七、队列
常用于辅助遍历树,设计队列先进先出特性的数据结构
7.1 滑动窗口的平均值
给定一个整数数据流和一个窗口大小,根据该滑动窗口的大小,计算滑动窗口里所有数字的平均值。
实现 MovingAverage 类:
-
MovingAverage(int size) 用窗口大小 size 初始化对象。
-
double next(int val) 成员函数 next 每次调用的时候都会往滑动窗口增加一个整数,请计算并返回数据流中最后 size 个值的移动平均值,即滑动窗口里所有数字的平均值。
示例:
输入:
inputs = [“MovingAverage”, “next”, “next”, “next”, “next”]
inputs = [[3], [1], [10], [3], [5]]
输出:
[null, 1.0, 5.5, 4.66667, 6.0]
解释:
- MovingAverage movingAverage = new MovingAverage(3);
- movingAverage.next(1); // 返回 1.0 = 1 / 1
- movingAverage.next(10); // 返回 5.5 = (1 + 10) / 2
- movingAverage.next(3); // 返回 4.66667 = (1 + 10 + 3) / 3
- movingAverage.next(5); // 返回 6.0 = (10 + 3 + 5) / 3
提示:
1 <= size <= 1000-105 <= val <= 105- 最多调用
next方法104次
思路: 使用队列 定义一个size表示队列最大元素个数,如果在添加元素时,队列元素个数等于size,就出队一个元素,再添加。维护一个sum,记录队列中元素和
注意点: sum最好直接定义为浮点类型
class MovingAverage {
Queue<Integer> queue;
int size;
double sum;
/**
* Initialize your data structure here.
*/
public MovingAverage(int size) {
queue = new LinkedList<>();
this.size = size;
sum = 0.0;
}
public double next(int val) {
if(queue.size() == size){
sum = sum - queue.poll();
}
queue.offer(val);
sum += val;
return sum / queue.size();
}
}
7.2 最近请求次数
原题链接
写一个 RecentCounter 类来计算特定时间范围内最近的请求。
请实现 RecentCounter 类:
-
RecentCounter()初始化计数器,请求数为 0 。 -
int ping(int t)在时间 t 添加一个新请求,其中 t 表示以毫秒为单位的某个时间,并返回过去 3000 毫秒内发生的所有请求数(包括新请求)。确切地说,返回在[t-3000, t]内发生的请求数。
保证 每次对 ping 的调用都使用比之前更大的 t 值。
示例:
输入:
inputs = [“RecentCounter”, “ping”, “ping”, “ping”, “ping”]
inputs = [[], [1], [100], [3001], [3002]]
输出:
[null, 1, 2, 3, 3]
解释:
RecentCounter recentCounter = new RecentCounter();recentCounter.ping(1);// requests = [1],范围是 [-2999,1],返回 1recentCounter.ping(100);// requests = [1, 100],范围是 [-2900,100],返回 2recentCounter.ping(3001);// requests = [1, 100, 3001],范围是 [1,3001],返回 3recentCounter.ping(3002);// requests = [1, 100, 3001, 3002],范围是 [2,3002],返回 3
提示:
1 <= t <= 109- 保证每次对
ping调用所使用的t值都 严格递增 - 至多调用
ping方法104次
思路: 使用队列数据结构,在ping时先将不符合的条件的值出队,然后返回队列元素个数即为符合条件的
注意点: 无
class RecentCounter {
Queue<Integer> queue;
public RecentCounter() {
queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
}
public int ping(int t) {
int num = t - 3000;
while(!queue.isEmpty() && queue.peek() < num){
queue.poll();
}
queue.offer(t);
return queue.size();
}
}
7.3往完全二叉树添加结点
完全二叉树是每一层(除最后一层外)都是完全填充(即,节点数达到最大,第 n 层有 2n-1 个节点)的,并且所有的节点都尽可能地集中在左侧。
设计一个用完全二叉树初始化的数据结构 CBTInserter,它支持以下几种操作:
-
CBTInserter(TreeNode root) 使用根节点为 root 的给定树初始化该数据结构;
-
CBTInserter.insert(int v) 向树中插入一个新节点,节点类型为 TreeNode,值为 v 。使树保持完全二叉树的状态,并返回插入的新节点的父节点的值;
-
CBTInserter.get_root() 将返回树的根节点。
示例 1:
-
输入:inputs = [“CBTInserter”,“insert”,“get_root”], inputs = [[[1]],[2],[]]
-
输出:[null,1,[1,2]]
提示:
-
最初给定的树是完全二叉树,且包含 1 到 1000 个节点。
-
每个测试用例最多调用 CBTInserter.insert 操作 10000 次。
-
给定节点或插入节点的每个值都在 0 到 5000 之间。
思路: 通过辅助队列层序遍历,将所有结点放入list集合中。由于完全二叉树的特性,若父节点序号为i,那么子节点序号为 2i,2i+1,因此我们通过list集合size /2 -1 就是父节点下标(下标从0开始需要-1)
注意点:先添加子节点,然后再根据 size /2-1计算父节点下标((2i/2) -1 、 (2i+1/2)-1)
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class CBTInserter {
List<TreeNode> list;
Queue<TreeNode> queue;
public CBTInserter(TreeNode root) {
list = new ArrayList();
queue = new LinkedList();
queue.offer(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
list.add(node);
if(node.left != null){
queue.offer(node.left);
}
if(node.right != null){
queue.offer(node.right);
}
}
}
public int insert(int v) {
TreeNode node = new TreeNode(v);
list.add(node);
// 结点 个数 /2 -1 就是 父节点下标
TreeNode parent= list.get(list.size() / 2 - 1);
if(parent.left == null){
parent.left = node;
}else if(parent.right == null){
parent.right = node;
}
return parent.val;
}
public TreeNode get_root() {
return list.get(0);
}
}
7.4二叉树的右侧视图
原题链接
给定一个二叉树的 根节点 root,想象自己站在它的右侧,按照从顶部到底部的顺序,返回从右侧所能看到的节点值。
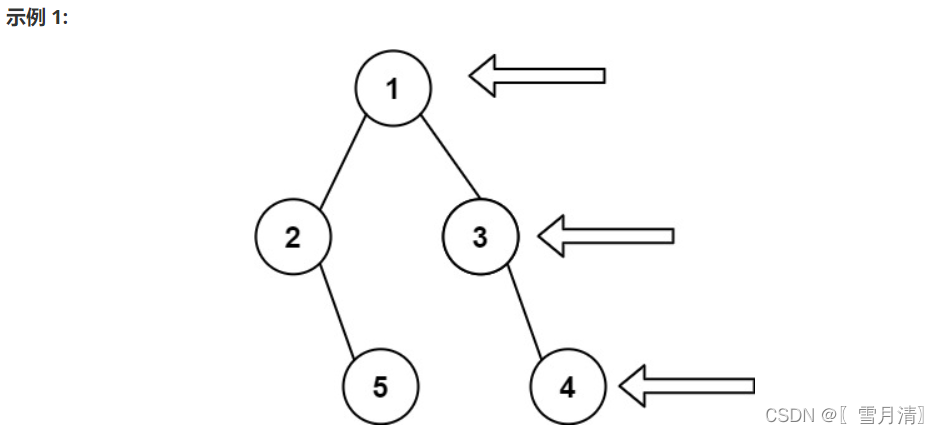
- 输入: [1,2,3,null,5,null,4]
- 输出: [1,3,4]
提示:
- 二叉树的节点个数的范围是
[0,100] -100 <= Node.val <= 100
思路: 层序遍历,每一层的最后一个结点即为所求。使用队列辅助层序遍历,维护一个count记录每层结点的个数,如果为0,就表示当前结点就是每一层最后一个结点,并使用队列长度更细count
注意点: count为每层的结点个数,并非队列中的节点个数,只有当一层遍历结束的时候,count为0才会使用队列长度更新count
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List<Integer> rightSideView(TreeNode root) {
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList();
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList();
if(root == null) return list;
int count = 1;
queue.add(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()){
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
count--;
if(node.left != null){
queue.offer(node.left);
}
if(node.right != null){
queue.offer(node.right);
}
if(count == 0){
// 遍历完一层 更新count 并记录最后一个结点
list.add(node.val);
count = queue.size();
}
}
return list;
}
}
7.5二叉树每层的最大值
给定一棵二叉树的根节点 root ,请找出该二叉树中每一层的最大值。
示例1:
-
输入: root = [1,3,2,5,3,null,9]
-
输出: [1,3,9]
-
解释:
1
/ \
3 2
/ \ \
5 3 9
提示:
- 二叉树的节点个数的范围是
[0,104] -231 <= Node.val <= 231 - 1
思路: 二叉树层序遍历,维护一个count记录每层结点个数,遍历每层时,一直更新max,在每层遍历结束,添加max,重置max和count
注意点: max在count为0就是每层遍历结束后要重新置为 最小值
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List<Integer> largestValues(TreeNode root) {
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList();
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList();
if(root == null) return list;
queue.offer(root);
// 表示每层元素
int count = 1;
int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
count--;
max = Math.max(max,node.val);
if(node.left != null){
queue.offer(node.left);
}
if(node.right != null){
queue.offer(node.right);
}
if(count == 0){
// 加入每层最大值
list.add(max);
// 重置 max 和 count
max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
count = queue.size();
}
}
return list;
}
}
7.6二叉树最底层最左边的值
给定一个二叉树的 根节点 root,请找出该二叉树的 最底层 最左边 节点的值。
假设二叉树中至少有一个节点。
示例 1:
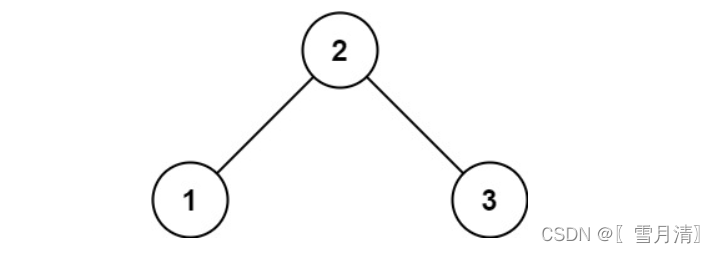
- 输入: root = [2,1,3]
- 输出: 1
提示:
- 二叉树的节点个数的范围是
[1,104] -231 <= Node.val <= 231 - 1
思路: 深度优先遍历,维护一个curHight记录二叉树的最大高度,在dfs的时候计算更新当前遍历的高度hight,如果hight大于curHight说明遍历到了新的一层,此时的结点就是这一层最左边的结点
注意点: 先遍历左节点
class Solution {
int curHight = 0;
int cur = 0;
public int findBottomLeftValue(TreeNode root) {
dfs(root,0);
return cur;
}
void dfs(TreeNode node, int hight){
if(node == null) return;
// 更新高度
hight++;
if(hight > curHight){
curHight = hight;
cur = node.val;
}
dfs(node.left,hight);
dfs(node.right,hight);
}
}