导入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.thymeleaf</groupId>
<artifactId>thymeleaf</artifactId>
<version>3.0.11.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.thymeleaf</groupId>
<artifactId>thymeleaf-spring5</artifactId>
<version>3.0.11.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
yml配置
thymeleaf:
mode: HTML #thymeleaf 的模板模型
cache: false #不适用缓存
encoding: UTF-8 #编码
prefix: classpath:/templates/ #前缀
suffix: .html #后面
html

@Controller
public class HelloController {
@Autowired
private UserDao userDao;
@RequestMapping("/test")
public String hello(Map map){
System.out.println("进来了");
List<User> users = userDao.getAll();
map.put("users",users);
System.out.println(users);
return "hello";
}
@RequestMapping("/delete")
public String delete(Integer id){
System.out.println(id);
Integer a=userDao.delete(id);
return "forward:/test";
}
@RequestMapping("/toUpdate")
public String getOne(Integer id,Map map){
System.out.println(id);
User user=userDao.getOne(id);
map.put("user",user);
return "one";
}
@RequestMapping("/toAdd")
public String toAdd(){
return "add";
}
}必须加入 <html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Hello</h1>
<table cellspacing="0" border="1">
<tr>
<th>ID</th>
<th>NAME</th>
<th>AGE</th>
<th>GENDER</th>
<th>BIRTHDAY</th>
<th>OPERA</th>
</tr>
<tr th:each="user:${users}">
<td th:text="${user.id}"></td>
<td th:text="${user.name}"></td>
<td th:text="${user.age}"></td>
<td th:text="${user.gender}"></td>
<td th:text="${#dates.format(user.birthday,'yyyy-MM-dd')}"></td>
<td><a th:href="@{/delete(id=${user.id})}">删除</a><a th:href="@{/toUpdate(id=${user.id})}">编辑</a></td>
</tr>
</table>
<a th:href="@{/toAdd}">去添加</a>
</body>
</html><!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<form th:action="@{/add}" method="post" >
<input name="id" placeholder="请输入id"><br/>
<input name="name" placeholder="请输入姓名"><br/>
<input name="age" placeholder="请输入年龄"><br/>
<input name="gender" placeholder="请输入性别" ><br/>
<input type="submit" value="添加">
</form>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- <form th:action="@{/update}" method="post" >
<input name="id" th:value="${user.id}" value="aa"><br/>
<input name="name" th:value="${user.name}"><br/>
<input name="age" th:value="${user.age}"><br/>
<input name="gender" th:value="${user.gender}"><br/>
<input type="submit" value="修改">
</form>-->
<form th:action="@{/update}" th:object="${user}" method="post" >
<input name="id" th:value="*{id}" value="aa"><br/>
<input name="name" th:value="*{name}"><br/>
<input name="age" th:value="*{age}"><br/>
<input name="gender" th:value="*{gender}"><br/>
<input type="submit" value="修改">
</form>
</body>
</html>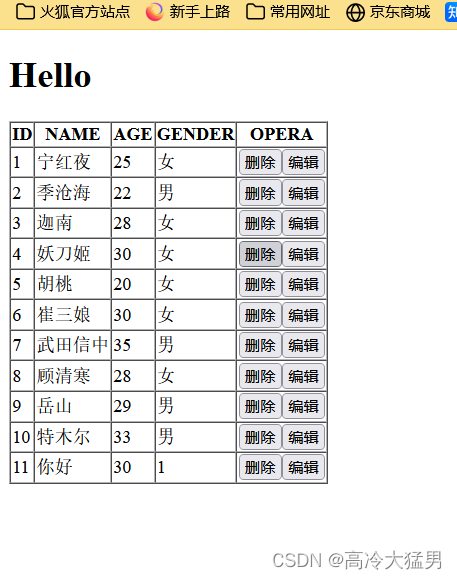
Thymeleaf模板
4.1 th 属性4.1.1 常用 th 属性解读html 有的属性, Thymeleaf 基本都有,而常用的属性大概有七八个。其中 th 属性执行的优先级从 1~8 ,数字越低优先级越高。一、 th:text :设置当前元素的文本内容,相同功能的还有 th:utext ,两者的区别在于前者不会转义 html 标签,后者会。优先级不高: order=7二、 th:value :设置当前元素的 value 值,类似修改指定属性的还有 th:src , th:href 。优先级不高: order=6三、 th:each :遍历循环元素,和 th:text 或 th:value 一起使用。注意该属性修饰的标签位置,详细往后看。优先级很高: order=2四、 th:if :条件判断,类似的还有 th:unless , th:switch , th:case 。优先级较高: order=3五、 th:insert :代码块引入,类似的还有 th:replace , th:include ,三者的区别较大,若使用不恰当会破坏 html 结构,常用于公共代码块提取的场景。优先级最高: order=1六、 th:fragment :定义代码块,方便被 th:insert 引用。优先级最低: order=8七、 th:object :声明变量,一般和 *{} 一起配合使用,达到偷懒的效果。优先级一般: order=4八、 th:attr :修改任意属性,实际开发中用的较少,因为有丰富的其他 th 属性帮忙,类似的还有 th:attrappend ,th:attrprepend 。优先级一般: order=54.1.2 常用 th 属性使用使用 Thymeleaf 属性需要注意点以下五点:一、若要使用 Thymeleaf 语法,首先要声明名称空间:xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"二、设置文本内容 th:text ,设置 input 的值 th:value ,循环输出 th:each ,条件判断 th:if ,插入代码块 th:insert ,定义代码块 th:fragment ,声明变量 th:object三、 th:each 的用法需要格外注意,打个比方:如果你要循环一个 div 中的 p 标签,则 th:each 属性必须放在 p 标签上。若你将 th:each 属性放在 div 上,则循环的是将整个 div 。四、变量表达式中提供了很多的内置方法,该内置方法是用 # 开头,请不要与 #{} 消息表达式弄混。五、 th:insert , th:replace , th:include 三种插入代码块的效果相似,但区别很大。pom.xml 引入 Thymeleaf 的依赖,并确定其版本
链接表达式好处不管是静态资源的引用, form 表单的请求,凡是链接都可以用 @{...} 。这样可以动态获取项目路径,即便项目名变了,依然可以正常访问链接表达式结构无参: @{/xxx}有参: @{/xxx(k1=v1,k2=v2)} 对应 url 结构: xxx?k1=v1&k2=v2引入本地资源: @{/ 项目本地的资源路径 }引入外部资源: @{/webjars/ 资源在 jar 包中的路径 }列举:第三部分的实战引用会详细使用该表达式









![[LeetCode周赛复盘] 第 92 场双周赛20221015](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/fe90b8cf343c48c7a75815560d3be358.png)