1. Pinia 介绍
1.1 Pinia 是什么
Pinia 官网
https://pinia.vuejs.org/
vuex Github
https://github.com/vuejs/vuex

上面是 Vuex Github 中置顶说明,我们可以得知:
Pinia 现在是新的默认设置,Vue 的官方状态管理库已更改为 Pinia,Vue3、4仍会维护,但不会添加新功能;
Pinia 具有与 Vuex 5 几乎完全相同或增强的 API,可以把他理解成 Vuex5,Pinia 适用于 Vue 2.x;
Pinia 和 Vuex 可以安装在同一个项目中,进行程序迁移;新项目强烈建议使用 Pinia;
1.2 Pinia 优势
Pinia 是 Vue.js 的轻量级状态管理库,最近很受欢迎。它使用 Vue 3 中的新反应系统来构建一个直观且完全类型化的状态管理库
轻巧(体积约 1KB)
完整的 TypeScript 支持
代码更简洁,取消 mutations modules,不再有模块嵌套,不再有命名空间
Devtools 对 Pinia 的支持很好,store 出现在使用它们的组件中(这个我在后面会演示)
服务器端渲染支持(这里我没有实际体验过,但是官网说:如果 export const state = reactive({}) 是服务器端呈现的,会使您的应用程序暴露于安全漏洞,而 Pinia 可以避免这种安全问题)
2. Pinia 基本使用
2.1 Pinia 安装
创建一个 vite 项目(注意选择 vue-ts)
npm create vite@latest
安装 Pinia
yarn add pinia
npm install pinia
注意此处的 vue 版本,这之下的版本我并没有试过
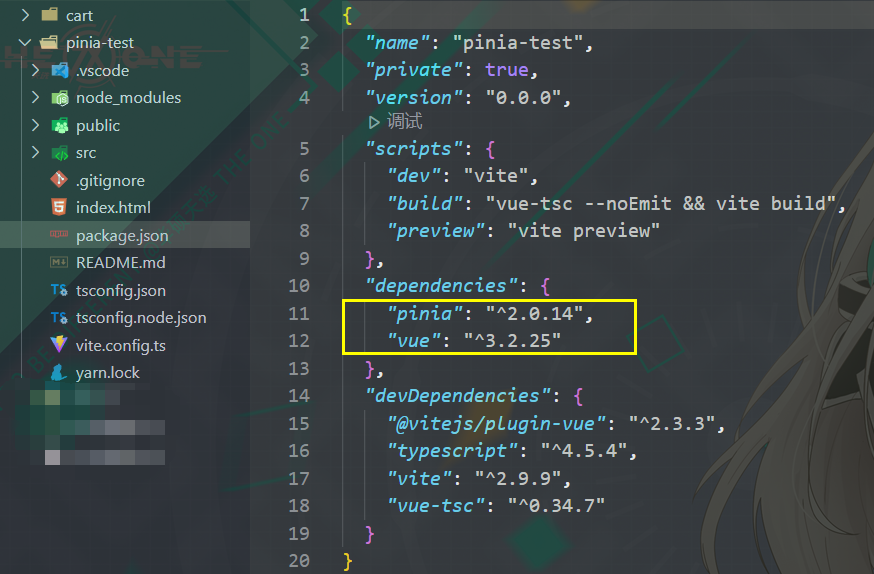
2.2 Pinia 初步封装
2.2.1 在 main.ts 中,引入 Pinia
import { createPinia } from 'pinia'
app.use(createPinia())2.2.2 定义 store
新建 store/index.ts
注意:将返回的函数命名为 use... 是跨可组合项的约定
import { defineStore } from 'pinia';
// 定义容器
export const useCountStore = defineStore('count', {
// state 变量(推荐使用 完整类型推断的 箭头函数)
state: () => ({
// 所有属性都将自动推断其类型
count: 0,
}),
// computed 计算属性
getters: {},
// actions 方法
actions: {},
});2.2.2.1 defineStore 方法接受的参数
id:字符串,表示 store 唯一 id,Pinia 使用它来将 store 连接到 Devtools
options:配置项,用于定义 store 需要的 变量、计算属性、方法
/**
* Creates a `useStore` function that retrieves the store instance
*
* @param id - id of the store (must be unique)
* @param options - options to define the store
*/
export declare function defineStore<Id extends string, S extends StateTree = {}, G extends _GettersTree<S> = {}, A = {}>(id: Id, options: Omit<DefineStoreOptions<Id, S, G, A>, 'id'>): StoreDefinition<Id, S, G, A>;2.2.2.2 使用箭头函数定义 state 的两点原因
服务器渲染,避免状态污染
利于 TypeScript 类型推导
2.3 在组件中使用 store
2.3.1 直接使用 store
<template>
<!-- 使用 store -->
<button type="button" @click="addCount">count is: {{ store.count }}</button>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
import { useCountStore } from '../store'
const store = useCountStore()
const addCount = () => {
store.count++
}
</script>
2.3.2 storeToRefs() 解构 store
store 是一个用 reactive 包裹的对象,这意味着不需要在 getter 之后写 .value,但是,就像 setup 中的 props 一样,不能对 store 进行直接解构,如果直接解构,会导致 store 中的变量,失去响应式效果
错误示例:const { name, doubleCount } = store
通过使用 storeToRefs(),它将为 store 中的任何响应式属性创建 refs,进而让我们可以采用解构赋值的形式,取得 store 中的某个变量(可以类比于 reactive,reactive 中的变量是通过 toRefs 解构出来的)
可以被解构出来的都是响应式的,比如 state、getters
不可以被解构出来的都是非响应式的,比如 actions
<template>
<!-- 使用 store -->
<!-- <button type="button" @click="addCount">count is: {{ store.count }}</button> -->
<!-- 使用 storeToRefs 解构赋值 store -->
<button type="button" @click="addCount">count is: {{ count }}</button>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
import { useCountStore } from '../store'
import { storeToRefs } from 'pinia'
// store
const store = useCountStore()
// storeToRefs 解构赋值
const { count } = storeToRefs(store)
// 错误示例:直接解构赋值
// const { count } = store
const addCount = () => {
store.count++
}
</script>2.4 改变 store 中数据的三种方法
2.4.1 直接修改 store
// store
const store = useCountStore()
// storeToRefs 解构赋值
const { count, msg } = storeToRefs(store)
/**
* 改变 store 中的值 - 直接修改
*/
const addCount = () => {
// 注意:此处不能直接使用解构出来的 count
store.count++
store.msg = 'Changed Message Directly'
store.arr.push(8)
}
2.4.2 使用 $patch 修改 store
2.4.2.1 $patch 修改简单数据
/**
* 改变 store 中的值 - $patch 修改简单数据
*/
const addCount = () => {
// 注意:这里也不是直接赋值,而是要通过 store.count 这么一步
store.$patch({
// 下面这么写,会导致数据无法被改变
// count: store.count++,
// 下面这么写,会报错
// arr: store.arr.push(4)
count: store.count + 1,
msg: 'Changed Message',
arr: [...store.arr, 4],
})
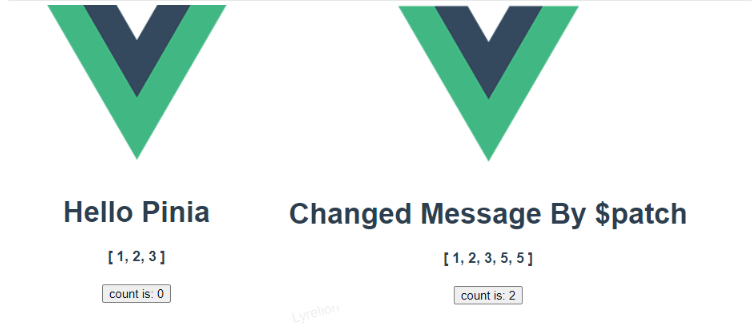
}2.4.2.2 $patch 修改复杂数据
$patch 可以传入以下两种内容:
一个对象:直接“重写”对象,逗号结尾(修改数组之类的,就比较费劲)
接收 state 的箭头函数:通过语句修改 state 某个属性值,分号结尾(修改复杂数据,就没那么费劲了)
/**
* 改变 store 中的值 - $patch 修改复杂数据
*/
const addCount = () => {
// 注意:这里接受了 state 参数,在回调函数里,通过一条条语句 修改 state
store.$patch((state) => {
// 下面这么写,会导致数据无法被改变
// state.count = store.count++
// 下面这么写,会报错
// state.arr = state.arr.push(5)
state.count = store.count + 1
state.msg = 'Changed Message'
state.arr.push(5)
})
}
2.4.3 使用 actions 修改 store
在 index.ts 中定义 actions
import { defineStore } from 'pinia';
// 定义容器
export const useCountStore = defineStore('count', {
// state 属性(必须是一个箭头函数)
state: () => ({
count: 0,
msg: 'Hello Pinia',
arr: [1, 2, 3],
}),
// computed 计算
getters: {},
// actions 方法
actions: {
// 定义一个 function
changeState(num: number) {
this.count += 10
this.msg = 'Changed Message By Actions'
this.arr.push(num)
},
},
});在组件中通过 store.xxx 使用 actions(xxx 为 actions 中定义的方法名)
/**
* 改变 store 中的值 - 使用 store.actions 中定义的方法
*/
const addCount = () => {
store.changeState(66);
}注意:actions 无法被解构出来,下面会报错
const { count, msg, arr, changeState } = storeToRefs(store)

2.4.4 复原 store、替换 state
恢复到 store 被修改之前的状态
const store = useStore()
store.$reset()只会替换原来就有的 count,不会自动添加原来没有的 name
const store = useStore()
store.$state = { count: 666, name: 'yeah' }2.5 “计算属性”getters
2.5.1 getters 的基本使用
使用 getters 的方法,分为以下两步:
在 index.ts 中定义 getters
在组件中通过 store.xxx 使用 getters(xxx 为 getters 中定义的方法名)
计算属性是可以被解构出来的
在 index.ts 中定义 getters
import { defineStore } from 'pinia';
// 定义容器
export const useCountStore = defineStore('count', {
// state 属性(必须是一个箭头函数)
state: () => ({
count: 0,
}),
// computed 计算
getters: {
// 通过 this 使用 state
doubleCountThis(): number {
return this.count * 2
},
},
});在组件中使用 getters
<!-- 通过 this 使用 state -->
<h4>{{ store.doubleCountThis }}</h4>
2.5.2 getters 中的 state
getters 中定义的函数,可以接收 state,如图所示:
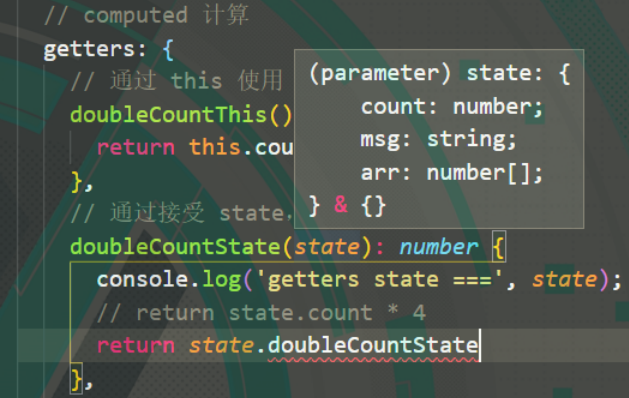
可以看出:参数state 包含了 上面的 state对象 定义的变量,不包含 getters 定义的“计算属性”
相较于 this 访问 state 中的数据,官网更推荐使用 state 接收参数,定义 getters
import { defineStore } from 'pinia';
// 定义容器
export const useCountStore = defineStore('count', {
// state 属性(必须是一个箭头函数)
state: () => ({
count: 0,
}),
// computed 计算
getters: {
// 通过 this 使用 state
doubleCountThis(): number {
return this.count * 2
},
// 通过接受 state,避免使用 this
doubleCountState(state): number {
console.log('getters state ===', state);
// 错误写法
// return state.doubleCountThis
return state.count * 4
},
},
}); <!-- 通过接受 state,避免使用 this -->
<h4>{{ store.doubleCountState }}</h4>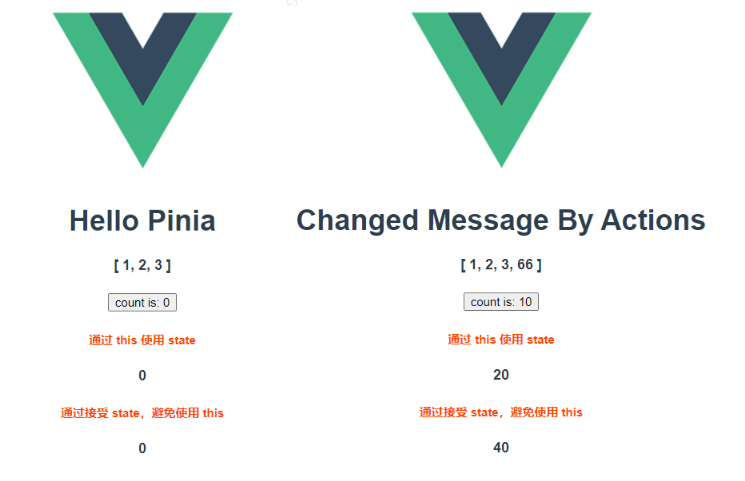
打印一下 getters 中的 state,如下图所示
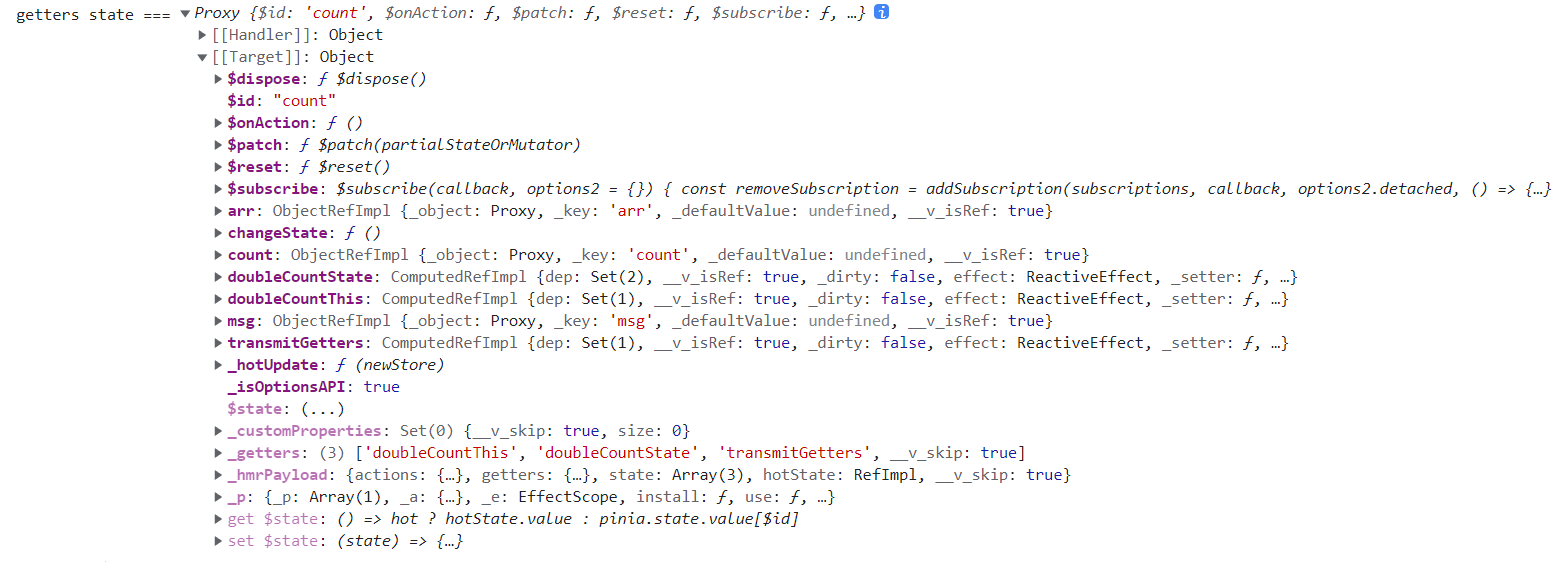
看起来似乎包含了 getters 中定义的计算属性
但实际上,不可以通过 state.xxx 使用计算属性,会报错
2.5.3 在 getters 中访问其他 getters
前面说过,无法通过 getters 接收的 state 参数使用前面定义的 getters;
在 getters 中,只能通过 this 的方式,使用前面定义的 getters;
import { defineStore } from 'pinia';
// 定义容器
export const useCountStore = defineStore('count', {
// state 属性(必须是一个箭头函数)
state: () => ({
count: 0,
}),
// computed 计算
getters: {
// 通过 this 使用 state
doubleCountThis(): number {
return this.count * 2
},
// 通过接受 state,避免使用 this
doubleCountState(state): number {
return state.count * 4
},
// getters 传递,只能通过 this
transmitGetters(): number {
return this.doubleCountState + 1
}
},
}); <!-- getters 传递,只能通过 this -->
<h4>{{ store.transmitGetters }}</h4>
2.5.4 getters 中接收参数
getters 只是幕后的 computed 属性,因此无法向它们传递任何参数
但是,可以从 getter 返回一个函数,以接受任何参数,举个栗子:
export const useCountStore = defineStore('count', {
getters: {
getUserById: (state) => {
// 可以从 getter 返回一个函数,以接受任何参数
return (userId) => state.users.find((user) => user.id === userId)
},
getArrItemByIndex(state) {
return (index: number) => state.arr.find((item, i) => i === index);
},
totalCount(state) {
return state.cartList.reduce((total, item) => {
return (total += item.quantity);
}, 0);
},
},
}) <!-- getters 传参 -->
<h4>{{ store.getArrItemByIndex(1) }}</h4>2.6 使用函数定义 store
可以使用一个函数(类似于一个组件 setup())来为更高级的用例定义一个 store
export const useCounterStore = defineStore('counter', () => {
const count = ref(0)
function increment() {
count.value++
}
return { count, increment }
})由于我自己更希望使用 Pinia 的感觉更像 Vuex,所以我没有仔细看这个函数定义 store 的方法
他们的区别在于第二个参数接受的是一个配置对象,还是一个箭头函数
2.7 访问其他 store 中的内容
直接在当前 store 内部实例化其他 store,并使用里面的内容即可
state、getters、actions 都行
import { useOtherStore } from './other-store'
import { useAuthStore } from './auth-store'
export const useCountStore = defineStore('count', {
state: () => ({
// ...
}),
getters: {
otherGetter(state) {
// 直接在当前 store 内部实例化其他 store,并使用里面的内容
const otherStore = useOtherStore()
return state.localData + otherStore.data
},
},
actions: {
async fetchUserPreferences(preferences) {
// 直接在当前 store 内部实例化其他 store,并使用里面的内容
const auth = useAuthStore()
if (auth.isAuthenticated) {
this.preferences = await fetchPreferences()
} else {
throw new Error('User must be authenticated')
}
},
},
})2.8 Pinia Plugin
2.8.1 什么是 Pinia 插件
Pinia 插件是一个函数,可以选择返回要添加到 store 的属性。 它需要一个可选参数,一个 context
export function myPiniaPlugin(context) {
context.pinia // 使用 `createPinia()` 创建的 pinia
context.app // 使用 `createApp()` 创建的当前应用程序(仅限 Vue 3)
context.store // 插件正在扩充的 store
context.options // 定义存储的选项对象传递给`defineStore()`
// ...
}使用 pinia.use() 将插件传递给 Pinia
pinia.use(myPiniaPlugin)2.8.2 使用插件扩充 store
下面两种写法,都可以实现:给所有的 store 实例,添加一个静态属性 hello
推荐写法一,因为写法一可以让 devtools 自动跟踪 hello 属性,让此静态属性在 devtools 中可见
举个例子:给所有 store 实例,添加静态属性 hello
// 写法一(推荐)
pinia.use(() => ({ hello: 'world' }))
// 写法二
pinia.use(({ store }) => {
store.hello = 'world'
})2.8.3 使用插件添加外部属性、其他库实例、非响应式内容
当添加以下内容时,需要先使用 markRaw() 包装对象,然后再传递给 Pinia
外部属性
来自其他库的类实例(比如路由)
仅仅是非响应式的内容
举个栗子:给每个 store 添加路由
import { markRaw } from 'vue'
// 路由
import { router } from './router'
pinia.use(({ store }) => {
store.router = markRaw(router)
})2.8.4 其他 Pinia 插件可以做的事
由于篇幅有限,上面我只列举了目前我在开发过程中,可能用到的情况
其实 Pinia 插件还可以做很多更高级的事情,有需要的同学建议以自行查阅
下面是官网列出的内容:
向 Store 添加新属性
定义 Store 时添加新选项
为 Store 添加新方法
包装现有方法
更改甚至取消操作
实现本地存储等副作用
仅适用于特定 Store
Pinia Plugins 官方文档:https://pinia.web3doc.top/core-concepts/plugins.html
2. Pinia 综合演示
2.1 需求说明
商品列表
展示商品列表
添加到购物车
计算购物车已有商品数量
购物车
展示购物车商品列表
计算总价格
结算
2.2 Pinia 和 Devtools
devtools 官网文档:https://devtools.vuejs.org/plugin/plugins-guide.html
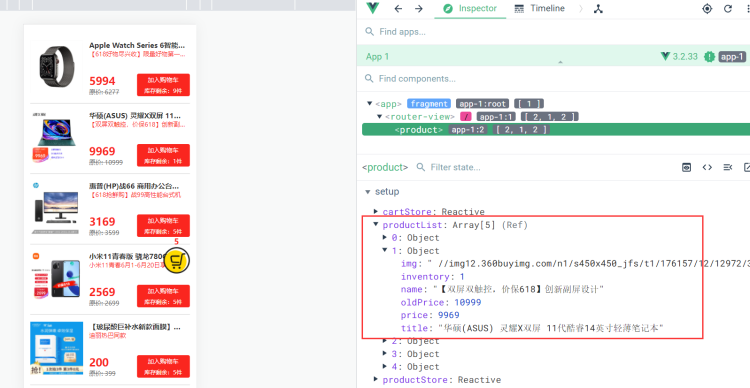
Pinia 和 Devtools 进行了很好的集成(如果你的工具没有出现小菠萝,则可以考虑重新装下 Devtools);
Devtools 会根据容器ID,列出所有的 store 实例(可以 容器ID 理解为:命名空间);
举个栗子:我定义了两个 store 实例: product、cart

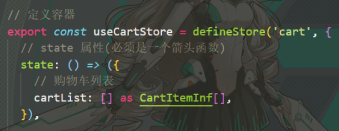
Devtools 显示效果如图,它不仅列出了我定义的两个 store 实例,还允许我们对容器内容进行各种操作
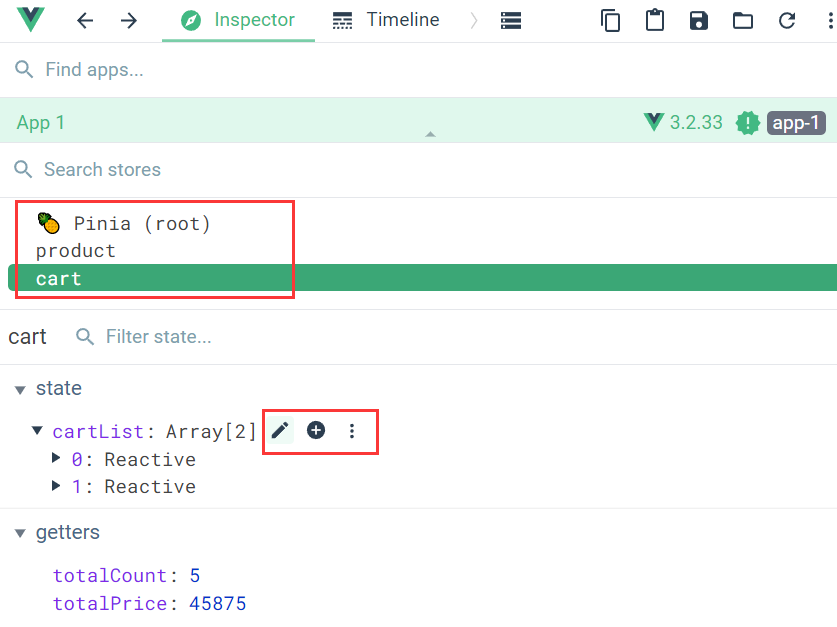
同时,Devtools 会把当前组件用到的 Pinia 内容,映射到组件调试工具中,同样可以直接进行编辑