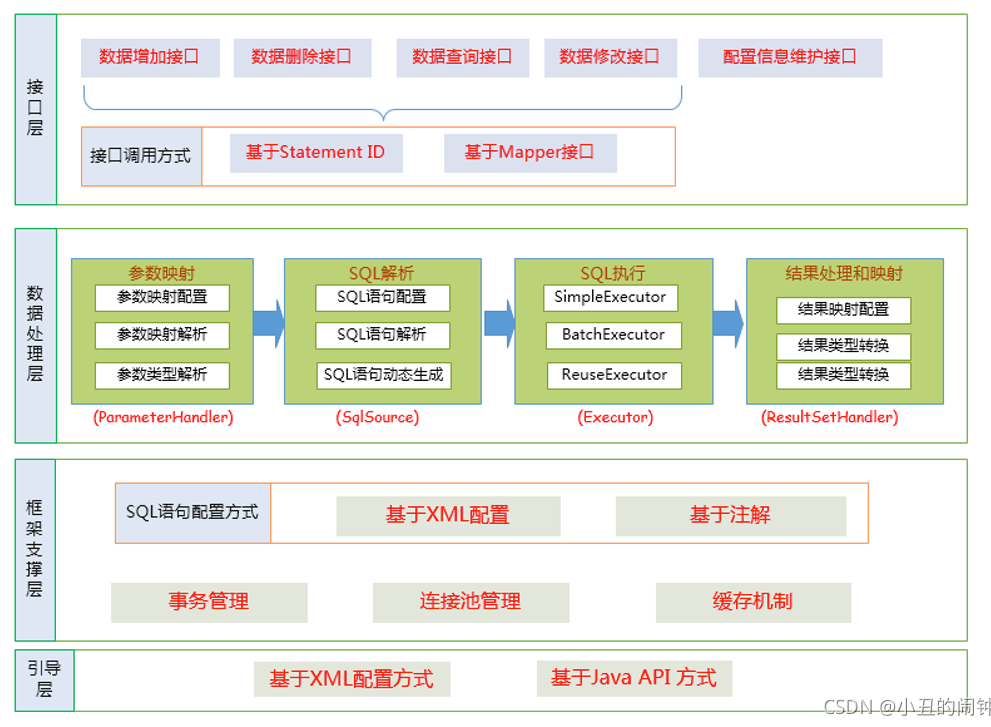
分层架构图
主要流程图
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-d9uhH9IK-1677658947721)(https://note.youdao.com/yws/public/resource/7f152b4b25320263d411a49583d3f4db/xmlnote/WEBRESOURCE9ea90840088eaeaa4a463bbc3f1912e8/17619)]
主要流程总结:
- 1.获取sqlSessionFactory对象
- 2.获取sqlSession对象
- 3.获取mapper接口的代理对象(MapperProxy)
- 4.执行增删改查方法
源码分析
0、mybatis的数据源配置文件
我们的项目一般都是spring,在集成mybatis的时候一定会有一个数据源的配置,用来初始化mybatis的各种内置组件、解析xml文件等功能。如:
@Configuration
@MapperScan(basePackages = "com.xxx.xxx.mapper", sqlSessionTemplateRef = "sqlSessionTemplate")
public class DataSourceConfig {
public static final Logger logger = LogManager.getLogger(DataSourceConfig.class);
@Value("${mysql.lion.mapperLocations}")
private String mapperLocations;
// 加载全局的配置文件
@Value("${mysql.configLocation}")
private String configLocation;
@Bean
public SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory(@Qualifier("routeDataSource") DataSource dataSource) {
logger.info("-------------------- sqlSessionFactory init ---------------------");
try {
SqlSessionFactoryBean sessionFactoryBean = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
sessionFactoryBean.setDataSource(dataSource);
// 设置mapper.xml文件所在位置
Resource[] resources = new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver().getResources(mapperLocations);
sessionFactoryBean.setMapperLocations(resources);
// 设置mybatis-config.xml配置文件位置
sessionFactoryBean.setConfigLocation(new DefaultResourceLoader().getResource(configLocation));
return sessionFactoryBean.getObject();
} catch (IOException e) {
logger.error("mybatis resolver mapper*xml is error", e);
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("mybatis sqlSessionFactoryBean create error", e);
}
return null;
}
}
断点打在这个的return处,我们启动项目,就能开始deug分析源码了,让我们发车!
1、SqlSessionFactoryBean
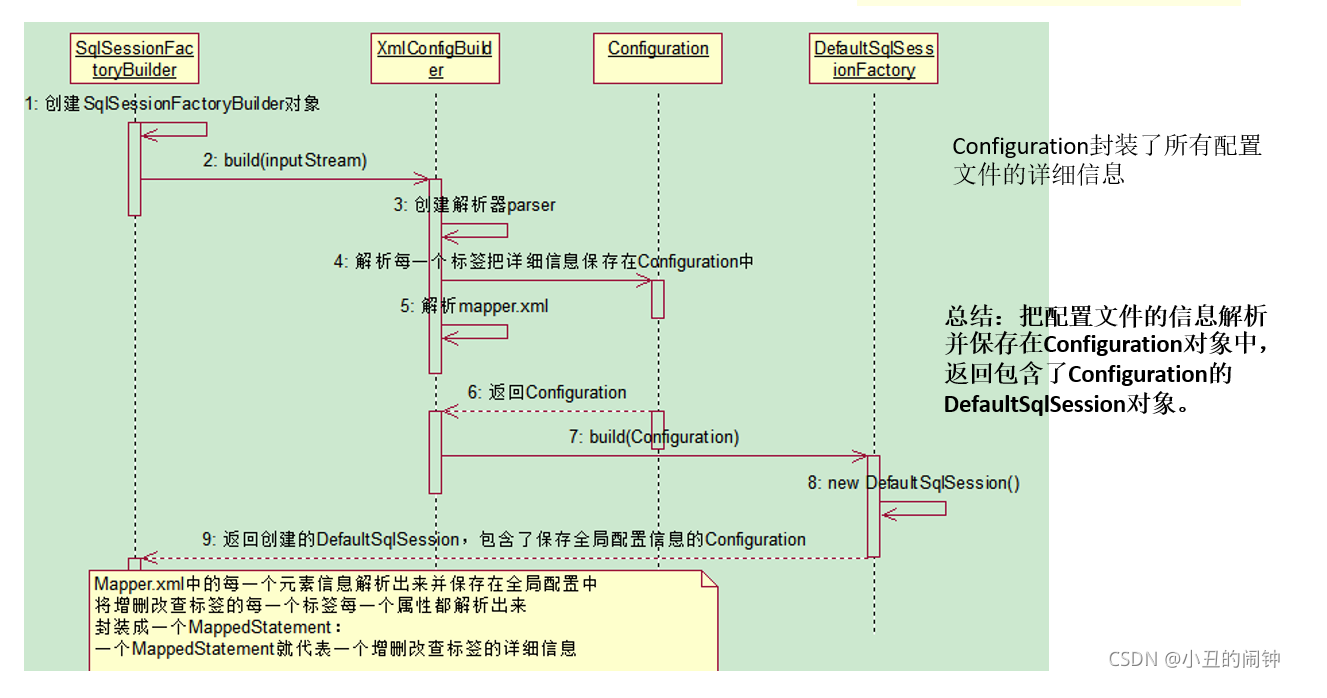
按照上面的步骤,我们一直跟踪源码,会发现得到了一个 DefaultSqlSessionFactory 对象,其实从类名字就不难看出,这是一个生成 SqlSession 对象的工厂类。具体时序图:
我们简单看一下最终初始化出来了的 SqlSessionFactory :
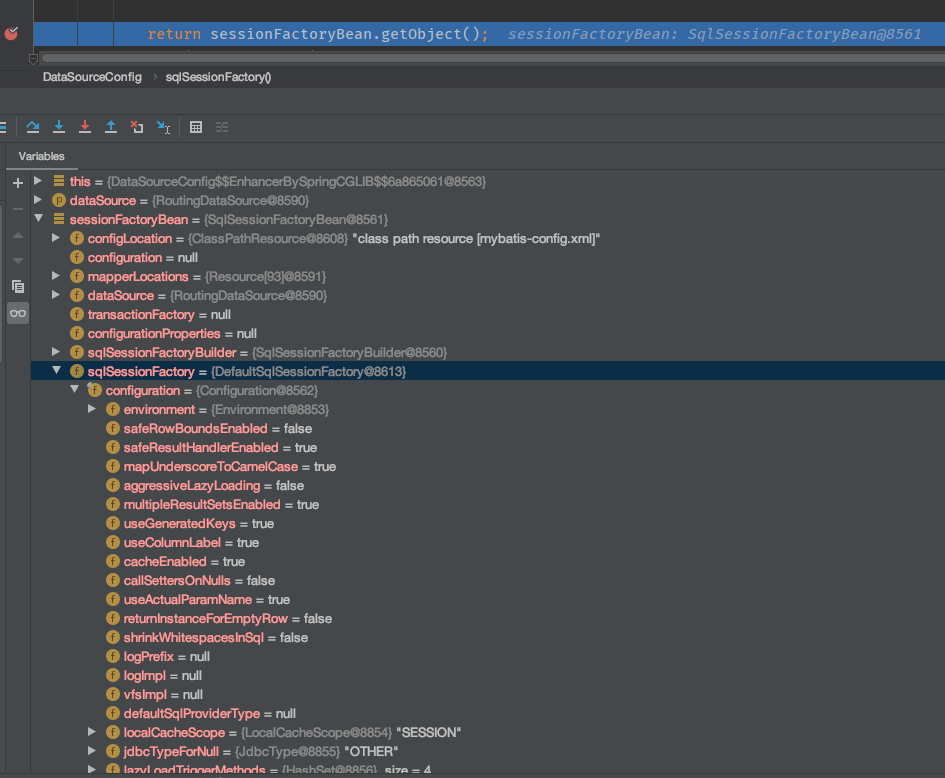
SqlSessionFactory是应用程序级别的,一次启动就只会初始化一个单例对象。
2、获取sqlSession对象
这个sqlSession对象比较复杂,因为要和spring集成,就存在代理的场景,我们先看服务启动的时候,debug结果:
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-OkjE5bKy-1677658947724)(https://note.youdao.com/yws/public/resource/7f152b4b25320263d411a49583d3f4db/xmlnote/WEBRESOURCEa6d69245d97e98e191c760dd0d0718d0/17717 “image”)]
注意这里的四大对象,都非常有用。
并且,这时候的sqlSession对象是代理对象。
项目启动完成之后,需要用到mybatis操作数据库的时候,每次请求都会创建一个sqlSession对象,也就是说这个对象是线程不安全的。
不知道你有没有这样的疑问,为什么这里的四个主流程是创建sqlSession对象在前,创建Mapper对象在后,一定是这样吗??在debug源码的时候怎么验证呢??
那么,这个代理对象的invoke方法是什么时候被执行的呢?我们一起debug一次请求,断点就放在这个方法处,断住以后,我们发现调用栈是:
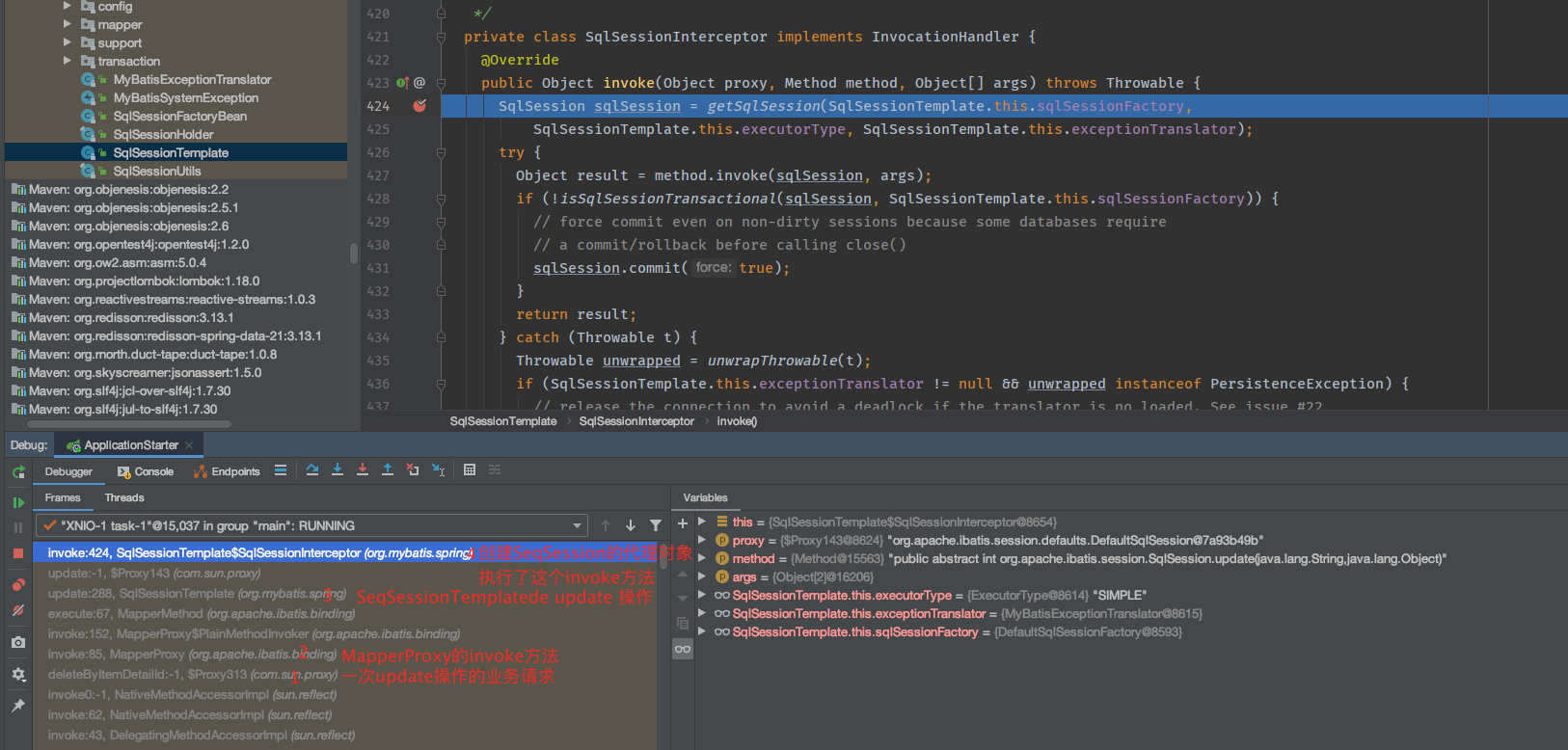
这就将sqlSession对象和Mapper对象的创建先后关系展示的很清楚了。
说清楚了这两个的先后关系,我们再来着重看一下SeqSession对象创建的时序图:
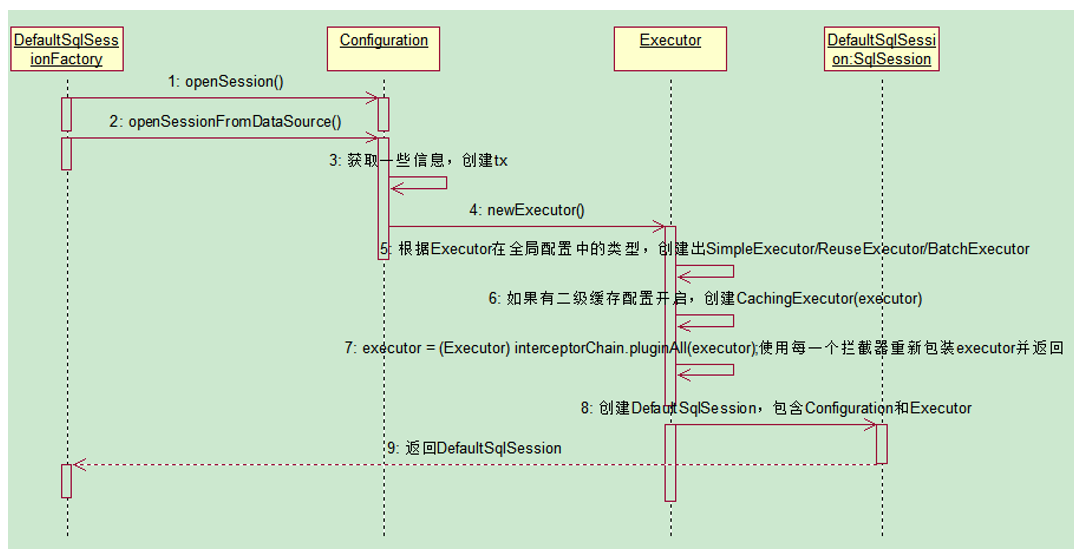
主流程代码粘贴:
private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) {
Transaction tx = null;
try {
final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment();
final TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment);
tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit);
final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType);
return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit);
} catch (Exception e) {
closeTransaction(tx); // may have fetched a connection so lets call close()
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
注意看这里的finally模块,每次创建完sqlSession对象都会reset 当前的sqlSession的相关信息。
3、获取Mapper
其实,在刚开始用mybatis的时候,我们可能都有疑惑,为什么我们定义了一个接口,加了@Mapper注解就能执行我们的SQL了?这里面用的就是代理技术,实际执行SQL的是代理类。
那么,在一次请求中,Mapper是如何获取的呢?
简单看下时序图:
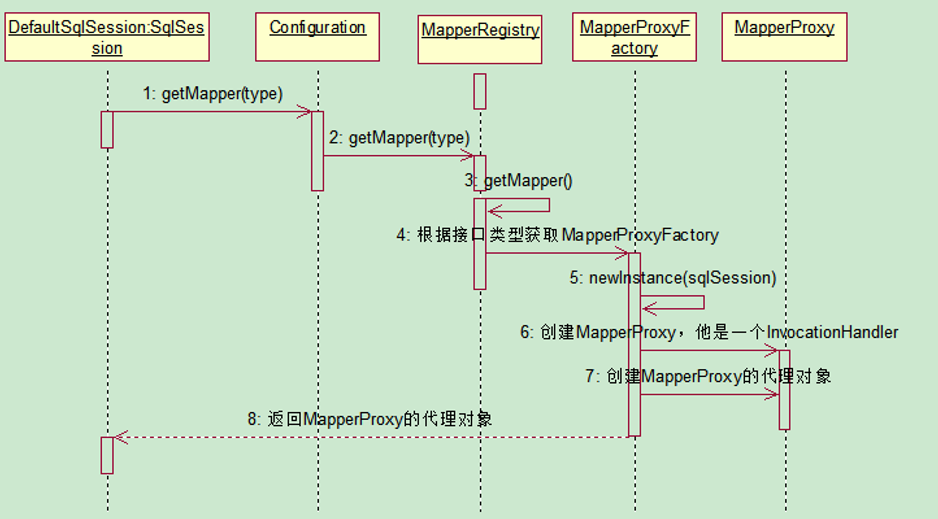
补充说明几个点:
-
Mapper中的数据主要分两部分,一部分是项目启动的时候解析出来,然后加载进去的,一部分是代理类执行了invoke方法附加进去的
-
在项目启动的时候就会把Mapper接口加载并解析存储到Configuration对象,这里从Configuration对象中再去拿具体的Mapper
这部分的代码比较直观,结合上面第二步的创建SeqSession对象的debug调用栈就能梳理清楚。
4、获取和使用目标对象
创建完Mapper代理对象之后,就要执行业务请求的具体操作了。
先看一下时序图:
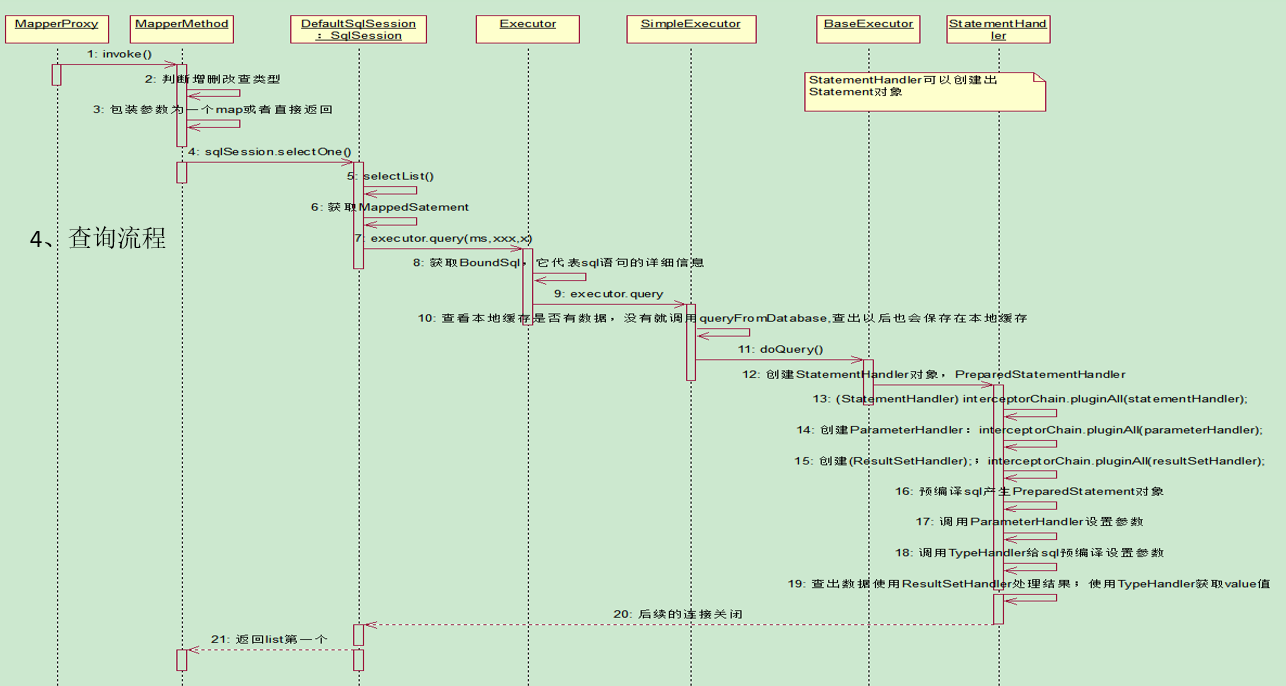
我们顺着时序图,一直跟踪下去,会的带断点图:
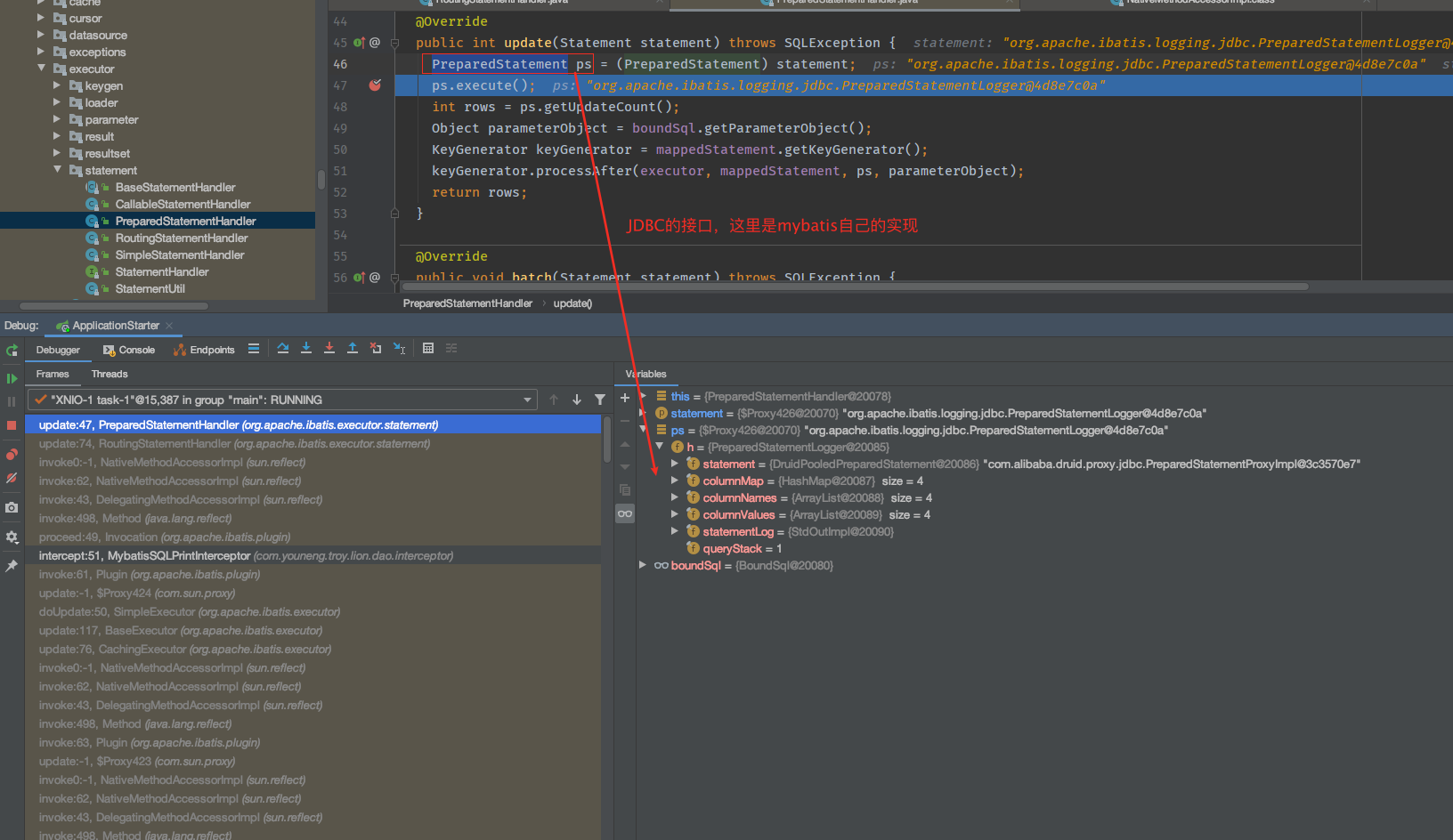
到这里,已经清楚地肯见了JDBC的接口,并且执行了具体的SQL操作。
对于查询请求,还有一个封装结果集的操作,我们再发起一个查询请求,debug一下:
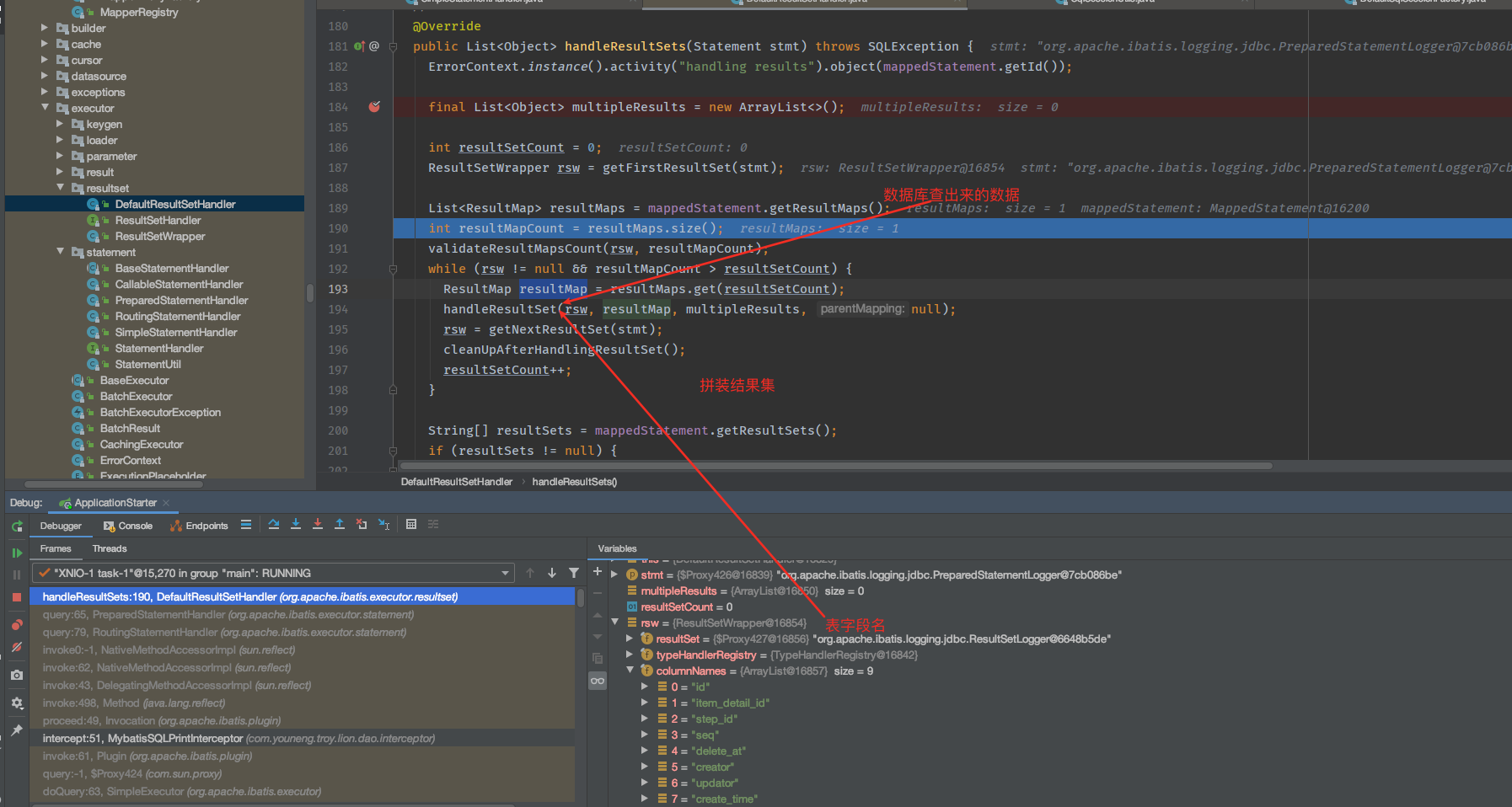
5、spring是怎么保证SeqSession线程安全性的
回答这个问题,我们想回顾一下第2步,创建SeqSession对象的逻辑,这里粘贴一下SeqSessionUtils的getSeqSession方法的源码:
public static SqlSession getSqlSession(SqlSessionFactory sessionFactory, ExecutorType executorType,
PersistenceExceptionTranslator exceptionTranslator) {
notNull(sessionFactory, NO_SQL_SESSION_FACTORY_SPECIFIED);
notNull(executorType, NO_EXECUTOR_TYPE_SPECIFIED);
// 注意这一行代码是如何获取SeqSession对象的
SqlSessionHolder holder = (SqlSessionHolder) TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource(sessionFactory);
SqlSession session = sessionHolder(executorType, holder);
if (session != null) {
return session;
}
LOGGER.debug(() -> "Creating a new SqlSession");
session = sessionFactory.openSession(executorType);
registerSessionHolder(sessionFactory, executorType, exceptionTranslator, session);
return session;
}
然后,我们将 TransactionSynchronizationManager 展开说说:
public abstract class TransactionSynchronizationManager {
private static final ThreadLocal<Map<Object, Object>> resources =
new NamedThreadLocal<>("Transactional resources");
private static final ThreadLocal<Set<TransactionSynchronization>> synchronizations =
new NamedThreadLocal<>("Transaction synchronizations");
private static final ThreadLocal<String> currentTransactionName =
new NamedThreadLocal<>("Current transaction name");
private static final ThreadLocal<Boolean> currentTransactionReadOnly =
new NamedThreadLocal<>("Current transaction read-only status");
private static final ThreadLocal<Integer> currentTransactionIsolationLevel =
new NamedThreadLocal<>("Current transaction isolation level");
private static final ThreadLocal<Boolean> actualTransactionActive =
new NamedThreadLocal<>("Actual transaction active");
所以,结论找到了:spring将SqlSession通过 TransactionSynchronizationManager 的ThreadLocal 管理起来了,由此实现了线程安全性。
补充
- SqlSessionTemplate是Mybatis为了接入Spring提供的Bean。通过TransactionSynchronizationManager中的ThreadLocal<Map<Object, Object>>保存线程对应的SqlSession,实现session的线程安全
- SqlSessionManager是Mybatis不接入Spring时用于管理SqlSession的Bean。通过SqlSessionManagger的ThreadLocal实现session的线程安全。