目录
1. 格雷编码
2. 矩阵问题
3. 搜索旋转排序数组 II
1. 格雷编码
格雷编码是一个二进制数字系统,在该系统中,两个连续的数值仅有一个位数的差异。
给定一个代表编码总位数的非负整数 n,打印其格雷编码序列。即使有多个不同答案,你也只需要返回其中一种。
格雷编码序列必须以 0 开头。
示例 1:
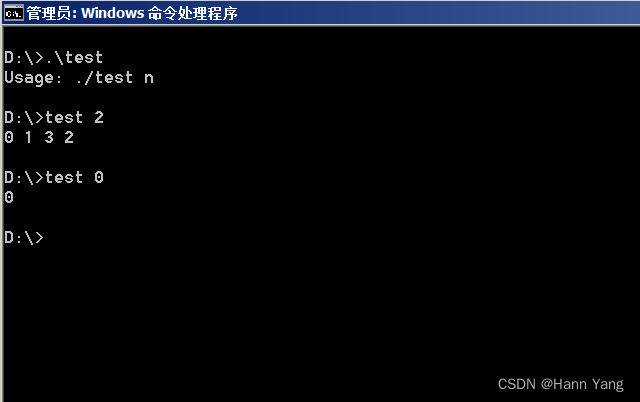
输入: 2 输出: [0,1,3,2] 解释:00 - 001 - 111 - 310 - 2对于给定的 n,其格雷编码序列并不唯一。例如,[0,2,3,1] 也是一个有效的格雷编码序列。00 - 010 - 211 - 301 - 1
示例 2:
输入: 0 输出: [0] 解释: 我们定义格雷编码序列必须以 0 开头。给定编码总位数为 n 的格雷编码序列,其长度为 2n。当 n = 0 时,长度为 20 = 1。因此,当 n = 0 时,其格雷编码序列为 [0]。
代码:(原题中的代码,已补充填空部分)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int *grayCode(int n, int *returnSize)
{
if (n < 0)
{
return NULL;
}
int i, count = 1 << n;
int *codes = (int*)malloc(count * sizeof(int));
for (i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
codes[i] = (i >> 1) ^ i;
}
*returnSize = 1 << n;
return codes;
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
if (argc != 2)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Usage: ./test n\n");
exit(-1);
}
int i, count;
int *list = grayCode(atoi(argv[1]), &count);
for (i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
printf("%d ", list[i]);
}
printf("\n");
return 0;
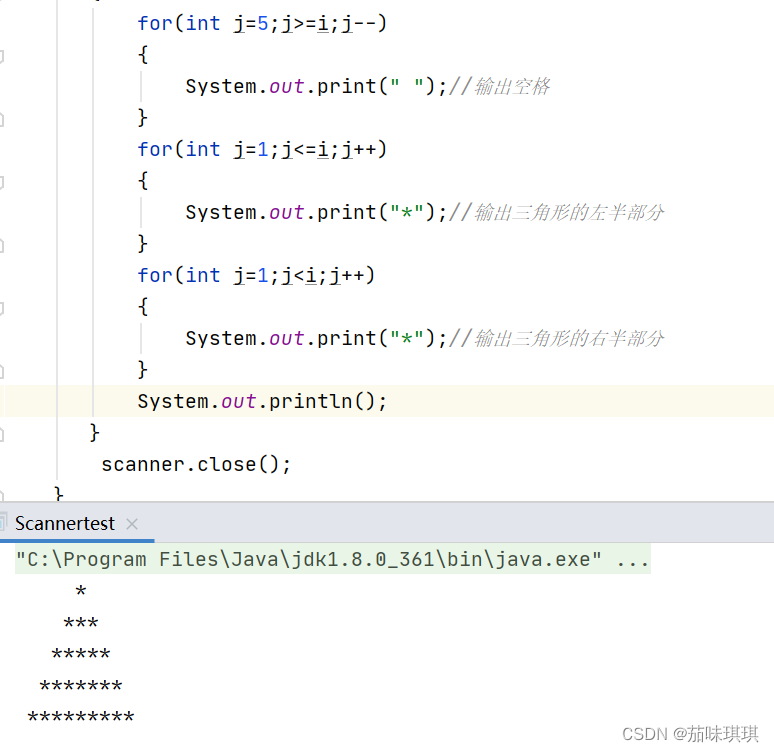
}执行:
相关阅读:
Python 格雷码转换公式 i^i//2,简洁优美 pythonic_python 格雷码转数字
2. 矩阵问题
编写以下函数:
(1)在一个二维数组中形成以下形式的n阶矩阵:
[1 1 1 1 1
2 1 1 1 1
3 2 1 1 1
4 3 2 1 1
5 4 3 2 1]
```
(2)去掉靠边的元素,生成新的n-2阶矩阵;
(3)求生成的n阶矩阵主对角线上的元素之和;
(4)以方阵形式输出数组。
在main函数中调用以上函数进行测试。
**输入**
输入生成矩阵的阶数(n>=2)
**输出**
以方阵形式输出生成的n阶矩阵、去掉靠边的元素生成的新的n-2阶矩阵、以及生成的n阶矩阵主对角线上的元素之和,最后一行要回车
**样例输入**
```json
5
样例输出
Generated matrix:
1 1 1 1 1
2 1 1 1 1
3 2 1 1 1
4 3 2 1 1
5 4 3 2 1
del the elements on the side:
1 1 1
2 1 1
3 2 1
The sum of the diagonal:5
代码:(原题中的代码,已补充填空部分)
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
while (1)
{
int a;
cin >> a;
int array[a][a];
for (int i = 0; i < a; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < a; j++)
{
if (j < i)
array[i][j] = i + 1 - j;
else
array[i][j] = 1;
}
cout << "Generated matrix:" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < a; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < a; j++)
{
cout << array[i][j];
}
cout << endl;
}
cout << "del the elements on the side:" << endl;
for (int i = 1; i < a - 1; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j < a - 1; j++)
{
cout << array[i][j];
}
cout << endl;
}
int sum = 0;
int i, j;
for (i = a - 2, j = 1; i >= 1; i--, j++)
{
sum += array[i][j];
}
cout << "The sum of the diagonal:" << sum << endl;
}
return 0;
}3. 搜索旋转排序数组 II
已知存在一个按非降序排列的整数数组 nums ,数组中的值不必互不相同。
在传递给函数之前,nums 在预先未知的某个下标 k(0 <= k < nums.length)上进行了 旋转 ,使数组变为 [nums[k], nums[k+1], ..., nums[n-1], nums[0], nums[1], ..., nums[k-1]](下标 从 0 开始 计数)。例如, [0,1,2,4,4,4,5,6,6,7] 在下标 5 处经旋转后可能变为 [4,5,6,6,7,0,1,2,4,4] 。
给你 旋转后 的数组 nums 和一个整数 target ,请你编写一个函数来判断给定的目标值是否存在于数组中。如果 nums 中存在这个目标值 target ,则返回 true ,否则返回 false 。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [2,5,6,0,0,1,2], target = 0 输出:true
示例 2:
输入:nums = [2,5,6,0,0,1,2], target = 3 输出:false
提示:
1 <= nums.length <= 5000-104 <= nums[i] <= 104- 题目数据保证
nums在预先未知的某个下标上进行了旋转 -104 <= target <= 104
进阶:
- 这是搜索旋转排序数组的延伸题目,本题中的
nums可能包含重复元素。 - 这会影响到程序的时间复杂度吗?会有怎样的影响,为什么?
代码:(原题中的代码,已补充填空部分)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
static bool search(int *nums, int numsSize, int target)
{
int lo = 0;
int hi = numsSize - 1;
while (lo <= hi)
{
int mid = lo + (hi - lo) / 2;
if (nums[mid] == target)
{
return true;
}
if (nums[lo] == nums[mid] && nums[mid] == nums[hi])
{
lo++;
hi--;
}
else if (nums[lo] <= nums[mid])
{
if (nums[lo] <= target && target < nums[mid])
{
hi = mid - 1;
}
else
{
lo = mid + 1;
}
}
else
{
if (nums[mid] < target && target <= nums[hi])
{
lo = mid + 1;
}
else
{
hi = mid - 1;
}
}
}
return false;
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int i;
int target = atoi(argv[1]);
int size = argc - 2;
int *nums = (int*)malloc(size * sizeof(int));
for (i = 0; i < argc - 2; i++)
{
nums[i] = atoi(argv[i + 2]);
}
printf("%d\n", search(nums, size, target));
return 0;
}代码2:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
bool search(vector<int> & nums, int target) {
for (auto & num : nums)
if (num == target) return true;
return false;
}
};
int main()
{
Solution s;
vector <int> nums = {2,5,6,0,0,1,2};
cout << s.search(nums, 0) << endl;
cout << s.search(nums, 3) << endl;
return 0;
}输出:
1
0