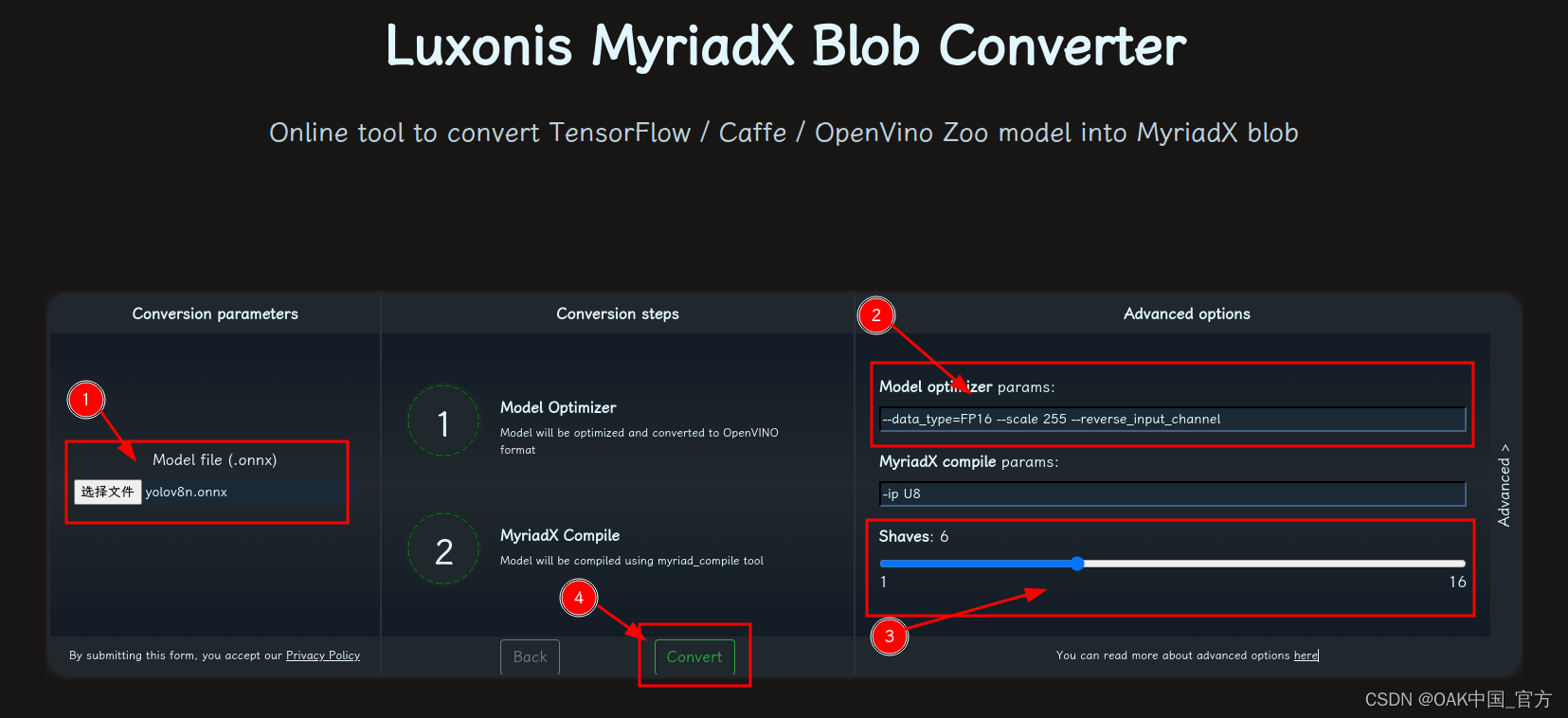
首先,本次重采样使用的是GDAL方法完成
参考了以下博客,并根据自己的需要进行了删改以及原理的探究:
重采样:栅格影像重采样
我使用了下该代码,发现是可行的,但是仍然存在一定的问题,即他的采样方式不是我想要的(最邻近采样,对于采样间隔较大的数据十分不友好),因此又探索了下,在此记录,也方便后续自己再次学习。
再次说明,这个代码不是我写的,原创我找不到,网上大家发布的都是一个代码,我只是对这个代码加了一个参数,然后分析了下!重要参数如下:resample_alg = gdalconst.GRIORA_Average,这个代表的是重采样过程每个重采样后的像元内所有数据求平均,还有双线性插值,最邻近插值等。
from osgeo import gdal, gdalconst
import os
import numpy as np
import glob
def resampling(source_file, target_file, scale):
"""
影像重采样
:param source_file: 源文件
:param target_file: 输出影像
:param scale: 像元缩放比例
:return:
"""
dataset = gdal.Open(source_file, gdalconst.GA_ReadOnly)
band_count = dataset.RasterCount # 波段数
if band_count == 0 or not scale > 0:
print("参数异常")
return
cols = dataset.RasterXSize # 列数
rows = dataset.RasterYSize # 行数
cols = int(cols * scale) # 计算新的行列数
rows = int(rows * scale)
geotrans = list(dataset.GetGeoTransform())
# print(dataset.GetGeoTransform())
# print(geotrans)
geotrans[1] = geotrans[1] / scale # 像元宽度变为原来的scale倍
geotrans[5] = geotrans[5] / scale # 像元高度变为原来的scale倍
print(geotrans)
if os.path.exists(target_file) and os.path.isfile(target_file): # 如果已存在同名影像
os.remove(target_file) # 则删除之
band1 = dataset.GetRasterBand(1)
data_type = band1.DataType
target = dataset.GetDriver().Create(target_file, xsize=cols, ysize=rows, bands=band_count,
eType=data_type)
target.SetProjection(dataset.GetProjection()) # 设置投影坐标
target.SetGeoTransform(geotrans) # 设置地理变换参数
total = band_count + 1
for index in range(1, total):
# 读取波段数据
# print("正在写入" + str(index) + "波段")
data = dataset.GetRasterBand(index).ReadAsArray(buf_xsize=cols, buf_ysize=rows, resample_alg = gdalconst.GRIORA_Average)
out_band = target.GetRasterBand(index)
# out_band.SetNoDataValue(dataset.GetRasterBand(index).GetNoDataValue())
out_band.WriteArray(data) # 写入数据到新影像中
out_band.FlushCache()
out_band.ComputeBandStats(False) # 计算统计信息
# print("正在写入完成")
del dataset
del target
if __name__ == "__main__":
dir_in=r'D:\dataset\ours'
dir_out=r'D:\dataset\our_1_average'
for file_i in glob.glob(os.path.join(dir_in,'*.tiff')):
file_name=os.path.split(file_i)[1]
source_file=file_i
target_file=os.path.join(dir_out,file_name)
resampling(source_file, target_file, scale=0.1)
print(file_name)
其他的几个重采样方式关键字:
'GRIORA_Average',
'GRIORA_Bilinear',
'GRIORA_Cubic',
'GRIORA_CubicSpline',
'GRIORA_Gauss',
'GRIORA_Lanczos',
'GRIORA_Mode',
'GRIORA_NearestNeighbour'
下面讲讲这个的平均大概是什么样的方式:
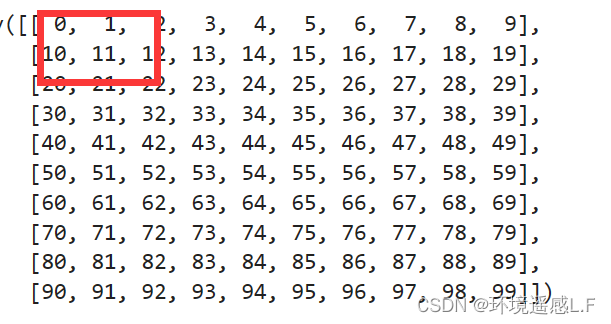
原始栅格如下:生成的一个10*10大小的顺序数组

1 重采样的分辨率刚好同原始分辨率成倍数关系:将其重采样成5*5
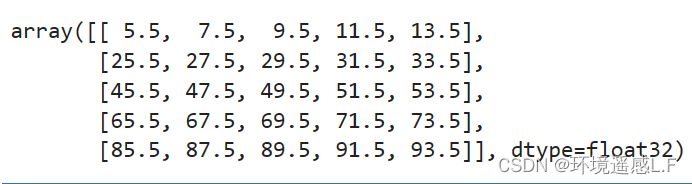
这里我们可以看到:第一个数字5.5 刚好就是(0+1+10+11)/4的结果其他的数据也是对应位置求平均,很好理解。
2 降采样成4*4呢?

那么这个是怎么计算的呢?以第一个数字为例:他的结果应该是这样,重采样后的像元将原始的前四个像元都是完全包了的(数值为0,1,10,11)然后(数值为2,12,20,21)四个像元都只能包含一半,数值为22的像元只能包含1/4。 所以同理,如果不等分,就是按照原始像元的覆盖率来进行求得平均:这儿的例子来讲:
8.8=((0+1+10+11)+((2+12+20+21)/2)+(22/4))/(4+4/2+1/4)
(0+1+10+11)代表四个完整的像元值
(2+12+20+21)四个像元只覆盖了一半,所以他的值应该只算一半
(22)只覆盖了1/4,所以只能算成22/4
(4+4/2+1/4)代表覆盖的原始像元个数。