这篇文章是承接着[rootfs]用busybox做一个rootfs(根文件系统)来的,再回看这篇我很久之前写的文章的时候,有一个问题出现在我的脑海中,创建了这个文件那个文件,但确实是每个文件都是必需的吗?
这篇文章我们就来讨论下这个问题。
1 busybox
当我们讨论精简文件问题的时候,busybox由于是直接编译出来的,我们暂且认为编译出来的所有binary都是必需的。
2 只有busybox行不行
busybox提供了rootfs所必须的文件,但是linux boot到最后的时候还会寻找root= 或者 init=,所以我们还需要这么一个文件告诉kernel一些必要的信息。
在这里我们把bootargs设为bootargs=console=ttyS0,115200 earlycon=sbi init=/sbin/init。
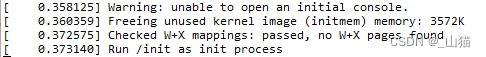
但是实际上启动的时候会进不了console
3 考虑添加一个init文件
在这里我们先不去探讨为什么直接设置init=/sbin/init会卡住,这个牵涉到linux启动的一些话题,后面再讨论。
我们只是简单地添加一个init文件,同时,修改bootargs
bootargs=console=ttyS0,115200 earlycon=sbi init=/init
内容如下,不要忘记修改权限$ chmod 0777 init
#!/bin/sh
PATH=/sbin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin
do_mount_fs() {
grep -q "$1" /proc/filesystems || return
test -d "$2" || mkdir -p "$2"
mount -t "$1" "$1" "$2"
}
do_mknod() {
test -e "$1" || mknod "$1" "$2" "$3" "$4"
}
mkdir -p /proc
mount -t proc proc /proc
do_mount_fs sysfs /sys
do_mount_fs devtmpfs /dev
do_mount_fs devpts /dev/pts
do_mount_fs tmpfs /dev/shm
mkdir -p /run
mkdir -p /var/run
do_mknod /dev/console c 5 1
do_mknod /dev/null c 1 3
do_mknod /dev/zero c 1 5
# use the /dev/console device node from devtmpfs if possible to not
# confuse glibc's ttyname_r().
# This may fail (E.G. booted with console=), and errors from exec will
# terminate the shell, so use a subshell for the test
if (exec 0</dev/console) 2>/dev/null; then
exec 0</dev/console
exec 1>/dev/console
exec 2>/dev/console
fi
exec /sbin/init "$@"
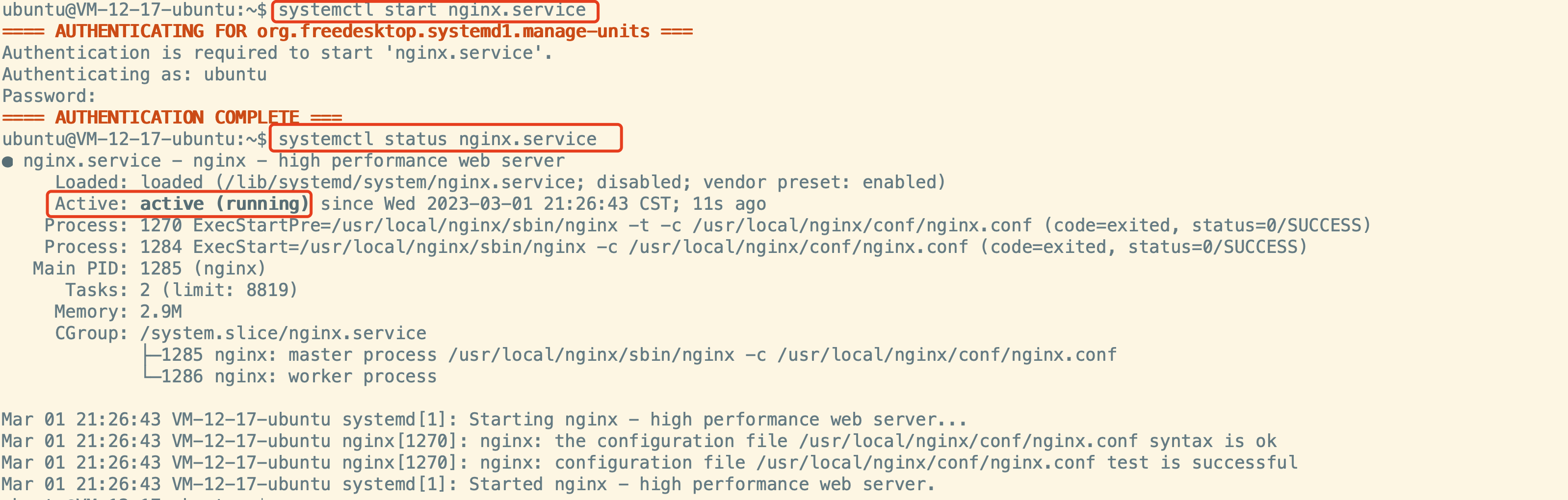
这时我们发现已经可以进console了。
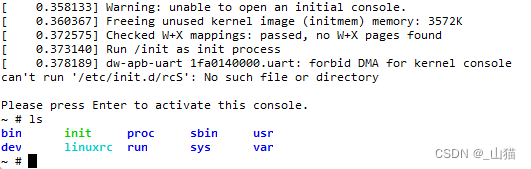
但是会有一个讨厌的提示:
can't run '/etc/init.d/rcS': No such file or directory
4 /sbin/init 做了什么
加载内核后,它会立即初始化和配置计算机的内存,并配置连接到系统的各种硬件,包括所有处理器、I/O 子系统和存储设备。 然后内核创建一个根设备,以只读方式挂载根分区,并释放所有未使用的内存。此时,内核被加载到内存中并开始运行。
然而,由于没有用户应用程序允许对系统进行有意义的输入,因此系统无法完成很多工作。为了设置用户环境,内核执行/sbin/init 程序。
/sbin/init 程序(也称为 init)协调引导过程的其余部分并为用户配置环境,即pid=1的进程,运行在内核态,也是唯一一个没有通过fork()或者kernel_thread()创建的进程。当 init 命令启动时,它成为系统上自动启动的所有进程的父进程或祖父进程。
下面从代码来看init做了什么:
busybox/1.36.0/source/init/init.c#L1058
#if ENABLE_FEATURE_USE_INITTAB
sigaddset(&G.delayed_sigset, SIGHUP); /* reread /etc/inittab */
#endif
......
check_delayed_sigs(&G.zero_ts);
--> reload_inittab();
--> parse_inittab();
再来看解析parse_inittab函数的实现:
/* NOTE that if CONFIG_FEATURE_USE_INITTAB is NOT defined,
* then parse_inittab() simply adds in some default
* actions (i.e., runs INIT_SCRIPT and then starts a pair
* of "askfirst" shells). If CONFIG_FEATURE_USE_INITTAB
* _is_ defined, but /etc/inittab is missing, this
* results in the same set of default behaviors.
*/
static void parse_inittab(void)
{
#if ENABLE_FEATURE_USE_INITTAB
char *token[4];
parser_t *parser = config_open2("/etc/inittab", fopen_for_read);
if (parser == NULL)
#endif
{
/* No inittab file - set up some default behavior */
/* Sysinit */
new_init_action(SYSINIT, INIT_SCRIPT, ""); // --> # define INIT_SCRIPT "/etc/init.d/rcS"
/* Askfirst shell on tty1-4 */
new_init_action(ASKFIRST, bb_default_login_shell, "");
//TODO: VC_1 instead of ""? "" is console -> ctty problems -> angry users
new_init_action(ASKFIRST, bb_default_login_shell, VC_2);
new_init_action(ASKFIRST, bb_default_login_shell, VC_3);
new_init_action(ASKFIRST, bb_default_login_shell, VC_4);
/* Reboot on Ctrl-Alt-Del */
new_init_action(CTRLALTDEL, "reboot", "");
/* Umount all filesystems on halt/reboot */
new_init_action(SHUTDOWN, "umount -a -r", "");
/* Swapoff on halt/reboot */
new_init_action(SHUTDOWN, "swapoff -a", "");
/* Restart init when a QUIT is received */
new_init_action(RESTART, "init", "");
return;
}
#if ENABLE_FEATURE_USE_INITTAB
/* optional_tty:ignored_runlevel:action:command
* Delims are not to be collapsed and need exactly 4 tokens
*/
while (config_read(parser, token, 4, 0, "#:",
PARSE_NORMAL & ~(PARSE_TRIM | PARSE_COLLAPSE))) {
/* order must correspond to SYSINIT..RESTART constants */
static const char actions[] ALIGN1 =
"sysinit\0""wait\0""once\0""respawn\0""askfirst\0"
"ctrlaltdel\0""shutdown\0""restart\0";
int action;
char *tty = token[0];
if (!token[3]) /* less than 4 tokens */
goto bad_entry;
action = index_in_strings(actions, token[2]);
if (action < 0 || !token[3][0]) /* token[3]: command */
goto bad_entry;
/* turn .*TTY -> /dev/TTY */
if (tty[0]) {
tty = concat_path_file("/dev/", skip_dev_pfx(tty));
}
new_init_action(1 << action, token[3], tty);
if (tty[0])
free(tty);
continue;
bad_entry:
message(L_LOG | L_CONSOLE, "Bad inittab entry at line %d",
parser->lineno);
}
config_close(parser);
#endif
}
根据上面的code flow,我们还需要创建一个/etc/inittab,如果不存在这个的话它会去找/etc/rcS等文件,说明如下:
# Note: BusyBox init works just fine without an inittab. If no inittab is
# found, it has the following default behavior:
# ::sysinit:/etc/init.d/rcS
# ::askfirst:/bin/sh
# ::ctrlaltdel:/sbin/reboot
# ::shutdown:/sbin/swapoff -a
# ::shutdown:/bin/umount -a -r
# ::restart:/sbin/init
# tty2::askfirst:/bin/sh
# tty3::askfirst:/bin/sh
# tty4::askfirst:/bin/sh
5 inittab文件
busybox已经提供了一个example,这里我们直接拿过来,注意需要修改一下,因为我们没打算用账号密码登录,如果有必要,可以创建/etc/passwd文件,但是密码不是明文存储的,有兴趣的读者可以研究一下。
我们直接把这个文件夹都copy过来,
busybox-1.36.0/examples/bootfloppy/etc/inittab
::sysinit:/etc/init.d/rcS
# ::respawn:-/bin/sh # -->注掉这一行,开机不需要登录
console::askfirst:-/bin/sh
::ctrlaltdel:/bin/umount -a -r
6 /etc/init.d/rcS
rcS也有一个example,内容如下
#! /bin/sh
/bin/mount -a
还有一种写法,就比较灵活了
#!/bin/sh
# Start all init scripts in /etc/init.d
# executing them in numerical order.
#
for i in /etc/init.d/S??* ;do
# Ignore dangling symlinks (if any).
[ ! -f "$i" ] && continue
case "$i" in
*.sh)
# Source shell script for speed.
(
trap - INT QUIT TSTP
set start
. $i
)
;;
*)
# No sh extension, so fork subprocess.
$i start
;;
esac
done
这种写法会遍历/etc/init.d/下所有S打头的配置文件,可以在这里做网络或者其他一些东西的初始化。
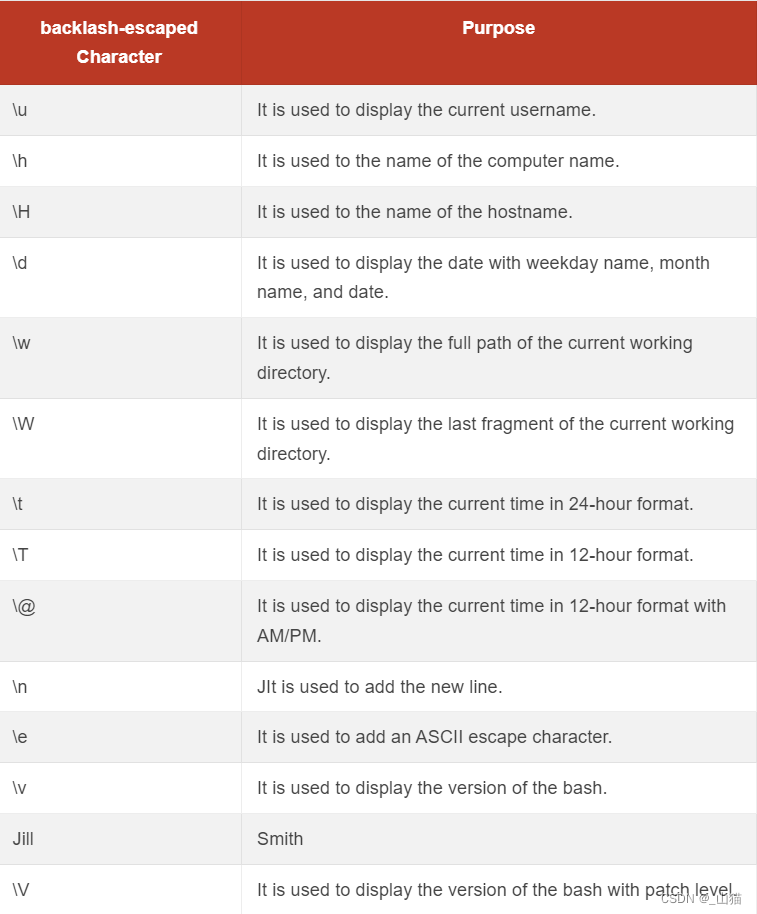
7 /etc/profile
/etc/profile文件主要设置一些全局环境变量之类的。
# /etc/profile: system-wide .profile file for the Bourne shell (sh(1))
# and Bourne compatible shells (bash(1), ksh(1), ash(1), ...).
if [ "${PS1-}" ]; then
if [ "${BASH-}" ] && [ "$BASH" != "/bin/sh" ]; then
# The file bash.bashrc already sets the default PS1.
# PS1='\h:\w\$ '
if [ -f /etc/bash.bashrc ]; then
. /etc/bash.bashrc
fi
else
if [ "`id -u`" -eq 0 ]; then
PS1='# '
else
PS1='$ '
fi
fi
fi
if [ -d /etc/profile.d ]; then
for i in /etc/profile.d/*.sh; do
if [ -r $i ]; then
. $i
fi
done
unset i
fi
8 /etc/fstab
/etc/fstab文件主要设置一些文件系统的挂载点之类的。
# stock fstab - you probably want to override this with a machine specific one
proc /proc proc defaults 0 0
devpts /dev/pts devpts mode=0620,ptmxmode=0666,gid=5 0 0
tmpfs /run tmpfs mode=0755,nodev,nosuid,strictatime 0 0
# uncomment this if your device has a SD/MMC/Transflash slot
#/dev/mmcblk0p1 /media/card auto defaults,sync,noauto 0 0
Reference:
- 1.2. A Detailed Look at the Boot Process
- busybox启动流程简单解析:从init到shell login
- Bash PS1 customization examples
- How to Change / Set up bash custom prompt (PS1) in Linux




![Mysql全解[基础篇]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/066c4d9a092f4ebc8c80ce145c024fd4.png)