zygote启动过程中涉及到以下模块:
- app_process
- zygote
- USAP
- socket
- FileDescriptor (FD)
- AndroidRuntime
- AppRuntime (定义于app_process模块,继承自AndroidRuntime。)
init进程启动zygote进程:
#init.zygote32_64.rc
service zygote /system/bin/app_process32 -Xzygote /system/bin --zygote --start-system-server --socket-name=zygote
class main
priority -20
user root
group root readproc reserved_disk
socket zygote stream 660 root system
socket usap_pool_primary stream 660 root system
onrestart exec_background - system system -- /system/bin/vdc volume abort_fuse
onrestart write /sys/power/state on
onrestart restart audioserver
onrestart restart cameraserver
onrestart restart media
onrestart restart netd
onrestart restart wificond
writepid /dev/cpuset/foreground/tasks
service zygote_secondary /system/bin/app_process64 -Xzygote /system/bin --zygote --socket-name=zygote_secondary
class main
priority -20
user root
group root readproc reserved_disk
socket zygote_secondary stream 660 root system
socket usap_pool_secondary stream 660 root system
onrestart restart zygote
writepid /dev/cpuset/foreground/tasks
一、绑定socket
init.zygote32_64.rc脚本中分别定义了32位(primary)和64位(secondary)zygote进程的启动参数,在/dev/socket/下创建UNIX域的socket,并把socket的fd传给对应的进程。

“ANDROID_SOCKET_zygote”,"ANDROID_SOCKET_zygote_secondary"分别为两个zygote的socket在环境变量中对应的key值,通过key获取对应的value,创建FileDescriptor对象。通过 “ls -l /proc/${pid}/fd” 命令可查看对应进程的所有fd指向的符号链接。
static LocalServerSocket createManagedSocketFromInitSocket(String socketName) {
int fileDesc;
final String fullSocketName = ANDROID_SOCKET_PREFIX + socketName; // ANDROID_SOCKET_zygote
try {
String env = System.getenv(fullSocketName);
fileDesc = Integer.parseInt(env); // env="20"
} catch (RuntimeException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("Socket unset or invalid: " + fullSocketName, ex);
}
try {
FileDescriptor fd = new FileDescriptor();
fd.setInt$(fileDesc);
return new LocalServerSocket(fd);
} catch (IOException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Error building socket from file descriptor: " + fileDesc, ex);
}
}
二、zygote启动
app_process进程:
//app_main.cpp
int main(int argc, char* const argv[])
{
//...
if (zygote) {
runtime.start("com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit", args, zygote);
} else if (className) {
runtime.start("com.android.internal.os.RuntimeInit", args, zygote);
}
}
变量runtime是AppRuntime对象,调用AndoridRuntime对象start()方法:
//AndroidRuntime.cpp
/*
* Start the Android runtime. This involves starting the virtual machine
* and calling the "static void main(String[] args)" method in the class
* named by "className".
*
* Passes the main function two arguments, the class name and the specified
* options string.
*/
void AndroidRuntime::start(const char* className, const Vector<String8>& options, bool zygote)
{
//...
/* start the virtual machine
* 1.启动Java虚拟机。
*/
JniInvocation jni_invocation;
jni_invocation.Init(NULL);
JNIEnv* env;
if (startVm(&mJavaVM, &env, zygote, primary_zygote) != 0) {
return;
}
onVmCreated(env);
/*
* Register android functions.
* 2.注册JNI方法。
*/
if (startReg(env) < 0) {
ALOGE("Unable to register all android natives\n");
return;
}
/*
* Start VM. This thread becomes the main thread of the VM, and will
* not return until the VM exits.
* 3.启动对应类的静态 main()。
*/
jmethodID startMeth = env->GetStaticMethodID(startClass, "main",
"([Ljava/lang/String;)V");
env->CallStaticVoidMethod(startClass, startMeth, strArray);
}
启动zygote时className变量是"com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit",查看其main()方法:
//ZygoteInit.java
public static void main(String[] argv) {
//...
/*
* 1. 执行预加载。
*/
if (!enableLazyPreload) {
preload(bootTimingsTraceLog);
}
/*
* 2. 实例化ZygoteServer()对象,
* 1).初始化 Zygote server socket。
* 2).初始化 USAP pool server socket。
* 3).初始化 USAP pool event FD。
*/
zygoteServer = new ZygoteServer(isPrimaryZygote);
/*
* 3. 启动 system_server进程,
*/
if (startSystemServer) {
Runnable r = forkSystemServer(abiList, zygoteSocketName, zygoteServer);
// {@code r == null} in the parent (zygote) process, and {@code r != null} in the
// child (system_server) process.
if (r != null) {
r.run();
return;
}
}
/*
* 4. 循环接受处理 socket 事件。
*/
// The select loop returns early in the child process after a fork and
// loops forever in the zygote.
caller = zygoteServer.runSelectLoop(abiList);
}
三、处理socket消息
ZygoteServer接收到socket消息后,调用processOneCommand方法解析消息参数。
//ZygoteServer.java
ZygoteConnection connection = peers.get(pollIndex);
final Runnable command = connection.processOneCommand(this);
最终在Zygote类的forkAndSpecialize方法中调用nativeForkAndSpecialize()方法fork新进程:
//Zygote.java
static int forkAndSpecialize(int uid, int gid, int[] gids, int runtimeFlags,
int[][] rlimits, int mountExternal, String seInfo, String niceName, int[] fdsToClose,
int[] fdsToIgnore, boolean startChildZygote, String instructionSet, String appDataDir,
boolean isTopApp, String[] pkgDataInfoList, String[] whitelistedDataInfoList,
boolean bindMountAppDataDirs, boolean bindMountAppStorageDirs) {
ZygoteHooks.preFork();
int pid = nativeForkAndSpecialize(
uid, gid, gids, runtimeFlags, rlimits, mountExternal, seInfo, niceName, fdsToClose,
fdsToIgnore, startChildZygote, instructionSet, appDataDir, isTopApp,
pkgDataInfoList, whitelistedDataInfoList, bindMountAppDataDirs,
bindMountAppStorageDirs);
ZygoteHooks.postForkCommon();
return pid;
}
重点查看ZygoteConnection类的processOneCommand()方法:
在nativeForkAndSpecialize()方法fork新进程后,通过判断返回的pid是否大于0区分母子进程。
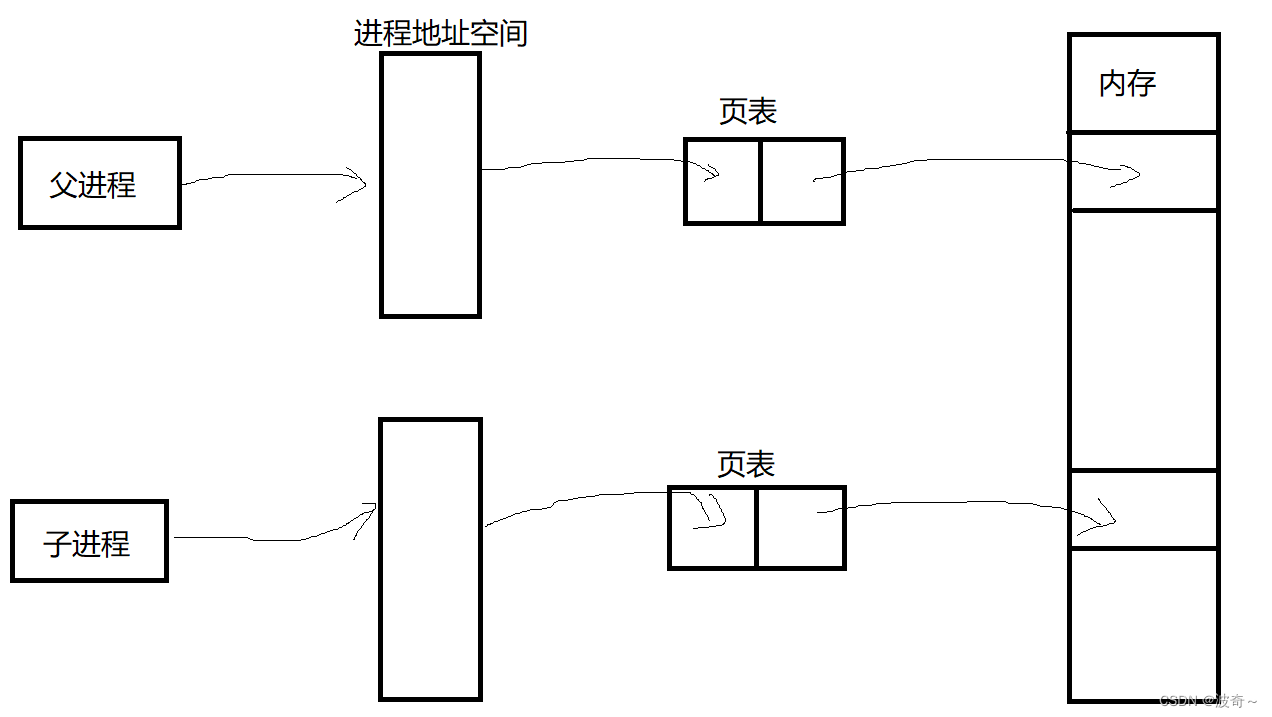
fork是类Unix操作系统上创建进程的主要方法。fork用于创建子进程(等同于当前进程的副本),新的进程要通过老的进程复制自身得到,这就是fork!
fork作为一个函数被调用。这个函数会有两次返回,将子进程的PID返回给父进程,0返回给子进程。(如果小于0,则说明创建子进程失败)。
//ZygoteConnection.java
Runnable processOneCommand(ZygoteServer zygoteServer) {
//...
pid = Zygote.forkAndSpecialize(parsedArgs.mUid, parsedArgs.mGid, parsedArgs.mGids,
parsedArgs.mRuntimeFlags, rlimits, parsedArgs.mMountExternal, parsedArgs.mSeInfo,
parsedArgs.mNiceName, fdsToClose, fdsToIgnore, parsedArgs.mStartChildZygote,
parsedArgs.mInstructionSet, parsedArgs.mAppDataDir, parsedArgs.mIsTopApp,
parsedArgs.mPkgDataInfoList, parsedArgs.mWhitelistedDataInfoList,
parsedArgs.mBindMountAppDataDirs, parsedArgs.mBindMountAppStorageDirs);
try {
if (pid == 0) {
// in child
zygoteServer.setForkChild();
zygoteServer.closeServerSocket();
IoUtils.closeQuietly(serverPipeFd);
serverPipeFd = null;
return handleChildProc(parsedArgs, childPipeFd, parsedArgs.mStartChildZygote);
} else {
// In the parent. A pid < 0 indicates a failure and will be handled in
// handleParentProc.
IoUtils.closeQuietly(childPipeFd);
childPipeFd = null;
handleParentProc(pid, serverPipeFd);
return null;
}
} finally {
IoUtils.closeQuietly(childPipeFd);
IoUtils.closeQuietly(serverPipeFd);
}
}
所以可以看到handleChildProc()和handleParentProc()分别处理的是子进程,母进程的逻辑。
最终子进程执行zygoteInit()方法完成一个Android 应用程序的启动(初始化):
public static final Runnable zygoteInit(int targetSdkVersion, long[] disabledCompatChanges,
String[] argv, ClassLoader classLoader) {
if (RuntimeInit.DEBUG) {
Slog.d(RuntimeInit.TAG, "RuntimeInit: Starting application from zygote");
}
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "ZygoteInit");
RuntimeInit.redirectLogStreams();
RuntimeInit.commonInit();
ZygoteInit.nativeZygoteInit();
return RuntimeInit.applicationInit(targetSdkVersion, disabledCompatChanges, argv,
classLoader);
}
ZygoteInit.nativeZygoteInit(); 使支持Binder进程间通信机制。
RuntimeInit.applicationInit(); 调用ActivityThread.main()方法,启动UI线程。