核心 Android 系统提供的调节音量的方法
核心 Android 系统提供了多种调节音量的方法,这些方法主要包括如下这些。
- 如在 Android Automotive 调节音量的过程 中我们看到的,
CarAudioService最终在CarAudioDeviceInfo中 (packages/services/Car/service/src/com/android/car/audio/CarAudioDeviceInfo.java) 通过AudioManager直接为设备设置音量:
// Input is in millibels
void setCurrentGain(int gainInMillibels) {
// Clamp the incoming value to our valid range. Out of range values ARE legal input
if (gainInMillibels < mMinGain) {
gainInMillibels = mMinGain;
} else if (gainInMillibels > mMaxGain) {
gainInMillibels = mMaxGain;
}
// Push the new gain value down to our underlying port which will cause it to show up
// at the HAL.
AudioGain audioGain = getAudioGain();
if (audioGain == null) {
Slog.e(CarLog.TAG_AUDIO, "getAudioGain() returned null.");
return;
}
// size of gain values is 1 in MODE_JOINT
AudioGainConfig audioGainConfig = audioGain.buildConfig(
AudioGain.MODE_JOINT,
audioGain.channelMask(),
new int[] { gainInMillibels },
0);
if (audioGainConfig == null) {
Slog.e(CarLog.TAG_AUDIO, "Failed to construct AudioGainConfig");
return;
}
int r = AudioManager.setAudioPortGain(getAudioDevicePort(), audioGainConfig);
if (r == AudioManager.SUCCESS) {
// Since we can't query for the gain on a device port later,
// we have to remember what we asked for
mCurrentGain = gainInMillibels;
} else {
Slog.e(CarLog.TAG_AUDIO, "Failed to setAudioPortGain: " + r);
}
}
这里看到的 AudioManager 的 setAudioPortGain(getAudioDevicePort(), audioGainConfig) 方法可以用于调节特定设备的音量,在 AudioManager 中,这个方法的实现 (frameworks/base/media/java/android/media/AudioManager.java) 为:
/**
* Set the gain on the specified AudioPort. The AudioGainConfig config is build by
* AudioGain.buildConfig()
* @hide
*/
public static int setAudioPortGain(AudioPort port, AudioGainConfig gain) {
if (port == null || gain == null) {
return ERROR_BAD_VALUE;
}
AudioPortConfig activeConfig = port.activeConfig();
AudioPortConfig config = new AudioPortConfig(port, activeConfig.samplingRate(),
activeConfig.channelMask(), activeConfig.format(), gain);
config.mConfigMask = AudioPortConfig.GAIN;
return AudioSystem.setAudioPortConfig(config);
}
AudioManager 的 setAudioPortGain(getAudioDevicePort(), audioGainConfig) 方法通过 AudioSystem 的静态方法 setAudioPortConfig(config) 来给设备设置音量,AudioSystem.setAudioPortConfig(config) 是一个在 frameworks/base/media/java/android/media/AudioSystem.java 中声明,并最终在 frameworks/base/core/jni/android_media_AudioSystem.cpp 中定义的 JNI 本地层方法:
static jint
android_media_AudioSystem_setAudioPortConfig(JNIEnv *env, jobject clazz,
jobject jAudioPortConfig)
{
ALOGV("setAudioPortConfig");
if (jAudioPortConfig == NULL) {
return AUDIO_JAVA_BAD_VALUE;
}
if (!env->IsInstanceOf(jAudioPortConfig, gAudioPortConfigClass)) {
return AUDIO_JAVA_BAD_VALUE;
}
struct audio_port_config nAudioPortConfig = {};
jint jStatus = convertAudioPortConfigToNative(env, &nAudioPortConfig, jAudioPortConfig, true);
if (jStatus != AUDIO_JAVA_SUCCESS) {
return jStatus;
}
status_t status = AudioSystem::setAudioPortConfig(&nAudioPortConfig);
ALOGV("AudioSystem::setAudioPortConfig() returned %d", status);
jStatus = nativeToJavaStatus(status);
return jStatus;
}
- App 可以通过
AudioManager调节某个STREAM_TYPE的音量,如:
private boolean setStreamVolume(int volume) {
Logging.d(TAG, "setStreamVolume(" + volume + ")");
assertTrue(audioManager != null);
if (isVolumeFixed()) {
Logging.e(TAG, "The device implements a fixed volume policy.");
return false;
}
audioManager.setStreamVolume(AudioManager.STREAM_VOICE_CALL, volume, 0);
return true;
}
这里看到的 setStreamVolume() 方法在 AudioManager 中的实现如下:
/**
* Sets the volume index for a particular stream.
* <p>This method has no effect if the device implements a fixed volume policy
* as indicated by {@link #isVolumeFixed()}.
* <p>From N onward, volume adjustments that would toggle Do Not Disturb are not allowed unless
* the app has been granted Do Not Disturb Access.
* See {@link NotificationManager#isNotificationPolicyAccessGranted()}.
* @param streamType The stream whose volume index should be set.
* @param index The volume index to set. See
* {@link #getStreamMaxVolume(int)} for the largest valid value.
* @param flags One or more flags.
* @see #getStreamMaxVolume(int)
* @see #getStreamVolume(int)
* @see #isVolumeFixed()
* @throws SecurityException if the volume change triggers a Do Not Disturb change
* and the caller is not granted notification policy access.
*/
public void setStreamVolume(int streamType, int index, int flags) {
final IAudioService service = getService();
try {
service.setStreamVolume(streamType, index, flags, getContext().getOpPackageName());
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
}
AudioManager中单步地调大或者调小特定流类型的adjustStreamVolume():
/**
* Adjusts the volume of a particular stream by one step in a direction.
* <p>
* This method should only be used by applications that replace the platform-wide
* management of audio settings or the main telephony application.
* <p>This method has no effect if the device implements a fixed volume policy
* as indicated by {@link #isVolumeFixed()}.
* <p>From N onward, ringer mode adjustments that would toggle Do Not Disturb are not allowed
* unless the app has been granted Do Not Disturb Access.
* See {@link NotificationManager#isNotificationPolicyAccessGranted()}.
*
* @param streamType The stream type to adjust. One of {@link #STREAM_VOICE_CALL},
* {@link #STREAM_SYSTEM}, {@link #STREAM_RING}, {@link #STREAM_MUSIC},
* {@link #STREAM_ALARM} or {@link #STREAM_ACCESSIBILITY}.
* @param direction The direction to adjust the volume. One of
* {@link #ADJUST_LOWER}, {@link #ADJUST_RAISE}, or
* {@link #ADJUST_SAME}.
* @param flags One or more flags.
* @see #adjustVolume(int, int)
* @see #setStreamVolume(int, int, int)
* @throws SecurityException if the adjustment triggers a Do Not Disturb change
* and the caller is not granted notification policy access.
*/
public void adjustStreamVolume(int streamType, int direction, int flags) {
final IAudioService service = getService();
try {
service.adjustStreamVolume(streamType, direction, flags,
getContext().getOpPackageName());
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
}
AudioManager中调节最相关的流的音量的adjustVolume()和adjustSuggestedStreamVolume():
/**
* Adjusts the volume of the most relevant stream. For example, if a call is
* active, it will have the highest priority regardless of if the in-call
* screen is showing. Another example, if music is playing in the background
* and a call is not active, the music stream will be adjusted.
* <p>
* This method should only be used by applications that replace the
* platform-wide management of audio settings or the main telephony
* application.
* <p>
* This method has no effect if the device implements a fixed volume policy
* as indicated by {@link #isVolumeFixed()}.
*
* @param direction The direction to adjust the volume. One of
* {@link #ADJUST_LOWER}, {@link #ADJUST_RAISE},
* {@link #ADJUST_SAME}, {@link #ADJUST_MUTE},
* {@link #ADJUST_UNMUTE}, or {@link #ADJUST_TOGGLE_MUTE}.
* @param flags One or more flags.
* @see #adjustSuggestedStreamVolume(int, int, int)
* @see #adjustStreamVolume(int, int, int)
* @see #setStreamVolume(int, int, int)
* @see #isVolumeFixed()
*/
public void adjustVolume(int direction, int flags) {
MediaSessionLegacyHelper helper = MediaSessionLegacyHelper.getHelper(getContext());
helper.sendAdjustVolumeBy(USE_DEFAULT_STREAM_TYPE, direction, flags);
}
/**
* Adjusts the volume of the most relevant stream, or the given fallback
* stream.
* <p>
* This method should only be used by applications that replace the
* platform-wide management of audio settings or the main telephony
* application.
* <p>
* This method has no effect if the device implements a fixed volume policy
* as indicated by {@link #isVolumeFixed()}.
*
* @param direction The direction to adjust the volume. One of
* {@link #ADJUST_LOWER}, {@link #ADJUST_RAISE},
* {@link #ADJUST_SAME}, {@link #ADJUST_MUTE},
* {@link #ADJUST_UNMUTE}, or {@link #ADJUST_TOGGLE_MUTE}.
* @param suggestedStreamType The stream type that will be used if there
* isn't a relevant stream. {@link #USE_DEFAULT_STREAM_TYPE} is
* valid here.
* @param flags One or more flags.
* @see #adjustVolume(int, int)
* @see #adjustStreamVolume(int, int, int)
* @see #setStreamVolume(int, int, int)
* @see #isVolumeFixed()
*/
public void adjustSuggestedStreamVolume(int direction, int suggestedStreamType, int flags) {
MediaSessionLegacyHelper helper = MediaSessionLegacyHelper.getHelper(getContext());
helper.sendAdjustVolumeBy(suggestedStreamType, direction, flags);
}
这两个方法最终通过 media session 服务调节音量 (frameworks/base/media/java/android/media/session/MediaSessionLegacyHelper.java) :
private MediaSessionLegacyHelper(Context context) {
mContext = context;
mSessionManager = (MediaSessionManager) context
.getSystemService(Context.MEDIA_SESSION_SERVICE);
}
public void sendAdjustVolumeBy(int suggestedStream, int delta, int flags) {
mSessionManager.dispatchAdjustVolume(suggestedStream, delta, flags);
if (DEBUG) {
Log.d(TAG, "dispatched volume adjustment");
}
}
AudioManager中为特定AudioAttributes设置音量的setVolumeIndexForAttributes()。
/**
* Sets the volume index for a particular {@link AudioAttributes}.
* @param attr The {@link AudioAttributes} whose volume index should be set.
* @param index The volume index to set. See
* {@link #getMaxVolumeIndexForAttributes(AudioAttributes)} for the largest valid value
* {@link #getMinVolumeIndexForAttributes(AudioAttributes)} for the lowest valid value.
* @param flags One or more flags.
* @see #getMaxVolumeIndexForAttributes(AudioAttributes)
* @see #getMinVolumeIndexForAttributes(AudioAttributes)
* @see #isVolumeFixed()
* @hide
*/
@SystemApi
@RequiresPermission(android.Manifest.permission.MODIFY_AUDIO_ROUTING)
public void setVolumeIndexForAttributes(@NonNull AudioAttributes attr, int index, int flags) {
Preconditions.checkNotNull(attr, "attr must not be null");
final IAudioService service = getService();
try {
service.setVolumeIndexForAttributes(attr, index, flags,
getContext().getOpPackageName());
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
}
AudioManager中调节最相关流的音量,且会基于所提供的组件名、uid 和 pid 值检查调用者是否有必要权限的adjustSuggestedStreamVolumeForUid()。
/**
* Adjusts the volume of the most relevant stream, or the given fallback
* stream.
* <p>
* This method should only be used by applications that replace the
* platform-wide management of audio settings or the main telephony
* application.
* <p>
* This method has no effect if the device implements a fixed volume policy
* as indicated by {@link #isVolumeFixed()}.
* <p>This API checks if the caller has the necessary permissions based on the provided
* component name, uid, and pid values.
* See {@link #adjustSuggestedStreamVolume(int, int, int)}.
*
* @param suggestedStreamType The stream type that will be used if there
* isn't a relevant stream. {@link #USE_DEFAULT_STREAM_TYPE} is
* valid here.
* @param direction The direction to adjust the volume. One of
* {@link #ADJUST_LOWER}, {@link #ADJUST_RAISE},
* {@link #ADJUST_SAME}, {@link #ADJUST_MUTE},
* {@link #ADJUST_UNMUTE}, or {@link #ADJUST_TOGGLE_MUTE}.
* @param flags One or more flags.
* @param packageName the package name of client application
* @param uid the uid of client application
* @param pid the pid of client application
* @param targetSdkVersion the target sdk version of client application
* @see #adjustVolume(int, int)
* @see #adjustStreamVolume(int, int, int)
* @see #setStreamVolume(int, int, int)
* @see #isVolumeFixed()
*
* @hide
*/
@SystemApi(client = SystemApi.Client.MODULE_LIBRARIES)
public void adjustSuggestedStreamVolumeForUid(int suggestedStreamType, int direction, int flags,
@NonNull String packageName, int uid, int pid, int targetSdkVersion) {
try {
getService().adjustSuggestedStreamVolumeForUid(suggestedStreamType, direction, flags,
packageName, uid, pid, UserHandle.getUserHandleForUid(uid), targetSdkVersion);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
}
AudioManager中单步地调大或者调小特定流类型的音量,且会基于所提供的组件名、uid 和 pid 值检查调用者是否有必要权限的adjustStreamVolumeForUid():
/**
* Adjusts the volume of a particular stream by one step in a direction.
* <p>
* This method should only be used by applications that replace the platform-wide
* management of audio settings or the main telephony application.
* <p>This method has no effect if the device implements a fixed volume policy
* as indicated by {@link #isVolumeFixed()}.
* <p>From N onward, ringer mode adjustments that would toggle Do Not Disturb are not allowed
* unless the app has been granted Do Not Disturb Access.
* See {@link NotificationManager#isNotificationPolicyAccessGranted()}.
* <p>This API checks if the caller has the necessary permissions based on the provided
* component name, uid, and pid values.
* See {@link #adjustStreamVolume(int, int, int)}.
*
* @param streamType The stream type to adjust. One of {@link #STREAM_VOICE_CALL},
* {@link #STREAM_SYSTEM}, {@link #STREAM_RING}, {@link #STREAM_MUSIC},
* {@link #STREAM_ALARM} or {@link #STREAM_ACCESSIBILITY}.
* @param direction The direction to adjust the volume. One of
* {@link #ADJUST_LOWER}, {@link #ADJUST_RAISE}, or
* {@link #ADJUST_SAME}.
* @param flags One or more flags.
* @param packageName the package name of client application
* @param uid the uid of client application
* @param pid the pid of client application
* @param targetSdkVersion the target sdk version of client application
* @see #adjustVolume(int, int)
* @see #setStreamVolume(int, int, int)
* @throws SecurityException if the adjustment triggers a Do Not Disturb change
* and the caller is not granted notification policy access.
*
* @hide
*/
@SystemApi(client = SystemApi.Client.MODULE_LIBRARIES)
public void adjustStreamVolumeForUid(int streamType, int direction, int flags,
@NonNull String packageName, int uid, int pid, int targetSdkVersion) {
try {
getService().adjustStreamVolumeForUid(streamType, direction, flags, packageName, uid,
pid, UserHandle.getUserHandleForUid(uid), targetSdkVersion);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
}
AudioManager中调节某个STREAM_TYPE的音量,且会基于所提供的组件名、uid 和 pid 值检查调用者是否有必要权限的setStreamVolumeForUid():
/**
* Sets the volume index for a particular stream.
* <p>This method has no effect if the device implements a fixed volume policy
* as indicated by {@link #isVolumeFixed()}.
* <p>From N onward, volume adjustments that would toggle Do Not Disturb are not allowed unless
* the app has been granted Do Not Disturb Access.
* See {@link NotificationManager#isNotificationPolicyAccessGranted()}.
* <p>This API checks if the caller has the necessary permissions based on the provided
* component name, uid, and pid values.
* See {@link #setStreamVolume(int, int, int)}.
*
* @param streamType The stream whose volume index should be set.
* @param index The volume index to set. See
* {@link #getStreamMaxVolume(int)} for the largest valid value.
* @param flags One or more flags.
* @param packageName the package name of client application
* @param uid the uid of client application
* @param pid the pid of client application
* @param targetSdkVersion the target sdk version of client application
* @see #getStreamMaxVolume(int)
* @see #getStreamVolume(int)
* @see #isVolumeFixed()
* @throws SecurityException if the volume change triggers a Do Not Disturb change
* and the caller is not granted notification policy access.
*
* @hide
*/
@SystemApi(client = SystemApi.Client.MODULE_LIBRARIES)
public void setStreamVolumeForUid(int streamType, int index, int flags,
@NonNull String packageName, int uid, int pid, int targetSdkVersion) {
try {
getService().setStreamVolumeForUid(streamType, index, flags, packageName, uid, pid,
UserHandle.getUserHandleForUid(uid), targetSdkVersion);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
}
总结一下,上面这些方法,从功能上来看主要包括这样一些:
- 直接给设备设置音量;
- 调节某个
STREAM_TYPE的音量; - 单步地调大或者调小特定流类型的音量;
- 调节最相关的流的音量;
- 为特定
AudioAttributes设置音量; - 调节最相关的流的音量,且会基于所提供的组件名、uid 和 pid 值检查调用者是否有必要权限;
- 单步地调大或者调小特定流类型的音量,且会基于所提供的组件名、uid 和 pid 值检查调用者是否有必要权限;
- 调节某个
STREAM_TYPE的音量,且会基于所提供的组件名、uid 和 pid 值检查调用者是否有必要权限。
AudioManager 主要是运行于 system_server 中的 audio 服务的客户端代理,但其中封装的一些操作也会直接通过 media session 服务或者 audio policy 服务等完成。上面除了第 1 和 第 4 项功能外,其它功能基本上都通过调用 audio 服务的同名方法完成。
接下来,逐个看下上面调用的 AudioService 的方法的实现。
- 在
AudioService中 (frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/audio/AudioService.java),与AudioManager中的方法对应的setStreamVolume()方法实现如下:
/** @see AudioManager#setStreamVolume(int, int, int)
* Part of service interface, check permissions here */
public void setStreamVolume(int streamType, int index, int flags, String callingPackage) {
if ((streamType == AudioManager.STREAM_ACCESSIBILITY) && !canChangeAccessibilityVolume()) {
Log.w(TAG, "Trying to call setStreamVolume() for a11y without"
+ " CHANGE_ACCESSIBILITY_VOLUME callingPackage=" + callingPackage);
return;
}
if ((streamType == AudioManager.STREAM_VOICE_CALL) && (index == 0)
&& (mContext.checkCallingOrSelfPermission(
android.Manifest.permission.MODIFY_PHONE_STATE)
!= PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED)) {
Log.w(TAG, "Trying to call setStreamVolume() for STREAM_VOICE_CALL and index 0 without"
+ " MODIFY_PHONE_STATE callingPackage=" + callingPackage);
return;
}
if ((streamType == AudioManager.STREAM_ASSISTANT)
&& (mContext.checkCallingOrSelfPermission(
android.Manifest.permission.MODIFY_AUDIO_ROUTING)
!= PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED)) {
Log.w(TAG, "Trying to call setStreamVolume() for STREAM_ASSISTANT without"
+ " MODIFY_AUDIO_ROUTING callingPackage=" + callingPackage);
return;
}
sVolumeLogger.log(new VolumeEvent(VolumeEvent.VOL_SET_STREAM_VOL, streamType,
index/*val1*/, flags/*val2*/, callingPackage));
setStreamVolume(streamType, index, flags, callingPackage, callingPackage,
Binder.getCallingUid(), callingOrSelfHasAudioSettingsPermission());
}
这个操作执行的过程大体为:
(1). 确保调用方具有足够的修改 stream type 的音量的权限;
(2). 为 stream type 设置音量。
这个操作最终回到了为 stream type 设置音量。
- 单步地调大或者调小特定流类型的音量
/** @see AudioManager#adjustStreamVolume(int, int, int)
* Part of service interface, check permissions here */
public void adjustStreamVolume(int streamType, int direction, int flags,
String callingPackage) {
if ((streamType == AudioManager.STREAM_ACCESSIBILITY) && !canChangeAccessibilityVolume()) {
Log.w(TAG, "Trying to call adjustStreamVolume() for a11y without"
+ "CHANGE_ACCESSIBILITY_VOLUME / callingPackage=" + callingPackage);
return;
}
sVolumeLogger.log(new VolumeEvent(VolumeEvent.VOL_ADJUST_STREAM_VOL, streamType,
direction/*val1*/, flags/*val2*/, callingPackage));
adjustStreamVolume(streamType, direction, flags, callingPackage, callingPackage,
Binder.getCallingUid(), Binder.getCallingPid(),
callingHasAudioSettingsPermission(), VOL_ADJUST_NORMAL);
}
这个操作执行的过程大体为:
(1). 确保调用方具有足够的修改 stream type 的音量的权限;
(2). 调整 stream type 的音量。
这个操作最终回到了调整 stream type 的音量。
-
调节最相关的流的音量的
adjustVolume()和adjustSuggestedStreamVolume()将经 media session 服务绕一道,最终回到调整 stream type 的音量或设置 stream type 的音量。 -
为特定
AudioAttributes设置音量
/** @see AudioManager#setVolumeIndexForAttributes(attr, int, int) */
public void setVolumeIndexForAttributes(@NonNull AudioAttributes attr, int index, int flags,
String callingPackage) {
enforceModifyAudioRoutingPermission();
Objects.requireNonNull(attr, "attr must not be null");
final int volumeGroup = getVolumeGroupIdForAttributes(attr);
if (sVolumeGroupStates.indexOfKey(volumeGroup) < 0) {
Log.e(TAG, ": no volume group found for attributes " + attr.toString());
return;
}
final VolumeGroupState vgs = sVolumeGroupStates.get(volumeGroup);
sVolumeLogger.log(new VolumeEvent(VolumeEvent.VOL_SET_GROUP_VOL, attr, vgs.name(),
index/*val1*/, flags/*val2*/, callingPackage));
vgs.setVolumeIndex(index, flags);
// For legacy reason, propagate to all streams associated to this volume group
for (final int groupedStream : vgs.getLegacyStreamTypes()) {
try {
ensureValidStreamType(groupedStream);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
Log.d(TAG, "volume group " + volumeGroup + " has internal streams (" + groupedStream
+ "), do not change associated stream volume");
continue;
}
setStreamVolume(groupedStream, index, flags, callingPackage, callingPackage,
Binder.getCallingUid(), true /*hasModifyAudioSettings*/);
}
}
这个过程大体为:
(1). 确保调用方具有足够的修改 audio routing 的权限;
(2). 根据传入的 AudioAttributes 获得音量组;
(3). 为音量组本身设置音量;
(4). 为音量组中的每个 stream type 设置音量。
这个操作最终回到了为 stream type 设置音量。
- 调节最相关的流的音量,且会基于所提供的组件名、uid 和 pid 值检查调用者是否有必要权限
private void adjustSuggestedStreamVolume(int direction, int suggestedStreamType, int flags,
String callingPackage, String caller, int uid, int pid, boolean hasModifyAudioSettings,
int keyEventMode) {
if (DEBUG_VOL) Log.d(TAG, "adjustSuggestedStreamVolume() stream=" + suggestedStreamType
+ ", flags=" + flags + ", caller=" + caller
+ ", volControlStream=" + mVolumeControlStream
+ ", userSelect=" + mUserSelectedVolumeControlStream);
if (direction != AudioManager.ADJUST_SAME) {
sVolumeLogger.log(new VolumeEvent(VolumeEvent.VOL_ADJUST_SUGG_VOL, suggestedStreamType,
direction/*val1*/, flags/*val2*/, new StringBuilder(callingPackage)
.append("/").append(caller).append(" uid:").append(uid).toString()));
}
boolean hasExternalVolumeController = notifyExternalVolumeController(direction);
new MediaMetrics.Item(mMetricsId + "adjustSuggestedStreamVolume")
.setUid(Binder.getCallingUid())
.set(MediaMetrics.Property.CALLING_PACKAGE, callingPackage)
.set(MediaMetrics.Property.CLIENT_NAME, caller)
.set(MediaMetrics.Property.DIRECTION, direction > 0
? MediaMetrics.Value.UP : MediaMetrics.Value.DOWN)
.set(MediaMetrics.Property.EXTERNAL, hasExternalVolumeController
? MediaMetrics.Value.YES : MediaMetrics.Value.NO)
.set(MediaMetrics.Property.FLAGS, flags)
.record();
if (hasExternalVolumeController) {
return;
}
final int streamType;
synchronized (mForceControlStreamLock) {
// Request lock in case mVolumeControlStream is changed by other thread.
if (mUserSelectedVolumeControlStream) { // implies mVolumeControlStream != -1
streamType = mVolumeControlStream;
} else {
final int maybeActiveStreamType = getActiveStreamType(suggestedStreamType);
final boolean activeForReal;
if (maybeActiveStreamType == AudioSystem.STREAM_RING
|| maybeActiveStreamType == AudioSystem.STREAM_NOTIFICATION) {
activeForReal = wasStreamActiveRecently(maybeActiveStreamType, 0);
} else {
activeForReal = mAudioSystem.isStreamActive(maybeActiveStreamType, 0);
}
if (activeForReal || mVolumeControlStream == -1) {
streamType = maybeActiveStreamType;
} else {
streamType = mVolumeControlStream;
}
}
}
final boolean isMute = isMuteAdjust(direction);
ensureValidStreamType(streamType);
final int resolvedStream = mStreamVolumeAlias[streamType];
// Play sounds on STREAM_RING only.
if ((flags & AudioManager.FLAG_PLAY_SOUND) != 0 &&
resolvedStream != AudioSystem.STREAM_RING) {
flags &= ~AudioManager.FLAG_PLAY_SOUND;
}
// For notifications/ring, show the ui before making any adjustments
// Don't suppress mute/unmute requests
// Don't suppress adjustments for single volume device
if (mVolumeController.suppressAdjustment(resolvedStream, flags, isMute)
&& !mIsSingleVolume) {
direction = 0;
flags &= ~AudioManager.FLAG_PLAY_SOUND;
flags &= ~AudioManager.FLAG_VIBRATE;
if (DEBUG_VOL) Log.d(TAG, "Volume controller suppressed adjustment");
}
adjustStreamVolume(streamType, direction, flags, callingPackage, caller, uid, pid,
hasModifyAudioSettings, keyEventMode);
}
. . . . . .
/** @see AudioManager#adjustSuggestedStreamVolumeForUid(int, int, int, String, int, int, int) */
@Override
public void adjustSuggestedStreamVolumeForUid(int streamType, int direction, int flags,
@NonNull String packageName, int uid, int pid, UserHandle userHandle,
int targetSdkVersion) {
if (Binder.getCallingUid() != Process.SYSTEM_UID) {
throw new SecurityException("Should only be called from system process");
}
// direction and stream type swap here because the public
// adjustSuggested has a different order than the other methods.
adjustSuggestedStreamVolume(direction, streamType, flags, packageName, packageName,
uid, pid, hasAudioSettingsPermission(uid, pid), VOL_ADJUST_NORMAL);
}
这个操作执行的过程大体为:
(1). 确保调用方的 UID 为 Process.SYSTEM_UID;
(2). 找到合适的 stream type;
(3). 调整 stream type 的音量。
这个操作最终回到了调整 stream type 的音量。
- 单步地调大或者调小特定流类型的音量,且会基于所提供的组件名、uid 和 pid 值检查调用者是否有必要权限;
/** @see AudioManager#adjustStreamVolumeForUid(int, int, int, String, int, int, int) */
@Override
public void adjustStreamVolumeForUid(int streamType, int direction, int flags,
@NonNull String packageName, int uid, int pid, UserHandle userHandle,
int targetSdkVersion) {
if (Binder.getCallingUid() != Process.SYSTEM_UID) {
throw new SecurityException("Should only be called from system process");
}
if (direction != AudioManager.ADJUST_SAME) {
sVolumeLogger.log(new VolumeEvent(VolumeEvent.VOL_ADJUST_VOL_UID, streamType,
direction/*val1*/, flags/*val2*/,
new StringBuilder(packageName).append(" uid:").append(uid)
.toString()));
}
adjustStreamVolume(streamType, direction, flags, packageName, packageName, uid, pid,
hasAudioSettingsPermission(uid, pid), VOL_ADJUST_NORMAL);
}
这个操作执行的过程大体为:
(1). 确保调用方的 UID 为 Process.SYSTEM_UID;
(2). 调整 stream type 的音量。
这个操作最终回到了调整 stream type 的音量。
- 调节某个
STREAM_TYPE的音量,且会基于所提供的组件名、uid 和 pid 值检查调用者是否有必要权限
/** @see AudioManager#setStreamVolumeForUid(int, int, int, String, int, int, int) */
@Override
public void setStreamVolumeForUid(int streamType, int index, int flags,
@NonNull String packageName, int uid, int pid, UserHandle userHandle,
int targetSdkVersion) {
if (Binder.getCallingUid() != Process.SYSTEM_UID) {
throw new SecurityException("Should only be called from system process");
}
setStreamVolume(streamType, index, flags, packageName, packageName, uid,
hasAudioSettingsPermission(uid, pid));
}
这个操作执行的过程大体为:
(1). 确保调用方的 UID 为 Process.SYSTEM_UID;
(2). 为 stream type 设置音量,传入的 uid 和 pid 用于检查权限。
这个操作最终回到了为 stream type 设置音量。
总体来看,AudioManager 除了直接调节设备音量的接口之外的其它接口,最终都会回到为 stream type 设置音量或调整 stream type 的音量。这里看一下为 stream type 设置音量的过程。
由上面这些调节音量的方法可以看到,Android Automotive 调节音量的动作有意在 Car 服务中直接对设备调节了音量,而没有继续经过核心 Android 系统的 audio 服务。
这里不再继续深入跟踪调整 stream type 的音量的过程,但可以看一下为 stream type 设置音量的过程。
为 stream type 设置音量
为 stream type 设置音量的 setStreamVolume() 方法定义如下:
private void setStreamVolume(int streamType, int index, int flags, String callingPackage,
String caller, int uid, boolean hasModifyAudioSettings) {
if (DEBUG_VOL) {
Log.d(TAG, "setStreamVolume(stream=" + streamType+", index=" + index
+ ", calling=" + callingPackage + ")");
}
if (mUseFixedVolume) {
return;
}
ensureValidStreamType(streamType);
int streamTypeAlias = mStreamVolumeAlias[streamType];
VolumeStreamState streamState = mStreamStates[streamTypeAlias];
final int device = getDeviceForStream(streamType);
int oldIndex;
// skip a2dp absolute volume control request when the device
// is not an a2dp device
if (!AudioSystem.DEVICE_OUT_ALL_A2DP_SET.contains(device)
&& (flags & AudioManager.FLAG_BLUETOOTH_ABS_VOLUME) != 0) {
return;
}
// If we are being called by the system (e.g. hardware keys) check for current user
// so we handle user restrictions correctly.
if (uid == android.os.Process.SYSTEM_UID) {
uid = UserHandle.getUid(getCurrentUserId(), UserHandle.getAppId(uid));
}
if (!checkNoteAppOp(STREAM_VOLUME_OPS[streamTypeAlias], uid, callingPackage)) {
return;
}
if (isAndroidNPlus(callingPackage)
&& wouldToggleZenMode(getNewRingerMode(streamTypeAlias, index, flags))
&& !mNm.isNotificationPolicyAccessGrantedForPackage(callingPackage)) {
throw new SecurityException("Not allowed to change Do Not Disturb state");
}
if (!volumeAdjustmentAllowedByDnd(streamTypeAlias, flags)) {
return;
}
synchronized (mSafeMediaVolumeStateLock) {
// reset any pending volume command
mPendingVolumeCommand = null;
oldIndex = streamState.getIndex(device);
index = rescaleIndex(index * 10, streamType, streamTypeAlias);
if (streamTypeAlias == AudioSystem.STREAM_MUSIC
&& AudioSystem.DEVICE_OUT_ALL_A2DP_SET.contains(device)
&& (flags & AudioManager.FLAG_BLUETOOTH_ABS_VOLUME) == 0) {
if (DEBUG_VOL) {
Log.d(TAG, "setStreamVolume postSetAvrcpAbsoluteVolumeIndex index=" + index
+ "stream=" + streamType);
}
mDeviceBroker.postSetAvrcpAbsoluteVolumeIndex(index / 10);
}
if (device == AudioSystem.DEVICE_OUT_HEARING_AID
&& streamType == getHearingAidStreamType()) {
Log.i(TAG, "setStreamVolume postSetHearingAidVolumeIndex index=" + index
+ " stream=" + streamType);
mDeviceBroker.postSetHearingAidVolumeIndex(index, streamType);
}
if (streamTypeAlias == AudioSystem.STREAM_MUSIC) {
setSystemAudioVolume(oldIndex, index, getStreamMaxVolume(streamType), flags);
}
flags &= ~AudioManager.FLAG_FIXED_VOLUME;
if (streamTypeAlias == AudioSystem.STREAM_MUSIC && isFixedVolumeDevice(device)) {
flags |= AudioManager.FLAG_FIXED_VOLUME;
// volume is either 0 or max allowed for fixed volume devices
if (index != 0) {
if (mSafeMediaVolumeState == SAFE_MEDIA_VOLUME_ACTIVE &&
mSafeMediaVolumeDevices.contains(device)) {
index = safeMediaVolumeIndex(device);
} else {
index = streamState.getMaxIndex();
}
}
}
if (!checkSafeMediaVolume(streamTypeAlias, index, device)) {
mVolumeController.postDisplaySafeVolumeWarning(flags);
mPendingVolumeCommand = new StreamVolumeCommand(
streamType, index, flags, device);
} else {
onSetStreamVolume(streamType, index, flags, device, caller, hasModifyAudioSettings);
index = mStreamStates[streamType].getIndex(device);
}
}
synchronized (mHdmiClientLock) {
if (streamTypeAlias == AudioSystem.STREAM_MUSIC
&& (oldIndex != index)) {
maybeSendSystemAudioStatusCommand(false);
}
}
sendVolumeUpdate(streamType, oldIndex, index, flags, device);
}
这个方法首先检查了是否配置使用固定音频策略 mUseFixedVolume,这个值来自于配置文件:frameworks/base/core/res/res/values/config.xml:
mUseFixedVolume = mContext.getResources().getBoolean(
com.android.internal.R.bool.config_useFixedVolume);
这个值可以被专门为设备定义的值覆盖掉。如对于车载版的模拟器,device/generic/car/emulator/audio/overlay/frameworks/base/core/res/res/values/config.xml 文件中定义的值覆盖了 framework 中定义的值。
这个是音频策略执行的主要的地方。
之后根据 stream type 通过 AudioSystem 获得 device 号 (frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/audio/AudioSystemAdapter.java) :
public int getDevicesForStream(int stream) {
if (!ENABLE_GETDEVICES_STATS) {
return getDevicesForStreamImpl(stream);
}
mMethodCallCounter[METHOD_GETDEVICESFORSTREAM]++;
final long startTime = SystemClock.uptimeNanos();
final int res = getDevicesForStreamImpl(stream);
mMethodTimeNs[METHOD_GETDEVICESFORSTREAM] += SystemClock.uptimeNanos() - startTime;
return res;
}
private int getDevicesForStreamImpl(int stream) {
if (USE_CACHE_FOR_GETDEVICES) {
Integer res;
synchronized (mDevicesForStreamCache) {
res = mDevicesForStreamCache.get(stream);
if (res == null) {
res = AudioSystem.getDevicesForStream(stream);
mDevicesForStreamCache.put(stream, res);
if (DEBUG_CACHE) {
Log.d(TAG, mMethodNames[METHOD_GETDEVICESFORSTREAM]
+ streamDeviceToDebugString(stream, res));
}
return res;
}
// cache hit
mMethodCacheHit[METHOD_GETDEVICESFORSTREAM]++;
if (DEBUG_CACHE) {
final int real = AudioSystem.getDevicesForStream(stream);
if (res == real) {
Log.d(TAG, mMethodNames[METHOD_GETDEVICESFORSTREAM]
+ streamDeviceToDebugString(stream, res) + " CACHE");
} else {
Log.e(TAG, mMethodNames[METHOD_GETDEVICESFORSTREAM]
+ streamDeviceToDebugString(stream, res)
+ " CACHE ERROR real dev=0x" + Integer.toHexString(real));
}
}
}
return res;
}
// not using cache
return AudioSystem.getDevicesForStream(stream);
}
这个调用堆栈如下:
getDevicesForStreamImpl:164, AudioSystemAdapter (com.android.server.audio)
getDevicesForStream:151, AudioSystemAdapter (com.android.server.audio)
observeDevicesForStream_syncVSS:6838, AudioService$VolumeStreamState (com.android.server.audio)
getDevicesForStreamInt:6111, AudioService (com.android.server.audio)
getDeviceForStream:6063, AudioService (com.android.server.audio)
setStreamVolume:3576, AudioService (com.android.server.audio)
setStreamVolume:3327, AudioService (com.android.server.audio)
onTransact:1529, IAudioService$Stub (android.media)
execTransactInternal:1179, Binder (android.os)
execTransact:1143, Binder (android.os)
通过 AudioSystem 获得的 device 号可能包含多个设备,每个具体的设备在这里的设备号中用一个二进制位表示,此时需要从这些设备中按优先级对具体的设备进行选择,这个过程 (frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/audio/AudioService.java) 如下:
/** only public for mocking/spying, do not call outside of AudioService */
@VisibleForTesting
public int getDeviceForStream(int stream) {
int device = getDevicesForStreamInt(stream);
if ((device & (device - 1)) != 0) {
// Multiple device selection is either:
// - speaker + one other device: give priority to speaker in this case.
// - one A2DP device + another device: happens with duplicated output. In this case
// retain the device on the A2DP output as the other must not correspond to an active
// selection if not the speaker.
// - HDMI-CEC system audio mode only output: give priority to available item in order.
// FIXME: Haven't applied audio device type refactor to this API
// as it is going to be deprecated.
if ((device & AudioSystem.DEVICE_OUT_SPEAKER) != 0) {
device = AudioSystem.DEVICE_OUT_SPEAKER;
} else if ((device & AudioSystem.DEVICE_OUT_HDMI_ARC) != 0) {
// FIXME(b/184944421): DEVICE_OUT_HDMI_EARC has two bits set,
// so it must be handled correctly as it aliases
// with DEVICE_OUT_HDMI_ARC | DEVICE_OUT_EARPIECE.
device = AudioSystem.DEVICE_OUT_HDMI_ARC;
} else if ((device & AudioSystem.DEVICE_OUT_SPDIF) != 0) {
device = AudioSystem.DEVICE_OUT_SPDIF;
} else if ((device & AudioSystem.DEVICE_OUT_AUX_LINE) != 0) {
device = AudioSystem.DEVICE_OUT_AUX_LINE;
} else {
for (int deviceType : AudioSystem.DEVICE_OUT_ALL_A2DP_SET) {
if ((deviceType & device) == deviceType) {
return deviceType;
}
}
}
}
return device;
}
之后对传入的音量值进行归一化 (frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/audio/AudioService.java):
private int rescaleIndex(int index, int srcStream, int dstStream) {
int srcRange = getIndexRange(srcStream);
int dstRange = getIndexRange(dstStream);
if (srcRange == 0) {
Log.e(TAG, "rescaleIndex : index range should not be zero");
return mStreamStates[dstStream].getMinIndex();
}
return mStreamStates[dstStream].getMinIndex()
+ ((index - mStreamStates[srcStream].getMinIndex()) * dstRange + srcRange / 2)
/ srcRange;
}
之后处理 stream type 为 AudioSystem.STREAM_MUSIC,使用了蓝牙,且设置绝对音量时的情况,即发送消息来设置音量值。
之后处理设备为 AudioSystem.DEVICE_OUT_HEARING_AID,且 stream type 为辅助听力时的情况,即发送消息给蓝牙设置音量。
之后,当 stream type 为 AudioSystem.STREAM_MUSIC,还会设置系统音频音量,主要是根据需要设置 HDMI 音量。
之后,如果 stream type 为 AudioSystem.STREAM_MUSIC,且设备为固定音量设备,则修正传入的音量值。
之后,检查修正后的音量值是否为安全音量,如果不是,则发送 stream 音量命令;如果是,则通过 onSetStreamVolume() 设置流音量。
onSetStreamVolume() 的实现如下:
private void onSetStreamVolume(int streamType, int index, int flags, int device,
String caller, boolean hasModifyAudioSettings) {
final int stream = mStreamVolumeAlias[streamType];
setStreamVolumeInt(stream, index, device, false, caller, hasModifyAudioSettings);
// setting volume on ui sounds stream type also controls silent mode
if (((flags & AudioManager.FLAG_ALLOW_RINGER_MODES) != 0) ||
(stream == getUiSoundsStreamType())) {
setRingerMode(getNewRingerMode(stream, index, flags),
TAG + ".onSetStreamVolume", false /*external*/);
}
// setting non-zero volume for a muted stream unmutes the stream and vice versa,
// except for BT SCO stream where only explicit mute is allowed to comply to BT requirements
if (streamType != AudioSystem.STREAM_BLUETOOTH_SCO) {
mStreamStates[stream].mute(index == 0);
}
}
. . . . . .
/**
* Sets the stream state's index, and posts a message to set system volume.
* This will not call out to the UI. Assumes a valid stream type.
*
* @param streamType Type of the stream
* @param index Desired volume index of the stream
* @param device the device whose volume must be changed
* @param force If true, set the volume even if the desired volume is same
* @param caller
* @param hasModifyAudioSettings true if the caller is granted MODIFY_AUDIO_SETTINGS or
* MODIFY_AUDIO_ROUTING permission
* as the current volume.
*/
private void setStreamVolumeInt(int streamType,
int index,
int device,
boolean force,
String caller, boolean hasModifyAudioSettings) {
if (isFullVolumeDevice(device)) {
return;
}
VolumeStreamState streamState = mStreamStates[streamType];
if (streamState.setIndex(index, device, caller, hasModifyAudioSettings) || force) {
// Post message to set system volume (it in turn will post a message
// to persist).
sendMsg(mAudioHandler,
MSG_SET_DEVICE_VOLUME,
SENDMSG_QUEUE,
device,
0,
streamState,
0);
}
}
这里首先会更新维护的关于 stream 的音量的信息,当音量真的发生改变时,还会发出 broadcast;然后发送消息去设置设备的音量。设置设备音量的方法如下:
/*package*/ void setDeviceVolume(VolumeStreamState streamState, int device) {
synchronized (VolumeStreamState.class) {
// Apply volume
streamState.applyDeviceVolume_syncVSS(device);
// Apply change to all streams using this one as alias
int numStreamTypes = AudioSystem.getNumStreamTypes();
for (int streamType = numStreamTypes - 1; streamType >= 0; streamType--) {
if (streamType != streamState.mStreamType &&
mStreamVolumeAlias[streamType] == streamState.mStreamType) {
// Make sure volume is also maxed out on A2DP device for aliased stream
// that may have a different device selected
int streamDevice = getDeviceForStream(streamType);
if ((device != streamDevice) && mAvrcpAbsVolSupported
&& AudioSystem.DEVICE_OUT_ALL_A2DP_SET.contains(device)) {
mStreamStates[streamType].applyDeviceVolume_syncVSS(device);
}
mStreamStates[streamType].applyDeviceVolume_syncVSS(streamDevice);
}
}
}
// Post a persist volume msg
sendMsg(mAudioHandler,
MSG_PERSIST_VOLUME,
SENDMSG_QUEUE,
device,
0,
streamState,
PERSIST_DELAY);
}
设置设备的音量时,先设置传入的设备的音量,然后设置别名设备的音量,之后发送消息将音量设置持久化。设置设备音量,最终还是要通过 AudioSystem 执行:
private void setStreamVolumeIndex(int index, int device) {
// Only set audio policy BT SCO stream volume to 0 when the stream is actually muted.
// This allows RX path muting by the audio HAL only when explicitly muted but not when
// index is just set to 0 to repect BT requirements
if (mStreamType == AudioSystem.STREAM_BLUETOOTH_SCO && index == 0
&& !isFullyMuted()) {
index = 1;
}
AudioSystem.setStreamVolumeIndexAS(mStreamType, index, device);
}
// must be called while synchronized VolumeStreamState.class
/*package*/ void applyDeviceVolume_syncVSS(int device) {
int index;
if (isFullyMuted()) {
index = 0;
} else if (AudioSystem.DEVICE_OUT_ALL_A2DP_SET.contains(device)
&& mAvrcpAbsVolSupported) {
index = getAbsoluteVolumeIndex((getIndex(device) + 5)/10);
} else if (isFullVolumeDevice(device)) {
index = (mIndexMax + 5)/10;
} else if (device == AudioSystem.DEVICE_OUT_HEARING_AID) {
index = (mIndexMax + 5)/10;
} else {
index = (getIndex(device) + 5)/10;
}
setStreamVolumeIndex(index, device);
}
AudioSystem 的 AudioSystem.setStreamVolumeIndexAS(mStreamType, index, device) 方法定义如下:
/** @hide Wrapper for native methods called from AudioService */
public static int setStreamVolumeIndexAS(int stream, int index, int device) {
if (DEBUG_VOLUME) {
Log.i(TAG, "setStreamVolumeIndex: " + STREAM_NAMES[stream]
+ " dev=" + Integer.toHexString(device) + " idx=" + index);
}
return setStreamVolumeIndex(stream, index, device);
}
. . . . . .
@UnsupportedAppUsage
private static native int setStreamVolumeIndex(int stream, int index, int device);
最终,通过在 frameworks/base/core/jni/android_media_AudioSystem.cpp 中定义的静态 JNI 本地层方法来完成:
static jint
android_media_AudioSystem_setStreamVolumeIndex(JNIEnv *env,
jobject thiz,
jint stream,
jint index,
jint device)
{
return (jint) check_AudioSystem_Command(
AudioSystem::setStreamVolumeIndex(static_cast <audio_stream_type_t>(stream),
index,
(audio_devices_t)device));
}
再回到 setStreamVolume(),之后,如果 stream type 为 AudioSystem.STREAM_MUSIC,且音量发生了改变,则向 HDMI service 发送报告。
最后,向 volume controller 发送音量更新报告。
我们看到了 AudioSystem 的 setAudioPortConfig(config) 和 AudioSystem.setStreamVolumeIndex(stream, index, device) 这两种给设备设置音量的方法,在这两个方法中,它们都通过 frameworks/av/media/libaudioclient/AudioSystem.cpp 定义的函数完成操作。在这个过程中,也可以看到 stream type 是本地层维护的概念。
Audio policy service 中的音量设置
接着上面的过程,继续来看 AudioSystem::setStreamVolumeIndex() 的实现。本地层的 AudioSystem 在 libaudioclient 中实现。AudioSystem::setStreamVolumeIndex() 函数的定义 (frameworks/av/media/libaudioclient/AudioSystem.cpp) 如下:
// establish binder interface to AudioPolicy service
const sp<IAudioPolicyService> AudioSystem::get_audio_policy_service() {
sp<IAudioPolicyService> ap;
sp<AudioPolicyServiceClient> apc;
{
Mutex::Autolock _l(gLockAPS);
if (gAudioPolicyService == 0) {
sp<IServiceManager> sm = defaultServiceManager();
sp<IBinder> binder;
do {
binder = sm->getService(String16("media.audio_policy"));
if (binder != 0)
break;
ALOGW("AudioPolicyService not published, waiting...");
usleep(500000); // 0.5 s
} while (true);
if (gAudioPolicyServiceClient == NULL) {
gAudioPolicyServiceClient = new AudioPolicyServiceClient();
}
binder->linkToDeath(gAudioPolicyServiceClient);
gAudioPolicyService = interface_cast<IAudioPolicyService>(binder);
LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL_IF(gAudioPolicyService == 0);
apc = gAudioPolicyServiceClient;
// Make sure callbacks can be received by gAudioPolicyServiceClient
ProcessState::self()->startThreadPool();
}
ap = gAudioPolicyService;
}
if (apc != 0) {
int64_t token = IPCThreadState::self()->clearCallingIdentity();
ap->registerClient(apc);
ap->setAudioPortCallbacksEnabled(apc->isAudioPortCbEnabled());
ap->setAudioVolumeGroupCallbacksEnabled(apc->isAudioVolumeGroupCbEnabled());
IPCThreadState::self()->restoreCallingIdentity(token);
}
return ap;
}
. . . . . .
status_t AudioSystem::setStreamVolumeIndex(audio_stream_type_t stream,
int index,
audio_devices_t device) {
const sp<IAudioPolicyService>& aps = AudioSystem::get_audio_policy_service();
if (aps == 0) return PERMISSION_DENIED;
media::AudioStreamType streamAidl = VALUE_OR_RETURN_STATUS(
legacy2aidl_audio_stream_type_t_AudioStreamType(stream));
int32_t indexAidl = VALUE_OR_RETURN_STATUS(convertIntegral<int32_t>(index));
int32_t deviceAidl = VALUE_OR_RETURN_STATUS(legacy2aidl_audio_devices_t_int32_t(device));
return statusTFromBinderStatus(
aps->setStreamVolumeIndex(streamAidl, deviceAidl, indexAidl));
}
AudioSystem 通过 binder 机制,访问 audio policy service 来设置 stream 的音量。
Audio policy service 是一个运行于 audioserver 中 (frameworks/av/media/audioserver) 的系统服务,其实现由多个组件及动态链接库组成,整体的结构如下:
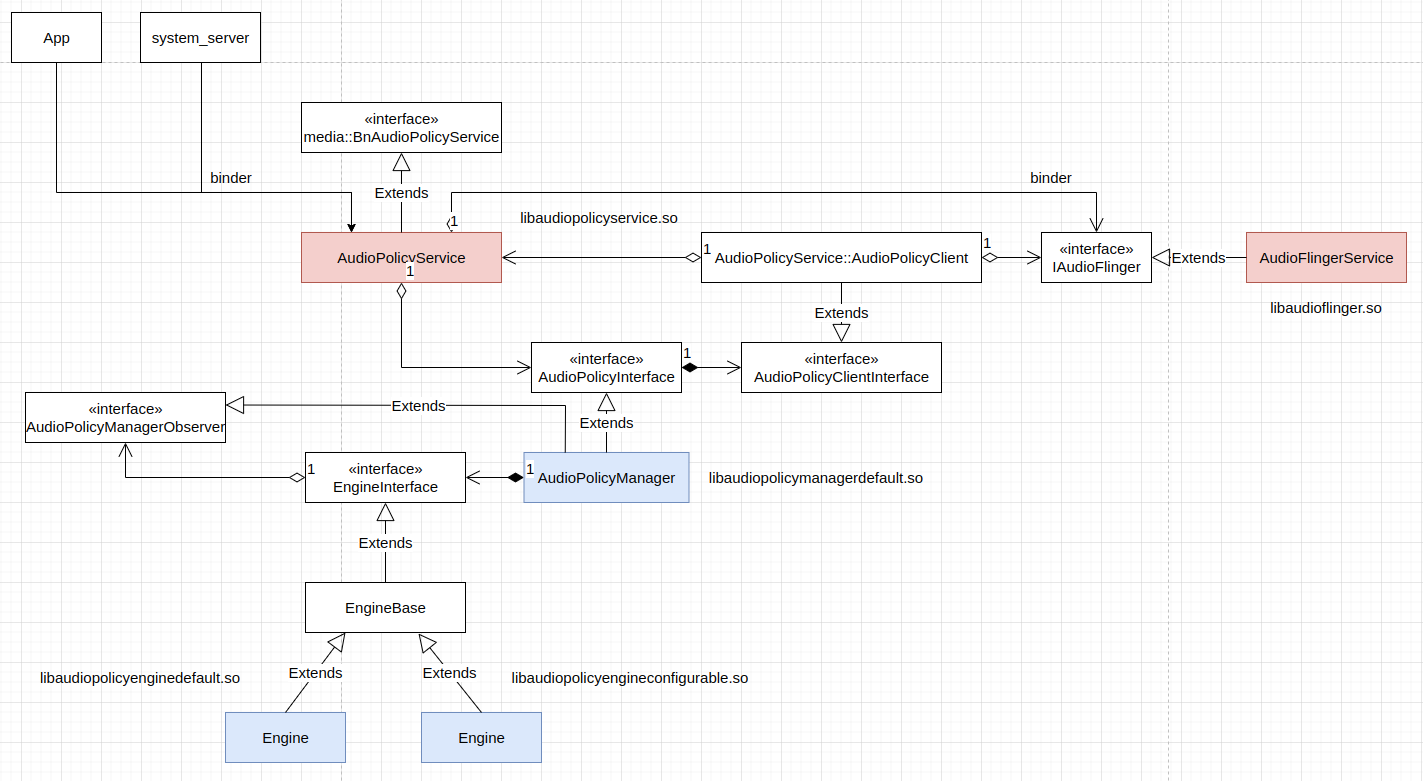
AudioPolicyService 类是 audio policy service 的 IPC 接口层,是服务端的代理,它直接接收客户端发过来的请求,同时也封装其它一些组件,协助完成一些具体操作。AudioPolicyService 类成员函数的具体实现主要分布在两个文件中,一是 frameworks/av/services/audiopolicy/service/AudioPolicyInterfaceImpl.cpp,如其文件名所指示的那样,主要是接口函数的实现;二是 frameworks/av/services/audiopolicy/service/AudioPolicyService.cpp,包含其它成员函数的实现。
AudioPolicyService 类封装的 AudioPolicyInterface,也就是 AudioPolicyManager 协助其完成主要的音频策略逻辑。AudioPolicyManager 的具体定制版实现可以被动态加载加载起来,具体定制版实现的动态链接库文件名需要是 libaudiopolicymanagercustom.so,android 系统提供了默认的实现,在定制版实现不存在,会采用这个默认实现。相关逻辑实现如下:
static AudioPolicyInterface* createAudioPolicyManager(AudioPolicyClientInterface *clientInterface)
{
AudioPolicyManager *apm = new AudioPolicyManager(clientInterface);
status_t status = apm->initialize();
if (status != NO_ERROR) {
delete apm;
apm = nullptr;
}
return apm;
}
static void destroyAudioPolicyManager(AudioPolicyInterface *interface)
{
delete interface;
}
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
AudioPolicyService::AudioPolicyService()
: BnAudioPolicyService(),
mAudioPolicyManager(NULL),
mAudioPolicyClient(NULL),
mPhoneState(AUDIO_MODE_INVALID),
mCaptureStateNotifier(false),
mCreateAudioPolicyManager(createAudioPolicyManager),
mDestroyAudioPolicyManager(destroyAudioPolicyManager) {
}
void AudioPolicyService::loadAudioPolicyManager()
{
mLibraryHandle = dlopen(kAudioPolicyManagerCustomPath, RTLD_NOW);
if (mLibraryHandle != nullptr) {
ALOGI("%s loading %s", __func__, kAudioPolicyManagerCustomPath);
mCreateAudioPolicyManager = reinterpret_cast<CreateAudioPolicyManagerInstance>
(dlsym(mLibraryHandle, "createAudioPolicyManager"));
const char *lastError = dlerror();
ALOGW_IF(mCreateAudioPolicyManager == nullptr, "%s createAudioPolicyManager is null %s",
__func__, lastError != nullptr ? lastError : "no error");
mDestroyAudioPolicyManager = reinterpret_cast<DestroyAudioPolicyManagerInstance>(
dlsym(mLibraryHandle, "destroyAudioPolicyManager"));
lastError = dlerror();
ALOGW_IF(mDestroyAudioPolicyManager == nullptr, "%s destroyAudioPolicyManager is null %s",
__func__, lastError != nullptr ? lastError : "no error");
if (mCreateAudioPolicyManager == nullptr || mDestroyAudioPolicyManager == nullptr){
unloadAudioPolicyManager();
LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL("could not find audiopolicymanager interface methods");
}
}
}
void AudioPolicyService::onFirstRef()
{
{
Mutex::Autolock _l(mLock);
// start audio commands thread
mAudioCommandThread = new AudioCommandThread(String8("ApmAudio"), this);
// start output activity command thread
mOutputCommandThread = new AudioCommandThread(String8("ApmOutput"), this);
mAudioPolicyClient = new AudioPolicyClient(this);
loadAudioPolicyManager();
mAudioPolicyManager = mCreateAudioPolicyManager(mAudioPolicyClient);
}
// load audio processing modules
sp<AudioPolicyEffects> audioPolicyEffects = new AudioPolicyEffects();
sp<UidPolicy> uidPolicy = new UidPolicy(this);
sp<SensorPrivacyPolicy> sensorPrivacyPolicy = new SensorPrivacyPolicy(this);
{
Mutex::Autolock _l(mLock);
mAudioPolicyEffects = audioPolicyEffects;
mUidPolicy = uidPolicy;
mSensorPrivacyPolicy = sensorPrivacyPolicy;
}
uidPolicy->registerSelf();
sensorPrivacyPolicy->registerSelf();
// Create spatializer if supported
if (mAudioPolicyManager != nullptr) {
Mutex::Autolock _l(mLock);
const audio_attributes_t attr = attributes_initializer(AUDIO_USAGE_MEDIA);
AudioDeviceTypeAddrVector devices;
bool hasSpatializer = mAudioPolicyManager->canBeSpatialized(&attr, nullptr, devices);
if (hasSpatializer) {
mSpatializer = Spatializer::create(this);
}
}
AudioSystem::audioPolicyReady();
}
void AudioPolicyService::unloadAudioPolicyManager()
{
ALOGV("%s ", __func__);
if (mLibraryHandle != nullptr) {
dlclose(mLibraryHandle);
}
mLibraryHandle = nullptr;
mCreateAudioPolicyManager = nullptr;
mDestroyAudioPolicyManager = nullptr;
}
AudioPolicyManager 会从 audio_policy_configuration.xml 等文件中加载配置信息,它借助于 EngineInterface 维护 stream type 和设备之间的关系之类的信息,同样 EngineInterface 也是动态加载获得的:
status_t AudioPolicyManager::initialize() {
{
std::string path = "libaudiopolicyengine" + getConfig().getEngineLibraryNameSuffix() + ".so";
ALOGD("%s: libaudiopolicyengine file path %s", __FUNCTION__, path.c_str());
auto engLib = EngineLibrary::load(path);
if (!engLib) {
ALOGE("%s: Failed to load the engine library", __FUNCTION__);
return NO_INIT;
}
mEngine = engLib->createEngine();
if (mEngine == nullptr) {
ALOGE("%s: Failed to instantiate the APM engine", __FUNCTION__);
return NO_INIT;
}
}
mEngine->setObserver(this);
status_t status = mEngine->initCheck();
if (status != NO_ERROR) {
LOG_FATAL("Policy engine not initialized(err=%d)", status);
return status;
}
mCommunnicationStrategy = mEngine->getProductStrategyForAttributes(
mEngine->getAttributesForStreamType(AUDIO_STREAM_VOICE_CALL));
// after parsing the config, mOutputDevicesAll and mInputDevicesAll contain all known devices;
// open all output streams needed to access attached devices
onNewAudioModulesAvailableInt(nullptr /*newDevices*/);
// make sure default device is reachable
if (mDefaultOutputDevice == 0 || !mAvailableOutputDevices.contains(mDefaultOutputDevice)) {
ALOGE_IF(mDefaultOutputDevice != 0, "Default device %s is unreachable",
mDefaultOutputDevice->toString().c_str());
status = NO_INIT;
}
// If microphones address is empty, set it according to device type
for (size_t i = 0; i < mAvailableInputDevices.size(); i++) {
if (mAvailableInputDevices[i]->address().empty()) {
if (mAvailableInputDevices[i]->type() == AUDIO_DEVICE_IN_BUILTIN_MIC) {
mAvailableInputDevices[i]->setAddress(AUDIO_BOTTOM_MICROPHONE_ADDRESS);
} else if (mAvailableInputDevices[i]->type() == AUDIO_DEVICE_IN_BACK_MIC) {
mAvailableInputDevices[i]->setAddress(AUDIO_BACK_MICROPHONE_ADDRESS);
}
}
}
ALOGW_IF(mPrimaryOutput == nullptr, "The policy configuration does not declare a primary output");
// Silence ALOGV statements
property_set("log.tag." LOG_TAG, "D");
updateDevicesAndOutputs();
return status;
}
android 提供了两个 EngineInterface 的实现,分别是位于 frameworks/av/services/audiopolicy/enginedefault 的 libaudiopolicyenginedefault.so 和位于 frameworks/av/services/audiopolicy/engineconfigurable 的 libaudiopolicyengineconfigurable.so,具体使用哪个由 audio_policy_configuration.xml 等配置文件中的 engine_library 配置项决定,默认使用 libaudiopolicyenginedefault.so。
libaudiopolicyenginedefault.so 等从配置文件 /vendor/etc/audio_policy_engine_configuration.xml 加载 audio policy engine 配置信息,其中主要包括产品策略,音量组等信息及其内容类型、usage 等信息。EngineInterface 的具体实现所需的设备信息从 AudioPolicyManager 获取。
我们回到设置音量的操作上来。在 audio policy service 中,这个操作请求首先来到 AudioPolicyService::setStreamVolumeIndex():
Status AudioPolicyService::setStreamVolumeIndex(media::AudioStreamType streamAidl,
int32_t deviceAidl, int32_t indexAidl) {
audio_stream_type_t stream = VALUE_OR_RETURN_BINDER_STATUS(
aidl2legacy_AudioStreamType_audio_stream_type_t(streamAidl));
int index = VALUE_OR_RETURN_BINDER_STATUS(convertIntegral<int>(indexAidl));
audio_devices_t device = VALUE_OR_RETURN_BINDER_STATUS(
aidl2legacy_int32_t_audio_devices_t(deviceAidl));
if (mAudioPolicyManager == NULL) {
return binderStatusFromStatusT(NO_INIT);
}
if (!settingsAllowed()) {
return binderStatusFromStatusT(PERMISSION_DENIED);
}
if (uint32_t(stream) >= AUDIO_STREAM_PUBLIC_CNT) {
return binderStatusFromStatusT(BAD_VALUE);
}
Mutex::Autolock _l(mLock);
AutoCallerClear acc;
return binderStatusFromStatusT(mAudioPolicyManager->setStreamVolumeIndex(stream,
index,
device));
}
在这里,首先转换传入的参数,随后操作被传给 AudioPolicyManager::setStreamVolumeIndex():
status_t AudioPolicyManager::setStreamVolumeIndex(audio_stream_type_t stream,
int index,
audio_devices_t device)
{
auto attributes = mEngine->getAttributesForStreamType(stream);
if (attributes == AUDIO_ATTRIBUTES_INITIALIZER) {
ALOGW("%s: no group for stream %s, bailing out", __func__, toString(stream).c_str());
return NO_ERROR;
}
ALOGD("%s: stream %s attributes=%s", __func__,
toString(stream).c_str(), toString(attributes).c_str());
return setVolumeIndexForAttributes(attributes, index, device);
}
status_t AudioPolicyManager::getStreamVolumeIndex(audio_stream_type_t stream,
int *index,
audio_devices_t device)
{
// if device is AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_DEFAULT_FOR_VOLUME, return volume for device selected for this
// stream by the engine.
DeviceTypeSet deviceTypes = {device};
if (device == AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_DEFAULT_FOR_VOLUME) {
deviceTypes = mEngine->getOutputDevicesForStream(
stream, true /*fromCache*/).types();
}
return getVolumeIndex(getVolumeCurves(stream), *index, deviceTypes);
}
status_t AudioPolicyManager::setVolumeIndexForAttributes(const audio_attributes_t &attributes,
int index,
audio_devices_t device)
{
// Get Volume group matching the Audio Attributes
auto group = mEngine->getVolumeGroupForAttributes(attributes);
if (group == VOLUME_GROUP_NONE) {
ALOGD("%s: no group matching with %s", __FUNCTION__, toString(attributes).c_str());
return BAD_VALUE;
}
ALOGD("%s: group %d matching with %s", __FUNCTION__, group, toString(attributes).c_str());
status_t status = NO_ERROR;
IVolumeCurves &curves = getVolumeCurves(attributes);
VolumeSource vs = toVolumeSource(group);
product_strategy_t strategy = mEngine->getProductStrategyForAttributes(attributes);
status = setVolumeCurveIndex(index, device, curves);
if (status != NO_ERROR) {
ALOGE("%s failed to set curve index for group %d device 0x%X", __func__, group, device);
return status;
}
DeviceTypeSet curSrcDevices;
auto curCurvAttrs = curves.getAttributes();
if (!curCurvAttrs.empty() && curCurvAttrs.front() != defaultAttr) {
auto attr = curCurvAttrs.front();
curSrcDevices = mEngine->getOutputDevicesForAttributes(attr, nullptr, false).types();
} else if (!curves.getStreamTypes().empty()) {
auto stream = curves.getStreamTypes().front();
curSrcDevices = mEngine->getOutputDevicesForStream(stream, false).types();
} else {
ALOGE("%s: Invalid src %d: no valid attributes nor stream",__func__, vs);
return BAD_VALUE;
}
audio_devices_t curSrcDevice = Volume::getDeviceForVolume(curSrcDevices);
resetDeviceTypes(curSrcDevices, curSrcDevice);
// update volume on all outputs and streams matching the following:
// - The requested stream (or a stream matching for volume control) is active on the output
// - The device (or devices) selected by the engine for this stream includes
// the requested device
// - For non default requested device, currently selected device on the output is either the
// requested device or one of the devices selected by the engine for this stream
// - For default requested device (AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_DEFAULT_FOR_VOLUME), apply volume only if
// no specific device volume value exists for currently selected device.
for (size_t i = 0; i < mOutputs.size(); i++) {
sp<SwAudioOutputDescriptor> desc = mOutputs.valueAt(i);
DeviceTypeSet curDevices = desc->devices().types();
if (curDevices.erase(AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_SPEAKER_SAFE)) {
curDevices.insert(AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_SPEAKER);
}
if (!(desc->isActive(vs) || isInCall())) {
continue;
}
if (device != AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_DEFAULT_FOR_VOLUME &&
curDevices.find(device) == curDevices.end()) {
continue;
}
bool applyVolume = false;
if (device != AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_DEFAULT_FOR_VOLUME) {
curSrcDevices.insert(device);
applyVolume = (curSrcDevices.find(
Volume::getDeviceForVolume(curDevices)) != curSrcDevices.end());
} else {
applyVolume = !curves.hasVolumeIndexForDevice(curSrcDevice);
}
if (!applyVolume) {
continue; // next output
}
// Inter / intra volume group priority management: Loop on strategies arranged by priority
// If a higher priority strategy is active, and the output is routed to a device with a
// HW Gain management, do not change the volume
if (desc->useHwGain()) {
applyVolume = false;
for (const auto &productStrategy : mEngine->getOrderedProductStrategies()) {
auto activeClients = desc->clientsList(true /*activeOnly*/, productStrategy,
false /*preferredDevice*/);
if (activeClients.empty()) {
continue;
}
bool isPreempted = false;
bool isHigherPriority = productStrategy < strategy;
for (const auto &client : activeClients) {
if (isHigherPriority && (client->volumeSource() != vs)) {
ALOGV("%s: Strategy=%d (\nrequester:\n"
" group %d, volumeGroup=%d attributes=%s)\n"
" higher priority source active:\n"
" volumeGroup=%d attributes=%s) \n"
" on output %zu, bailing out", __func__, productStrategy,
group, group, toString(attributes).c_str(),
client->volumeSource(), toString(client->attributes()).c_str(), i);
applyVolume = false;
isPreempted = true;
break;
}
// However, continue for loop to ensure no higher prio clients running on output
if (client->volumeSource() == vs) {
applyVolume = true;
}
}
if (isPreempted || applyVolume) {
break;
}
}
if (!applyVolume) {
continue; // next output
}
}
//FIXME: workaround for truncated touch sounds
// delayed volume change for system stream to be removed when the problem is
// handled by system UI
status_t volStatus = checkAndSetVolume(
curves, vs, index, desc, curDevices,
((vs == toVolumeSource(AUDIO_STREAM_SYSTEM))?
TOUCH_SOUND_FIXED_DELAY_MS : 0));
if (volStatus != NO_ERROR) {
status = volStatus;
}
}
mpClientInterface->onAudioVolumeGroupChanged(group, 0 /*flags*/);
return status;
}
status_t AudioPolicyManager::setVolumeCurveIndex(int index,
audio_devices_t device,
IVolumeCurves &volumeCurves)
{
// VOICE_CALL stream has minVolumeIndex > 0 but can be muted directly by an
// app that has MODIFY_PHONE_STATE permission.
bool hasVoice = hasVoiceStream(volumeCurves.getStreamTypes());
if (((index < volumeCurves.getVolumeIndexMin()) && !(hasVoice && index == 0)) ||
(index > volumeCurves.getVolumeIndexMax())) {
ALOGD("%s: wrong index %d min=%d max=%d", __FUNCTION__, index,
volumeCurves.getVolumeIndexMin(), volumeCurves.getVolumeIndexMax());
return BAD_VALUE;
}
if (!audio_is_output_device(device)) {
return BAD_VALUE;
}
// Force max volume if stream cannot be muted
if (!volumeCurves.canBeMuted()) index = volumeCurves.getVolumeIndexMax();
ALOGD("%s device %08x, index %d", __FUNCTION__ , device, index);
volumeCurves.addCurrentVolumeIndex(device, index);
return NO_ERROR;
}
. . . . . .
status_t AudioPolicyManager::checkAndSetVolume(IVolumeCurves &curves,
VolumeSource volumeSource,
int index,
const sp<AudioOutputDescriptor>& outputDesc,
DeviceTypeSet deviceTypes,
int delayMs,
bool force)
{
// do not change actual attributes volume if the attributes is muted
if (outputDesc->isMuted(volumeSource)) {
ALOGVV("%s: volume source %d muted count %d active=%d", __func__, volumeSource,
outputDesc->getMuteCount(volumeSource), outputDesc->isActive(volumeSource));
return NO_ERROR;
}
VolumeSource callVolSrc = toVolumeSource(AUDIO_STREAM_VOICE_CALL);
VolumeSource btScoVolSrc = toVolumeSource(AUDIO_STREAM_BLUETOOTH_SCO);
bool isVoiceVolSrc = callVolSrc == volumeSource;
bool isBtScoVolSrc = btScoVolSrc == volumeSource;
bool isScoRequested = isScoRequestedForComm();
// do not change in call volume if bluetooth is connected and vice versa
// if sco and call follow same curves, bypass forceUseForComm
if ((callVolSrc != btScoVolSrc) &&
((isVoiceVolSrc && isScoRequested) ||
(isBtScoVolSrc && !isScoRequested))) {
ALOGV("%s cannot set volume group %d volume when is%srequested for comm", __func__,
volumeSource, isScoRequested ? " " : "n ot ");
// Do not return an error here as AudioService will always set both voice call
// and bluetooth SCO volumes due to stream aliasing.
return NO_ERROR;
}
if (deviceTypes.empty()) {
deviceTypes = outputDesc->devices().types();
}
float volumeDb = computeVolume(curves, volumeSource, index, deviceTypes);
if (outputDesc->isFixedVolume(deviceTypes) ||
// Force VoIP volume to max for bluetooth SCO device except if muted
(index != 0 && (isVoiceVolSrc || isBtScoVolSrc) &&
isSingleDeviceType(deviceTypes, audio_is_bluetooth_out_sco_device))) {
volumeDb = 0.0f;
}
outputDesc->setVolume(
volumeDb, volumeSource, curves.getStreamTypes(), deviceTypes, delayMs, force);
if (outputDesc == mPrimaryOutput && (isVoiceVolSrc || isBtScoVolSrc)) {
float voiceVolume;
// Force voice volume to max or mute for Bluetooth SCO as other attenuations are managed by the headset
if (isVoiceVolSrc) {
voiceVolume = (float)index/(float)curves.getVolumeIndexMax();
} else {
voiceVolume = index == 0 ? 0.0 : 1.0;
}
if (voiceVolume != mLastVoiceVolume) {
mpClientInterface->setVoiceVolume(voiceVolume, delayMs);
mLastVoiceVolume = voiceVolume;
}
}
return NO_ERROR;
}
AudioPolicyManager 根据音量的 index 值,计算 db 值,随后通过 AudioOutputDescriptor 设置音量。AudioOutputDescriptor 在 android 中有两个实现,分别是 SwAudioOutputDescriptor 和 HwAudioOutputDescriptor,音量设置的执行来到 SwAudioOutputDescriptor::setVolume():
bool SwAudioOutputDescriptor::setVolume(float volumeDb,
VolumeSource vs, const StreamTypeVector &streamTypes,
const DeviceTypeSet& deviceTypes,
uint32_t delayMs,
bool force)
{
ALOGD("SwAudioOutputDescriptor::%s: volumeDb %f", __FUNCTION__, volumeDb);
StreamTypeVector streams = streamTypes;
if (!AudioOutputDescriptor::setVolume(volumeDb, vs, streamTypes, deviceTypes, delayMs, force)) {
return false;
}
if (streams.empty()) {
streams.push_back(AUDIO_STREAM_MUSIC);
}
for (const auto& devicePort : devices()) {
// APM loops on all group, so filter on active group to set the port gain,
// let the other groups set the stream volume as per legacy
// TODO: Pass in the device address and check against it.
if (isSingleDeviceType(deviceTypes, devicePort->type()) &&
devicePort->hasGainController(true) && isActive(vs)) {
ALOGV("%s: device %s has gain controller", __func__, devicePort->toString().c_str());
// @todo: here we might be in trouble if the SwOutput has several active clients with
// different Volume Source (or if we allow several curves within same volume group)
//
// @todo: default stream volume to max (0) when using HW Port gain?
float volumeAmpl = Volume::DbToAmpl(0);
for (const auto &stream : streams) {
mClientInterface->setStreamVolume(stream, volumeAmpl, mIoHandle, delayMs);
}
AudioGains gains = devicePort->getGains();
int gainMinValueInMb = gains[0]->getMinValueInMb();
int gainMaxValueInMb = gains[0]->getMaxValueInMb();
int gainStepValueInMb = gains[0]->getStepValueInMb();
int gainValueMb = ((volumeDb * 100)/ gainStepValueInMb) * gainStepValueInMb;
gainValueMb = std::max(gainMinValueInMb, std::min(gainValueMb, gainMaxValueInMb));
audio_port_config config = {};
devicePort->toAudioPortConfig(&config);
config.config_mask = AUDIO_PORT_CONFIG_GAIN;
config.gain.values[0] = gainValueMb;
return mClientInterface->setAudioPortConfig(&config, 0) == NO_ERROR;
}
}
// Force VOICE_CALL to track BLUETOOTH_SCO stream volume when bluetooth audio is enabled
float volumeAmpl = Volume::DbToAmpl(getCurVolume(vs));
if (hasStream(streams, AUDIO_STREAM_BLUETOOTH_SCO)) {
mClientInterface->setStreamVolume(AUDIO_STREAM_VOICE_CALL, volumeAmpl, mIoHandle, delayMs);
}
for (const auto &stream : streams) {
ALOGD("%s output %d for volumeSource %d, volume %f, delay %d stream=%s", __func__,
mIoHandle, vs, volumeDb, delayMs, toString(stream).c_str());
mClientInterface->setStreamVolume(stream, volumeAmpl, mIoHandle, delayMs);
}
return true;
}
SwAudioOutputDescriptor 又通过 AudioPolicyClientInterface 设置音量;AudioPolicyClientInterface 的实现为 AudioPolicyService::AudioPolicyClient,设置音量的动作经 AudioPolicyService::AudioPolicyClient 转回 AudioPolicyService,只是这次调用的是 AudioPolicyService::setStreamVolume();在 AudioPolicyService::setStreamVolume() 中, 会构造音频命令,并发送命令给音频命令线程;音频命令线程在其命令执行循环中,通过 AudioSystem::setStreamVolume() 设置音量:
case SET_VOLUME: {
VolumeData *data = (VolumeData *)command->mParam.get();
ALOGD("AudioCommandThread() processing set volume stream %d, \
volume %f, output %d", data->mStream, data->mVolume, data->mIO);
mLock.unlock();
command->mStatus = AudioSystem::setStreamVolume(data->mStream,
data->mVolume,
data->mIO);
mLock.lock();
}break;
AudioSystem::setStreamVolume() 将请求 AudioFlinger 设置音量:
status_t AudioSystem::setStreamVolume(audio_stream_type_t stream, float value,
audio_io_handle_t output) {
if (uint32_t(stream) >= AUDIO_STREAM_CNT) return BAD_VALUE;
const sp<IAudioFlinger>& af = AudioSystem::get_audio_flinger();
if (af == 0) return PERMISSION_DENIED;
af->setStreamVolume(stream, value, output);
return NO_ERROR;
}
这样,调节音量的动作在 audio policy service 中流转的过程如下图:
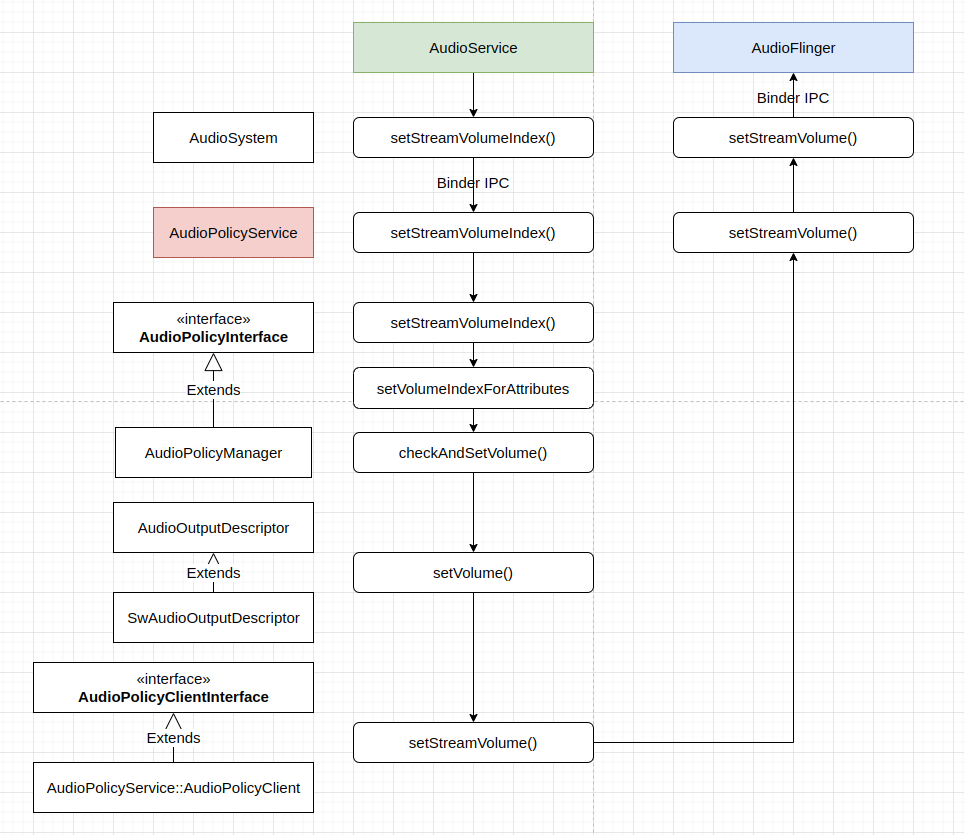
Audio policy service 接收 index 形式的音量值,将音量的 index 值转为db 值,又转为增益值,最后将音量增益设置给 audio flinger。
Audio flinger 中的音量设置
先来看一下 AudioFlinger 服务 IPC 接口层的实现结构:
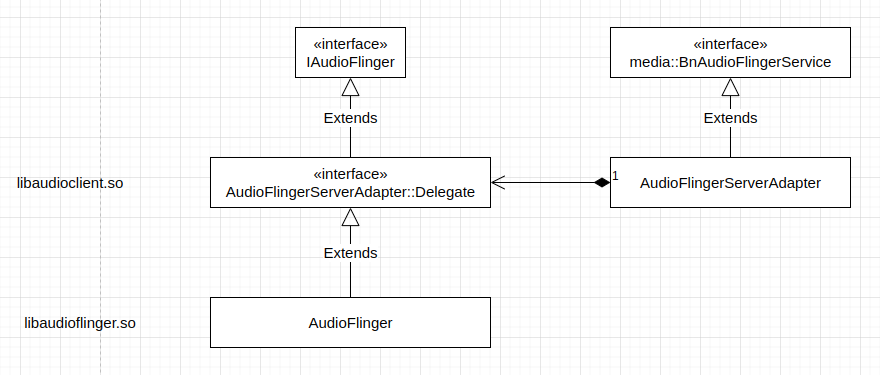
如上图所示,AudioFlinger 服务 IPC 接口层实现为 AudioFlingerServerAdapter,它的代码其实在动态链接库 libaudioclient.so 中,它接收请求,并在收到请求之后,将请求传给服务的真正实现者,也就是位于 frameworks/av/services/audioflinger/AudioFlinger.cpp 的 AudioFlinger。
接着上面的过程,AudioFlinger::setStreamVolume() 的实现如下:
status_t AudioFlinger::setStreamVolume(audio_stream_type_t stream, float value,
audio_io_handle_t output)
{
ALOGD("AudioFlinger::%s, stream %d, volume %f, output %d", __func__,
static_cast<int>(stream), value, static_cast<int>(output));
// check calling permissions
if (!settingsAllowed()) {
return PERMISSION_DENIED;
}
status_t status = checkStreamType(stream);
if (status != NO_ERROR) {
return status;
}
if (output == AUDIO_IO_HANDLE_NONE) {
return BAD_VALUE;
}
LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL_IF(stream == AUDIO_STREAM_PATCH && value != 1.0f,
"AUDIO_STREAM_PATCH must have full scale volume");
AutoMutex lock(mLock);
VolumeInterface *volumeInterface = getVolumeInterface_l(output);
if (volumeInterface == NULL) {
return BAD_VALUE;
}
volumeInterface->setStreamVolume(stream, value);
return NO_ERROR;
}
. . . . . .
// checkPlaybackThread_l() must be called with AudioFlinger::mLock held
AudioFlinger::VolumeInterface *AudioFlinger::getVolumeInterface_l(audio_io_handle_t output) const
{
VolumeInterface *volumeInterface = mPlaybackThreads.valueFor(output).get();
if (volumeInterface == nullptr) {
MmapThread *mmapThread = mMmapThreads.valueFor(output).get();
if (mmapThread != nullptr) {
if (mmapThread->isOutput()) {
MmapPlaybackThread *mmapPlaybackThread =
static_cast<MmapPlaybackThread *>(mmapThread);
volumeInterface = mmapPlaybackThread;
}
}
}
return volumeInterface;
}
AudioFlinger 根据 audio_io_handle_t 获得 AudioFlinger::VolumeInterface,随后将 stream 的音量设置给它。AudioFlinger 中的这些 Thread 的结构如下:
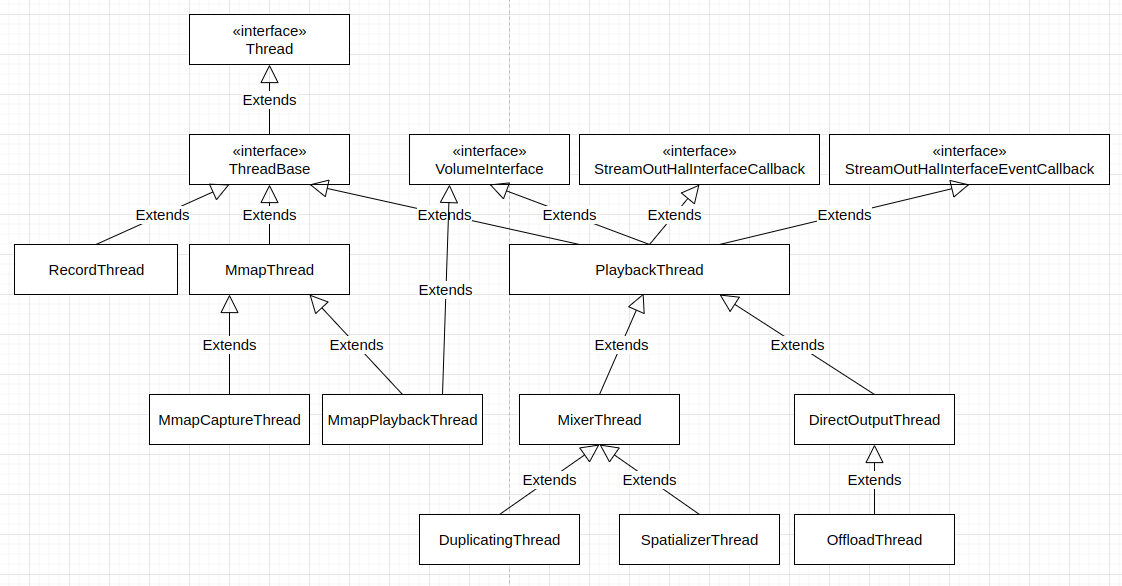
frameworks/av/services/audioflinger/Threads.cpp 中 AudioFlinger::PlaybackThread 的 setStreamVolume() 的定义如下:
void AudioFlinger::PlaybackThread::setStreamVolume(audio_stream_type_t stream, float value)
{
Mutex::Autolock _l(mLock);
mStreamTypes[stream].volume = value;
broadcast_l();
}
AudioFlinger::MmapPlaybackThread 的 setStreamVolume() 的定义如下:
void AudioFlinger::MmapPlaybackThread::setStreamVolume(audio_stream_type_t stream, float value)
{
Mutex::Autolock _l(mLock);
if (stream == mStreamType) {
mStreamVolume = value;
broadcast_l();
}
}
即流的音量增益值被保存起来,后续在处理数据时,用来对音频数据做增益。
核心 Android 系统调节音量的过程到 Audio flinger 这一层大体如此。
参考文档:
Android音量控制曲线
Done.


![[ 攻防演练演示篇 ] 利用通达OA 文件上传漏洞上传webshell获取主机权限](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/5aef87cb78a94c29a10e8633cbd8aae5.png)