Spring 6 and JUnit 5 组合
Spring 6 and JUnit 5 只需引入相关的包,不过偶尔可能会出现 no tests were found,最后有解决方案。
引入相关依赖包
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>jakarta.annotation</groupId>
<artifactId>jakarta.annotation-api</artifactId>
<version>2.1.1</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>6.0.5</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-test</artifactId>
<version>6.0.5</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-jupiter-api</artifactId>
<version>5.9.2</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mockito</groupId>
<artifactId>mockito-core</artifactId>
<version>4.8.1</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>1.18.22</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
创建相关测试环境类
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("pr.iceworld.fernando.spring6.junit5")
public class TestConfig {
}
@ContextConfiguration(classes = TestConfig.class)
@ExtendWith(SpringExtension.class)
@Slf4j
class BaseTest {
@BeforeEach
public void setUp() {
MockitoAnnotations.openMocks(this);
log.info("@BeforeEach");
}
@BeforeAll
public static void staticInit() {
log.info("@BeforeAll");
}
@AfterEach
public void tearDown() {
log.info("@AfterEach");
}
@AfterAll
public static void staticFinished() {
log.info("@AfterAll");
}
}
编写测试用例
@DisplayName("This is a test class - for Fruit")
@Slf4j
public class TestFruit extends BaseTest {
@InjectMocks
FruitService fruitService;
@Mock
FruitRepository fruitRepository;
@DisplayName("test get one fruit by id")
@Test
public void testGetOneFruitById() {
Fruit apple = new Fruit();
Long id = 301L;
apple.setId(id);
apple.setName("apple");
when(fruitRepository.getById(id)).thenReturn(apple);
Fruit foundFruit = fruitService.getFruitById(id);
assertEquals(apple.getId(), foundFruit.getId());
}
@Disabled
@Test
public void testDisableMethod() {
log.info("@Disabled, specific this method will still run, if run test whole class, this will be ignore");
}
@Disabled
@Test
public void testassertEqualsFailed() {
assertEquals(5, 6);
}
@Disabled
@Test
public void testDisabledRuntimeException() {
throw new RuntimeException("RuntimeException");
}
}
创建对应的测试用例相关类及方法
public class Fruit {
private Long id;
private String name;
// getter or setter
}
@Repository
public class FruitRepository {
static List<Fruit> fruits = new ArrayList<>();
public List<Fruit> getFruits() {
return fruits;
}
public Fruit getById(Long id) {
return fruits.stream().filter(e -> e.getId() == id).findFirst().orElseGet(() -> new Fruit());
}
public void save(Fruit fruit) {
fruits.add(fruit);
}
}
@Service
public class FruitService {
@Resource
FruitRepository fruitRepository;
public List<Fruit> getFruits() {
return fruitRepository.getFruits();
}
public void save(Fruit fruit) {
fruitRepository.save(fruit);
}
public Fruit getFruitById(Long id) {
return fruitRepository.getById(id);
}
}
注意事项
@Disabled
全类测试,@Disabled 生效
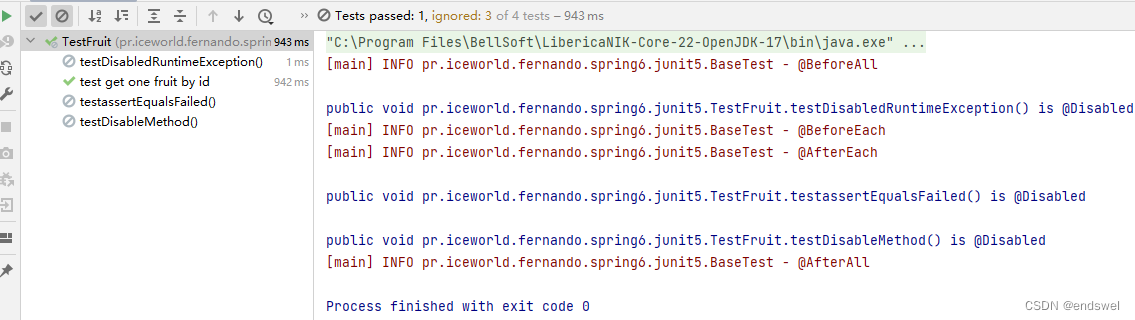
方法测试,@Disabled 不生效
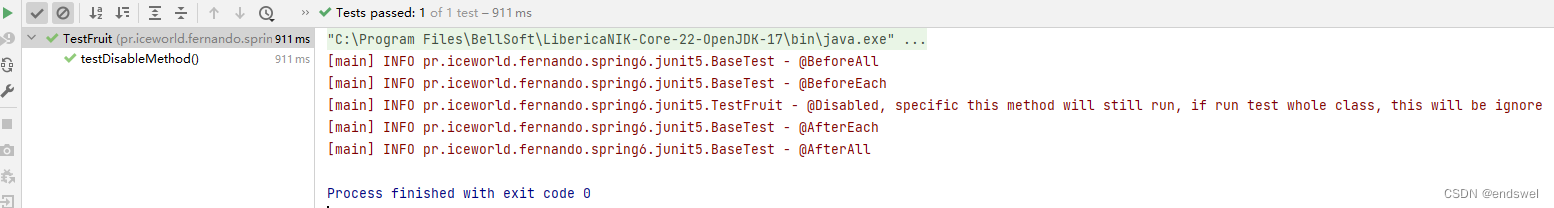
no tests were found
如果出现 no tests were found ,则对pom.xml更新
<!-- ... -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.platform</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-platform-launcher</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-jupiter-engine</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.vintage</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-vintage-engine</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- ... -->
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-bom</artifactId>
<version>5.9.2</version>
<scope>import</scope>
<type>pom</type>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-surefire-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.0.0-M9</version>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-failsafe-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.0.0-M9</version>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
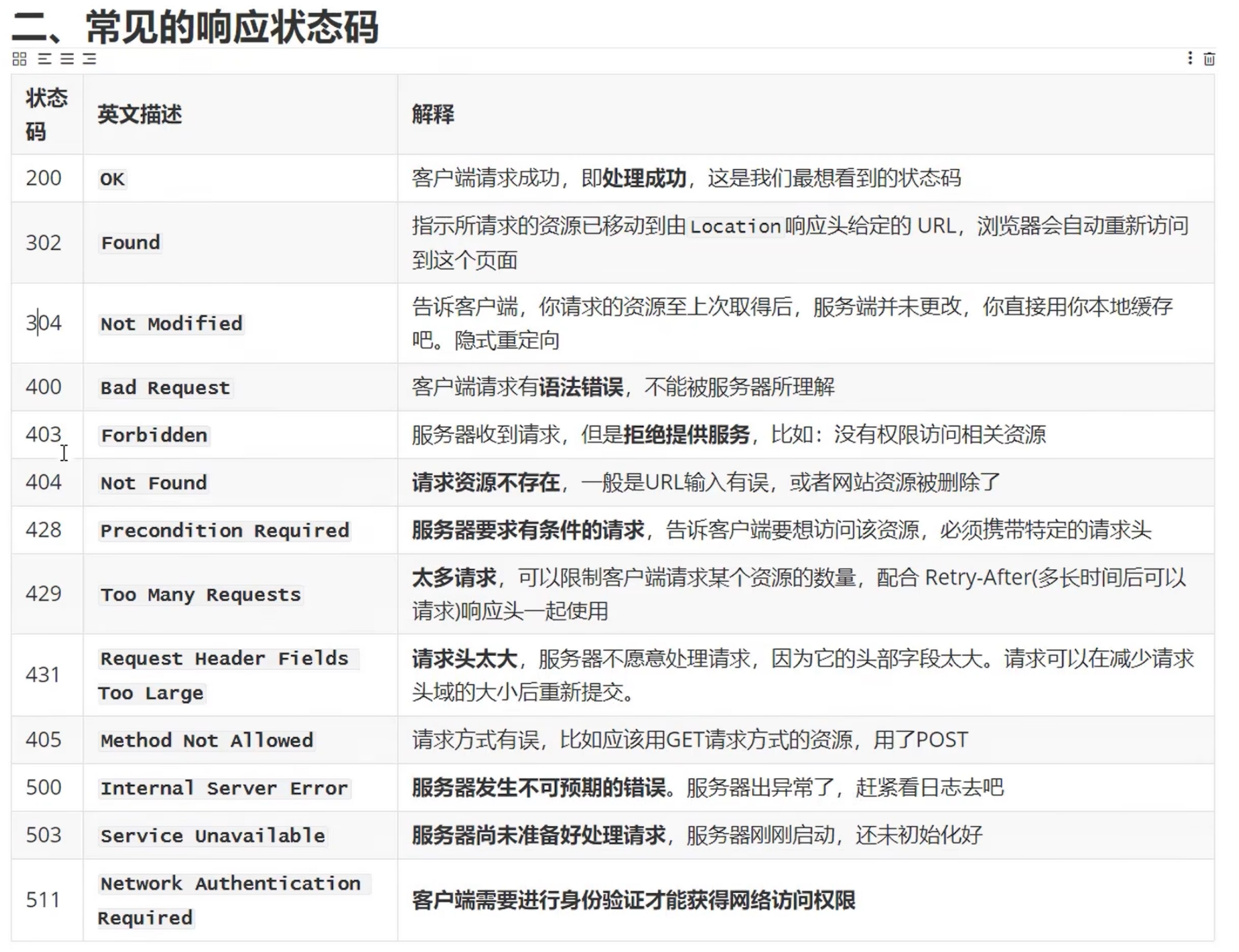
JUnit 5 注释
| Annotation | Description |
|---|---|
| @Test | Denotes that a method is a test method. Unlike JUnit 4’s @Test annotation, this annotation does not declare any attributes, since test extensions in JUnit Jupiter operate based on their own dedicated annotations. Such methods are inherited unless they are overridden. |
| @ParameterizedTest | Denotes that a method is a parameterized test. Such methods are inherited unless they are overridden. |
| @RepeatedTest | Denotes that a method is a test template for a repeated test. Such methods are inherited unless they are overridden. |
| @TestFactory | Denotes that a method is a test factory for dynamic tests. Such methods are inherited unless they are overridden. |
| @TestTemplate | Denotes that a method is a template for test cases designed to be invoked multiple times depending on the number of invocation contexts returned by the registered providers. Such methods are inherited unless they are overridden. |
| @TestClassOrder | Used to configure the test class execution order for @Nested test classes in the annotated test class. Such annotations are inherited. |
| @TestMethodOrder | Used to configure the test method execution order for the annotated test class; similar to JUnit 4’s @FixMethodOrder. Such annotations are inherited. |
| @TestInstance | Used to configure the test instance lifecycle for the annotated test class. Such annotations are inherited. |
| @DisplayName | Declares a custom display name for the test class or test method. Such annotations are not inherited. |
| @DisplayNameGeneration | Declares a custom display name generator for the test class. Such annotations are inherited. |
| @BeforeEach | Denotes that the annotated method should be executed before each @Test, @RepeatedTest, @ParameterizedTest, or @TestFactory method in the current class; analogous to JUnit 4’s @Before. Such methods are inherited – unless they are overridden or superseded (i.e., replaced based on signature only, irrespective of Java’s visibility rules). |
| @AfterEach | Denotes that the annotated method should be executed after each @Test, @RepeatedTest, @ParameterizedTest, or @TestFactory method in the current class; analogous to JUnit 4’s @After. Such methods are inherited – unless they are overridden or superseded (i.e., replaced based on signature only, irrespective of Java’s visibility rules). |
| @BeforeAll | Denotes that the annotated method should be executed before all @Test, @RepeatedTest, @ParameterizedTest, and @TestFactory methods in the current class; analogous to JUnit 4’s @BeforeClass. Such methods are inherited – unless they are hidden, overridden, or superseded, (i.e., replaced based on signature only, irrespective of Java’s visibility rules) – and must be static unless the “per-class” test instance lifecycle is used. |
| @AfterAll | Denotes that the annotated method should be executed after all @Test, @RepeatedTest, @ParameterizedTest, and @TestFactory methods in the current class; analogous to JUnit 4’s @AfterClass. Such methods are inherited – unless they are hidden, overridden, or superseded, (i.e., replaced based on signature only, irrespective of Java’s visibility rules) – and must be static unless the “per-class” test instance lifecycle is used. |
| @Nested | Denotes that the annotated class is a non-static nested test class. On Java 8 through Java 15, @BeforeAll and @AfterAll methods cannot be used directly in a @Nested test class unless the “per-class” test instance lifecycle is used. Beginning with Java 16, @BeforeAll and @AfterAll methods can be declared as static in a @Nested test class with either test instance lifecycle mode. Such annotations are not inherited. |
| @Tag | Used to declare tags for filtering tests, either at the class or method level; analogous to test groups in TestNG or Categories in JUnit 4. Such annotations are inherited at the class level but not at the method level. |
| @Disabled | Used to disable a test class or test method; analogous to JUnit 4’s @Ignore. Such annotations are not inherited. |
| @Timeout | Used to fail a test, test factory, test template, or lifecycle method if its execution exceeds a given duration. Such annotations are inherited. |
| @ExtendWith | Used to register extensions declaratively. Such annotations are inherited. |
| @RegisterExtension | Used to register extensions programmatically via fields. Such fields are inherited unless they are shadowed. |
| @TempDir | Used to supply a temporary directory via field injection or parameter injection in a lifecycle method or test method; located in the org.junit.jupiter.api.io package. |