引言
Lambda表达式是从C++ 11版本引入的特性,利用它可以很方便的定义匿名函数对象,通常作为回调函数来使用。大家会经常拿它和函数指针,函数符放在一起比较,很多场合下,它们三者都可以替换着用。
语法
[ captures ] ( params ) specs requires (optional) {body}
上面是完整的Lambda表达式结构,从左到右分别是:
- capture–捕获列表
- params–参数列表
- specification列表-- 可选部分,这块部分主要由变量说明符、异常、返回类型等组成
- requires – C++20 版本开始增加的
- body-- 函数体
关于specification和requires部分的详细描述可以参考:https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/language/lambda
我们平时的开发工作可能不会基于C++20版本,一般都是C++17及以下,所以就先记录一下,平时开发所接触的Lambda表达式。哪些新版本增加的相关特性就暂不讨论。
常见的Lambda表达式语法:
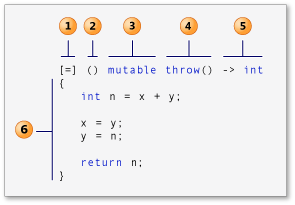
图片引自 微软C++课程
结构描述:
- 捕获列表,可以捕获外部变量
- 形参列表 (可选)
- 变量说明符(可选)属于specification列表,用来表示可以修改值捕获的变量,后面会详细说明
- exception (可选)属于specification列表,用来表示是否会有异常
- 返回类型 (可选)
- 函数体
从上面的结构描述,我们能看到,最简洁的lambda表达式应该是这样:
[]{}
我们常用的lambda表达式有以下几种:
[capture list]{body}
[capture list](params){body}
[capture list](params)->return type {body}
捕获列表
lambda表达式有两种捕获其作用域外部变量的方式,一种是值捕获,一种是引用捕获。
值捕获
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
int a = 100;
auto test = [a]() mutable {
a++;
cout << "inside, a:" << a << endl;
};
test();
cout << "outsize, a:" << a << endl;
return 0;
}
输出结果:
inside, a:101
outsize, a:100
值捕获的情况下,如果需要某个特地的外部变量,那么直接在捕获列表里面写相应的变量名即可,如果想要值捕获所以外部变量,可使用如下形式:
[=]
上面的例子中有mutable,这个关键字的作用是运行lambda内部可以修改值捕获的变量,默认情况下,值捕获的变量是只读的。
引用捕获
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
int a = 100;
auto test = [&a]() {
a++;
cout << "inside, a:" << a << endl;
};
test();
cout << "outsize, a:" << a << endl;
return 0;
}
输出结果:
inside, a:101
outsize, a:101
引用捕获外部变量的话,需要在变量名前加上**&,如果想要以引用捕获的方式访问所以外部变量,可以使用:[&]**
注意,这里我们移除了mutable关键字。
值捕获&引用捕获
因为是捕获列表嘛,所以当然可以互相组合搭配了,不然怎么能达到列表的定义呢。例如,我们想要以值捕获的方式捕获factor变量,以引用捕获的方式捕获total变量,那么可以用如下的方式:
[&total, factor]
[factor, &total]
[&, factor]
[=, &total]
以上面第一个方式举个例子:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
int total = 100;
float factor = 0.2f;
auto test = [&total, factor]() mutable {
factor = 0.5f;
total = static_cast<int>(total * factor);
cout << "inside, total:" << total << ", factor:" << factor << endl;
};
test();
cout << "outsize, total:" << total << ",factor:" << factor << endl;
return 0;
}
输出结果:
inside, total:50, factor:0.5
outsize, total:50,factor:0.2
在两种捕获方式互相搭配的使用过程中,需要注意一点的是,当捕获列表中已经使用了**&来捕获所以外部变量,就不能再使用&变量名**,捕获指定变量了,同理,值捕获也是这样。例如:
struct S { void f(int i); };
void S::f(int i) {
[&, i]{}; // OK
[&, &i]{}; // ERROR: i preceded by & when & is the default
[=, this]{}; // ERROR: this when = is the default
[=, *this]{ }; // OK: captures this by value. See below.
[i, i]{}; // ERROR: i repeated
}
注意
上面的例子中,访问外部的变量,都必须通过捕获列表“处理”一下,内部才能访问,其实还有一些情况是不需要捕获,lambda就能访问的。例如:
- 当lambda要访问的变量是全局的或者静态(static)的,可以直接使用
- Thread Local 变量
- constant expression 并且没有mutable成员 (只读)
- const修饰的non-volatile int型字面量 或者 由constant expression初始化的枚举类型 (只读)
下面举一些例子:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int total = 100;
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
static float factor = 0.2f;
auto test = []() {
factor = 0.5f;
total = static_cast<int>(total * factor);
cout << "inside,global total:" << total << ", static factor:" << factor
<< endl;
};
test();
cout << "outsize,global total:" << total << ", static factor:" << factor
<< endl;
return 0;
}
输出结果:
inside,global total:50, static factor:0.5
outsize,global total:50, static factor:0.5
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
const int x = 1024;
enum TYPE { kTypeApp = 0, kTypeUser };
auto test = []() {
cout << "type:" << kTypeUser << endl;
cout << "x:" << x << endl;
};
test();
return 0;
}
输出结果:
type:1
x:1024
参数列表&返回类型
lambda除了通过捕获列表的方式访问外部变量,也可以通过传递参数来与外界交流。跟普通函数没啥区别,这个没啥好说的。需要知道的是lambda支持它的参数也可以是lambda表示式。
返回类型跟普通函数差别也不大,同样需要注意的是,跟参数列表一样,也是支持返回lambda表达式的。同时,如果不指定返回类型的话,那么可以用auto关键字接收返回结果,自动推导结果。
#include <functional>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
auto addtwointegers = [](int x) -> function<int(int)> {
return [=](int y) { return x + y; };
};
auto higherorder = [](const function<int(int)>& f, int z) {
return f(z) * 2;
};
auto answer = higherorder(addtwointegers(7), 8);
cout << answer << endl;
}
输出结果:
30
lambda嵌套
lambda表达式内部还可以创建lambda表达式,套娃的感觉🪆。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int ret = [](int x) { return [](int y) { return y * 2; }(x) + 3; }(5);
cout << ret << endl;
}
输出结果:
13
参考
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/cpp/cpp/examples-of-lambda-expressions?view=msvc-170
https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/language/lambda