📫作者简介:zhz小白
公众号:小白的Java进阶之路
专业技能:
1、Java基础,并精通多线程的开发,熟悉JVM原理
2、熟悉Java基础,并精通多线程的开发,熟悉JVM原理,具备⼀定的线上调优经验
3、熟悉MySQL数据库调优,索引原理等,⽇志原理等,并且有出过⼀篇专栏
4、了解计算机⽹络,对TCP协议,滑动窗⼝原理等有⼀定了解
5、熟悉Spring,Spring MVC,Mybatis,阅读过部分Spring源码
6、熟悉SpringCloud Alibaba体系,阅读过Nacos,Sentinel,Seata,Dubbo,Feign,Gateway核⼼源码与设计,⼆次开发能⼒
7、熟悉消息队列(Kafka,RocketMQ)的原理与设计
8、熟悉分库分表ShardingSphere,具有真实⽣产的数据迁移经验
9、熟悉分布式缓存中间件Redis,对其的核⼼数据结构,部署架构,⾼并发问题解决⽅案有⼀定的积累
10、熟悉常⽤设计模式,并运⽤于实践⼯作中
11、了解ElasticSearch,对其核⼼的原理有⼀定的了解
12、了解K8s,Jekins,GitLab
13、了解VUE,GO
14、⽬前有正在利⽤闲暇时间做互游游戏,开发、运维、运营、推销等
本人著作git项目:https://gitee.com/zhouzhz/star-jersey-platform,有兴趣的可以私聊博主一起编写,或者给颗star
领域:对支付(FMS,FUND,PAY),订单(OMS),出行行业等有相关的开发领域
🔥如果此文还不错的话,还请👍关注、点赞、收藏三连支持👍一下博主~
文章目录
- 1、@PostConstruct
- 1.1、源码分析
- 2、@PreDestroy
- 2.1、源码分析
- 3、使用
- 3.1、创建对象
- 3.2、创建配置类
- 3.3、测试类
- 3.4、运行结果
在之前的文章中,我们介绍了如何使用@Bean注解指定初始化和销毁的方法,也介绍了使用InitializingBean和DisposableBean来处理bean的初始化和销毁。除此之外,在JDK中还提供了两个注解能够在bean创建完成并且属性赋值完成之后执行一些初始化工作和在容器销毁bean之前通知我们进行一些清理工作。今天,我们就一起来看看这两个注解的用法。
1、@PostConstruct
1.1、源码分析
首先我们看一下@PostConstruct注解他是Java原生的,并不是Spring的,让我们看一下其源码,代码如下所示
/*
* Copyright (c) 2005, 2013, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
* ORACLE PROPRIETARY/CONFIDENTIAL. Use is subject to license terms.
*/
package javax.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
import static java.lang.annotation.ElementType.*;
import static java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy.*;
/**
* The PostConstruct annotation is used on a method that needs to be executed
* after dependency injection is done to perform any initialization. This
* method MUST be invoked before the class is put into service. This
* annotation MUST be supported on all classes that support dependency
* injection. The method annotated with PostConstruct MUST be invoked even
* if the class does not request any resources to be injected. Only one
* method can be annotated with this annotation. The method on which the
* PostConstruct annotation is applied MUST fulfill all of the following
* criteria:
* <p>
* <ul>
* <li>The method MUST NOT have any parameters except in the case of
* interceptors in which case it takes an InvocationContext object as
* defined by the Interceptors specification.</li>
* <li>The method defined on an interceptor class MUST HAVE one of the
* following signatures:
* <p>
* void <METHOD>(InvocationContext)
* <p>
* Object <METHOD>(InvocationContext) throws Exception
* <p>
* <i>Note: A PostConstruct interceptor method must not throw application
* exceptions, but it may be declared to throw checked exceptions including
* the java.lang.Exception if the same interceptor method interposes on
* business or timeout methods in addition to lifecycle events. If a
* PostConstruct interceptor method returns a value, it is ignored by
* the container.</i>
* </li>
* <li>The method defined on a non-interceptor class MUST HAVE the
* following signature:
* <p>
* void <METHOD>()
* </li>
* <li>The method on which PostConstruct is applied MAY be public, protected,
* package private or private.</li>
* <li>The method MUST NOT be static except for the application client.</li>
* <li>The method MAY be final.</li>
* <li>If the method throws an unchecked exception the class MUST NOT be put into
* service except in the case of EJBs where the EJB can handle exceptions and
* even recover from them.</li></ul>
* @since Common Annotations 1.0
* @see javax.annotation.PreDestroy
* @see javax.annotation.Resource
*/
@Documented
@Retention (RUNTIME)
@Target(METHOD)
public @interface PostConstruct {
}
- @PostConstruct是Java中的注解,不是Spring的注解。
- @PostConstruct注解被用来修饰一个非静态的void()方法。被@PostConstruct注解修饰的方法会在服务器加载Servlet的时候运行,并且只会被服务器执行一次。被@PostConstruct注解修饰的方法通常在构造函数之后,init()方法之前执行。
- 通常我们是会在Spring框架中使用到@PostConstruct注解的,该注解的方法在整个bean初始化中的执行顺序如下:
- Constructor(构造方法)→@Autowired(依赖注入)→@PostConstruct(注释的方法)
2、@PreDestroy
2.1、源码分析
@PreDestroy注解也并不是Spring的注解,也是Java提供的注解,只不过Spring内部会兼容。我们来看一下其源码:
/*
* Copyright (c) 2005, 2013, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
* ORACLE PROPRIETARY/CONFIDENTIAL. Use is subject to license terms.
*/
package javax.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
import static java.lang.annotation.ElementType.*;
import static java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy.*;
/**
* The PreDestroy annotation is used on methods as a callback notification to
* signal that the instance is in the process of being removed by the
* container. The method annotated with PreDestroy is typically used to
* release resources that it has been holding. This annotation MUST be
* supported by all container managed objects that support PostConstruct
* except the application client container in Java EE 5. The method on which
* the PreDestroy annotation is applied MUST fulfill all of the following
* criteria:
* <p>
* <ul>
* <li>The method MUST NOT have any parameters except in the case of
* interceptors in which case it takes an InvocationContext object as
* defined by the Interceptors specification.</li>
* <li>The method defined on an interceptor class MUST HAVE one of the
* following signatures:
* <p>
* void <METHOD>(InvocationContext)
* <p>
* Object <METHOD>(InvocationContext) throws Exception
* <p>
* <i>Note: A PreDestroy interceptor method must not throw application
* exceptions, but it may be declared to throw checked exceptions including
* the java.lang.Exception if the same interceptor method interposes on
* business or timeout methods in addition to lifecycle events. If a
* PreDestroy interceptor method returns a value, it is ignored by
* the container.</i>
* </li>
* <li>The method defined on a non-interceptor class MUST HAVE the
* following signature:
* <p>
* void <METHOD>()
* </li>
* <li>The method on which PreDestroy is applied MAY be public, protected,
* package private or private.</li>
* <li>The method MUST NOT be static.</li>
* <li>The method MAY be final.</li>
* <li>If the method throws an unchecked exception it is ignored except in the
* case of EJBs where the EJB can handle exceptions.</li>
* </ul>
*
* @see javax.annotation.PostConstruct
* @see javax.annotation.Resource
* @since Common Annotations 1.0
*/
@Documented
@Retention (RUNTIME)
@Target(METHOD)
public @interface PreDestroy {
}
- 被@PreDestroy注解修饰的方法会在服务器卸载Servlet的时候运行,并且只会被服务器调用一次,类似于Servlet的destroy()方法。被@PreDestroy注解修饰的方法会在destroy()方法之后,Servlet被彻底卸载之前执行。执行顺序如下所示:
- 调用destroy()方法→@PreDestroy→destroy()方法→bean销毁
3、使用
3.1、创建对象
package com.zhz.bean;
import lombok.Data;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.DisposableBean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
import javax.annotation.PreDestroy;
/**
* @author zhouhengzhe
* @date 2022/11/23
*/
public class PostPerson implements InitializingBean, DisposableBean {
// 在对象创建完成并且属性赋值完成之后调用
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
System.out.println("构造之后");
}
// 在容器销毁(移除)对象之前调用
@PreDestroy
public void preDestroy() {
System.out.println("销毁之前");
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("属性赋值");
}
@Override
public void destroy() throws Exception {
System.out.println("销毁");
}
}
3.2、创建配置类
package com.zhz.config;
import com.zhz.bean.Person;
import com.zhz.bean.PostPerson;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Scope;
/**
* 生命周期相关配置
* @author zhouhengzhe
* @date 2022/11/21
*/
@Configuration
public class MainConfigByLifeCycle {
@Bean
public PostPerson personPerson() {
return new PostPerson();
}
}
3.3、测试类
@Test
public void test4ByPostConstruct(){
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfigByLifeCycle.class);
System.out.println("容器创建完成");
PostPerson postPerson = applicationContext.getBean(PostPerson.class);
applicationContext.close();
}
3.4、运行结果
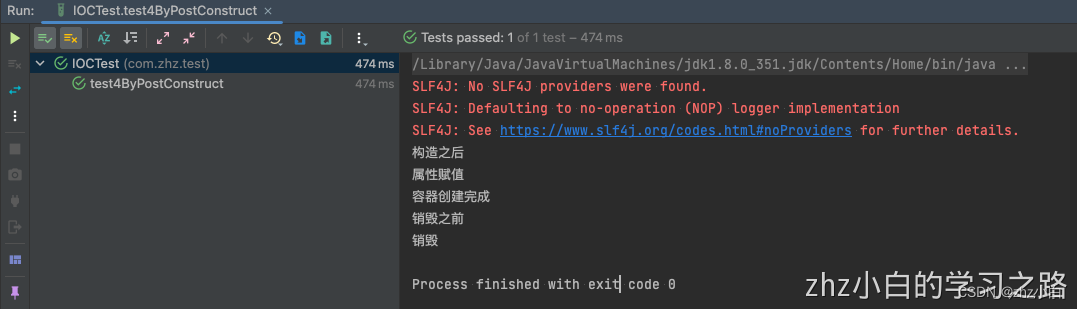
我们可以看出:
- 被@PostConstruct注解修饰的方法是在bean创建完成并且属性赋值完成之后才执行的,
- 而被@PreDestroy注解修饰的方法是在容器销毁bean之前执行的,通常是进行一些清理工作。




![[BUG] runtime network not ready: NetworkReady=false reason:NetworkPluginNotRead](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/40fececd7a70482b9aed3bc95ef33265.png)