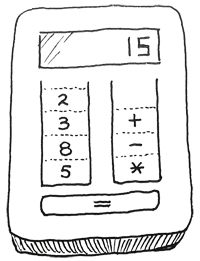
本题要求你为初学数据结构的小伙伴设计一款简单的利用堆栈执行的计算器。如上图所示,计算器由两个堆栈组成,一个堆栈 S1 存放数字,另一个堆栈 S2 存放运算符。计算器的最下方有一个等号键,每次按下这个键,计算器就执行以下操作:
- 从 S1 中弹出两个数字,顺序为 n1 和 n2;
- 从 S2 中弹出一个运算符 op;
- 执行计算 n2 op n1;
- 将得到的结果压回 S1。
直到两个堆栈都为空时,计算结束,最后的结果将显示在屏幕上。
输入格式:
输入首先在第一行给出正整数 N(1<N≤103),为 S1 中数字的个数。
第二行给出 N 个绝对值不超过 100 的整数;第三行给出 N−1 个运算符 —— 这里仅考虑 +、-、*、/ 这四种运算。一行中的数字和符号都以空格分隔。
输出格式:
将输入的数字和运算符按给定顺序分别压入堆栈 S1 和 S2,将执行计算的最后结果输出。注意所有的计算都只取结果的整数部分。题目保证计算的中间和最后结果的绝对值都不超过 109。
如果执行除法时出现分母为零的非法操作,则在一行中输出:ERROR: X/0,其中 X 是当时的分子。然后结束程序。
输入样例 1:
5
40 5 8 3 2
/ * - +
输出样例 1:
2输入样例 2:
5
2 5 8 4 4
* / - +
输出样例 2:
ERROR: 5/0AC代码:
import javax.print.DocFlavor;
import java.io.*;
import java.math.BigInteger;
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
static Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
static BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
static PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out)));
static int N = (int)40;
static Stack<Integer> stack_num = new Stack<>();
static Stack<Character> stack_op = new Stack<>();
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException
{
br.readLine();
String[] s = br.readLine().split(" ");
for(int i = 0; i < s.length ; i ++)
{
int temp = Integer.parseInt(s[i]);
stack_num.push(temp);
}
s = br.readLine().split(" ");
for(int i = 0; i < s.length;i++)
{
char temp = s[i].charAt(0);
stack_op.push(temp);
}
while(stack_op.size() != 0)
{
int n1 = stack_num.pop();
int n2 = stack_num.pop();
char temp = stack_op.pop();
int res = 0;
if(temp == '/')
{
if(n1 == 0)
{
System.out.printf("ERROR: %d/0",n2);
System.exit(0);
}
else res = n2 / n1;
}
else if(temp == '+') res = n2 + n1;
else if(temp == '-') res = n2 - n1;
else res = n2 * n1;
stack_num.push(res);
}
pw.print(stack_num.pop());
pw.flush();
}
}
class rd
{
static BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
static StringTokenizer tokenizer = new StringTokenizer("");
static String nextLine() throws IOException { return reader.readLine(); }
static String next() throws IOException
{
while(!tokenizer.hasMoreTokens()) tokenizer = new StringTokenizer(reader.readLine());
return tokenizer.nextToken();
}
static int nextInt() throws IOException { return Integer.parseInt(next()); }
static double nextDouble() throws IOException { return Double.parseDouble(next()); }
static long nextLong() throws IOException { return Long.parseLong(next()); }
static BigInteger nextBigInteger() throws IOException
{
BigInteger d = new BigInteger(rd.nextLine());
return d;
}
}
class PII
{
int x,y;
public PII(int x, int y)
{
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}








![[数据结构]栈的深入学习-java实现](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/bec4322e33dd46e78ca00edfb2654de6.png)