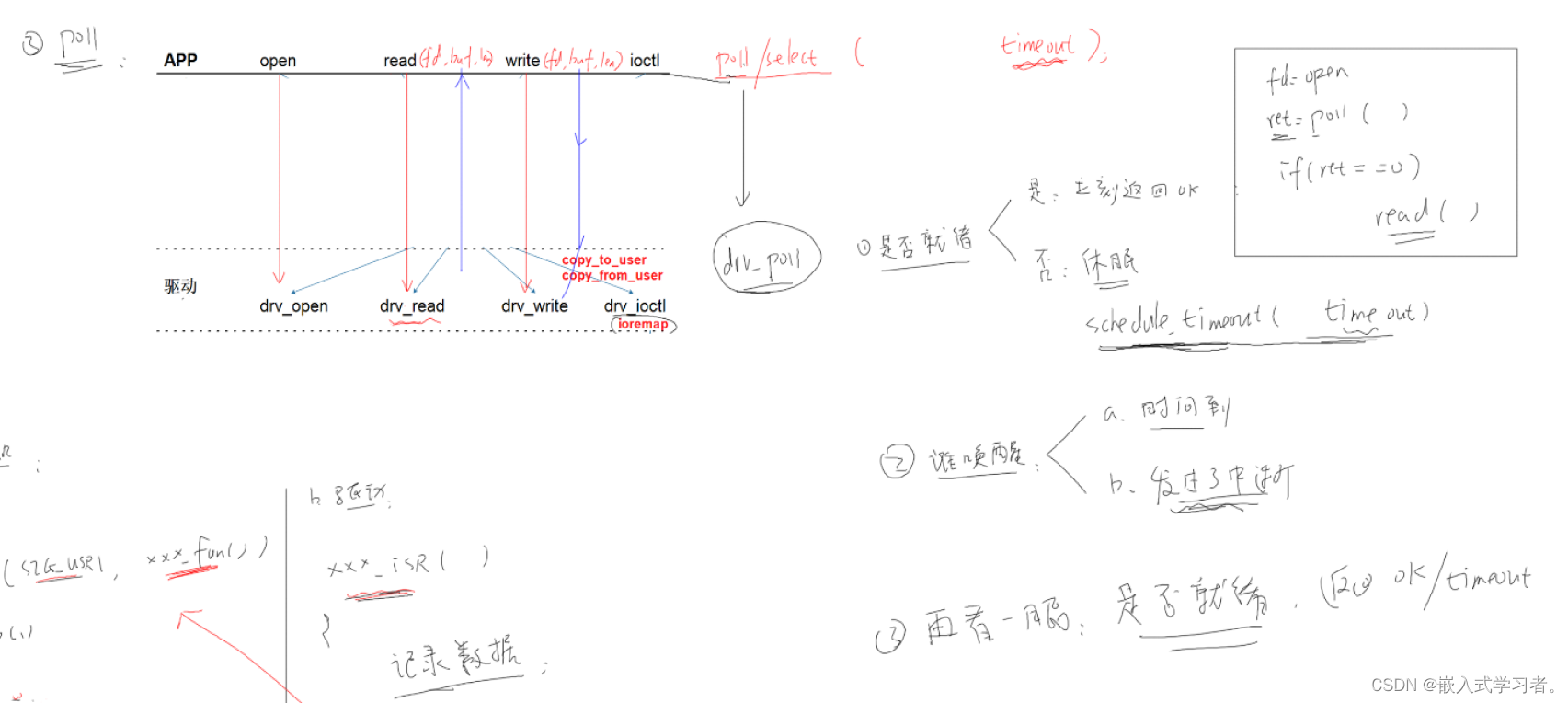
四、 APP使用驱动的4种方式
1、驱动程序:提供能力,不提供策略
-
非阻塞(查询)
-
阻塞(休眠-唤醒)
-
poll(定个闹钟)
-
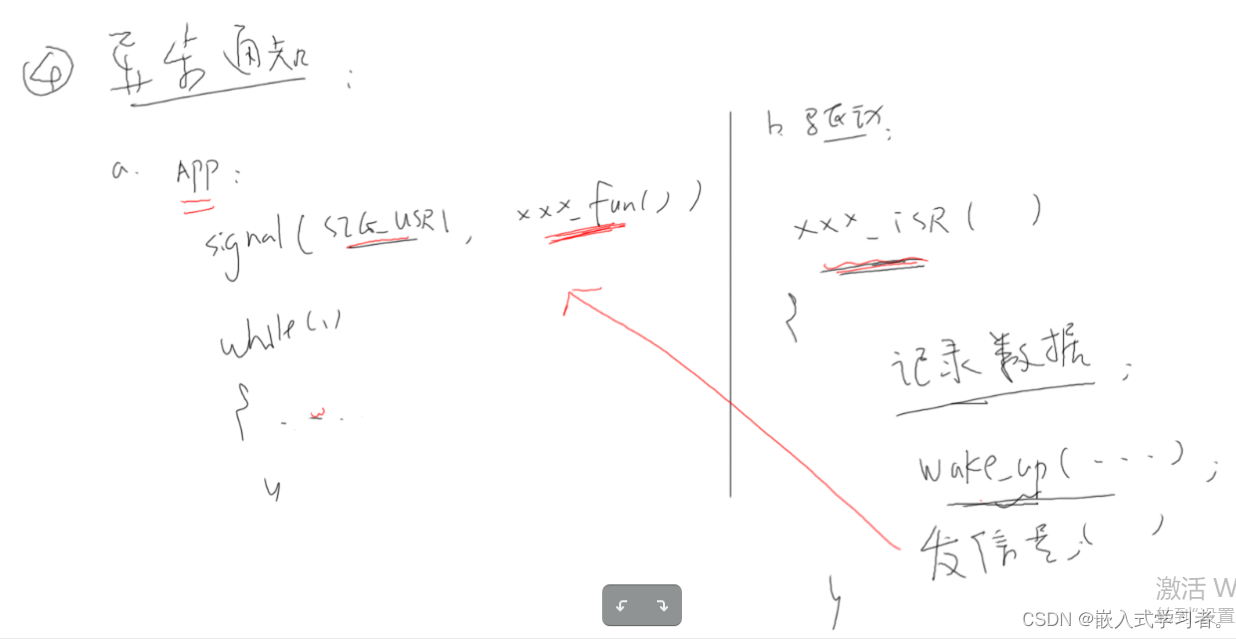
异步通知

妈妈怎么知道卧室里小孩醒了? -
时不时进房间看一下: 查询方式
- 简单,但是累
-
进去房间陪小孩一起睡觉,小孩醒了会吵醒她: 休眠-唤醒
-
不累,但是妈妈干不了活了
-
妈妈要干很多活,但是可以陪小孩睡一会,定个闹钟: poll 方式
- 要浪费点时间, 但是可以继续干活。
- 妈妈要么是被小孩吵醒,要么是被闹钟吵醒。
-
妈妈在客厅干活,小孩醒了他会自己走出房门告诉妈妈: 异步通知
- 妈妈、小孩互不耽误
2、中断的引入
- 非阻塞:没有解除睡眠立即返回错误
- 阻塞如下图:

- poll机制如下图
- 异步通知
五、 字符设备的另一种注册方法cdev
驱动程序
#include "asm-generic/errno-base.h"
#include "asm/cacheflush.h"
#include "linux/cdev.h"
#include "linux/fs.h"
#include <linux/mm.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/miscdevice.h>
#include <linux/slab.h>
#include <linux/vmalloc.h>
#include <linux/mman.h>
#include <linux/random.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/raw.h>
#include <linux/tty.h>
#include <linux/capability.h>
#include <linux/ptrace.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
#include <linux/highmem.h>
#include <linux/backing-dev.h>
#include <linux/shmem_fs.h>
#include <linux/splice.h>
#include <linux/pfn.h>
#include <linux/export.h>
#include <linux/io.h>
#include <linux/uio.h>
#include <linux/uaccess.h>
static struct class *hello_class;
static struct cdev hello_cdev;
static dev_t dev;
static unsigned char hello_buf[100];
static int hello_open (struct inode *node, struct file *filp)
{
printk("%s %s %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
return 0;
}
static ssize_t hello_read (struct file *filp, char __user *buf, size_t size, loff_t *offset)
{
unsigned long len = size > 100 ? 100 : size;
printk("%s %s %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
copy_to_user(buf, hello_buf, len);
return len;
}
static ssize_t hello_write(struct file *filp, const char __user *buf, size_t size, loff_t *offset)
{
unsigned long len = size > 100 ? 100 : size;
printk("%s %s %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
copy_from_user(hello_buf, buf, len);
return len;
}
static int hello_release (struct inode *node, struct file *filp)
{
printk("%s %s %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
return 0;
}
/* 1. create file_operations */
static const struct file_operations hello_drv = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.read = hello_read,
.write = hello_write,
.open = hello_open,
.release = hello_release,
};
/* 2. register_chrdev */
/* 3. entry function */
static int hello_init(void)
{
int ret;
// register_chrdev
//参数一:分配设备号成功后用来存放分配到的设备号,分配结束后要把主设备号提取出来(major = MAJOR(devno);)因为主设备号会变所以要将变得重新赋值
//参数二:起始的次设备号,一般为0
//参数三:count:申请的设备数量,从起始设备号累加。如果在创建一个设备,主设备号跟前一个一样,次设备号为1的设备,依然可以访问,就是同一个设备。
//参数四:/proc/devices文件中与该设备对应的名字,方便用户层查询主次设备号
ret = alloc_chrdev_region(&dev, 0, 2, "hello"); //自动注册设备
if (ret < 0)
{
printk(KERN_ERR "alloc_chrdev_region() failed for hello\n");
return -EINVAL;
}
cdev_init(&hello_cdev, &hello_drv); //将hello_drv与hello_cdev链接起来
ret = cdev_add(&hello_cdev, dev, 2);//将设备号添加到设备结构体
if (ret)
{
printk(KERN_ERR "cdev_add() failed for hello\n");
return -EINVAL;
}
hello_class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "hello_class");
if (IS_ERR(hello_class)) {
printk("failed to allocate class\n");
return PTR_ERR(hello_class);
}
//创建一名字为hello的设备
device_create(hello_class, NULL, dev, NULL, "hello"); /* /dev/hello */
return 0;
}
/* 4. exit function */
static void hello_exit(void)
{
device_destroy(hello_class, dev);
class_destroy(hello_class);
//unregister_chrdev(major, "100ask_hello");
cdev_del(&hello_cdev);
unregister_chrdev_region(dev, 2);
}
module_init(hello_init);
module_exit(hello_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
app
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
/* 写: ./hello_test /dev/xxx 100ask
* 读: ./hello_test /dev/xxx
*/
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int fd;
int len;
char buf[100];
if (argc < 2)
{
printf("Usage: \n");
printf("%s <dev> [string]\n", argv[0]);
return -1;
}
// open
fd = open(argv[1], O_RDWR);
if (fd < 0)
{
printf("can not open file %s\n", argv[1]);
return -1;
}
if (argc == 3)
{
// write
len = write(fd, argv[2], strlen(argv[2])+1);
printf("write ret = %d\n", len);
}
else
{
// read
len = read(fd, buf, 100);
buf[99] = '\0';
printf("read str : %s\n", buf);
}
// close
close(fd);
return 0;
}
六、 通用框架1
1、GPIO子系统
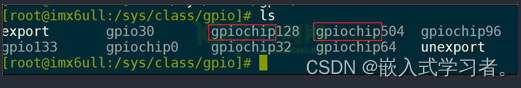
在开发板上执行如下命令查看已经在使用的GPIO状态:
# cat /sys/kernel/debug/gpio
gpiochip0: GPIOs 0-15, parent: platform/soc:pin-controller@50002000, GPIOA:
gpio-10 ( |heartbeat ) out lo
gpio-14 ( |shutdown ) out hi
gpiochip1: GPIOs 16-31, parent: platform/soc:pin-controller@50002000, GPIOB:
gpio-26 ( |reset ) out hi ACTIVE LOW
gpiochip2: GPIOs 32-47, parent: platform/soc:pin-controller@50002000, GPIOC:
gpiochip3: GPIOs 48-63, parent: platform/soc:pin-controller@50002000, GPIOD:
怎么确定GPIO引脚的编号?方法如下:
① 先在开发板的/sys/class/gpio目录下,找到各个gpiochipXXX目录:(这个后面的数是起始地址,不跟上面那个查到的组数一样)
② 然后进入某个gpiochipXXX目录,查看文件label的内容,就可以知道起始号码XXX对于哪组GPIO
那么GPIO4_14的号码是96+14=110,可以如下操作读取按键值:
[root@100ask:~]# echo 110 > /sys/class/gpio/export // gpio_request
[root@100ask:~]# echo in > /sys/class/gpio/gpio110/direction // gpio_direction_input
[root@100ask:~]# cat /sys/class/gpio/gpio110/value // gpio_get_value
[root@100ask:~]# echo 110 > /sys/class/gpio/unexport // gpio_free
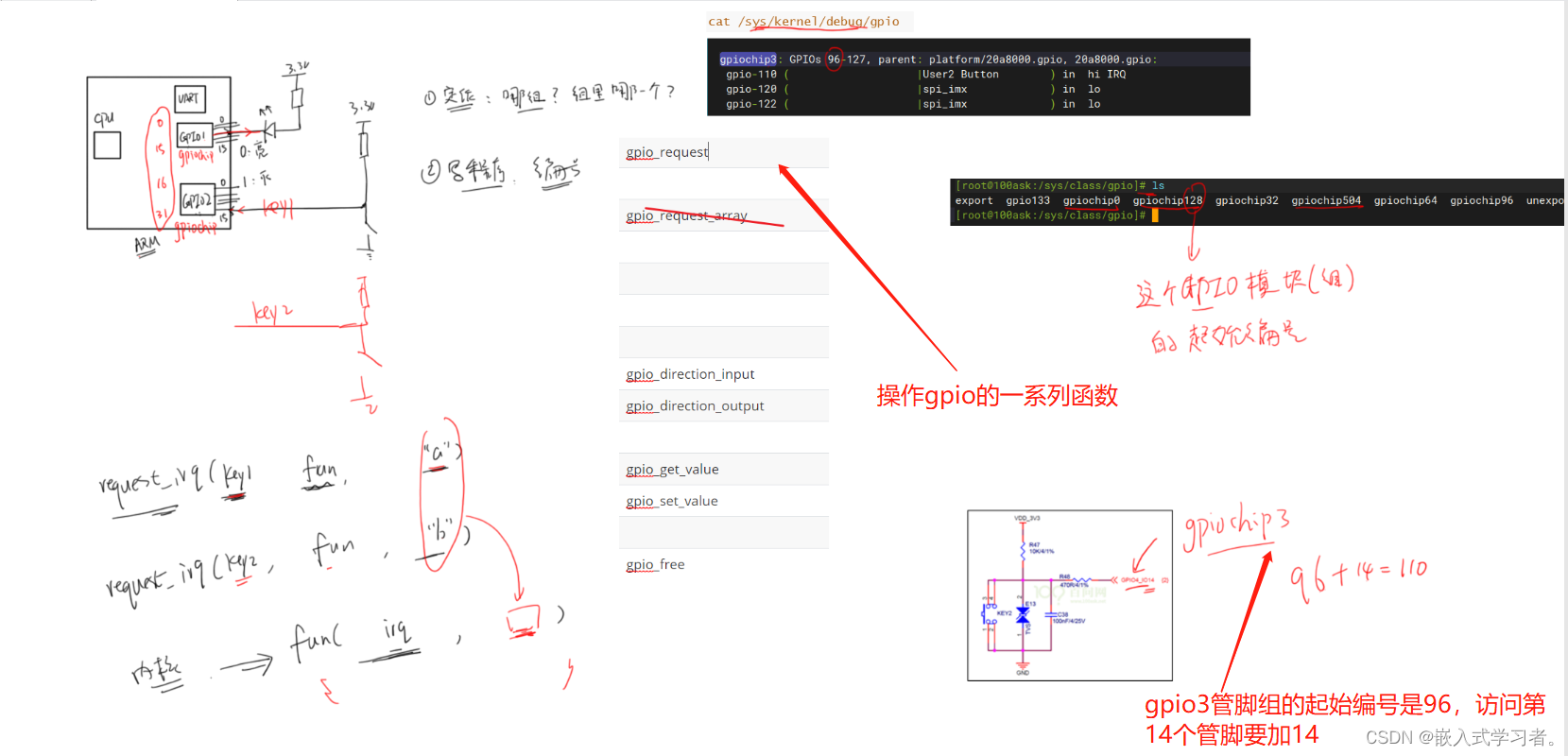
GPIO子系统函数有新、老两套:
| descriptor-based | legacy |
|---|---|
| 获得GPIO | |
| gpiod_get | gpio_request |
| gpiod_get_index | |
| gpiod_get_array | gpio_request_array |
| devm_gpiod_get | |
| devm_gpiod_get_index | |
| devm_gpiod_get_array | |
| 设置方向 | |
| gpiod_direction_input | gpio_direction_input |
| gpiod_direction_output | gpio_direction_output |
| 读值、写值 | |
| gpiod_get_value | gpio_get_value |
| gpiod_set_value | gpio_set_value |
| 释放GPIO | |
| gpio_free | gpio_free |
| gpiod_put | gpio_free_array |
| gpiod_put_array | |
| devm_gpiod_put | |
| devm_gpiod_put_array |
2、中断函数
2.1 使用中断的流程
在驱动程序里使用中断的流程如下:
-
确定中断号
-
注册中断处理函数,函数原型如下:
int request_irq(unsigned int irq, irq_handler_t handler, unsigned long flags, const char *name, void *dev);
-
在中断处理函数里
- 分辨中断
- 处理中断
- 清除中断
2.2 函数细节
request_irq函数的第1个参数是中断号,可以根据GPIO函数获得中断号:
int gpio_to_irq(unsigned int gpio);
int gpiod_to_irq(const struct gpio_desc *desc);
request_irq函数的第2个参数是函数指针:
enum irqreturn {
IRQ_NONE = (0 << 0),
IRQ_HANDLED = (1 << 0),
IRQ_WAKE_THREAD = (1 << 1),
};
typedef enum irqreturn irqreturn_t;
typedef irqreturn_t (*irq_handler_t)(int irq, void *dev);
request_irq函数的第3个参数有如下取值:
(上升沿触发、下降沿触发…)
#define IRQF_TRIGGER_NONE 0x00000000
#define IRQF_TRIGGER_RISING 0x00000001
#define IRQF_TRIGGER_FALLING 0x00000002
#define IRQF_TRIGGER_HIGH 0x00000004
#define IRQF_TRIGGER_LOW 0x00000008
#define IRQF_SHARED 0x00000080
request_irq函数的第4个参数是中断的名字,可以在执行cat /proc/interrupts的结果里查看。
request_irq函数的第5个参数是给中断处理函数使用的。
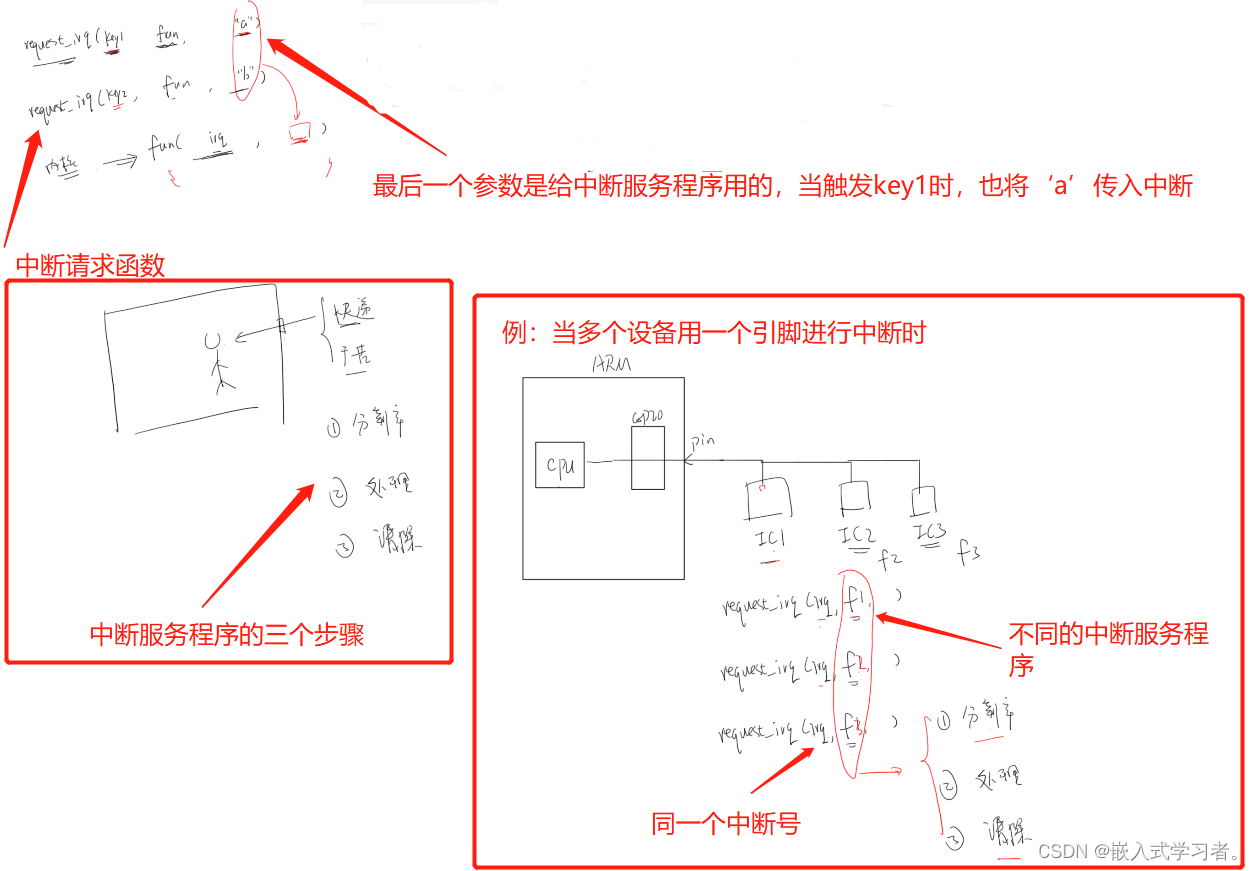
2.3 代码
driver
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/poll.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/errno.h>
#include <linux/miscdevice.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/major.h>
#include <linux/mutex.h>
#include <linux/proc_fs.h>
#include <linux/seq_file.h>
#include <linux/stat.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
#include <linux/tty.h>
#include <linux/kmod.h>
#include <linux/gfp.h>
#include <linux/gpio/consumer.h>
#include <linux/platform_device.h>
#include <linux/of_gpio.h>
#include <linux/of_irq.h>
#include <linux/interrupt.h>
#include <linux/irq.h>
#include <linux/slab.h>
#include <linux/fcntl.h>
#include <linux/timer.h>
struct gpio_desc{ //定义一个中断结构体
int gpio;
int irq;
char *name;
int key;
struct timer_list key_timer;
} ;
static struct gpio_desc gpios[2] = { //中断结构体赋初值
{131, 0, "gpio_100ask_1", 1,},
{132, 0, "gpio_100ask_2", 2,},
};
/* 主设备号 */
static int major = 0;
static struct class *gpio_class;
/* 环形缓冲区 */
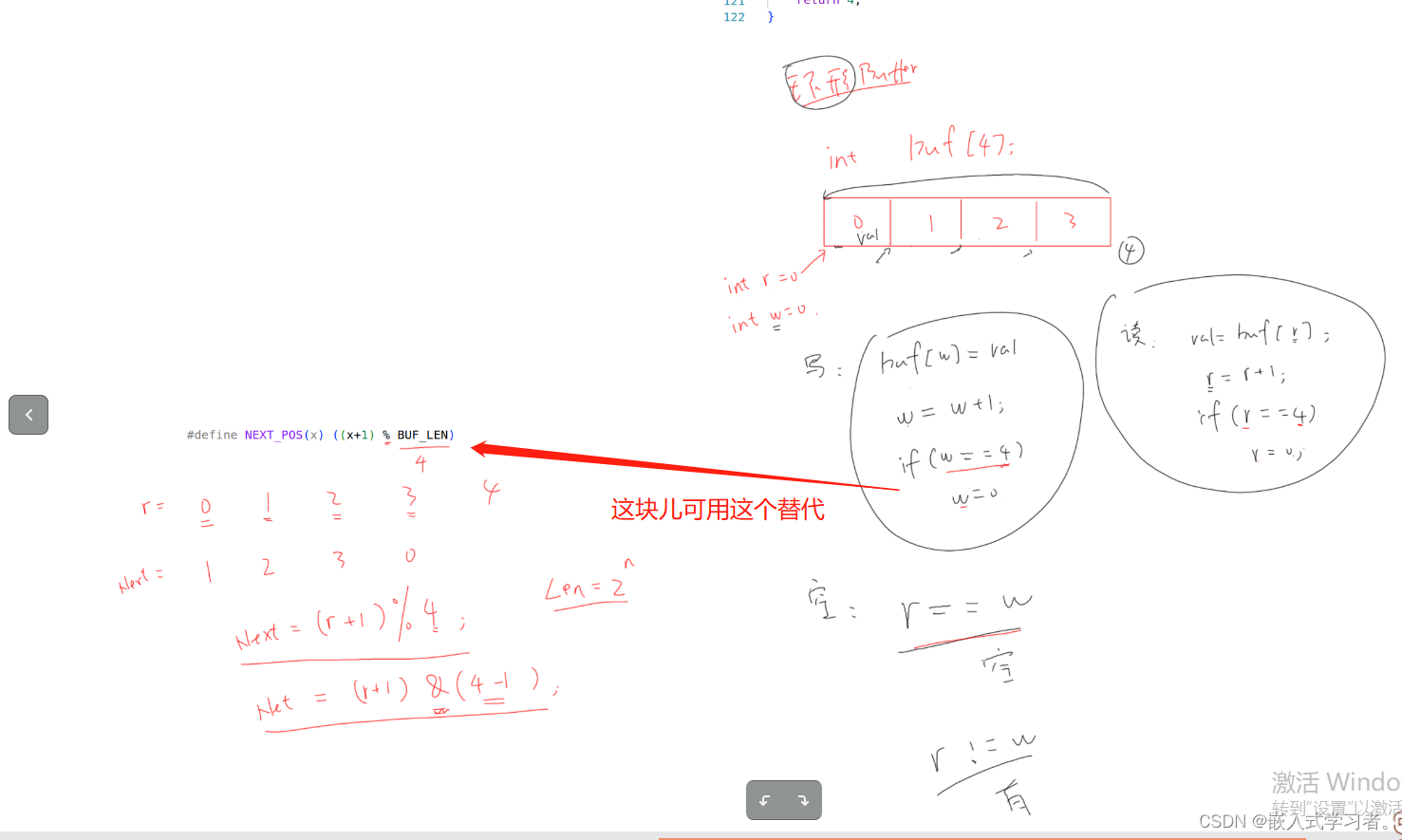
#define BUF_LEN 128
static int g_keys[BUF_LEN];
static int r, w;
struct fasync_struct *button_fasync;
#define NEXT_POS(x) ((x+1) % BUF_LEN)
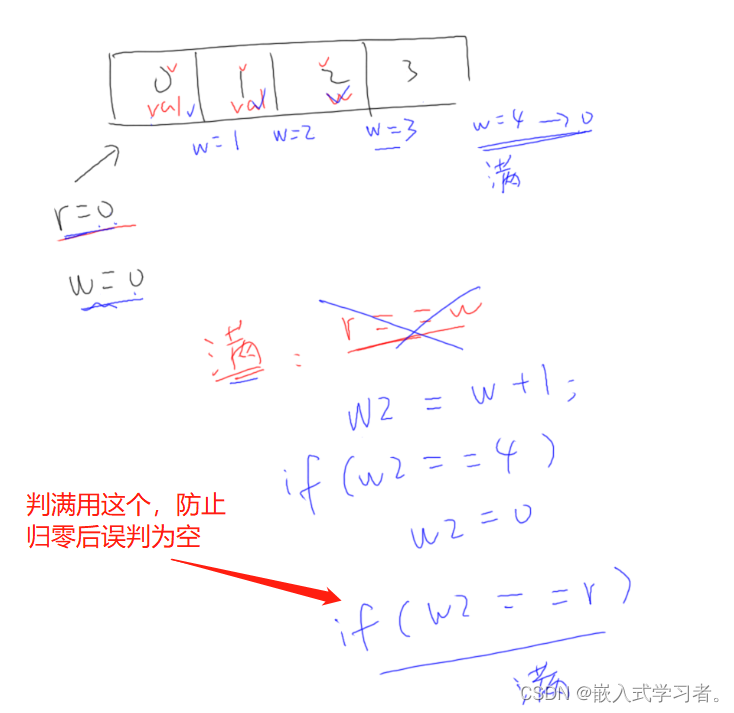
static int is_key_buf_empty(void)
{
return (r == w);
}
static int is_key_buf_full(void)
{
return (r == NEXT_POS(w));
}
static void put_key(int key)
{
if (!is_key_buf_full())
{
g_keys[w] = key;
w = NEXT_POS(w);
}
}
static int get_key(void)
{
int key = 0;
if (!is_key_buf_empty())
{
key = g_keys[r];
r = NEXT_POS(r);
}
return key;
}
static DECLARE_WAIT_QUEUE_HEAD(gpio_wait);
// static void key_timer_expire(struct timer_list *t)
static void key_timer_expire(unsigned long data)
{
/* data ==> gpio */
// struct gpio_desc *gpio_desc = from_timer(gpio_desc, t, key_timer);
struct gpio_desc *gpio_desc = (struct gpio_desc *)data;
int val;
int key;
val = gpio_get_value(gpio_desc->gpio); //读取引脚 0或1
//printk("key_timer_expire key %d %d\n", gpio_desc->gpio, val);
key = (gpio_desc->key) | (val<<8); //key值用来放在环形数组中,用key第八位看按键是否按下
put_key(key);//放入环形数组
wake_up_interruptible(&gpio_wait);
kill_fasync(&button_fasync, SIGIO, POLL_IN);
}
/* 实现对应的open/read/write等函数,填入file_operations结构体 */
static ssize_t gpio_drv_read (struct file *file, char __user *buf, size_t size, loff_t *offset)
{
//printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
int err;
int key;
if (is_key_buf_empty() && (file->f_flags & O_NONBLOCK))
return -EAGAIN;
wait_event_interruptible(gpio_wait,!is_key_buf_empty());
key = get_key();
err = copy_to_user(buf, &key, 4);
return 4;
}
static ssize_t gpio_drv_write(struct file *file, const char __user *buf, size_t size, loff_t *offset)
{
unsigned char ker_buf[2];
int err;
if (size != 2)
return -EINVAL;
err = copy_from_user(ker_buf, buf, size);
if (ker_buf[0] >= sizeof(gpios)/sizeof(gpios[0]))
return -EINVAL;
gpio_set_value(gpios[ker_buf[0]].gpio, ker_buf[1]);
return 2;
}
static unsigned int gpio_drv_poll(struct file *fp, poll_table * wait)
{
//printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
poll_wait(fp, &gpio_wait, wait);
return is_key_buf_empty() ? 0 : POLLIN | POLLRDNORM;
}
static int gpio_drv_fasync(int fd, struct file *file, int on)
{
if (fasync_helper(fd, file, on, &button_fasync) >= 0)
return 0;
else
return -EIO;
}
/* 定义自己的file_operations结构体 */
static struct file_operations gpio_key_drv = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.read = gpio_drv_read,
.write = gpio_drv_write,
.poll = gpio_drv_poll,
.fasync = gpio_drv_fasync,
};
static irqreturn_t gpio_key_isr(int irq, void *dev_id)
{
struct gpio_desc *gpio_desc = dev_id;
printk("gpio_key_isr key %d irq happened\n", gpio_desc->gpio);
//jiffies是全局变量
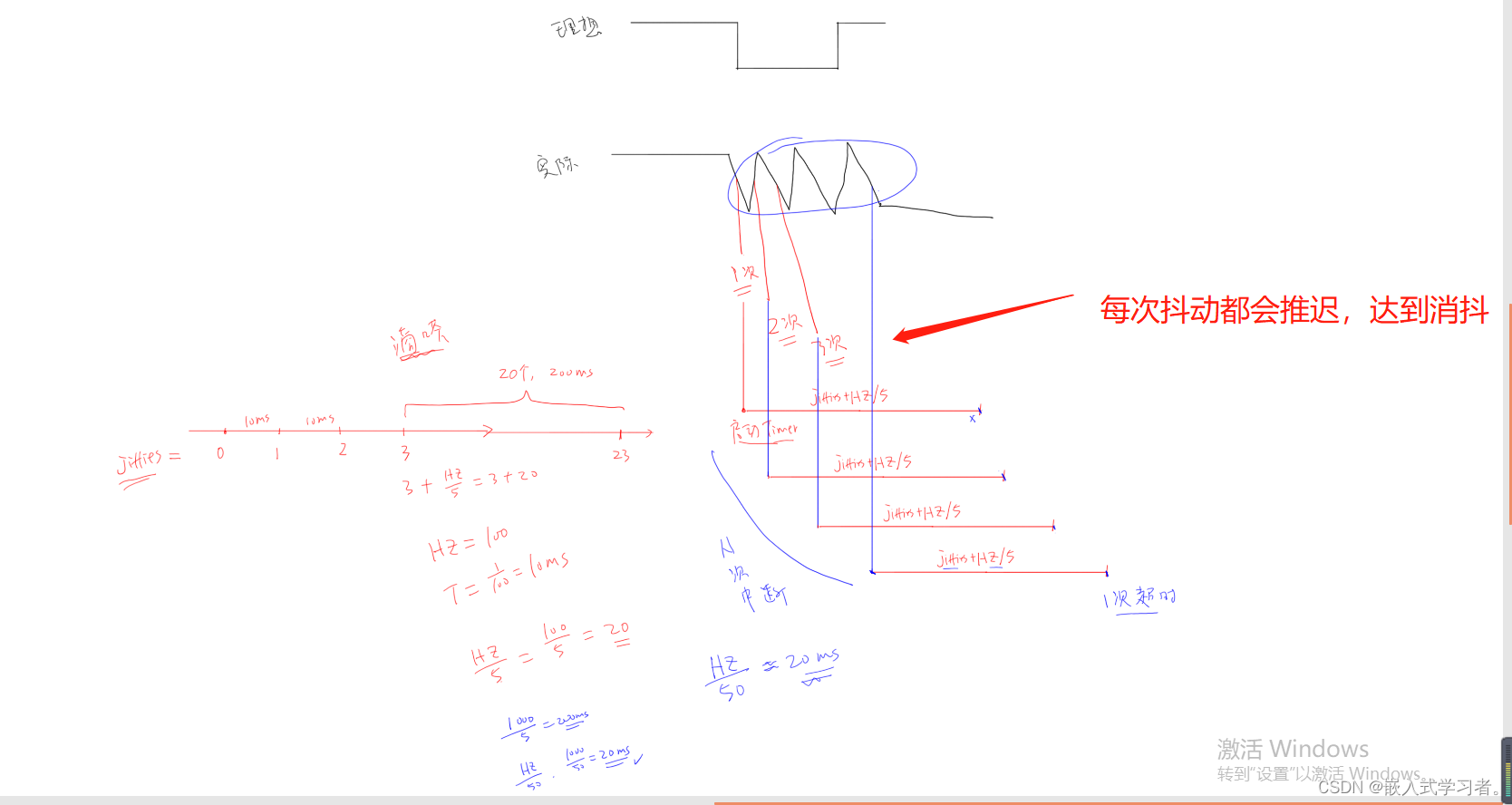
mod_timer(&gpio_desc->key_timer, jiffies + HZ/5); //消抖,每次抖动时长小于(HZ/5)*Tms,都会推迟进入中断服务程序
return IRQ_HANDLED;
}
/* 在入口函数 */
static int __init gpio_drv_init(void)
{
int err;
int i;
int count = sizeof(gpios)/sizeof(gpios[0]);
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
for (i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
gpios[i].irq = gpio_to_irq(gpios[i].gpio); //调用函数获得中断号
//定时器初始化函数 参数一:定时器时间 参数二:中断服务程序 参数三:传入中断服务程序的参数
setup_timer(&gpios[i].key_timer, key_timer_expire, (unsigned long)&gpios[i]);
//timer_setup(&gpios[i].key_timer, key_timer_expire, 0);
gpios[i].key_timer.expires = ~0;
add_timer(&gpios[i].key_timer);
err = request_irq(gpios[i].irq, gpio_key_isr, IRQF_TRIGGER_RISING | IRQF_TRIGGER_FALLING, "100ask_gpio_key", &gpios[i]); //注册中断
}
/* 注册file_operations */
major = register_chrdev(0, "100ask_gpio_key", &gpio_key_drv); /* /dev/gpio_desc */
gpio_class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "100ask_gpio_key_class");
if (IS_ERR(gpio_class)) {
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
unregister_chrdev(major, "100ask_gpio_key");
return PTR_ERR(gpio_class);
}
device_create(gpio_class, NULL, MKDEV(major, 0), NULL, "100ask_gpio"); /* /dev/100ask_gpio */
return err;
}
/* 有入口函数就应该有出口函数:卸载驱动程序时,就会去调用这个出口函数
*/
static void __exit gpio_drv_exit(void)
{
int i;
int count = sizeof(gpios)/sizeof(gpios[0]);
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
device_destroy(gpio_class, MKDEV(major, 0));
class_destroy(gpio_class);
unregister_chrdev(major, "100ask_gpio_key");
for (i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
free_irq(gpios[i].irq, &gpios[i]);
del_timer(&gpios[i].key_timer);
}
}
/* 7. 其他完善:提供设备信息,自动创建设备节点 */
module_init(gpio_drv_init);
module_exit(gpio_drv_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
app
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <poll.h>
#include <signal.h>
static int fd;
/*
* ./button_test /dev/100ask_button0
*
*/
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int val;
struct pollfd fds[1];
int timeout_ms = 5000;
int ret;
int flags;
int i;
/* 1. 判断参数 */
if (argc != 2)
{
printf("Usage: %s <dev>\n", argv[0]);
return -1;
}
/* 2. 打开文件 */
fd = open(argv[1], O_RDWR | O_NONBLOCK);
if (fd == -1)
{
printf("can not open file %s\n", argv[1]);
return -1;
}
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
if (read(fd, &val, 4) == 4)
printf("get button: 0x%x\n", val);
else
printf("get button: -1\n");
}
flags = fcntl(fd, F_GETFL);
fcntl(fd, F_SETFL, flags & ~O_NONBLOCK);
while(1)
{
if (read(fd, &val, 4) == 4)
printf("get button: 0x%x\n", val);
else
printf("while get button: -1\n");
}
close(fd);
return 0;
}