🍒🍒🍒欢迎关注🌈🌈🌈
📝个人主页:我爱Matlab
👍点赞➕评论➕收藏 == 养成习惯(一键三连)🌻🌻🌻🍌希望大家多多支持🍓~一起加油 🤗
💬语录:将来的我一定会感谢现在奋斗的自己!
🍁🥬🕒摘要🕒🥬🍁
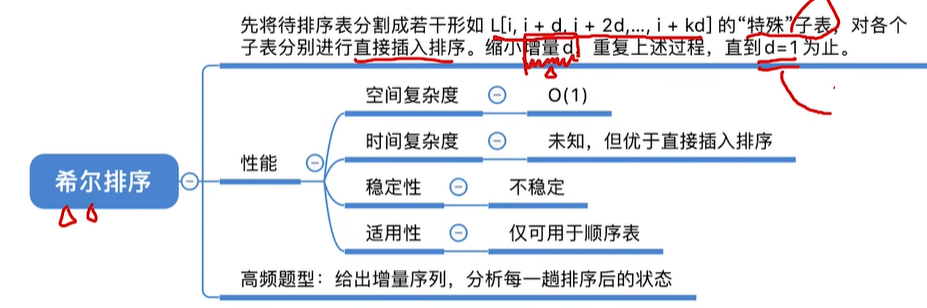
现代战争对雷达目标识别提出了更高的要求,由于现役雷达大部分是低分辨雷达,对其开展目标识别技术的研究具有重要军事意义。在小样本、样本不均衡等复杂电磁环境条件下,传统低分辨雷达目标识别方法存在泛化性较差、识别率较低等问题。本文围绕深度学习方法对低分辨雷达目标识别技术开展研究,主要研究内容如下:传统低分辨雷达目标识别技术采用先提取信号特征,再基于特征进行识别的两步识别方法。
✨🔎⚡运行结果⚡🔎✨
FFT 操作
- 在混合信号上实现一维FFT
- 将向量重塑为 Nr*Nd 数组。
- 沿量程箱尺寸 (Nr) 对节拍信号运行 FFT
- 规范化 FFT 输出。
- 取该输出的绝对值。
- 保留一半的信号
- 绘制输出
- 目标初始位置应有一个峰值
- 结果如下:

- 第二个FFT将生成一个范围多普勒图,如下图所示,它将由变量“RDM”给出。
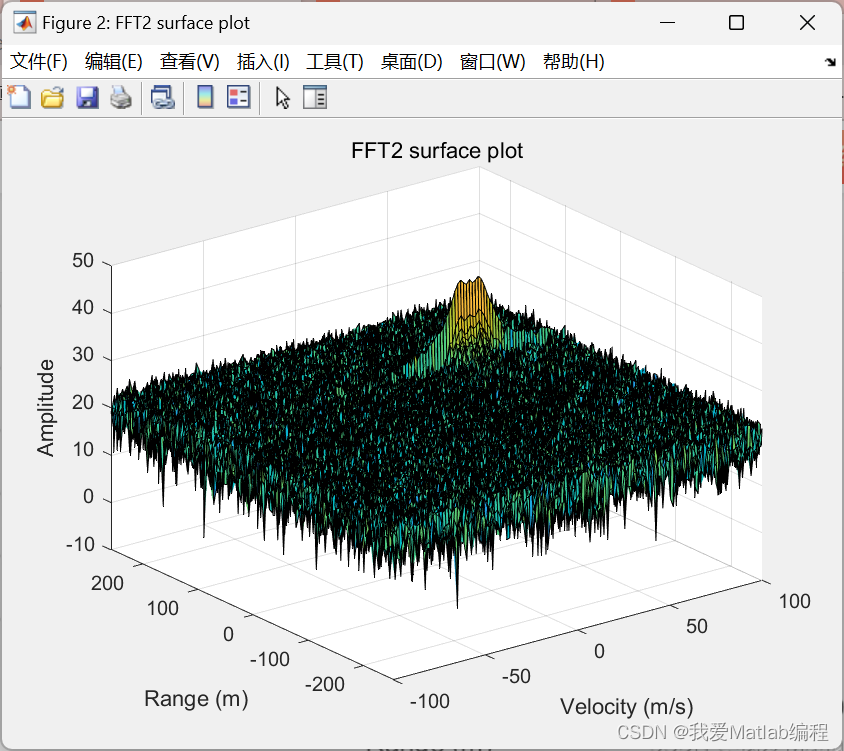
- 第二个FFT将生成一个范围多普勒图,如下图所示,它将由变量“RDM”给出
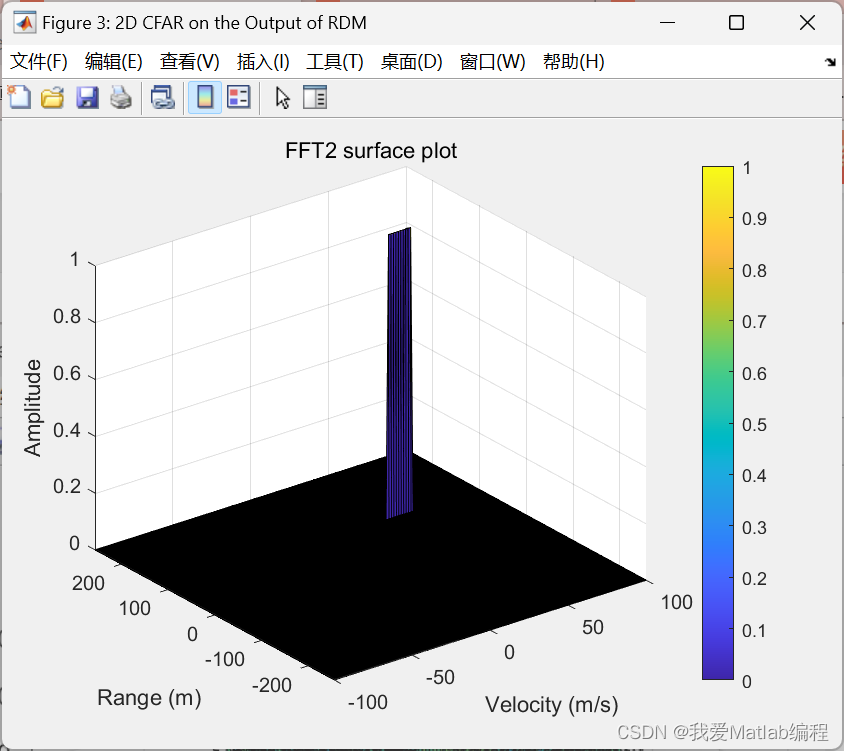
-
最后,对第二个FFT的输出执行CFAR处理以显示目标。
-
2D CFAR处理应该能够抑制噪声并分离 目标信号。输出应与演练中共享的图像匹配。
-
确定每个维度的训练单元数。同样,选择保护单元的数量。
-
在整个矩阵上滑动被测单元格。确保 CUT 从边缘留出训练和守卫单元的余量。
-
对于每次迭代,对所有训练单元内的信号电平求和。求和 使用 db2pow 函数将值从对数转换为线性。
-
平均使用的所有训练单元的总和值。平均后,使用 pow2db 将其转换回对数。
-
进一步添加偏移量以确定阈值。
-
接下来,将 CUT 下的信号与此阈值进行比较。
-
如果 CUT 级别>阈值为其分配值 1,否则将其等同于 0。
-
上述过程将生成一个阈值块,该块小于距离多普勒图,因为由于存在目标和防护单元,CUT不能位于矩阵的边缘。因此,这些单元格不会被阈值化。
-
要使映射大小与 CFAR 之前相同,请将所有非阈值像元等同于 0。
💂♨️👨🎓Matlab代码👨🎓♨️💂
clear;
close all;
clc;
%% Radar Specifications
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
% Frequency of operation = 77GHz
% Max Range = 200m
% Range Resolution = 1 m
% Max Velocity = 100 m/s
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
% Declare the variables
Range_max = 200; % in meters
Range_resolution = 1; % in meters
Velocity_max = 100; % in m/s
c = 3e8; %speed of light
%speed of light = 3e8
%% User Defined Range and Velocity of target
% *%TODO* :
% define the target's initial position and velocity. Note : Velocity
% remains contant
Target_range = 100; % in meters
Target_velocity = 50; % in m/s
%% FMCW Waveform Generation
% *%TODO* :
%Design the FMCW waveform by giving the specs of each of its parameters.
% Calculate the Bandwidth (B), Chirp Time (Tchirp) and Slope (slope) of the FMCW
% chirp using the requirements above.
%To calculate Bandwidth
B = c / (2 * Range_resolution);
%To find the chirp time
%Sweep time has to ben knowsn and it should be around 5 -6 times the round trip time
Tsweep = 5.5;
Tchirp = Tsweep * (2 * Range_max / c) ;
%To find slope of FMCW
slope = B / Tchirp;
%Operating carrier frequency of Radar
fc= 77e9; %carrier freq
%The number of chirps in one sequence. Its ideal to have 2^ value for the ease of running the FFT
%for Doppler Estimation.
Nd=128; % #of doppler cells OR #of sent periods % number of chirps
%The number of samples on each chirp.
Nr=1024; %for length of time OR # of range cells
% Timestamp for running the displacement scenario for every sample on each
% chirp
t=linspace(0,Nd*Tchirp,Nr*Nd); %total time for samples
%Creating the vectors for Tx, Rx and Mix based on the total samples input.
Tx=zeros(1,length(t)); %transmitted signal
Rx=zeros(1,length(t)); %received signal
Mix = zeros(1,length(t)); %beat signal
%Similar vectors for range_covered and time delay.
r_t=zeros(1,length(t));
td=zeros(1,length(t));
[1]易重辉. 基于深度学习的低空监视雷达目标检测的研究[D].四川大学,2021.DOI:10.27342/d.cnki.gscdu.2021.000528.