前言:
pytorch与tensorflow中均有nn.dropout,两者之间的使用方法,下面将介绍。
一、torch.nn.dropout
说明文档:
r"""During training, randomly zeroes some of the elements of the input
tensor with probability :attr:`p` using samples from a Bernoulli
distribution. Each channel will be zeroed out independently on every forward
call.
This has proven to be an effective technique for regularization and
preventing the co-adaptation of neurons as described in the paper
`Improving neural networks by preventing co-adaptation of feature
detectors`_ .
Furthermore, the outputs are scaled by a factor of :math:`\frac{1}{1-p}` during
training. This means that during evaluation the module simply computes an
identity function.
大致的翻译:
在训练期间,随机地将输入的一些元素归零,以概率为`p`,使用伯努利分布的样本。每个通道将在每次前向调用时被独立清零。
这已被证明是一种有效的正则化技术,可以 防止神经元的共同适应,如论文中所述 "Improving neural networks by preventing co-adaptation of feature detectors"。
此外,训练过程中,输出的比例为:math:`frac{1}{1-p}`【a1*(1-p)=a】。这意味着,在评估过程中,该模块只需计算一个 识别函数。
1.1对于一维度向量的dropout
import torch
a = torch.randn(10)
p = 0.3 # probability of an element to be zeroed
Dropout = torch.nn.Dropout(p)
a1 = Dropout(a)
print(a)
print(a1)程序输出结果为
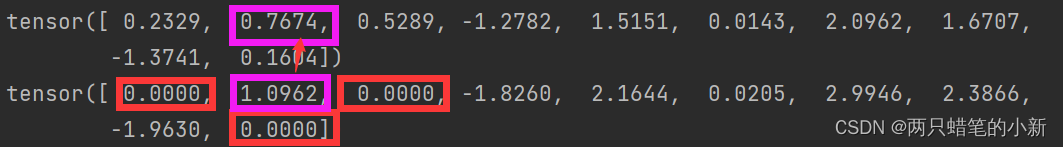
由上图可以知道,:
0.p的作用:元素被清零的概率
1.红色框框部分:10个元素,其中有三个被置零,概率为0.3
2.紫色框框的元素:output = input/(1-p)
1.2对于二维卷积特征图的操作
import torch
a = torch.randn([2,2,3,4])
p = 0.3 # probability of an element to be zeroed
Dropout = torch.nn.Dropout(p)
a1 = Dropout(a)
print(a)
print(a1)程序的输入:batch_size = 2, channel=2,w=3,h=4=>[2,2,3,4]
输出结果如图所示:
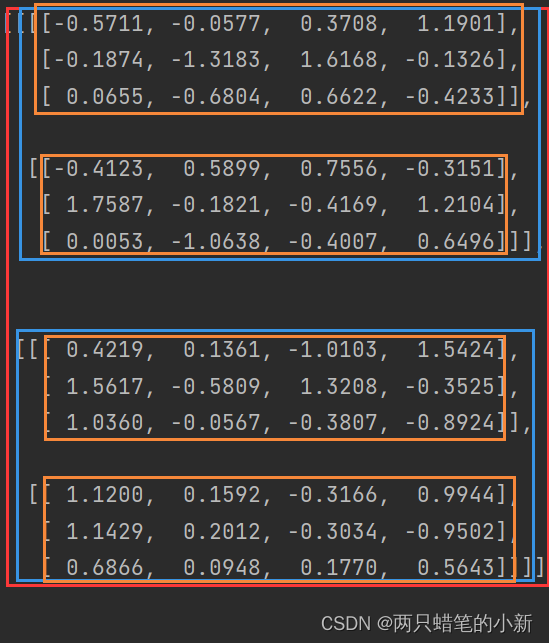
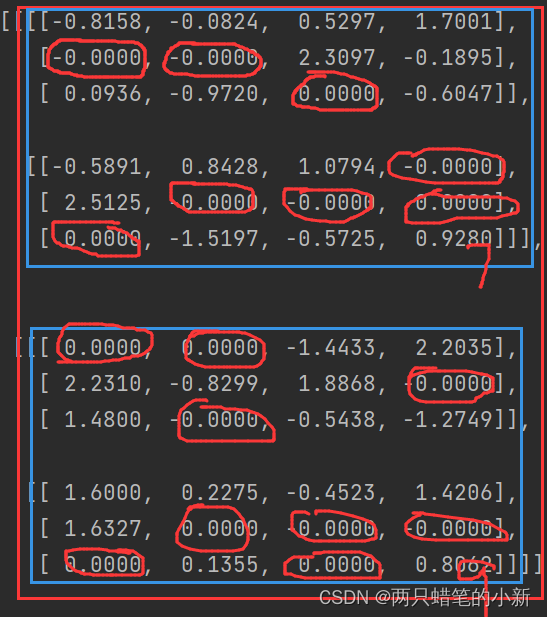
有兴趣可以多测试机组,按batch计算概率,通道之间累加,看图意会一下。
![BUUCTF-[ACTF新生赛2020]Splendid_MineCraft](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/d7cbfec2fa1a405a81ffb5148a4f93eb.png)