hash函数
- 一种算法
- 任意长度的二进制数据映射为固定长度的二进制数据
hash函数的特点
- 确定性------对同一个输入数据每次都能得到相同的结果
- 单向性------对一个数据可以很容易计算出hash值,但是对于一个hash值非常难反推出数据
- 隐秘性------没有可行的方法算出hash函数的输入值
- 抗篡改------对于数据一个bit位的改动,对hash值的改动也是非常大
- 抗碰撞------对于两个不同的数据,hash值相同的可能性很小
hash值的实现
- MD系列
- SHA系列,推荐SHA256,SHA3
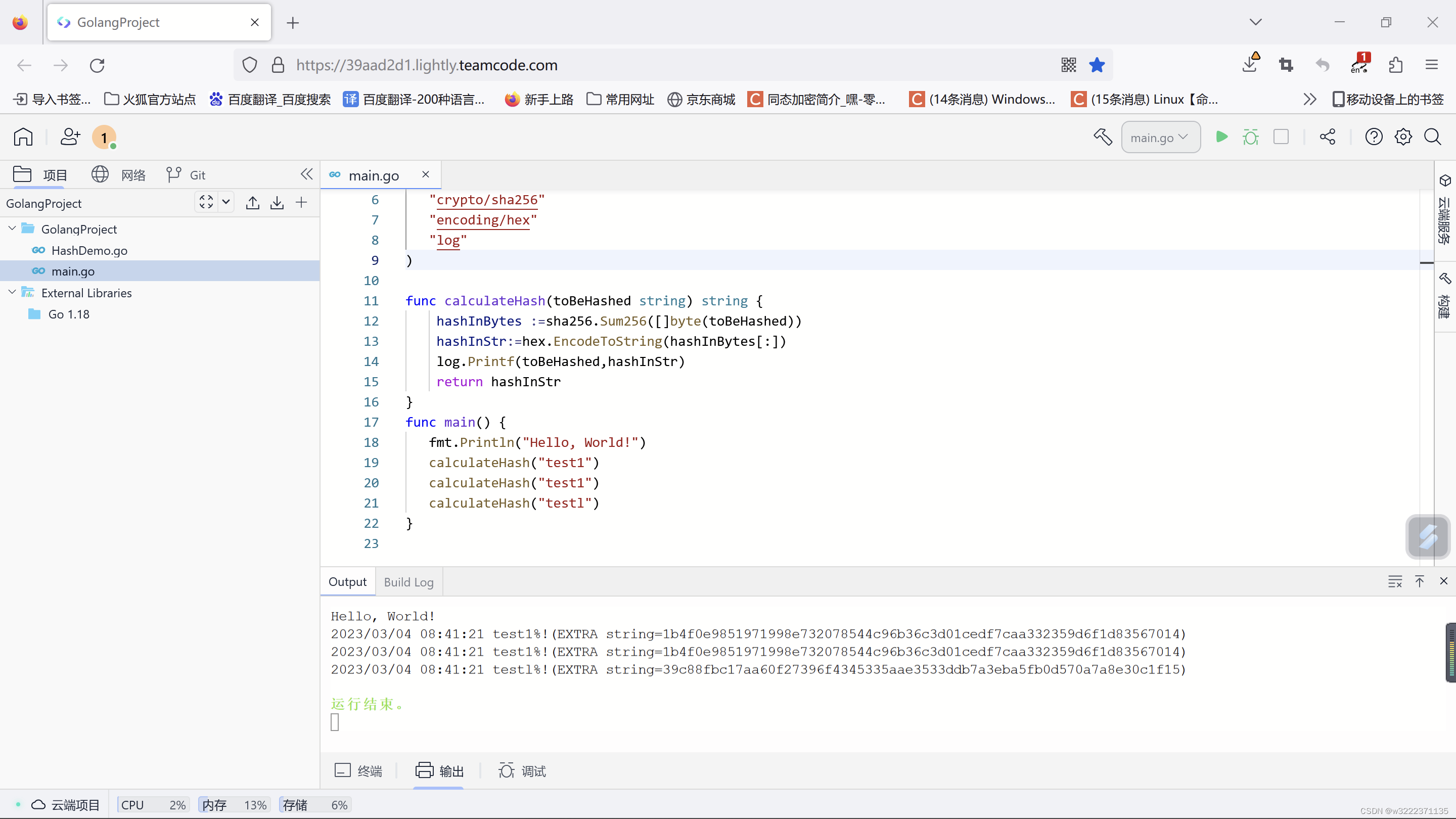
代码实现
package main
import "fmt"
import (
"crypto/sha256"
"encoding/hex"
"log"
)
func calculateHash(toBeHashed string) string {
hashInBytes :=sha256.Sum256([]byte(toBeHashed))
hashInStr:=hex.EncodeToString(hashInBytes[:])
log.Printf(toBeHashed,hashInStr)
return hashInStr
}
func main() {
fmt.Println("Hello, World!")
calculateHash("test1")
calculateHash("test1")
calculateHash("testl")
}
运行结果
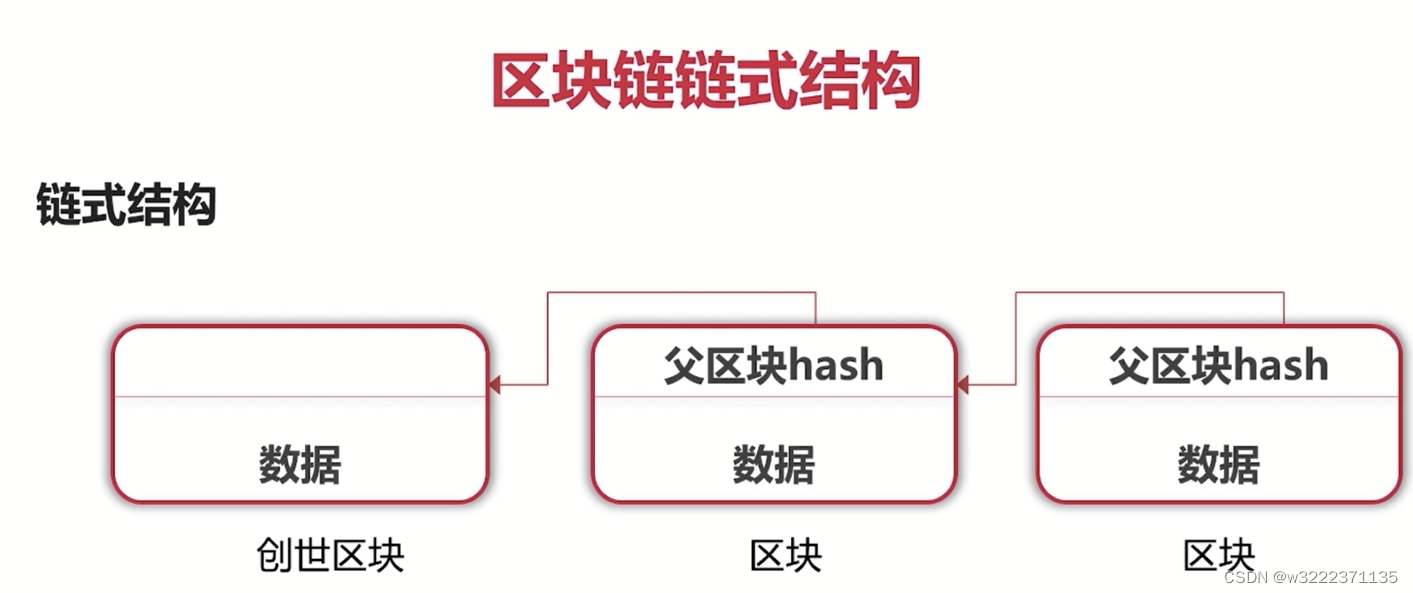
连式结构
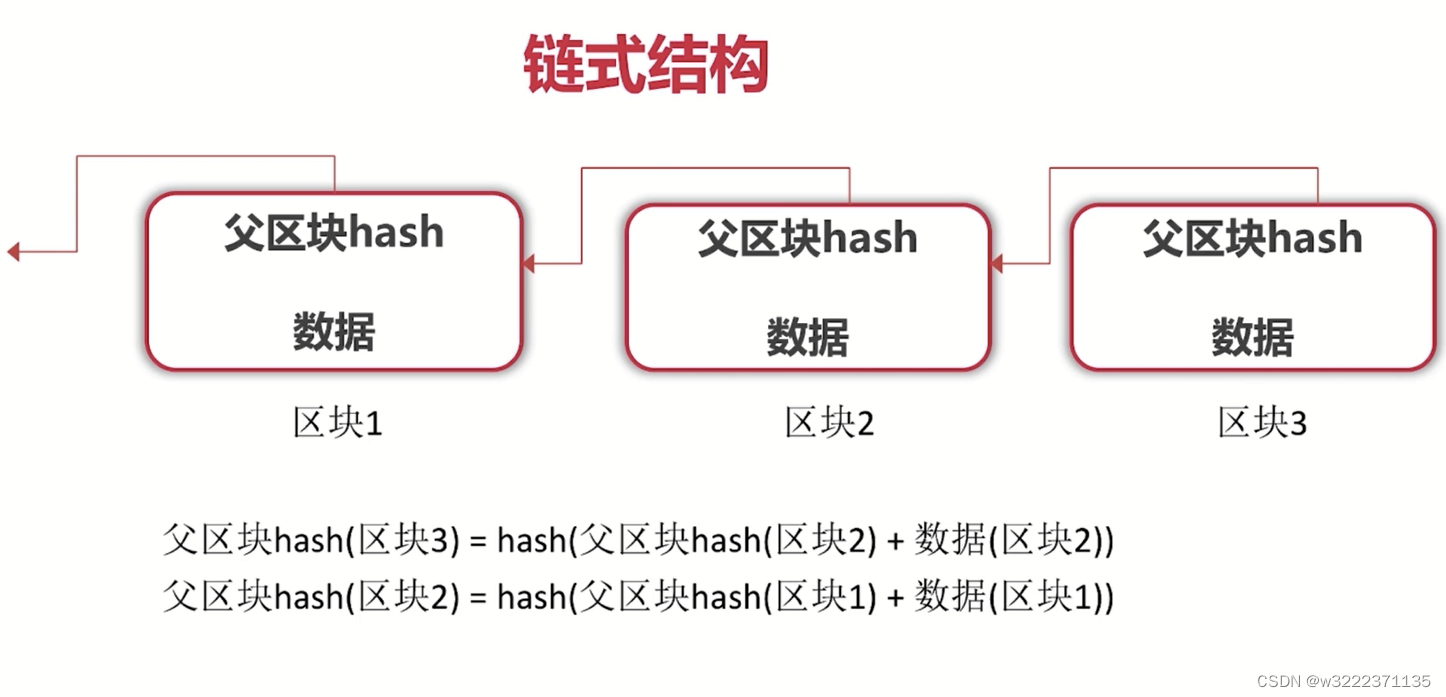 如果区块1的数据发生改变,区块2不发生相应的改变,则指向区块2的hash指针不在有效。如果要使得引用有效,则就要改变区块2的hash值,后面的区块都要发生改变。
如果区块1的数据发生改变,区块2不发生相应的改变,则指向区块2的hash指针不在有效。如果要使得引用有效,则就要改变区块2的hash值,后面的区块都要发生改变。
构建自己的区块链
- 实现链式结构
- 实现一个简单的http server,对外暴露读写接口
步骤
- 创建block
- 创建blockchain
- 创建http server
创建Block
- 新建工程demochain
- 创建Block文件
- 创建Block结构体与相关函数
package demochain
import (
"crypto/sha256"
"encoding/hex"
"time"
)
//区块结构体
type Block struct{
Index int64 //区块编号
Timestamp int64 //区块时间戳
PrevBlockHash string //上一个区块的哈希值
Hash string //当前区块哈希值
Data string //区块数据
}
//计算hsah值
func calculateHash(b Block) string {
//计算hash值包含除了当前区块哈希值的其他数据
blockData:=string(b.Index)+string(b.Timestamp)+b.PrevBlockHash+b.Data
hashInBytes:=sha256.Sum256([]byte(blockData))
return hex.EncodeToString(hashInBytes[:])
}
//生成新区块
func GenerateNewBlock(preBlock Block,data string) Block {
newBlock:=Block{}
newBlock.Index=preBlock.Index+1
newBlock.PrevBlockHash=preBlock.Hash
newBlock.Timestamp=time.Now().Unix()
newBlock.Data=data
newBlock.Hash=calculateHash(newBlock)
return newBlock
}
//创始区块
func GenerateGenesisBlock(){
preBlock :=Block{}
preBlock.Index=-1
preBlock.Hash=""
GenerateNewBlock(preBlock,"Genesis Block")
}
创建Blockchain
- 创建Blockchain文件
- 创建Blockchain结构体及相关方法
package demochain
import (
"fmt"
"log"
)
type Blockchain struct {
Blocks []*Block
}
//创建新的区块链
func NewBlockchain() *Blockchain {
//创始区块
genesisBlock := GenerateGenesisBlock()
blockchain := Blockchain{}
blockchain.AppendBlock(&genesisBlock)
return &blockchain
}
//在区块上增加数据
func (bc *Blockchain) SendData(data string) {
preBlock := bc.Blocks[len(bc.Blocks)-1]
newBlock := GenerateNewBlock(*preBlock, data)
bc.AppendBlock(&newBlock)
}
//添加区块
func (bc *Blockchain) AppendBlock(newBlock *Block) {
if len(bc.Blocks) == 0 {
bc.Blocks = append(bc.Blocks, newBlock)
return
}
if isValid(*newBlock, *bc.Blocks[len(bc.Blocks)-1]) {
bc.Blocks = append(bc.Blocks, newBlock)
} else {
log.Fatal("invalid block")
}
}
//打印区块链里面的数据
func (bc *Blockchain) Print() {
for _, block := range bc.Blocks {
fmt.Printf("Index: %d\n", block.Index)
fmt.Printf("PrevHash: %s\n", block.PrevBlockHash)
fmt.Printf("CurrHash: %s\n", block.Hash)
fmt.Printf("Data: %s\n", block.Data)
fmt.Printf("Timestamp: %d\n", block.Timestamp)
fmt.Println()
}
}
//添加区块前校验
func isValid(newBlock Block, oldBlock Block) bool {
if newBlock.Index-1 != oldBlock.Index {
return false
}
if newBlock.PrevBlockHash != oldBlock.Hash {
return false
}
if calculateHash(newBlock) != newBlock.Hash {
return false
}
return true
}
创建区块链
package main
import "go-blockchain/core"
func main() {
bc := core.NewBlockchain()
bc.SendData("Send 1 BTC to Alice")
bc.SendData("Send 1 EOS to Bob")
bc.Print()
}
结果
创建Http Server
步骤
- 创建http server
- 提供API访问接口
package main
import (
"encoding/json"
"go-blockchain/core"
"io"
"net/http"
)
//全局的blockchain变量
var blockchain *core.Blockchain
//提供http服务
func run() {
http.HandleFunc("/blockchain/get", blockchainGetHandler)
http.HandleFunc("/blockchain/write", blockchainWriteHandler)
//监听端口
http.ListenAndServe("localhost:8888", nil)
}
//get请求的方法
func blockchainGetHandler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
//把任意对象转换为json格式
bytes, error := json.Marshal(blockchain)
if error != nil {
http.Error(w, error.Error(), http.StatusInternalServerError)
return
}
//转换成string
io.WriteString(w, string(bytes))
}
//write请求的方法
func blockchainWriteHandler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
blockData := r.URL.Query().Get("data")
blockchain.SendData(blockData)
blockchainGetHandler(w, r)
}
func main() {
blockchain = core.NewBlockchain()
run()
}