什么是全局状态共享?
常规B端项目中往往需要一些全局通用的状态来实现跨组件层级甚至整个系统全局的共享,比如:当前用户的信息、某些业务状态等。
都有什么解决方案?
业内常规的成熟方案一般有:mobx、redux等专门的全局状态管理库,相对而言基本可以覆盖支持所有的复杂业务场景,再也就简单粗暴通过多个Context嵌套来实现共享。
多层Context嵌套这种‘太粗暴’的方案基本上就不要考虑了qwq,但对于一些状态逻辑相对单一且通过服务端获取以后不需要长链路复杂处理共享的状态来讲其实是引入专门的库是没有太大必要的。拿redux为例,在react中使用需要引入react-redux来配合处理异步状态还需要redux-thunk或者redux-saga等类似中间件,然后自己定义和管理action和reducer的处理逻辑,整体来讲是比较繁重的。(当然redux中间件的洋葱模型设计一定程度上为用户提供了规范的自定义通用状态处理逻辑的方案是非常优秀的,尤其在复杂业务状态数据处理场景上)。
我们可以怎么做?
但是嘞~当我们状态很简单,比如我就要存一下当前用户信息,跨组件全局状态联动很少等等(很多情况就是一个地方初始化某个状态以后就在各个地方读就好了)没有其他操作,而恰恰我们的项目又是支持React Hooks的,那我们就有了简单是实现方案。本质全局状态存储的原理还是基于React自带的Context来实现的。

首先我们要知道的是,当通过Context做全局状态存储时,一旦其value改变,那么对应依赖其value值的组件将重新的渲染,所以当我们使用同一个Context存储所有全局状态时,就不得不考虑来避免更新某个值而造成所有依赖其value组件重新渲染的扯淡行为。由此我们便需要保证value值或者其引用地址不变。便可以借助useRef来实现。
import React, { useRef } from 'react';
interface PropsType {}
export const GlobalStoreContext = React.createContext<{
[x: string]: any
}>({});
const GlobalStore: React.FC<PropsType> = (props) => {
/**
* 通过ref保证同一份引用,使context的value不变,避免由context value改变导致所有依赖组件更新
*/
const contextValue = useRef<any>({});
return (
<GlobalStoreContext.Provider
value={contextValue.current}
>
{props.children}
</GlobalStoreContext.Provider>
);
};
export default GlobalStore;
避免更新解决了,但是现在彻底不更新了,然后要考虑怎么做到按需触发相关组件触发。问题便成为了常规的按需触发某些回调的更新机制,由此便可以考虑到发布-订阅模式(redux也是基于类似原理实现的)。同时借助useReducer来实现数据定义及更新。考虑到对象的某个值改变同时要生成一个新的对象来触发’中心发布’引入了immutable。
import React, { useLayoutEffect, useReducer, useRef } from 'react';
import Store from './Store';
import {fromJS} from 'immutable'
interface PropsType {}
+ const initialState = fromJS({});
+ function reducer(state: Immutable.Map<string, any>, action: {key: string, value: any}) {
+ if (action?.key) {
+ return state.set(action.key, action.value);
+ }
+ return state;
+ }
export const GlobalStoreContext = React.createContext<{
state: Immutable.Map<string, any>,
dispatch: React.Dispatch<{
key: string;
value: any;
}>,
listeners?: Set<(v: {[x: string]: any}) => void>,
[x: string]: any
}>({
state: fromJS({}),
dispatch: () => {}
});
const GlobalStore: React.FC<PropsType> = (props) => {
+ const [state, dispatch] = useReducer(reducer, initialState);
/**
* 通过ref保证同一份引用,使context的value不变,避免由context value改变导致所有依赖组件更新
*/
const contextValue = useRef<any>({
+ state,
+ dispatch: dispatch || (() => {}),
// 订阅回调,Set结构避免重复订阅
+ listeners: new Set()
});
// '订阅中心-处理发布'
+ useLayoutEffect(() => {
+ contextValue.current.state = state;
+ contextValue.current?.listeners?.forEach((l: (v: any) => void) => l(state));
+ }, [state]);
return (
<GlobalStoreContext.Provider
value={contextValue.current}
>
{props.children}
</GlobalStoreContext.Provider>
);
};
export default GlobalStore;
至此,数据存储更新的功能有了,中心发布能力也具备了,还差对外提供状态值以及订阅能力。这一层可以借助自定义的hooks来实现,通过useState来做依赖业务组件的状态中间存储,来触发业务组件的更新,为了避免无效的更新我们通过Object.is来判断值的更新情况。通过useLayoutEffect来做初始化的订阅工作。
import { useCallback, useContext, useLayoutEffect, useState } from 'react';
import { GlobalStoreContext } from '.';
/**
*
* @param 监听:key
* @returns
*/
export const useStore = (key: string) => {
const { state, dispatch, listeners } = useContext(GlobalStoreContext);
const [value, setValue] = useState<any>(state.get(key));
const listener = useCallback((state: {[x: string]: any}) => {
// 判断是否需要更新
if(!Object.is(value, state.get(key))) {
setValue(state.get(key));
}
}, [value])
useLayoutEffect(() => {
// console.log('添加 listener', key);
listeners?.add(listener);
// 添加监听时先执行一遍获取当前状态值
listener(state);
return () => {
// console.log('移除 listener', key);
listeners?.delete(listener)
}
}, [listener])
const updateValue = useCallback(
(v: any) => {
dispatch({
key,
value: v,
});
},
[key, dispatch],
);
return [value, updateValue];
};
/**
* 本着专一的原则,获取单次更新但各个值的更新方法,
* 当然也可以根据自己的习惯,通过变通 reducer的处理逻辑
* 自己定义dispatch逻辑
* @returns
*/
export const useStoreDispatch = () => {
const { dispatch } = useContext(GlobalStoreContext);
const update = useCallback(
(key: string, v: any) => {
dispatch({
key,
value: v,
});
},
[dispatch],
);
return [update];
};
100多行代码,一个简单的全局状态管理机制就实现了。
要怎么用?
东西有了,用起来就比较简单了。
wrap.tsx
import React from 'react';
import Store from './store';
interface PropsType {}
const Wrap: React.FC<PropsType> = props => {
return (
<GlobalStore>
<Store></Store>
</GlobalStore>
)
}
export default Wrap;
store.tsx
import React, { useEffect } from 'react';
import { useStoreDispatch } from './use-store';
import Detail1 from '../detail';
import Detail2 from '../detail2';
interface PropsType {}
/**
* 这一层可用于初始化全局数据
* @param props
* @returns
*/
const Store: React.FC<PropsType> = (props) => {
const [dispatchStore] = useStoreDispatch();
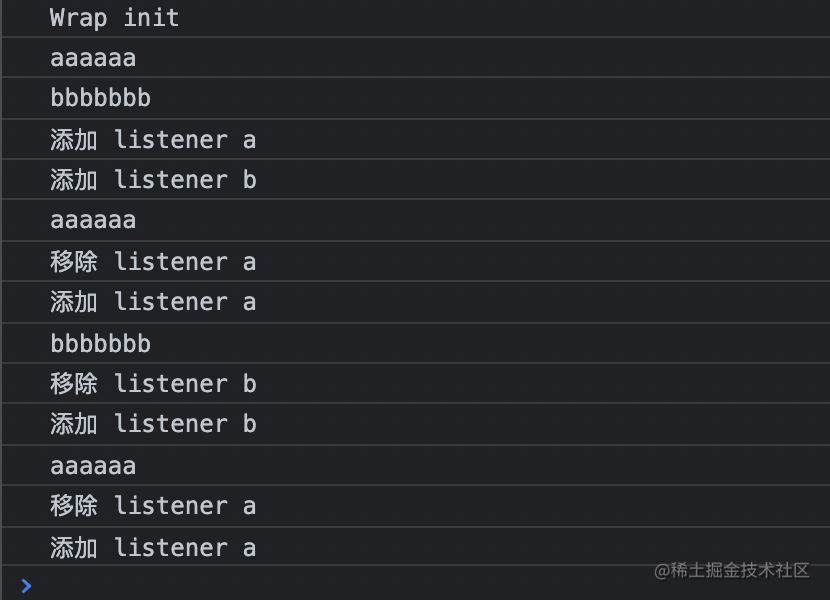
useEffect(() => {
dispatchStore('a', 111111);
dispatchStore('b', 222222);
setTimeout(() => {
dispatchStore('a', 'aaaaaaa');
}, 5000);
setTimeout(() => {
dispatchStore('b', 'bbbbb');
}, 7000);
setTimeout(() => {
dispatchStore('a', 'aaaaaaa111');
}, 10000);
}, [ dispatchStore]);
return (
<>
<Detail1/>
<Detail2/>
</>
);
};
export default Store;
detail.tsx
import { useStore } from "@/components/global-store/use-store";
function Detail1() {
const [a, updateA] = useStore('a');
return (
<div>
{
(() => {
console.log('aaaaaa');
return (
<h1>{a}</h1>
)
})()
}
</div>
)
}
export default Detail1;
detail2.tsx
import { useStore } from "@/components/global-store/use-store";
function Detail1() {
const [b] = useStore('b');
return (
<div>
{
(() => {
console.log('bbbbbbb');
return (
<h1>{b}</h1>
)
})()
}
</div>
)
}
export default Detail1;
执行结果记录:
END…