文章目录
- Qt界面开发必备知识
- UI界面与控件类型介绍
- Qt设计器原理
- 控件类型的介绍
- 信号与槽机制处理
- 常用控件创建与设置
- 常见展示型控件创建与设置
- 常见动作型控件创建与设置
- 常见输入型控件创建与设置
- 常见列表控件创建于设置
- Qt中对象树的介绍
- 项目源码结构刨析
- .pro
- .h
- main.cpp
- .cpp
- Qt界面开发美化处理
- QSS样式设计与修改
- 样式表语法基础
- 衍生语法规则
- 盒模型
- 图片资源导入与设置
- 图片资源导入
- 图片资源设置
- 窗体布局管理器之Ui布局
- 布局方式
- 布局管理器之代码布局
- Qt应用窗口创建之QDialog
- 窗口创建之QMainWindow
- Qt事件处理机制之定时器事件
- Qt事件处理机制之鼠标键盘事件
- 绘图事件与事件传递原理
- 绘图事件
- 事件传递过程与过滤方式
- 动画处理与特性
- 启动画面
- 动画设计与特效处理
- Qt工具与扩展
- 容器类的介绍
- 工具类的介绍
- QString字符串类的介绍
- 音频文件处理与播放
- 视频文件处理与播放
- 图表处理与美化
- 网络通信之TCP
- 网络通信之UDP
- Qt中多线程处理
- 线程处理代码实现方式(一)
- 线程处理代码实现方式(二)
Qt界面开发必备知识
UI界面与控件类型介绍
Qt设计器原理
Qt设计器(UI界面)是用于设计和构建带有Qt Widgets 的图形用户界面(QT GUI)。注意:必须在建立项目时勾选上.ui文件这一项
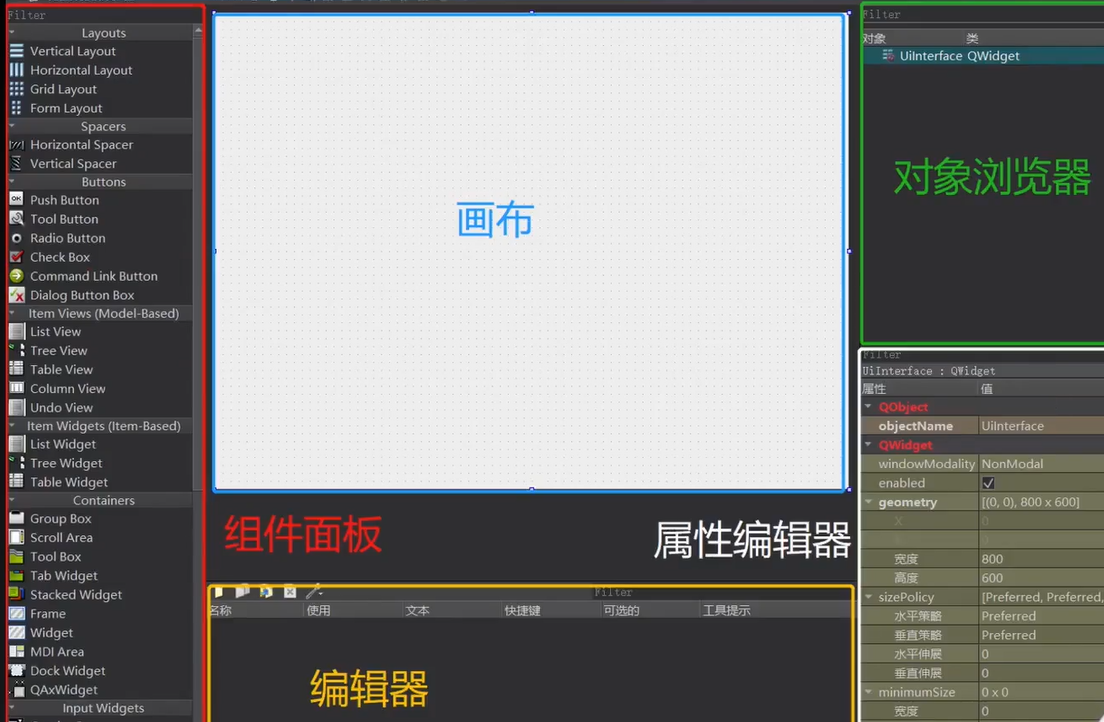
控件类型的介绍
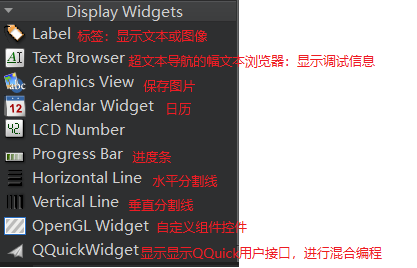
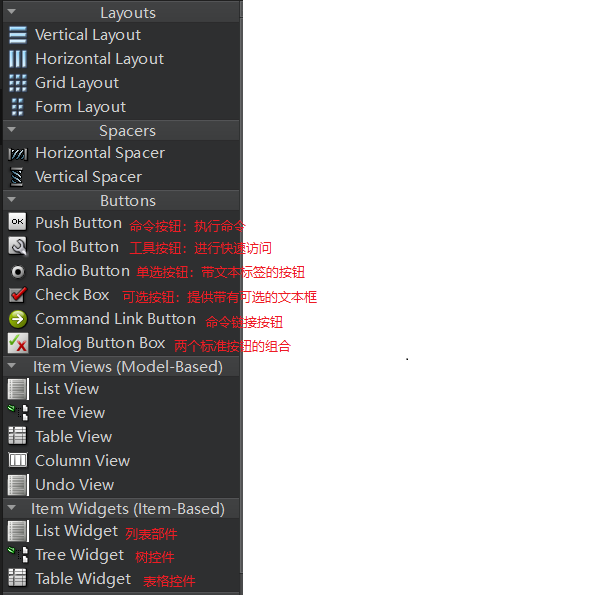
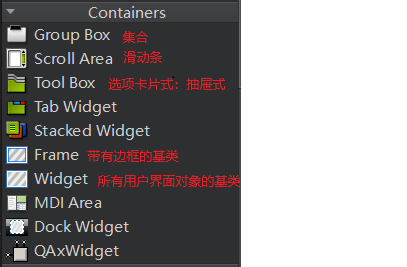
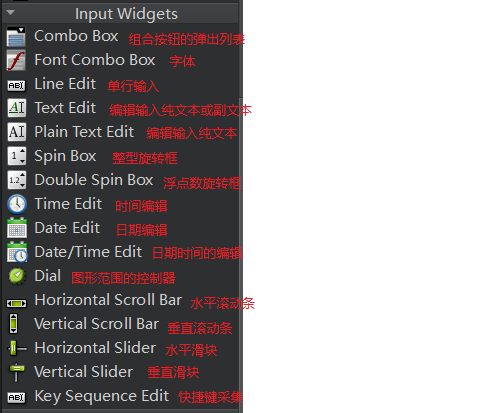
信号与槽机制处理
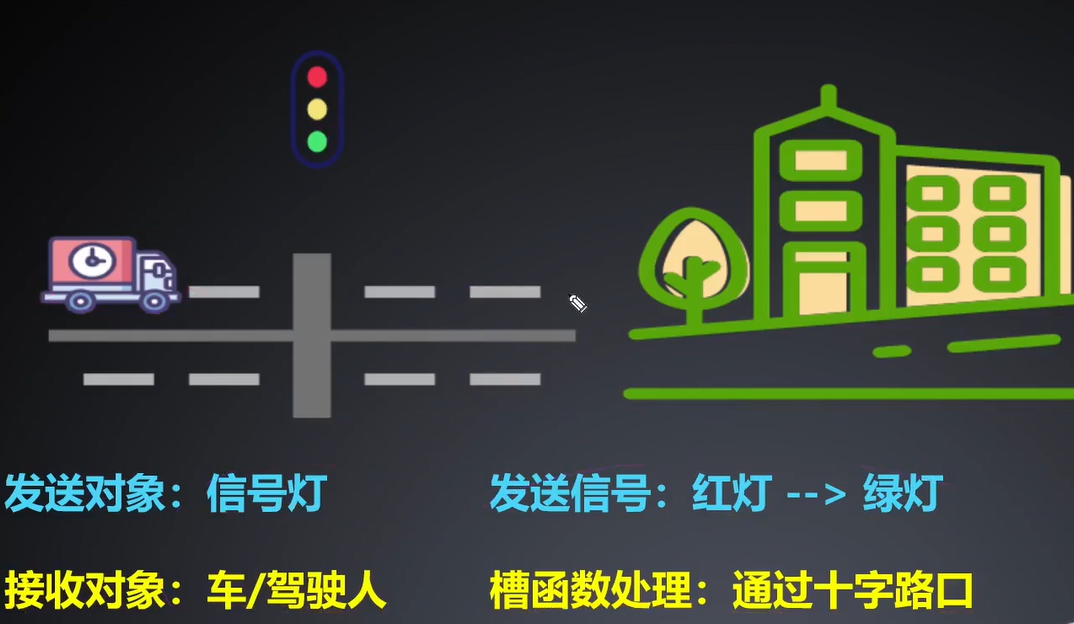
信号与槽是用与对象之间的通信,是Qt的核心
注意:信号与槽不是C++标准代码,是Qt特有的,最终通过moc(Meta-Object Complier)进行重新编译生成C++标准的语法
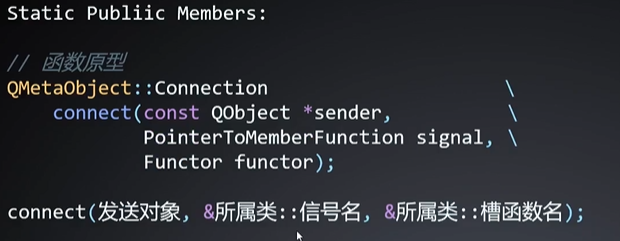
常见信号与槽的实现方式
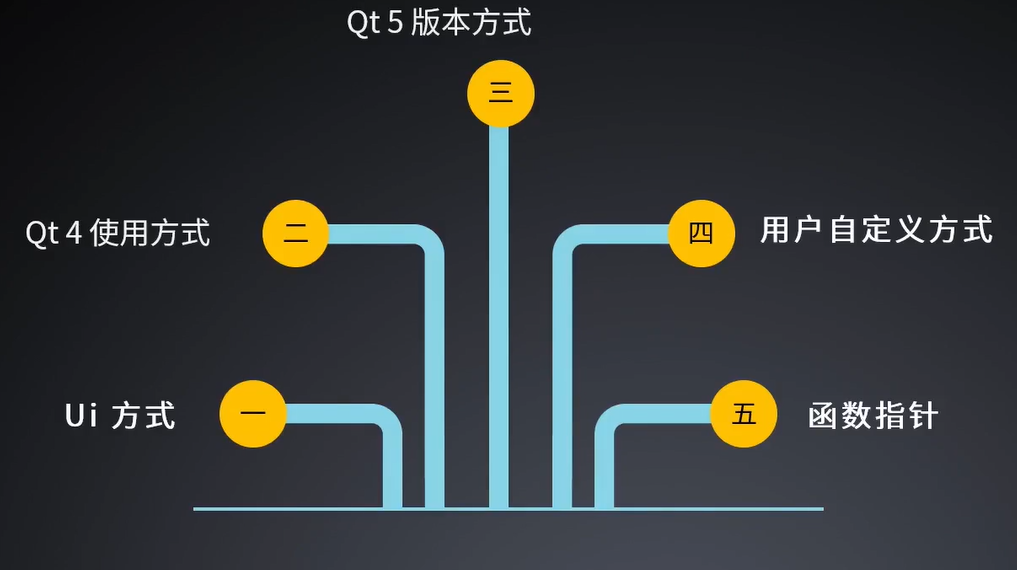
信号与槽函数原型(一)

信号与槽函数原型(二)

信号与槽函数原型(三)

信号与槽函数原型(四)
信号与槽函数原型(五)

信号与槽函数原型(六)不推荐

SignalAndSlot::SignalAndSlot(QWidget *parent)
: QWidget(parent)
, ui(new Ui::SignalAndSlot)
{
ui->setupUi(this);
//二、Qt 4 方式(纯代码完成)
// 好处:信号与槽相对直观
//坏处:1、使用宏定义的时候,如果说存在任何错误,在编译阶段是不会报错,运行阶段会报错
// 2、宏定义里面的函数里的参数,它是不能够加参数名,只能加参数类型
// 3、普通函数它不能作为槽函数去使用的
connect(ui->pushButton_3, SIGNAL(clicked(bool)), this, SLOT(close()));
//三、 Qt 5 方式
//好处:能够完美解决Qt4所遗留下来的问题
// 普通函数它作为槽函数去使用的
connect(ui->pushButton_4, &QPushButton::clicked, this, &QWidget::close);
//四、 Qt 5方式 Lambda
// 条件:加入CONFIG += c++11 .pro文件夹中
connect(ui->pushButton_5, &QPushButton::clicked, this, [=](){
this->close();
});
//五、自定义方式
connect(ui->pushButton_6, &QPushButton::clicked, this, [=](){
//函数调用
emit customSignal();
});
connect(this, &SignalAndSlot::customSignal, this, &SignalAndSlot::customSolt);
//六、函数指针
//好处:告诉编译器使用的是哪一种重载方式,避免编译器产生歧义
void (SignalAndSlot::*closeWidgest)() = &SignalAndSlot::customSolt;
connect(ui->pushButton_7, &QPushButton::clicked, this, closeWidgest);
}
void SignalAndSlot::customSolt() {
this->close();
}
SignalAndSlot::~SignalAndSlot()
{
delete ui;
}
/**
* 一、Ui方式
* @brief 好处:使用非常方便
* 坏处:对应初学者,不利于学习的。
*/
void SignalAndSlot::on_pushButton_clicked()
{
this->close();
}
常用控件创建与设置
常见展示型控件创建与设置
DisplayWidget::DisplayWidget(QWidget *parent)
: QWidget(parent)
{
this->setFixedSize(800, 800);
/*
* 创建应该标签,考虑使用哪一个功能(纯文本、副副本、图片、数字)
*
*/
//1、纯文本
//QLabel *label = new QLabel(this);
//指定父对象为QWidget
QLabel *label = new QLabel;
label->setFrameStyle(QFrame::Box);
label->setText("这是第一个标签");
label->setAlignment(Qt::AlignRight);
label->resize(100, 100);
label->setParent(this);
//2、富文本
QLabel *label2 = new QLabel("<a href=http://kaikeba.com>这是第二个标签</a>", this);
//允许打开 外部链接
label2->setOpenExternalLinks(true);
label2->setGeometry(this->width() / 3, 0, 300, 50);
//3、数字
//默认这里识别数字1,如果小数点后面没有有效数字的话,默认QLabel显示的是整型
//堆区 程序结束之后 对象树 无需进行手动 delete
QLabel *label3 = new QLabel;
label3->setParent(this);
label3->setGeometry(this->width() / 3 * 2, 0, 300, 50);
double d = 2.0000;
label3->setNum(d);
//栈区 {}
//不推荐使用
//QLabel label4;
/*
* 2.QProgressBar:范围、进度值,垂直水平,加载方向,文本字符串
* 如果说进度条垂直、默认文本字符串是消失,只有设置水平,文本字符串出现
* 进度条公式 % = distance_value - minimum / maxnimum - minimum
*/
QProgressBar *progressBar1 = new QProgressBar(this);
progressBar1->setGeometry(0, this->height() / 2, 300, 50);
progressBar1->setMinimum(0);
progressBar1->setMaximum(100);
progressBar1->setValue(30);
progressBar1->setOrientation(Qt::Horizontal);
progressBar1->setInvertedAppearance(true);
double e = 23.2;
QProgressBar *progressBar2 = new QProgressBar(this);
progressBar2->setGeometry(this->width() / 2, this->height() / 2, 300, 50);
progressBar2->setMinimum(0.0);
progressBar2->setMaximum(100.0);
progressBar2->setValue(e);
progressBar2->setFormat(QString("重量:%1g").arg(QString::number(e, 'f', 1)));
}
常见动作型控件创建与设置
ButtonWidget::ButtonWidget(QWidget *parent)
: QWidget(parent)
{
/*1、QPushButton
* 分类:
* 自动默认按钮:当我们满足一定条件下(焦点),此时自动默认按钮它就会转化成默认按钮
* 默认按钮:当我们触发回车(enter),此时默认按钮就会触发
*
*/
QPushButton *btn1 = new QPushButton("这是一个标准按钮", this);
btn1->resize(200, 30);
connect(btn1, &QPushButton::clicked, this, [=](){
qDebug() << "这是一个标准按钮";
});
QPushButton *btn2 = new QPushButton("这是一个默认按钮", this);
btn2->setGeometry(this->width() / 4, 0, 200, 30);
btn2->setDefault(true);
connect(btn2, &QPushButton::clicked, this, [=](){
qDebug() << "这是一个默认按钮";
});
QPushButton *btn3 = new QPushButton("这是一个取消了自动默认按钮", this);
btn3->setGeometry(this->width() / 2, 0, 200, 30);
btn3->setAutoDefault(false);
connect(btn3, &QPushButton::clicked, this, [=](){
qDebug() << "这是一个取消了自动默认按钮";
});
QPushButton *btn4 = new QPushButton("这是一个自动默认按钮", this);
btn4->setGeometry(this->width() / 3 * 2, 0, 200, 30);
btn4->setAutoDefault(true);
connect(btn3, &QPushButton::clicked, this, [=](){
qDebug() << "这是一个自动默认按钮";
});
QPushButton *btn5 = new QPushButton("这是一个设置flat属性的按钮", this);
btn5->setGeometry(0, this->height() / 4, 200, 30);
btn5->setFlat(true);
connect(btn3, &QPushButton::clicked, this, [=](){
qDebug() << "这是一个设置flat属性的按钮";
});
/*
* 2、QToolButton:设置成快速按钮(图标、图标+文字)
*/
QToolButton *toolBtn1 = new QToolButton(this);
toolBtn1->setGeometry(this->width() / 4, this->height() / 4, 200, 30);
toolBtn1->setArrowType(Qt::UpArrow);
connect(toolBtn1, &QToolButton::clicked, this, [=](){
qDebug() << "这是一个快速按钮";
});
QToolButton *toolBtn2 = new QToolButton(this);
toolBtn1->setGeometry(this->width() / 4, this->height() / 4, 200, 30);
toolBtn2->setText("文件夹");
toolBtn2->setIcon(QIcon(":/1.jpg"));
toolBtn2->setIconSize(QSize(44, 44));
toolBtn2->setToolButtonStyle(Qt::ToolButtonTextBesideIcon);
/*
*3、QRadioButton:单选按钮
* 它是与QButtonGroup配合使用
*/
QRadioButton *trueRadioBtn = new QRadioButton(this);
QRadioButton *falseRadioBtn = new QRadioButton(this);
trueRadioBtn->setGeometry(0, this->height() / 3, 200, 30);
falseRadioBtn->setGeometry(this->width() / 2, this->height() / 3, 200, 30);
trueRadioBtn->setText("正确");
falseRadioBtn->setText("错误");
QButtonGroup *btnGroup = new QButtonGroup(this);
btnGroup->addButton(trueRadioBtn, 0);
btnGroup->addButton(falseRadioBtn, 1);
trueRadioBtn->setCheckable(true);
//5.15///
// connect(btnGroup, &QButtonGroup::idClicked, this, [=](int id){
// qDebug() << id;
// });
/*
*4、QCheckBox 复选框
*
*/
QCheckBox *checkBox1 = new QCheckBox("A", this);
QCheckBox *checkBox2 = new QCheckBox("B", this);
QCheckBox *checkBox3 = new QCheckBox("C", this);
checkBox1->setGeometry(0, this->height() / 2, 200, 30);
checkBox2->setGeometry(this->width() / 3, this->height() / 2, 200, 30);
checkBox3->setGeometry(this->width() / 3 * 2, this->height() / 2, 200, 30);
checkBox2->setTristate(true);
//初始化状态
checkBox2->setCheckState(Qt::Checked);
//状态触发、切换触发
connect(checkBox1, &QCheckBox::stateChanged, this, [=](int state){
qDebug() << "state connect" << state;
});
//切换触发
//半选中属于:true
connect(checkBox2, &QCheckBox::toggled, this, [=](bool check){
qDebug() << "check connect" << check;
});
}
ButtonWidget::~ButtonWidget()
{
}
常见输入型控件创建与设置
InputWidget::InputWidget(QWidget *parent)
: QMainWindow(parent)
{
this->setFixedSize(800, 800);
/*
*1、QLineEdit 单行编辑
* 剪切、复制、粘贴、对应快捷键
*/
QLineEdit *lineEdit = new QLineEdit(this);
lineEdit->resize(200, 50);
QPushButton *btn = new QPushButton("获取",this);
btn->setGeometry(200, 0, 50, 50);
// 设置限定字符串长度
lineEdit->setMaxLength(2);
//设置小黑点
lineEdit->setEchoMode(QLineEdit::PasswordEchoOnEdit);
// 验证器主要的功能:限定我们输入的大范围(限定输入的位数,而不是小范围),然后输入数字,而字母使不能输入的。0到100是限定0到999
//小范围需要使用正则表达式(QRegExpValidator)
QIntValidator *validator = new QIntValidator(0, 100, this);
lineEdit->setValidator(validator);
connect(btn, &QPushButton::clicked, this, [=]{
// 获取并打印文本内容
qDebug() << lineEdit->text();
});
/*
* 2、多行输入 QTextEdit(富文本): 提供多行输入文本框,并且支持 HTML 语法
*/
QTextEdit *textEdit = new QTextEdit(this);
textEdit->setGeometry(this->width() / 2, 0, 300, 300);
textEdit->setText("第一行内容<br/>第二行内容");
/*
* 3、多行输入 QPlainTextEdit(纯文本)
*/
QPlainTextEdit *plainTextEdit = new QPlainTextEdit(this);
plainTextEdit->setGeometry(0, this->height() / 4, 300, 300);
plainTextEdit->setPlainText("第一行内容<br/>第二行内容");
/*
* 4、QSpinBox 调整框或旋转框
*/
QSpinBox *spinBox = new QSpinBox(this);
spinBox->setGeometry(0, this->height() / 4 * 3, 100, 50);
spinBox->setRange(0, 100);
//按下时间越长,增长/减小速度越快
spinBox->setAccelerated(true);
spinBox->setSingleStep(5);
//是否能循环变化
spinBox->setWrapping(false);
spinBox->setPrefix("前缀");
spinBox->setSuffix("后缀");
/*
* 4、QSlider 进度条
*/
QSlider *slider = new QSlider(this);
slider->setGeometry(100, this->height() / 4 * 3, 200, 30);
slider->setMinimum(0);
slider->setMaximum(100);
slider->setOrientation(Qt::Horizontal);
slider->setSingleStep(5);
// connect(spinBox, QOverload<int>::of(&QSpinBox::valueChanged), this, [=](int i){
// slider->setValue(i);
// });
connect(spinBox, QOverload<int>::of(&QSpinBox::valueChanged), slider, &QSlider::setValue);
connect(slider, &QSlider::valueChanged, spinBox, &QSpinBox::setValue);
}
InputWidget::~InputWidget()
{
}
常见列表控件创建于设置
ItemWidget::ItemWidget(QWidget *parent)
: QMainWindow(parent)
{
this->setFixedSize(800, 800);
/*
* 1、列表(QListWidget),与之配合QListWidgetItem
*/
QListWidget *listWidget = new QListWidget(this);
listWidget->setGeometry(0, 0, 200, 200);
listWidget->addItem("苹果");
listWidget->addItem(new QListWidgetItem("西瓜"));
listWidget->addItem("香蕉");
//以图标模式进行展示
listWidget->setViewMode(QListView::IconMode);
QLabel *label = new QLabel(this);
label->setGeometry(this->width() / 2, 0, 200, 200);
connect(listWidget, &QListWidget::currentTextChanged, label, &QLabel::setText);
/*
* 2、树列表(QTreeWidget),与之配合QTreeWidgetItem
* 标题、根、子节点(项目)
*/
QTreeWidget *treeWidget = new QTreeWidget(this);
treeWidget->setGeometry(0, this->height() / 3, 400, 300);
//添加标题
QStringList title;
title << "科目" << "分数";
treeWidget->setHeaderLabels(title);
//添加根节点
QStringList name;
name << "小文";
QTreeWidgetItem *root = new QTreeWidgetItem(treeWidget, name);
//添加子节点
QStringList score;
score << "语文" << "70";
QTreeWidgetItem *node = new QTreeWidgetItem(root, score);
root->addChild(node);
/*
* 3、表格控件(QTableWidget),与之配合QTableWidgetItem
* 设置行/列数量、标题、项目
*/
QTableWidget *tableWidget = new QTableWidget(3, 3, this);
tableWidget->setGeometry(this->width() / 2, this->height() / 3, 400, 300);
//添加标题
QStringList stringList;
stringList << "姓名" << "性别" << "年龄";
tableWidget->setHorizontalHeaderLabels(stringList);
//添加项目
tableWidget->setItem(0, 0, new QTableWidgetItem("小文"));
tableWidget->setItem(0, 1, new QTableWidgetItem("男"));
tableWidget->setItem(0, 2, new QTableWidgetItem("50"));
}
ItemWidget::~ItemWidget()
{
}
Qt中对象树的介绍
是用来组织和管理所有QObject及其子类创建的对象
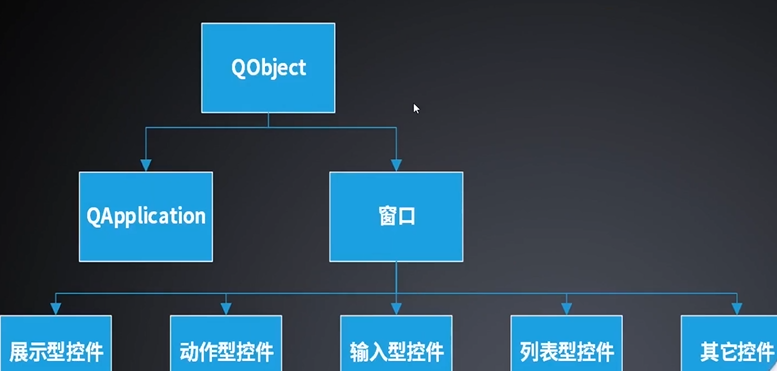
对象树创建规则:
对应Qt程序来说,父对象通常创建在栈上。
子对象应创建在堆中(new),无需手动delet删除
对象树删除规则:
父对象拥有子对象的所有权,如果父对象被删除,那么子对象也随之被删除。
正常情况下,最后被创建出来的对象,会被先析构掉。
手动删除子对象,会把该子对象从父对象的列表(children())中删除,以防触发QT对象树规则,再删除一次。
父对象创建子对象之后,则子对象会被删除两次。
其他规则:
确保每一个QObject对象在QApplication之后创建,保证在QApplication之前销毁,因此QObject对象不能用static存储类型
项目源码结构刨析
.pro
QT += core gui
#core是核心模块,很多模块都是以它为基准去扩展;gui模块关于使用图片界面的模块
greaterThan(QT_MAJOR_VERSION, 4): QT += widgets
#如果Qt版本超过4的就要包括这句话
CONFIG += c++11
#使用c++11标准
# You can make your code fail to compile if it uses deprecated APIs.
# In order to do so, uncomment the following line.
#DEFINES += QT_DISABLE_DEPRECATED_BEFORE=0x060000 # disables all the APIs deprecated before Qt 6.0.0
## 上面的意思就是是否要在Qt6版本中使用Qt5Qt4的规则,如果不要使用就注释掉
SOURCES += \
main.cpp \
mywidget.cpp
HEADERS += \
mywidget.h
FORMS += \
mywidget.ui
#上面是文件配置信息
# Default rules for deployment.
qnx: target.path = /tmp/$${TARGET}/bin
else: unix:!android: target.path = /opt/$${TARGET}/bin
!isEmpty(target.path): INSTALLS += target
#上面这几句是关于部署到Android系统的
.h
#ifndef MYWIDGET_H
#define MYWIDGET_H
#include <QWidget>
// 配置界面的组件信息
QT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE
namespace Ui { class MyWidget; }
QT_END_NAMESPACE
class MyWidget : public QWidget
{
// 支持信号与槽
Q_OBJECT
public:
//父对象的指定
MyWidget(QWidget *parent = nullptr);
~MyWidget();
private:
// 访问Ui 界面当中的组件
Ui::MyWidget *ui;
};
#endif // MYWIDGET_H
main.cpp
#include "mywidget.h"
#include <QApplication>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
//创建并定义应用程序
QApplication a(argc, argv);
//创建并定义窗口
MyWidget w;
//显示
w.show();
// 事件处理、消息循环(使应用程序处于一个阻塞状态)
return a.exec();
}
.cpp
#include "mywidget.h"
#include "ui_mywidget.h"
MyWidget::MyWidget(QWidget *parent)
: QWidget(parent)
, ui(new Ui::MyWidget)
{
// 实现窗口的生成、属性的设置、信号与槽的配置
ui->setupUi(this);
}
MyWidget::~MyWidget()
{
delete ui;
}
Qt界面开发美化处理
QSS样式设计与修改
QSS(Qt Style Sheet)一个非常强大的用于自定义外观的机制,语法与CSS相似
设置整个应用程序的样式表:QApplication::setStyleSheet()
设置部件及其子部件的样式表:QWidget::setStyleSheet()
样式表语法基础
selector{attribute : value;}
QPushButton{color : red;}
注意点:
selector(选择器):选择特定的类,一般为可以定制样式表的Qt表。
attribute(属性)和value(值)
可以有多个选择器用逗号“,”分隔
可以有多个属性和值,用分号“;”分隔
selector 后指定类的对象名,用“#”加对象名方式
衍生语法规则
1、选择器{属性:值;}
QPushButton{color:red;}
2、选择器,选择器,选择器{属性:值;}
QLineEdit,QPushButton,QCheckBox{color:red;}
3、选择器:伪状态{属性:值;}
QPushButton:hover{color:red;}
4、选择器:伪状态,选择器:伪状态{属性:值;}
QPushButton:hover,QPushButton:pressed{color:red;}
5、选择器::辅助控制器{属性:值;}
QComboBox::down-arrow{background-color:red;}
6、选择器::辅助控制器,选择器::辅助控制器{属性:值;}
QTabBar::tab:selected,QTabBar::tab:hover{
background:qlineargradient(x1:0,y1:0,x2:0,y2:1,
stop: 0#fafafa, stop: 0.4#f4f4f4
stop: 0.53e7e7e7, stop: 1.0#fafafa;)
}
代码演示:
#include "setstylesheet.h"
#include "ui_setstylesheet.h"
SetStyleSheet::SetStyleSheet(QWidget *parent)
: QMainWindow(parent)
, ui(new Ui::SetStyleSheet)
{
ui->setupUi(this);
//设置几种样式办法
ui->pushButton->setStyleSheet("background-color: blue");
//设置多个属性
ui->pushButton_2->setStyleSheet("background-color: blue;"
"color: white;");
//设置多个属性
ui->pushButton_3->setStyleSheet("QPushButton{background-color: blue;"
"color: white;}");
//前面样式表设置会被后面样式表设置覆盖
this->setStyleSheet("QPushButton#pushButton_4{background-color: blue;"
"color: white;}");
//背景:黄色,字体是一个红色
ui->pushButton_4->setStyleSheet("background-color: yellow;");
//背景:绿色,字体是一个白色
ui->pushButton_4->setStyleSheet("background-color: green;"
"color: white");
//增加伪状态
ui->pushButton_5->setStyleSheet("QPushButton:hover{color: red;}");
//增加辅助控制器
ui->comboBox->setStyleSheet("QComboBox:down-arrow{background-color: yellow}");
}
SetStyleSheet::~SetStyleSheet()
{
delete ui;
}
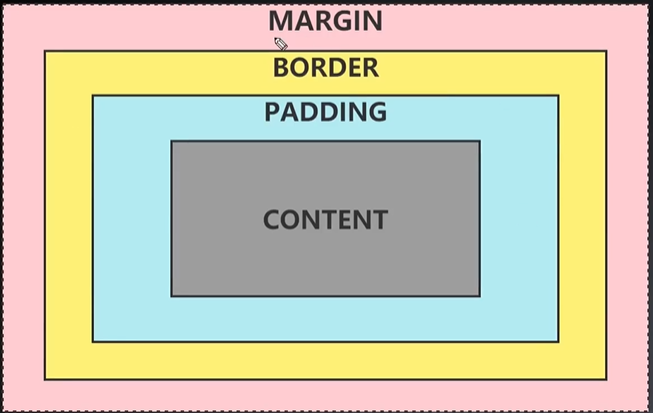
盒模型
MARGIN:外边距,当前这个控件与其他控件的距离
BORDER:外边框,当前这个控件所能看到的整个边框
PADDING:控件里面的文本内容边框和外边框的距离
CONTENT:所显示的文本内容
图片资源导入与设置
图片资源导入
1、复制图片到项目路径下
2、建立资源文件。右击项目名称,找到Add new且点击。然后点击Qt选项,在Qt选项的子项中选中Qt Resource File(表示要添加Qt的资源文件),如果根据提示点击下一步,然后点击完成
最终展示
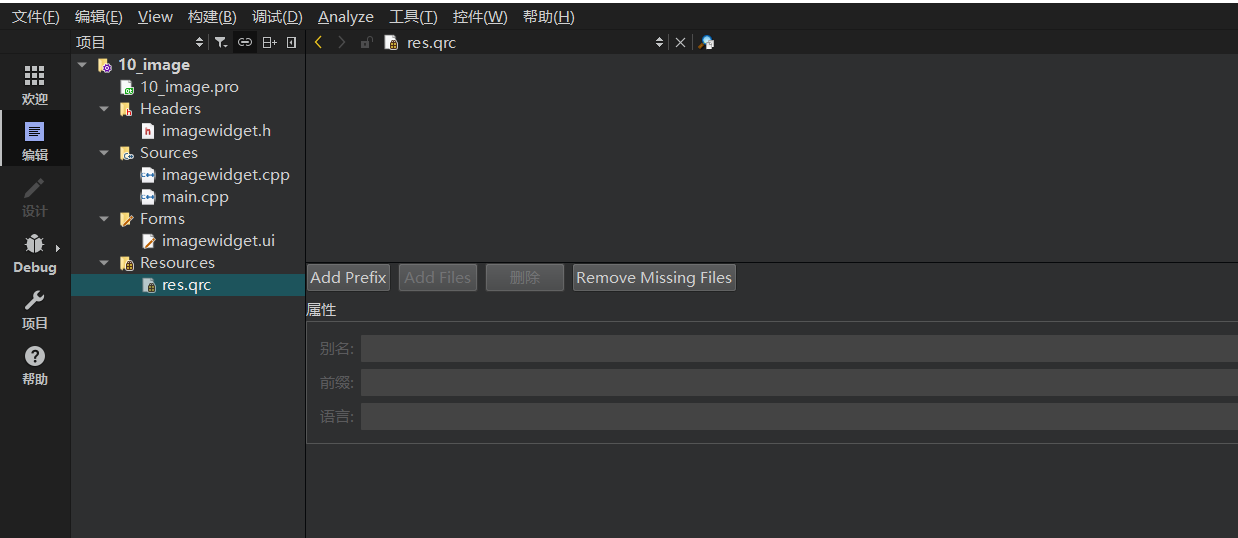
3、添加资源。点击Add prefix,然后填写一个前缀,再然后点击Add Files,然后选中图片
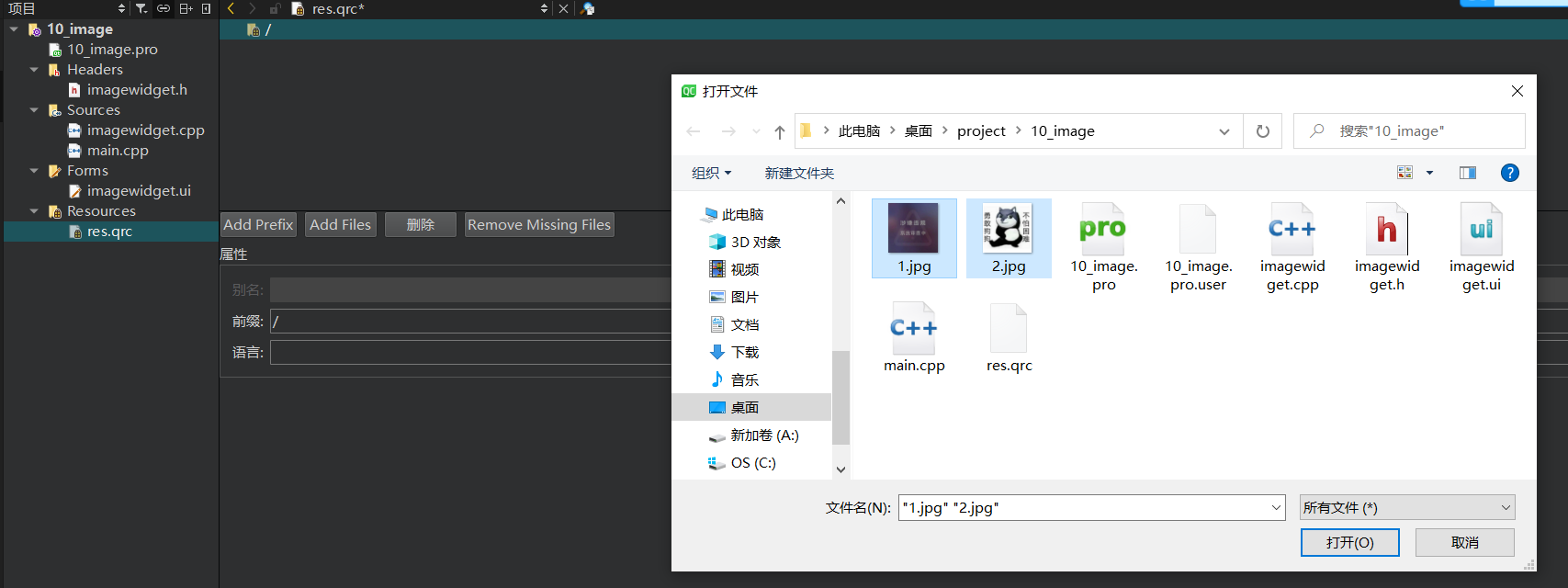
最终展示
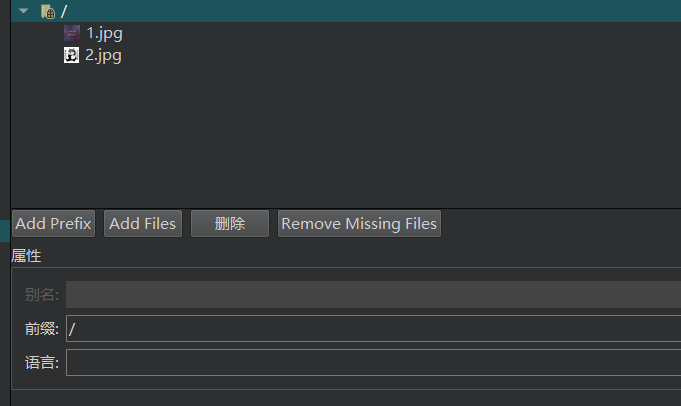
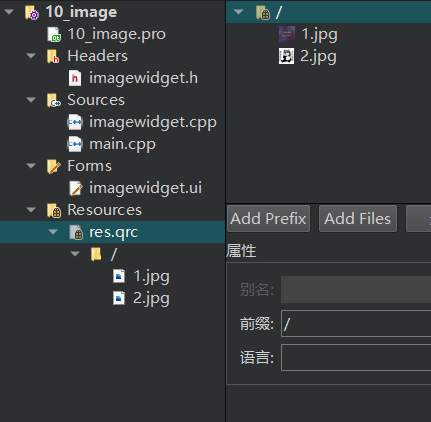
4、最终点击构建项目(小锤子),就可以看到项目出现资源文件
图片资源设置
imageWidget::imageWidget(QWidget *parent)
: QWidget(parent)
, ui(new Ui::imageWidget)
{
ui->setupUi(this);
/*
* 在ui界面添加 label 边框,然后在QFrame中frame shpe中设置box边框,然后右击ui界面中边框且选中 改变样式表 ,然后添加背景图
* 三种设置背景图的区别
* 1、background-image:原图片大小不变,当我们边框比原图片大,原图片复制出来多份,
* 当我们边框比原图片小,原图片大小不变,只能够显示根据边框显示的大小
* 2、border-image:原图片随着边框大小变化而变化,在盒模型中,也就内边距恒等于0
* 3、image:当我们边框大于原图片,图片大小不变,但内边距它是有改变的。
* 当我们边框小于原图片,图片大小是有改变的,并且成一定的比例去进行一个缩放的,而且内边距恒等于0
*/
// 其他设置背景图方式
// QPixmap QImage Qpicture 设置静图
QPixmap pixmap(":/1.jpg");
ui->label->setPixmap(pixmap);
ui->label->setScaledContents(true);//设置成border-image
QImage image(":/1.jpg");
ui->label_2->setPixmap(QPixmap::fromImage(image));
// QMovie 实现动图设置
QMovie *movie = new QMovie(":/1.jpg");
movie->setParent(this);
ui->label_3->setMovie(movie);
ui->label_3->setScaledContents(true);
movie->start();
//对整个Ui进行刷背景图
QPalette pal;
QImage image1(":/1.jpg");
pal.setBrush(QPalette::Background, QBrush(image));
this->setPalette(pal);
//QWidget 设置背景图片,父部件它是不生效的,而子部件是生效的
//QDialog 和 QMainWindow 设置背景图片,父部件它是生效的,子部件也是生效的
//this->setStyleSheet("background-image: url(:/1.jpg)");
}
imageWidget::~imageWidget()
{
delete ui;
}
窗体布局管理器之Ui布局
布局方式
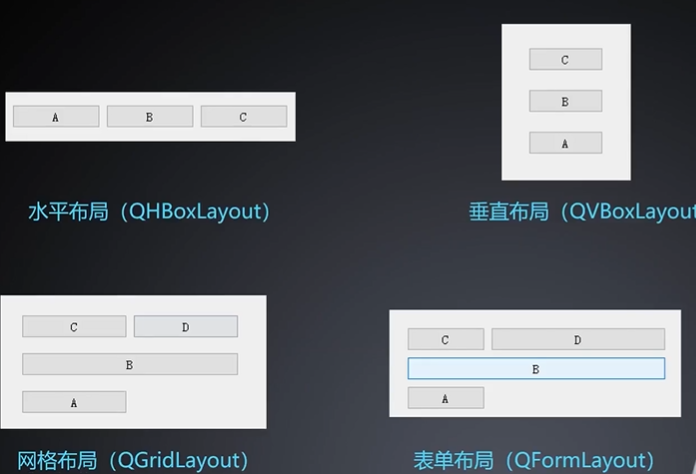
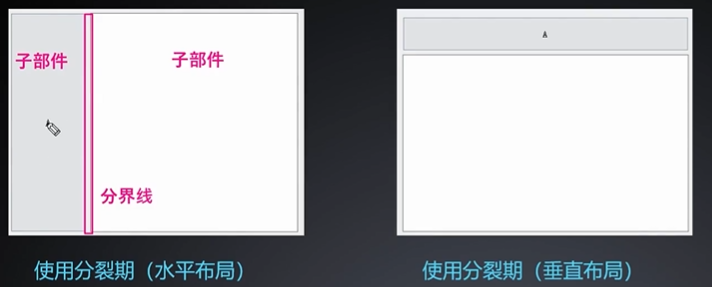
布局管理器之代码布局
#include "layoutwidget.h"
#include <QHBoxLayout>
#include <QPushButton>
#include <QGridLayout>
#include <QFormLayout>
#include <QLineEdit>
#include <QSplitter>
#include <QTextEdit>
LayoutWidget::LayoutWidget(QWidget *parent)
: QWidget(parent)
{
this->setFixedSize(800, 800);
//1、水平布局
QWidget *HWidget = new QWidget(this);
QPushButton *HBtnA = new QPushButton("A", HWidget);
QPushButton *HBtnB = new QPushButton("B", HWidget);
QPushButton *HBtnC = new QPushButton("C", HWidget);
QPushButton *HBtnD = new QPushButton("D", HWidget);
// 把控件添加道布局
QHBoxLayout *HLayout = new QHBoxLayout(HWidget);
HLayout->addWidget(HBtnA);
HLayout->addWidget(HBtnB);
HLayout->addWidget(HBtnC);
HLayout->addWidget(HBtnD);
//把布局设置到widget
HWidget->setLayout(HLayout);
//2、垂直布局
QWidget *VWidget = new QWidget(this);
VWidget->move(this->width() / 2, 0);
QPushButton *VBtnA = new QPushButton("E", VWidget);
QPushButton *VBtnB = new QPushButton("F", VWidget);
QPushButton *VBtnC = new QPushButton("G", VWidget);
QPushButton *VBtnD = new QPushButton("H", VWidget);
// 把控件添加道布局
QVBoxLayout *VLayout = new QVBoxLayout(VWidget);
VLayout->addWidget(VBtnA);
VLayout->addWidget(VBtnB);
VLayout->addWidget(VBtnC);
VLayout->addWidget(VBtnD);
//把布局设置到widget
VWidget->setLayout(VLayout);
//3、网格布局
QWidget *GWidget = new QWidget(this);
GWidget->move(0, this->height() / 3);
QPushButton *GBtnA = new QPushButton("A", VWidget);
QPushButton *GBtnB = new QPushButton("B", VWidget);
QPushButton *GBtnC = new QPushButton("C", VWidget);
QPushButton *GBtnD = new QPushButton("D", VWidget);
QPushButton *GBtnE = new QPushButton("E", VWidget);
//把控件添加到布局
QGridLayout *GLayout = new QGridLayout(GWidget);
GLayout->addWidget(GBtnA, 0, 0);
GLayout->addWidget(GBtnB, 0, 1);
GLayout->addWidget(GBtnC, 1, 0, 1, 2);
GLayout->addWidget(GBtnD, 2, 0);
GLayout->addWidget(GBtnE, 2, 1);
//把布局设置到widget
GWidget->setLayout(GLayout);
//4、表单布局
QWidget *FWidget = new QWidget(this);
FWidget->move(this->width() / 2, this->height() / 3);
QLineEdit *nameText = new QLineEdit(FWidget);
QLineEdit *setText = new QLineEdit(FWidget);
QLineEdit *ageText = new QLineEdit(FWidget);
QFormLayout *FLayout = new QFormLayout(FWidget);
FLayout->addRow("姓名", nameText);
FLayout->addRow("性别", setText);
FLayout->addRow("年龄", ageText);
FWidget->setLayout(FLayout);
//5、使用分裂器完成布局
QSplitter *HSplitter = new QSplitter(Qt::Horizontal, this);
HSplitter->move(0, this->height() / 3 *2);
QPushButton *SBtn = new QPushButton("S", this);
QTextEdit *text = new QTextEdit(this);
HSplitter->addWidget(SBtn);
HSplitter->addWidget(text);
}
LayoutWidget::~LayoutWidget()
{
}
Qt应用窗口创建之QDialog
我们统称窗口和控件为部件(QWidget)。没有嵌入到其他部件中的部件,称之为窗口,相反为控件(非窗口部件)。
QWidget是所有用户界面对象的基类。
窗口创建之Qdialog
#include "widget.h"
#include "ui_widget.h"
#include <QDialog>
#include <QDebug>
#include <QMessageBox>
#include <QFileDialog>
#include <QColorDialog>
#include <QFontDialog>
Widget::Widget(QWidget *parent)
: QWidget(parent)
, ui(new Ui::Widget)
{
ui->setupUi(this);
connect(ui->pushButton, &QPushButton::clicked, this, [=]{
//两种功能,模态对话框/非模态对话框
QDialog dlg;
dlg.resize(300, 300);
//在我们没有关闭这窗口之前,当前状态是阻塞的状态
dlg.exec();
qDebug() << "test";
//几种类型:消息对话框、颜色对话框、字体对话框、文件对话框
//消息对话框
QMessageBox::warning(this, "警告对话框", "提示这是一个警告");
//文件对话框
QString file;
file = QFileDialog::getOpenFileName(this, "文件对话框", "", "文本文件(*.txt)");
qDebug() << file;
//QFile
//颜色对话框
qDebug() << QColorDialog::getColor(Qt::red, this, "颜色对话框");
//字体对话框
bool flag;
qDebug() << QFontDialog::getFont(&flag, this);
if (flag) {
qDebug() << "front is set to the font the user deleted";
} else {
qDebug() << "the user canceled the dialog";
}
});
}
Widget::~Widget()
{
delete ui;
}
窗口创建之QMainWindow
QMainWindow组成部分
Central Widget:中心部件,只有一个
Dock Widget:浮动窗口(可停靠窗口),可以设置成上下左右多个地方,还可以设置多个
Tool Bar:工具栏,可以设置成上下左右多个地方
Menu Bar:菜单栏,默认只有一个,可以添加一些菜单选项
Status Bar:状态栏,可以设置成左或右地方,还可以设置多个
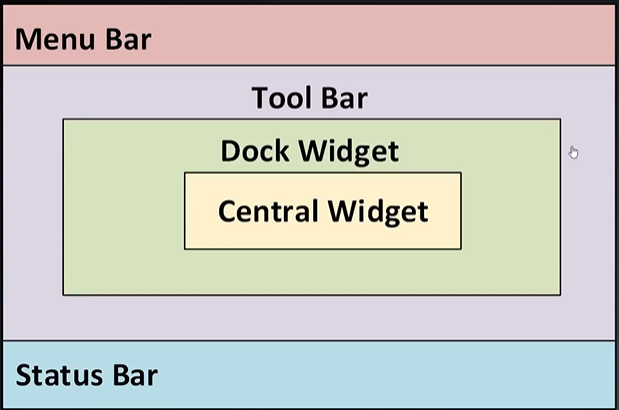
例子:
#include "mainwindow.h"
#include <QMenu>
#include <QMenuBar>
#include <QAction>
#include <QToolBar>
#include <QPushButton>
#include <QDockWidget>
#include <QTextEdit>
#include <QStatusBar>
#include <QLabel>
MainWindow::MainWindow(QWidget *parent)
: QMainWindow(parent)
{
this->setFixedSize(500, 500);
//创建菜单栏,有且只有一个,菜单列表、菜单选项
QMenuBar *menuBar = new QMenuBar(this);
this->setMenuBar(menuBar);
//ALT + F 触发文件按钮
QMenu *fileMenu = menuBar->addMenu("文件(&F)");
menuBar->addMenu("编辑");
fileMenu->addAction("打开");
//添加分割线
fileMenu->addSeparator();
QAction *closeAction = fileMenu->addAction("关闭");
closeAction->setShortcut(QKeySequence(tr("Ctrl+4")));
connect(closeAction, &QAction::triggered, this, &QWidget::close);
//创建工具栏
QToolBar *toolBar = new QToolBar(this);
this->addToolBar(Qt::TopToolBarArea, toolBar);
toolBar->addAction("文件");
toolBar->addAction("编辑");
toolBar->addAction(QIcon(""), "新建");
toolBar->addAction(QIcon(""), "打开");
QPushButton *btn = new QPushButton("按钮", this);
toolBar->addWidget(btn);
//创建浮动窗口
QDockWidget *dock = new QDockWidget(this);
this->addDockWidget(Qt::TopDockWidgetArea, dock);
//创建中心部件
QTextEdit *text = new QTextEdit(this);
this->setCentralWidget(text);
//创建状态栏
QStatusBar *statusBar = new QStatusBar(this);
this->setStatusBar(statusBar);
QLabel *leftInfo = new QLabel("左侧提示信息", this);
statusBar->addWidget(leftInfo);
QLabel *rightInfo = new QLabel("右侧提示信息", this);
statusBar->addPermanentWidget(rightInfo);
}
Qt事件处理机制之定时器事件
#include "eventwidget.h"
#include "ui_eventwidget.h"
#include <QTimer>
EventWidget::EventWidget(QWidget *parent)
: QWidget(parent)
, ui(new Ui::EventWidget)
{
ui->setupUi(this);
id = this->startTimer(2000);
//QTimer 实现定时器功能
QTimer *timer = new QTimer(this);
static int index = 0;
connect(timer, &QTimer::timeout, this, [=](){
index++;
ui->label_2->setNum(index);
if (index == 10) {
timer->stop();
index = 0;
}
});
timer->start(500);
}
EventWidget::~EventWidget()
{
delete ui;
}
/**
* @brief 定时器
* @param event
*/
void EventWidget::timerEvent(QTimerEvent *event) {
static int i = 0;
if (event->timerId() == id) {
i++;
ui->label->setNum(i);
//判断定时器是否达到10秒的时间,如果是,停止定时器工作
if (i == 5) {
i = 0;
this->killTimer(id);
}
}
}
Qt事件处理机制之鼠标键盘事件
/**
* @brief 鼠标事件(按下、双击、移动、释放)
* @param event
*/
void EventWidget::mousePressEvent(QMouseEvent *event) {
//左键
if (event->button() == Qt::LeftButton) {
ui->label_3->setText(QString("x: %1, y=%2").arg(event->x()).arg(event->y()));
}
//右键
else if (event->button() == Qt::RightButton) {
ui->label_4->setText(QString("x: %1, y=%2").arg(event->globalX()).arg(event->globalY()));
}
//中键
else if (event->button() == Qt::MiddleButton) {
ui->label_5->setText("按下鼠标中键");
}
}
/**
* @brief 按键事件(按下、释放)
* @param event
*/
void EventWidget::keyPressEvent(QKeyEvent *event) {
//某单一按键按下
if (event->key() == Qt::Key_F) {
qDebug() << "F 按键按下";
}
//组合按键按下 Ctrl + F
if (event->modifiers() == Qt::ControlModifier) {
if (event->key() == Qt::Key_F) {
qDebug() << "Ctrl + F 按键按下";
}
}
}
绘图事件与事件传递原理
绘图事件
/**
* @brief 绘图事件
* @param event
*/
void EventWidget::paintEvent(QPaintEvent *event) {
Q_UNUSED(event);
QPainter painter(this);
QPen pen;
pen.setWidth(3);
pen.setStyle(Qt::DotLine);
pen.setColor(Qt::blue);
painter.setPen(pen);
painter.save();//保存
pen.setColor(Qt::yellow);
pen.setWidth(8);
painter.setPen(pen);
painter.drawLine(0, 0, this->width(), this->height());
painter.restore();//恢复颜色
painter.save();
painter.drawRect(this->width() / 2, this->height() / 2, 100, 100);
painter.restore();
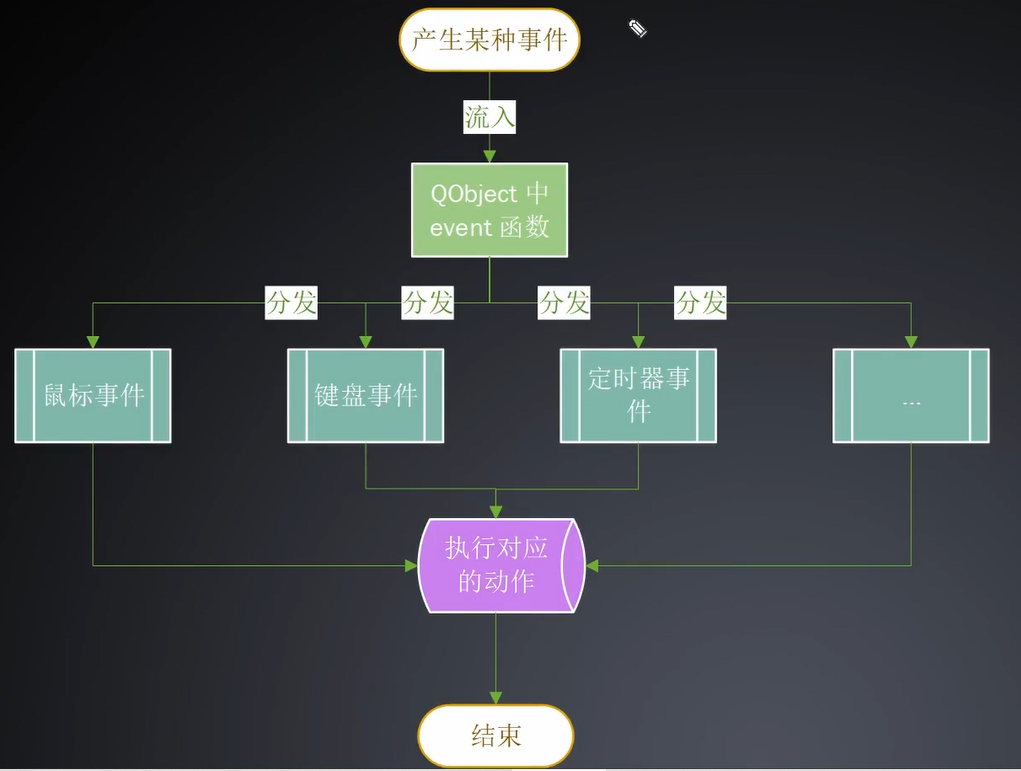
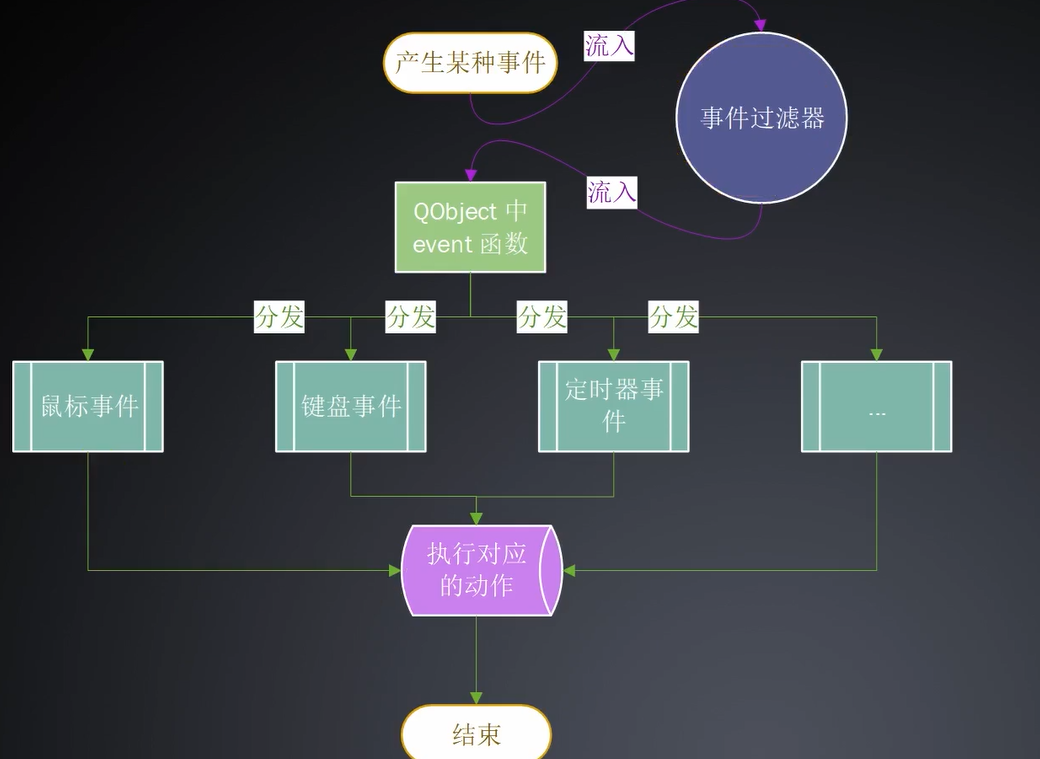
事件传递过程与过滤方式
事件传递过程:
事件过滤器:
#include "mylineedit.h"
#include <QEvent>
#include <QDebug>
MyLineEdit::MyLineEdit(QWidget *parent)
:QLineEdit(parent)
{
}
/**
* @brief 重写QObject当中的event,不推荐这么使用
* @param ev
* @return
*/
bool MyLineEdit::event(QEvent *ev) {
//鼠标双击事件
if (ev->type() == QEvent::MouseButtonDblClick) {
qDebug() << "event 函数产生拦截";
return true;
}
//系统帮助我们分发事件,这是一个向下传递的过程
return QWidget::event(ev);
}
void MyLineEdit::mouseDoubleClickEvent(QMouseEvent *event) {
qDebug() << "没有产生拦截,执行鼠标双击的操作";
}
void MyLineEdit::mousePressEvent(QMouseEvent *event) {
qDebug() << "没有产生拦截,执行鼠标单击的操作";
}
#include "widget.h"
#include "mylineedit.h"
#include <QEvent>
#include <QDebug>
Widget::Widget(QWidget *parent)
: QWidget(parent)
{
lineEdit = new MyLineEdit(this);
lineEdit->resize(200, 200);
/*
* 2、事件过滤器使用方式:
* A.安装事件过滤器
* B.重写eventfilter 函数
*
*/
lineEdit->installEventFilter(this);
}
Widget::~Widget()
{
}
bool Widget::eventFilter(QObject *obj, QEvent *event) {
if (obj == lineEdit) {
if (event->type() == QEvent::KeyPress) {
qDebug() << "事件过滤器产生拦截";
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
return QWidget::eventFilter(obj,event);
}
void Widget::keyReleaseEvent(QKeyEvent *event) {
Q_UNUSED(event);
qDebug() << "没有产生拦截, 按键释放";
}
void Widget::keyPressEvent(QKeyEvent *event) {
Q_UNUSED(event);
qDebug() << "没有产生拦截,按键释放";
}
动画处理与特性
启动画面
#include "widget.h"
#include <QApplication>
#include <QSplashScreen>
#include <QThread>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
QApplication a(argc, argv);
//设置启动画面
QSplashScreen *splash = new QSplashScreen(QPixmap(":/1.jpg"));
splash->showMessage("loading...", Qt::AlignCenter, Qt::white);
splash->show();
QThread::sleep(5);
//保证主线程正常运行
a.processEvents();
Widget w;
w.show();
splash->finish(&w);
return a.exec();
}
动画设计与特效处理
#include "widget.h"
#include "ui_widget.h"
#include <QPropertyAnimation>
#include <QStateMachine>
#include <QState>
#include <QSignalTransition>
#include <QGraphicsBlurEffect>
#include <QGraphicsColorizeEffect>
#include <QGraphicsDropShadowEffect>
#include <QGraphicsOpacityEffect>
#include <QTimer>
Widget::Widget(QWidget *parent)
: QWidget(parent)
, ui(new Ui::Widget)
{
ui->setupUi(this);
//单一动画
QPropertyAnimation *animation = new QPropertyAnimation(ui->pushButton, "pos");
//飞入
animation->setDuration(1000);
animation->setStartValue(ui->pushButton->pos());
animation->setEndValue(ui->pushButton->pos() + QPoint(0, 300));
//animation->setEasingCurve(QEasingCurve::OutBounce);//弹跳
animation->start();
//状态机: 飞入+按钮大小有变化
QPropertyAnimation *animation1 = new QPropertyAnimation(ui->pushButton_2, "geometry");
//设置状态机
QStateMachine *machine = new QStateMachine(this);
//设置状态
QState *starState = new QState(machine);
QState *endState = new QState(machine);
//设置动作
starState->assignProperty(ui->pushButton_2, "geometry", QRect(0, 0, 50, 50));
endState->assignProperty(ui->pushButton_2, "geometry", QRect(100, 100, 300, 300));
//初始化状态
machine->setInitialState(starState);
//单次转换
QSignalTransition *transition = starState->addTransition(ui->pushButton_2,\
&QPushButton::clicked, \
endState);
QSignalTransition *transition1 = endState->addTransition(ui->pushButton_2,\
&QPushButton::clicked, \
starState);
//添加动作
transition->addAnimation(animation1);
transition1->addAnimation(animation1);
//启动状态机,只需要启动一次
machine->start();
//动画特效
/*
* 1. 模糊效果 QGraphicsBlurEffect
*
* 2.染色效果 QGraphicsColorizeEffect
*
* 3.阴影效果 QGraphicsDropShadowEffect
*
* 4.透明效果 QGraphicsOpacityEffect
*
*/
//模糊效果
ui->label->setStyleSheet("border-image: url(:/1.jpg)");
QGraphicsBlurEffect *blur = new QGraphicsBlurEffect(this);
ui->label->setGraphicsEffect(blur);
static int i = 100;
QTimer *timer = new QTimer(this);
connect(timer, &QTimer::timeout, this, [=](){
//设置模糊度,数值越大,图片越模糊
blur->setBlurRadius(i);
if (i == 0) {
timer->stop();
}
i--;
});
timer->start(100);
}
Widget::~Widget()
{
delete ui;
}
Qt工具与扩展
容器类的介绍
顺序容器:
QList
QLinkedList
QVector
QStack
QQueue
关联容器:
QMap
QMultiMap
QHash
QMultiHash
QSet
#include <QApplication>
#include <QList>
#include <QDebug>
#include <QMap>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
QApplication a(argc, argv);
/*
* 1、顺序容器使用方式(QList)
*/
QList<QString> list;
list << "dog" << "cat" << "pig";
qDebug()<< "原始的数据:";
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
qDebug() << list[i];
}
if (list[1] == "cat") list[1] = "brid";
list.replace(2, "snake");
qDebug()<< "已更改的数据:";
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
qDebug() << list[i];
}
//往列表当中从尾部、头部添加元素
list.append("mouse");
list.prepend("tiger");
//往列表当中某一个位置添加元素
list.insert(3, "fish");
qDebug()<< "已更改的数据:";
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
qDebug() << list[i];
}
/*
* 2、关联容器使用方式(QMap)
*/
QMap<QString, int> map;
map["one"] = 1;
map["two"] = 2;
map["four"] = 4;
//插入
//如果说原有的键存在,那么我们直接的修改的是值,反之,键不存在的情况下,修改的是键和值
map.insert("one", 7);
map.insert("three", 3);
//获取
//如果说有键的存在,那么我们直接获取的是值,反之,键不存在的话,所去获取的值为0
//并且系统会自动添加键
int val = map["one"];
int val1 = map["seven"];
qDebug() << val << val1;
/*
* 3、如何进行遍历容器
* Java风格的迭代器 是在Qt 4被引入的,它的使用更加的简单,但是效率角度触发,
* STL风格的迭代器效率会好一些,
*/
//遍历
QMapIterator<QString, int> i(map);
qDebug() << "Java 风格的迭代器";
//如果不为空
while (i.hasNext()) {
i.next();
qDebug() << i.key() << ":" << i.value();
}
//STL风格的迭代器
qDebug() << "STL 风格的迭代器";
QMap<QString, int>::const_iterator index = map.constBegin();
while (index != map.constEnd()) {
qDebug() << index.key() << ":" << index.value();
index++;
}
return 0;
}
工具类的介绍
QString字符串类的介绍
QString统一编码为Unicode编码,存的是QChar(16bit)类型,相比C++中的const char *,QString提供一个内存隐式共享,主要是提供当前内存去减少一些使用,避免一些不必要的数据的内存占用。
#include <QApplication>
#include <QString>
#include <QDebug>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
QString str = QString("hello world");
qDebug() << "字符串内容:" << str;
//如果使用 tr 办法去完成,str1可以使用Qt特有工具(Qt Linguist),其他语言编译
QString str1 = QObject::tr("hello world");
qDebug() << "字符串内容:" << str;
//编辑操作
qDebug() << "=========编辑操作=====";
//Hello world
str[0] = QChar('H');
qDebug() << "字符串大小:" << str.size();
//Hello world Qt
str.append(" Qt");
//HeXXX world Qt
str.replace(2, 3, "XXX");
//HEXXX world Qt
str.insert(1, 'E');
qDebug() << "修改后的内容:" << str;
//查询操作
qDebug() << "=========查询操作=====";
qDebug() << "字符串左部分的内容:" << str.left(4);
qDebug() << "字符串右部分的内容:" << str.right(4);
qDebug() << "字符串指定位置的内容:" << str.at(3);
//转换操作
qDebug() << "=========转换操作=====";
str = "99";
qDebug() << "从字符串转换成整型:" << str.toInt();
int num = 20;
str = QString::number(num);
qDebug() << "从整型转换成字符串:" << str;
str = "abc";
qDebug() << "从小写转大写:" << str.toUpper();
str = "ABC";
qDebug() << "从大写转小写:" << str.toLower();
//参数传递
qDebug() << "=========参数操作=====";
QString name = "hzh";
QString sex = "男";
str = QString("个人信息:%1 %2 %3").arg(name).arg(sex).arg(num);
qDebug() << str;
str = "%1 ------- %2";
qDebug() << str.arg("hzh", "男");
qDebug() << str.arg("%1GGGGGGGGGGGGGGGG").arg("男");
return 0;
}
音频文件处理与播放
#include "musicwidget.h"
#include "ui_musicwidget.h"
#include <QFileDialog>
#include <QDebug>
#include <QFileInfo>
MusicWidget::MusicWidget(QWidget *parent)
: QWidget(parent)
, ui(new Ui::MusicWidget)
{
ui->setupUi(this);
/*
* 1、音乐播放器
*
* 媒体播放器需要引入模块 Qt Multimedia
*
* 在win环境、使用DirectShow解码器,LAV filers,安装完之后,重启电脑
*
*/
player = new QMediaPlayer(this);
playlist = new QMediaPlaylist(this);
connect(ui->pushButton, &QPushButton::clicked, this, [=](){
path = QFileDialog::getOpenFileNames(this, "读取音乐", "/", "*.mp3");
QList<QString> list(path);
qDebug() << path;
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
QFileInfo file(list.at(i));
fileName = file.fileName();
filePath = file.filePath();
qDebug() << fileName;
qDebug() << filePath;
//file.fileTime();
//将每个歌单的路径添加到我们的音乐列表当中
playlist->addMedia(QUrl::fromLocalFile(filePath));
//ui->listWidget->addItem();
}
player->setPlaylist(playlist);
// 添加歌单至QListWidget显示
ui->listWidget->addItems(path);
});
//完成歌单的切换以及播放
connect(ui->listWidget, &QListWidget::currentRowChanged,\
this, [=](int index){
//系统歌曲切换
playlist->setCurrentIndex(index);
//播放歌曲
player->play();
});
}
视频文件处理与播放
#include <QApplication>
#include <QMediaPlayer>
#include <QVideoWidget>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
QApplication a(argc, argv);
// 创建窗口
QVideoWidget *video = new QVideoWidget;
video->setFixedSize(500, 500);
//video->setAspectRatioMode(Qt::IgnoreAspectRatio);
//创建媒体播放器
QMediaPlayer *player = new QMediaPlayer;
player->setMedia(QUrl::fromLocalFile("A:/前端/下载.mp4"));
player->setVideoOutput(video);
video->show();
player->play();
return a.exec();
}
图表处理与美化
#include "charswidget.h"
#include "ui_charswidget.h"
#include <QtCharts>
#include <QChartView>
#include <QHBoxLayout>
#include <QValueAxis>
#include <QScatterSeries>
#include <QLineSeries>
#include <QTimer>
CharsWidget::CharsWidget(QWidget *parent)
: QWidget(parent)
, ui(new Ui::CharsWidget)
{
ui->setupUi(this);
this->setFixedSize(900, 450);
/*
*1、图标需要额外一个模块(Qt Charts), 这是一个独立模块,还需要在.pro 文件添加配置信息
* QT += charts
*
* 结构分析:
* 1、图表视图
* 2、图表
* 3、坐标系
* 刻度(范围、分度、含义)
* 4、样式
* 点状图、饼状图、条形图、曲线图、折线图、特殊图形(极坐标系图)
*/
/* 折线图的创建 */
/* 1、图表的添加设置 */
QChartView *chartView = new QChartView(this);
QChart *chart = new QChart;
//将图表视图与图表进行绑定
chartView->setChart(chart);
//添加坐标系
QValueAxis *axisX = new QValueAxis(this);
QValueAxis *axisY = new QValueAxis(this);
//刻度范围
axisX->setRange(0, 100);
axisY->setRange(0, 50);
//分度
axisX->setTickCount(10);
axisY->setTickCount(5);
//含义
axisX->setTitleText("刻度");
//把坐标系与图表绑定
chart->addAxis(axisX, Qt::AlignBottom);
chart->addAxis(axisY, Qt::AlignRight);
/* 2、图表配置与数据展示 */
QLineSeries *lineSeries = new QLineSeries(this);
QScatterSeries *rectSeries = new QScatterSeries(this);
QScatterSeries *circleSeries = new QScatterSeries(this);
circleSeries->setMarkerShape(QScatterSeries::MarkerShapeCircle);
rectSeries->setMarkerShape(QScatterSeries::MarkerShapeRectangle);
//配置与图表绑定
chart->addSeries(lineSeries);
chart->addSeries(circleSeries);
chart->addSeries(rectSeries);
//配置与坐标系绑定
lineSeries->attachAxis(axisX);
lineSeries->attachAxis(axisY);
circleSeries->attachAxis(axisX);
circleSeries->attachAxis(axisY);
rectSeries->attachAxis(axisX);
rectSeries->attachAxis(axisY);
*lineSeries << QPoint(10, 0) << QPoint(20, 10) << QPoint(30, 20);
*circleSeries << QPoint(10, 0) << QPoint(20, 10) << QPoint(30, 20);
*rectSeries << QPoint(10, 0) << QPoint(20, 10) << QPoint(30, 20);
/*3、实现数据的实时刷新*/
QTimer *timer = new QTimer(this);
static int i= 0;
connect(timer, &QTimer::timeout, this, [=](){
*lineSeries << QPoint(i, rand() % 50);
if (i > 100) {
chart->scroll(40, 0);
}
chart->scroll(40, 0);
i += 20;
});
timer->start(500);
/* 极坐标系图的创建 QPolarChart */
//进行布局
QHBoxLayout *layout = new QHBoxLayout(this);
layout->addWidget(chartView);
this->setLayout(layout);
}
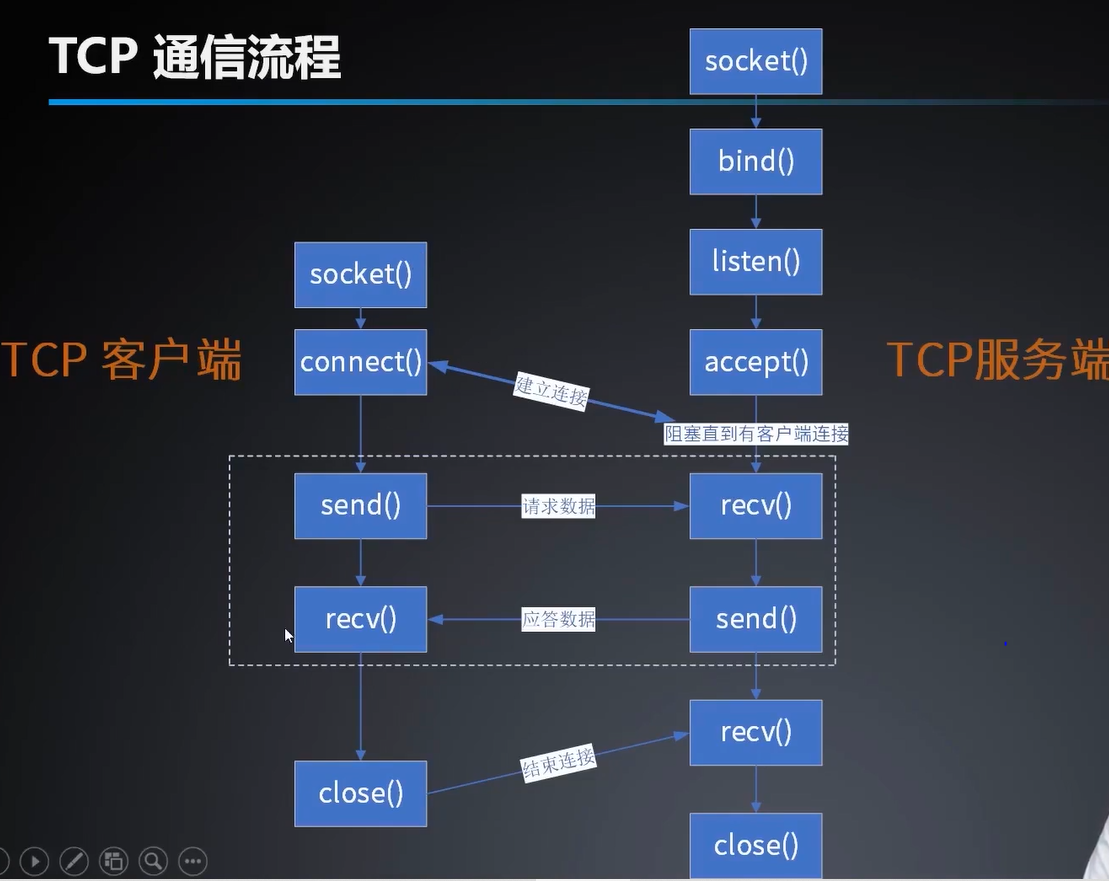
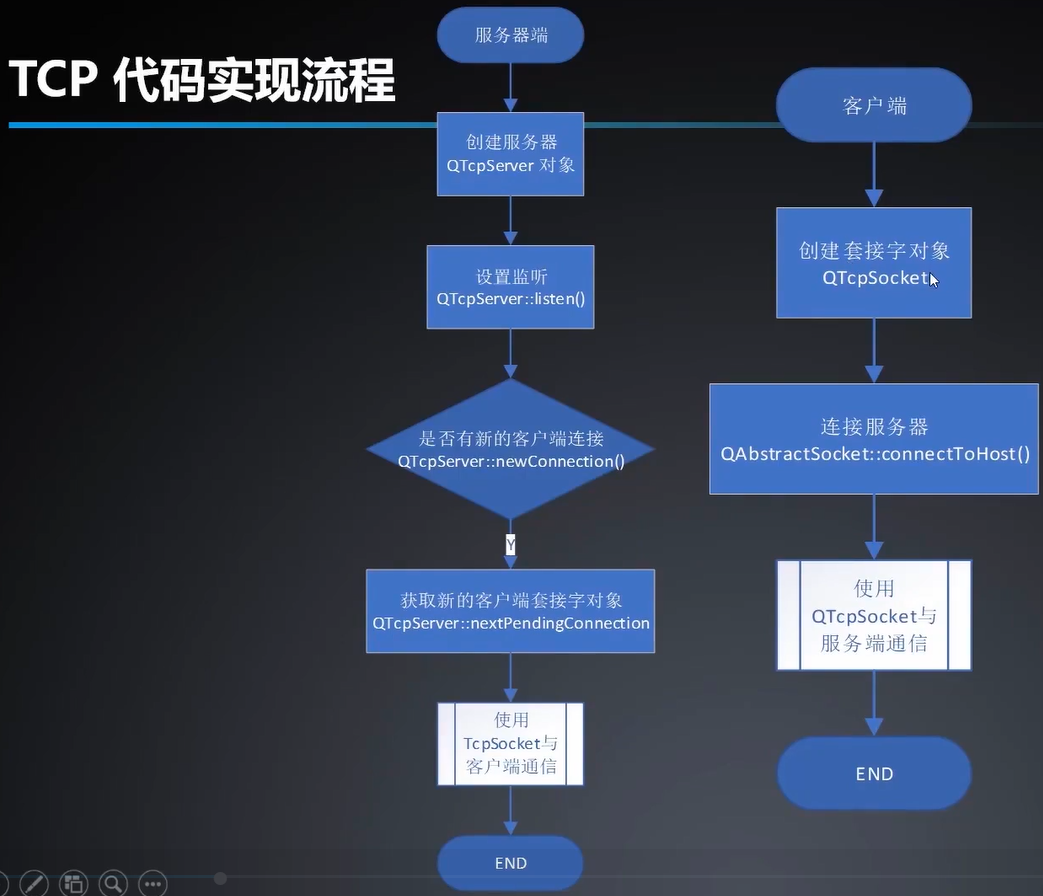
网络通信之TCP
TCP :传输控制协议面向连接,可靠的数据传输协议
UDP:用户数据报协议无连接,不可靠的数据传输协议
#include "networkwidget.h"
#include "ui_networkwidget.h"
NetWorkWidget::NetWorkWidget(QWidget *parent)
: QWidget(parent)
, ui(new Ui::NetWorkWidget)
{
ui->setupUi(this);
/*
* 网路通信是一个独立模块,需要安装对应版本的network 模块
*
*
*/
//对TCP客户端进行初始化
//initTcpClient();
//对TCP服务端进行初始化
initTcpServer();
}
NetWorkWidget::~NetWorkWidget()
{
delete ui;
}
void NetWorkWidget::initTcpClient() {
//创建套接字
QTcpSocket *socket = new QTcpSocket();
//连接服务器 127.0.0.1 回送地址, 一般作为测试使用
socket->connectToHost("127.0.0.1", 4884);
//读取数据
connect(socket, &QTcpSocket::readyRead, this, [=](){
//QByteAarry 字节数组
//QString
buffer = socket->readAll();
qDebug() << "接受数据" << buffer;
//QByteAarry 转换成QString
QString str = QString(buffer).toUtf8();
//显示到接受区域
ui->recvEdit->setText(str);
});
//发送数据
connect(ui->sendButton, &QPushButton::clicked, this, [=](){
QString buffer = ui->sentEdit->toPlainText();
qDebug() << "发送数据" << buffer;
// 通过套接字写数据
socket->write(buffer.toUtf8());
});
}
void NetWorkWidget::initTcpServer() {
// 创建服务端对象
QTcpServer *server = new QTcpServer(this);
//创建套接字对象
QTcpSocket *socket = new QTcpSocket(this);
//设置监听IP PORT
server->listen(QHostAddress::Any, 4000);
//监测是否客户端连接
connect(server, &QTcpServer::newConnection, this, [=, &socket](){
//获取客户端ID
socket = server->nextPendingConnection();
qDebug() << "发送数据ID" << socket;
//读取数据
connect(socket, &QTcpSocket::readyRead, this, [=](){
//QByteAarry 字节数组
//QString
buffer = socket->readAll();
qDebug() << "接受数据" << buffer;
//QByteAarry 转换成QString
QString str = QString(buffer).toUtf8();
//显示到接受区域
ui->recvEdit->setText(str);
});
//发送数据
connect(ui->sendButton, &QPushButton::clicked, this, [=](){
QString buffer = ui->sentEdit->toPlainText();
qDebug() << "发送数据" << buffer;
// 通过套接字写数据
socket->write(buffer.toUtf8());
});
});
}
网络通信之UDP
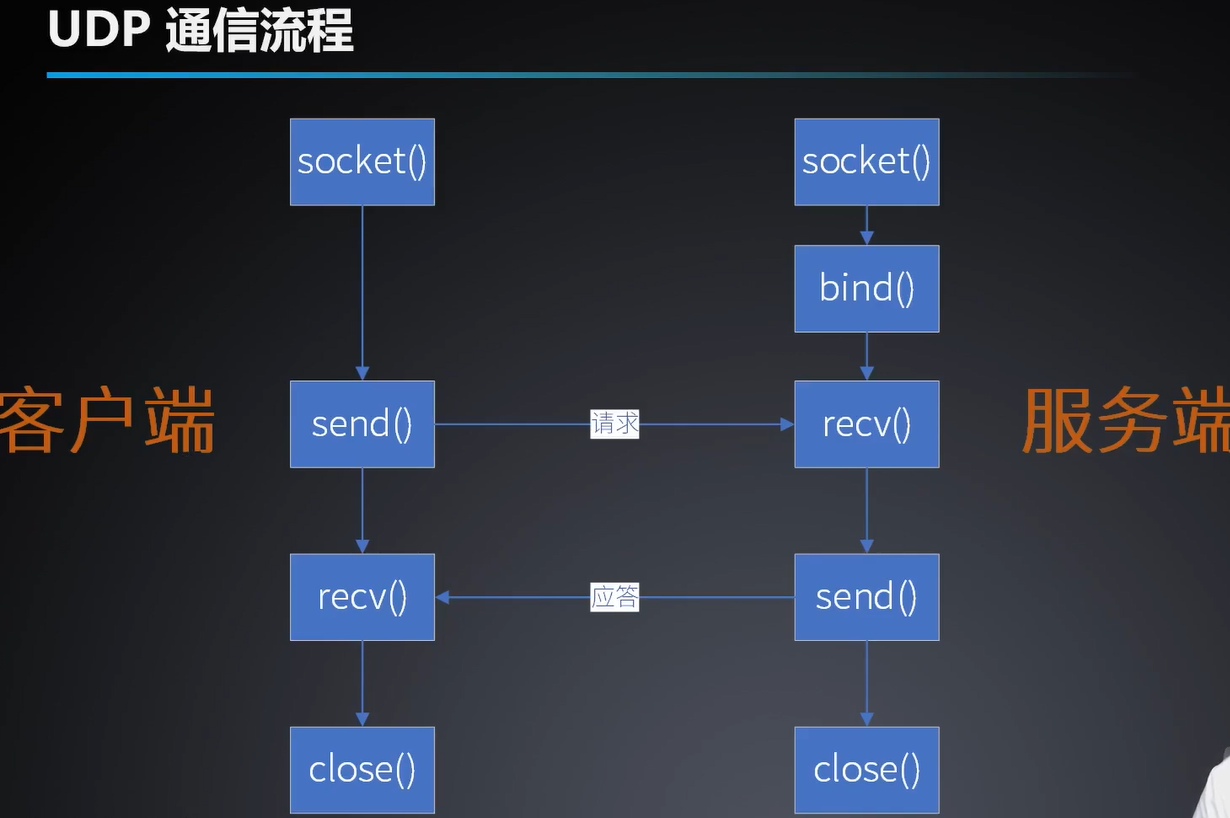
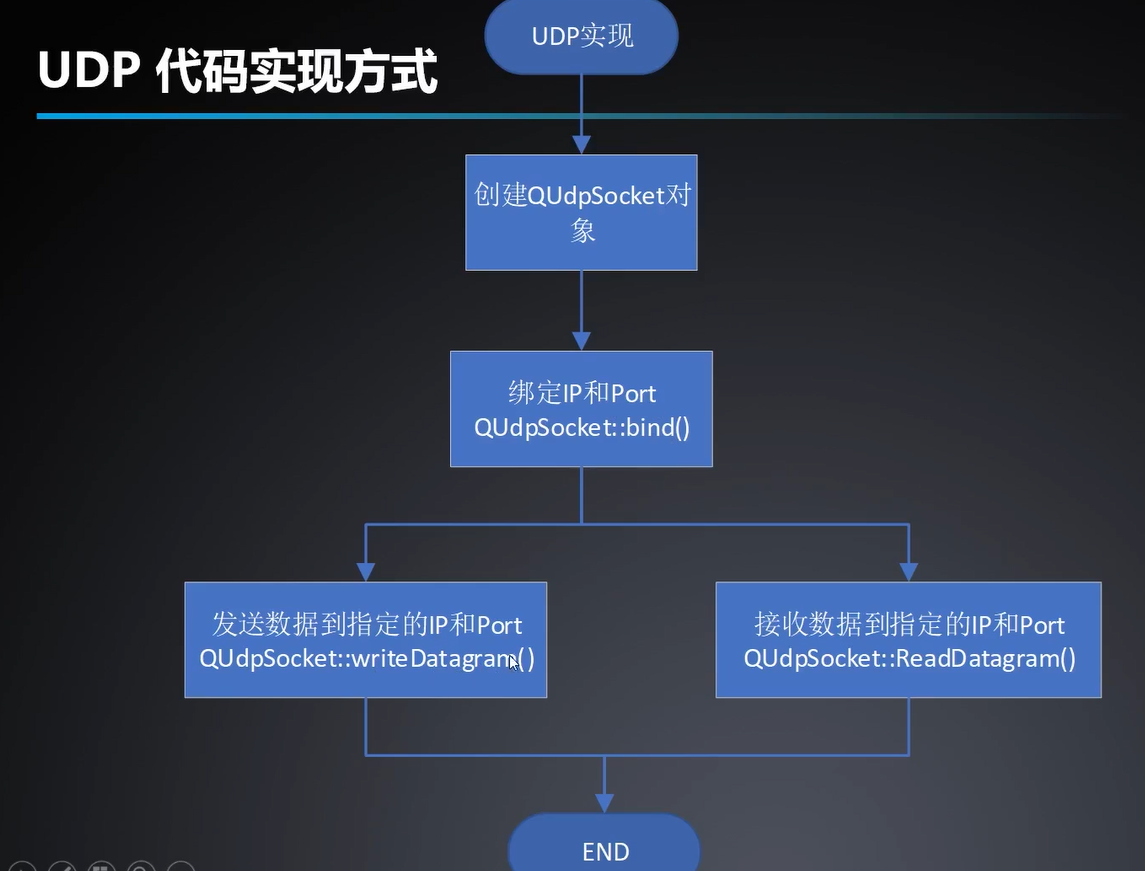
void NetWorkWidget::initUdpServer() {
QUdpSocket *socket = new QUdpSocket(this);
socket->bind(QHostAddress("127.0.0.1"), 6320);
//接受数据
connect(socket, &QUdpSocket::readyRead, this, [=](){
QByteArray buffer;
QHostAddress addr;
//0~65535
quint16 port;
buffer.resize(socket->bytesAvailable());
socket->readDatagram(buffer.data(), buffer.size(), &addr, &port);
qDebug() << "接受数据:" << buffer;
QString str = QString(buffer).toUtf8();
//
ui->recvEdit->setText(str);
});
//发送数据
connect(ui->sendButton, &QPushButton::clicked, this, [=](){
QString buffer = ui->sentEdit->toPlainText();
qDebug() << "发送数据" << buffer;
// 通过套接字写数据
socket->writeDatagram(buffer.toUtf8(), QHostAddress("127.0.0.1"), 1000);
});
}
Qt中多线程处理
线程是操作系统调度器可调度的最小执行单元
对应Qt来说,每次出现启动都有一个线程,称之为GUI(主)线程
线程处理实现方式
方式一:创建一个类,继承于QThread类,重写run函数
方式二:创建一个类,继承QObject类,将此类移动到线程中运行
线程处理代码实现方式(一)
/* 1、创建一个子类,继承于QThread*/
class MyThread : public QThread {
// ...
}
/* 2、重写父类中的run()办法,该函数主要实现要处理的复杂业务逻辑 */
class MyThread : public QThread {
protected:
void run();
}
/* 3、在主线程中创建一个子线程对象 */
MyThread *myThread = new MyThread(this);
/* 4、启动子线程 */
myThread->start();
子线程(创建一个子类):
#include "threadwidget.h"
#include <QDebug>
ThreadWidget::ThreadWidget(QObject *parent) : QThread(parent)
{
}
/**
* @brief 子线程的程序入口
* 注意:子线程没办法直接访问界面部件类, connect、QOject、QTcpsocket可以使用
*/
void ThreadWidget::run() {
qDebug() << "子线程ID" <<QThread::currentThreadId();
//模拟复杂数据处理
QThread::sleep(5);
emit isDone();
}
主线程
#include "thread.h"
#include "ui_thread.h"
#include <QTimer>
#include <QThread>
#include "threadwidget.h"
#include <QDebug>
Thread::Thread(QWidget *parent)
: QWidget(parent)
, ui(new Ui::Thread)
{
ui->setupUi(this);
this->setFixedSize(600, 400);
QTimer *time = new QTimer(this);
//创建线程对象
ThreadWidget *thread = new ThreadWidget(this);
static int i = 0;
connect(time, &QTimer::timeout, this, [=](){
ui->label->setNum(i);
i++;
});
connect(ui->pushButton, &QPushButton::clicked, this, [=](){
if (!time->isActive()) {
time->start(500);
//开启子线程
thread->start();
}
qDebug() << "主线程ID " << QThread::currentThreadId();
});
connect(thread, &ThreadWidget::isDone, this, [=](){
if (time->isActive()) {
time->stop();
}
});
connect(this, &QWidget::destroyed, this, [=](){
//等待子线程处理完成之后,才能够退出
thread->quit();
thread->wait();
});
}
Thread::~Thread()
{
delete ui;
}
线程处理代码实现方式(二)
/* 1、创建一个类,继承于QObject */
class MyThread : public QObject {
// ...
}
/* 2、在此类中添加公共的成员函数,此函数题就是要执行的业务逻辑 */
class MyThread : public QObject {
public:
void handler();
}
/* 3、在主线程中创建一个QThread 对象 */
QThread *sub = new QThread(this);
/* 4、在主线程中创建一个工作对象,不允许指定父对象 */
MyThread *work = new MyThread;
/* 5、将创建好的sub 对象移动到work对象中 */
work->moveToThread(sub);
/* 6、启动子线程,还需调用handler函数,才能运行work线程 */
sub->start();
connect(this, &Widget::startThread, work, &MyThread::fun, Qt::QueueConnection);
子线程类
#include "mythread.h"
#include <QThread>
#include <QDebug>
MyThread::MyThread(QObject *parent)
: QObject{parent}
{
qDebug() << "ID" <<QThread::currentThreadId();
}
/**
* @brief 子线程的复杂数据处理
*/
void MyThread::handler() {
//处理复杂数据,经过5s的时间
QThread::sleep(5);
qDebug() << "子线程ID" <<QThread::currentThreadId();
// 通过信号与槽机制完成通讯
}
主线程类:
#include "threadwidget.h"
#include "ui_threadwidget.h"
#include <QThread>
#include "mythread.h"
#include <QTimer>
#include <QDebug>
ThreadWidget::ThreadWidget(QWidget *parent)
: QWidget(parent)
, ui(new Ui::ThreadWidget)
{
ui->setupUi(this);
this->setFixedSize(600, 400);
QTimer *time = new QTimer(this);
//创建线程对象
static int i = 0;
connect(time, &QTimer::timeout, this, [=](){
ui->label->setNum(i);
i++;
});
// 创建 sub 对象
QThread *sub = new QThread(this);
//创建工作对象,不能指定父对象
MyThread *work = new MyThread;
//把 sub 移动到work中
//线程池
work->moveToThread(sub);
connect(ui->pushButton, &QPushButton::clicked, this, [=](){
if (!time->isActive()) {
time->start(500);
//开启子线程
sub->start();
emit startThread();
}
qDebug() << "主线程ID " << QThread::currentThreadId();
});
connect(this, &ThreadWidget::startThread, work, &MyThread::handler);
connect(this, &QWidget::destroyed, this, [=](){
//等待子线程处理完成之后,才能够退出
sub->quit();
sub->wait();
});
}








![[算法]计数排序和基数排序](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/6b35d818ace64ef09ea555075d06503f.png)