Linux下 JNI的使用
学习 Android 其中涉及对 JNI 的使用;JNI的使用对于 Android 来说又是十分的重要和关键。那么到底 Java 到底是如何调用 C/C++ 的,

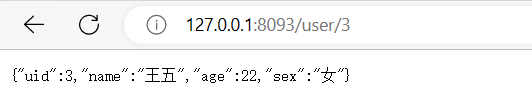
下面是非常简单的计算器源码,只是用来熟悉JNI的基本语法,其中我自己碰到过的一个问题
就是LoadLibrary()调用之后,程序直接崩溃,最开始以为是模拟器是x86的模式,而编译的so文件是arm的模式,但是将模拟器改成arm之后还是崩溃,最后无奈在自己手机上测试也是如此,一打开就直接崩溃,在网上能找到的各种方法都试了,最后发现是so命名的问题
我们经常会写如下的代码输出日志:
Log.d(TAG,”Debug Log”);
我们就以Log系统为例来学习JNI。
我们先看一下Log类的内容,在android源码的\frameworks\base\core\java\android\Log.java文件中
/**
* Send a {@link #DEBUG} log message.
* @param tag Used to identify the source of a log message. It usually identifies
* the class or activity where the log call occurs.
* @param msg The message you would like logged.
*/
publicstaticintd(String tag, String msg) {
returnprintln_native(LOG_ID_MAIN, DEBUG, tag, msg);
}
/** @hide */publicstaticfinalint LOG_ID_MAIN = 0;
/** @hide */publicstaticfinalint LOG_ID_RADIO = 1;
/** @hide */publicstaticfinalint LOG_ID_EVENTS = 2;
/** @hide */publicstaticfinalint LOG_ID_SYSTEM = 3;
/** @hide */publicstatic native intprintln_native(int bufID,
int priority, String tag, String msg);
复制代码可以看到所有的Log的方法都调用了native 的println_native方法,在android源码中的\frameworks\base\core\jni\android_until_Log.cpp文件中实现:
/*
* In class android.util.Log:
* public static native int println_native(int buffer, int priority, String tag, String msg)
*//*
*JNI方法增加了JNIEnv和jobject两参数,其余的参数和返回值只是将Java层参数映**射成JNI的数据类型,然后通过调用本地库和JNIEnv提供的JNI函数处理数据,最后返给java层
*/
static jint android_util_Log_println_native(JNIEnv* env, jobject clazz,
jint bufID, jint priority, jstring tagObj, jstring msgObj)
{
const char* tag = NULL;
const char* msg = NULL;
if (msgObj == NULL) { //异常处理
jclass npeClazz;
npeClazz = env->FindClass("java/lang/NullPointerException");
assert(npeClazz != NULL);
//抛出异常
env->ThrowNew(npeClazz, "println needs a message");
return -1;
}
if (bufID < 0 || bufID >= LOG_ID_MAX) {
jclass npeClazz;
npeClazz = env->FindClass("java/lang/NullPointerException");
assert(npeClazz != NULL);
env->ThrowNew(npeClazz, "bad bufID");
return -1;
}
if (tagObj != NULL)
tag = env->GetStringUTFChars(tagObj, NULL);
msg = env->GetStringUTFChars(msgObj, NULL);
//向内核写入日志
int res = __android_log_buf_write(bufID, (android_LogPriority)priority, tag, msg);
if (tag != NULL)
env->ReleaseStringUTFChars(tagObj, tag);
env->ReleaseStringUTFChars(msgObj, msg);
return res;
}
复制代码至此,JNI层已经实现了在java层声明的Native层方法,但是这两个又是如何联系到一起的呢?我们再看android_util_Log.cpp的源码
/*
* JNI registration.
*/static JNINativeMethod gMethods[] = {
/* name, signature, funcPtr */
{ "isLoggable", "(Ljava/lang/String;I)Z", (void*) android_util_Log_isLoggable },
{"println_native","(IILjava/lang/String;Ljava/lang/String;)I",(void*)android_util_Log_println_native },
};
复制代码在\dalvik\libnativehelper\include\nativehelper\Jni.h文件中有JNINativeMethod 的定义:
typedefstruct {
constchar* name; //java层声明的native函数的函数名
constchar* signature; //Java函数的签名
void* fnPtr; //函数指针,指向JNI层的实现方法
} JNINativeMethod;
复制代码我们可以看到printIn_native的对应关系:
{"println_native","(IILjava/lang/String;Ljava/lang/String;)I",(void*)android_util_Log_println_native }
复制代码Java层声明的函数名是print_native
Java层声明的native函数的签名为(IILjava/lang/String;Ljava/lang/String;)I
JNI方法实现方法的指针为(void*)android_util_Log_println_native
我们知道了java层和JNI层的映射关系,但是如何把这种关系告诉Dalvik虚拟机呢?,我们继续看android_util_Log.cpp的源码
int register_android_util_Log(JNIEnv* env)
{
jclass clazz = env->FindClass("android/util/Log");
if (clazz == NULL) {
LOGE("Can't find android/util/Log");
return -1;
}
levels.verbose = env->GetStaticIntField(clazz, env->GetStaticFieldID(clazz, "VERBOSE", "I"));
levels.debug = env->GetStaticIntField(clazz, env->GetStaticFieldID(clazz, "DEBUG", "I"));
levels.info = env->GetStaticIntField(clazz, env->GetStaticFieldID(clazz, "INFO", "I"));
levels.warn = env->GetStaticIntField(clazz, env->GetStaticFieldID(clazz, "WARN", "I"));
levels.error = env->GetStaticIntField(clazz, env->GetStaticFieldID(clazz, "ERROR", "I"));
levels.assert = env->GetStaticIntField(clazz, env->GetStaticFieldID(clazz, "ASSERT", "I"));
return AndroidRuntime::registerNativeMethods(env, "android/util/Log", gMethods, NELEM(gMethods));
}
}; // namespace android复制代码这个函数的最后调用了AndroidRuntime::registerNativeMethods函数
可以在\frameworks\base\core\jni\AndroidRuntime.cpp 中找到registerNativeMethods的实现
/*
* Register native methods using JNI.
*//*static*/intAndroidRuntime::registerNativeMethods(JNIEnv* env,
constchar* className, const JNINativeMethod* gMethods, int numMethods){
returnjniRegisterNativeMethods(env, className, gMethods, numMethods);
}
复制代码他的内部实现只是调用了jniRegisterNativeMethods ()。
在\dalvik\libnativehelper\JNIHelp.c中jniRegisterNativeMethods函数的实现
/*
* Register native JNI-callable methods.
*
* "className" looks like "java/lang/String".
*/
int jniRegisterNativeMethods(JNIEnv* env, const char* className,
const JNINativeMethod* gMethods, int numMethods)
{
jclass clazz;
LOGV("Registering %s natives\n", className);
clazz = (*env)->FindClass(env, className);
if (clazz == NULL) {
LOGE("Native registration unable to find class '%s'\n", className);
return -1;
}
int result = 0;
if ((*env)->RegisterNatives(env, clazz, gMethods, numMethods) < 0) {
LOGE("RegisterNatives failed for '%s'\n", className);
result = -1;
}
(*env)->DeleteLocalRef(env, clazz);
return result;
}
复制代码这里是调用了JNIEnv的RegisterNatives函数,可以阅读函数的注释,注册一个类的Native方法。已经告诉了虚拟机java层和native层的映射关系。
/*
* Register one or more native functions in one class.
*
* This can be called multiple times on the same method, allowing the
* caller to redefine the method implementation at will.
*/
static jint RegisterNatives(JNIEnv* env, jclass jclazz,
const JNINativeMethod* methods, jint nMethods)
{
JNI_ENTER();
ClassObject* clazz = (ClassObject*) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(env, jclazz);
jint retval = JNI_OK;
int i;
if (gDvm.verboseJni) {
LOGI("[Registering JNI native methods for class %s]\n",
clazz->descriptor);
}
for (i = 0; i < nMethods; i++) {
if (!dvmRegisterJNIMethod(clazz, methods[i].name,
methods[i].signature, methods[i].fnPtr))
{
retval = JNI_ERR;
}
}
JNI_EXIT();
return retval;
}
复制代码其作用是向clazz参数指定的类注册本地方法,这样,虚拟机就能得到Java层和JNI层之间的对应关系,就可以实现java和native层代码的交互了。我们注意到在Log系统的实例中,JNI层实现方法和注册方法中都使用了JNIEnv这个指针,通过它调用JNI函数,访问Dalvik虚拟机,进而操作Java对象
我们可以在\Dalvik\libnativehelper\include\nativehelper\jni.h中找到JNIEnv的定义:
struct_JNIEnv;
struct_JavaVM;
typedefconststructJNINativeInterface* C_JNIEnv;
#if defined(__cplusplus) //定义了C++typedef _JNIEnv JNIEnv; //C++中的JNIEnv的类型typedef _JavaVM JavaVM;
#elsetypedefconststructJNINativeInterface* JNIEnv;
typedefconststructJNIInvokeInterface* JavaVM;
#endif复制代码这里只是用关键字typedef关键字做了类型定义,那么_JNIEnv和JNINativeInterface的定义
/*
* C++ object wrapper.
*
* This is usually overlaid on a C struct whose first element is a
* JNINativeInterface*. We rely somewhat on compiler behavior.
*/
struct _JNIEnv {
/* do not rename this; it does not seem to be entirely opaque */
const struct JNINativeInterface* functions;
#if defined(__cplusplus)
jint GetVersion()
{ return functions->GetVersion(this); }
jclassDefineClass(const char *name, jobject loader, const jbyte* buf,
jsize bufLen)
{ return functions->DefineClass(this, name, loader, buf, bufLen); }
jclassFindClass(const char* name)
{ return functions->FindClass(this, name); }
jmethodID FromReflectedMethod(jobject method)
{ return functions->FromReflectedMethod(this, method); }
………..
复制代码_JNIEnv只是对const struct JNINativeInterface类型的封装,并间接调用const struct JNINativeInterface上定义的方法
/*
* Table of interface function pointers.
*/
struct JNINativeInterface {
……
jclass (*FindClass)(JNIEnv*, const char*);
jboolean (*IsSameObject)(JNIEnv*, jobject, jobject);
……
};
复制代码这里才真正涉及JNI函数的调用,也只是一个接口
但是我们可以得出如下结论:
C++中: JNIEnv就是struct _JNIEnv。JNIEnv *env 等价于 struct _JNIEnv env ,在调用JNI函数的时候,只需要env->FindClass(JNIEnv,const char ),就会间接调用JNINativeInterface结构体里面定义的函数指针,而无需首先对env解引用。
C中: JNIEnv就是const struct JNINativeInterface *。JNIEnv env 等价于const struct JNINativeInterface ** env,因此要得到JNINativeInterface结构体里面的函数指针就必须先对env解引用得到( env),得到const struct JNINativeInterface *,才是真正指向JNINativeInterface结构体的指针,然后再通过它调用具体的JNI函数,因此需要这样调用:
(env)->FindClass(JNIEnv,const char*)。
尾述
最后这里放上一张大佬推荐的 音视频开发 的脑图,并根据脑图整理了一份 系统学习的资料笔记和配套视频; 音视频开发技术相关的知识点在 笔记中都有详细的 解读,并且把每个 技术点整理成了 PDF 文档(知识脉络 + 诸多细节)有需要的小伙伴点击文末的卡片或者【 点击这里】