鉴于特征仓库热度下降,特将历史库存放出😄
背景
数据工程师与算法工程师在数据存取上存在沟通成本,基于现状存在以下问题:
- 提供训练使用的离线特征与在线服务使用的在线特征,构造方式存在差异,离线、在线特征数据一致性存疑
- 算法工程师使用特征存在冗余,重复造轮子不仅会出现特征质量参差而且效率低下
- 同步离线特征与在线特征能缩短训练到服务pipeline的开发时间,能提高模型迭代速度
简介
从业务背景、公司技术栈现状、框架重量、二次开发门槛、热度等方面考量,特征仓库的方案选型feast-spark(feast 0.9)
特征仓库的定位是管理,所以特征仓库既不研发离线数据仓库也不提供实时计算。
特征仓库提供特征元数据与离线、在线数据的关联,同时提供离线数据与在线数据的同步;最终实现特征复用、离线和在线特征数据一致性
原理
feast core存储、管理特征表的元数据
特征表的元数据,记录了特征的字段信息、关联的特征数据存储地址(如离线仓库在s3或hdfs,在线仓库在redis或es)
离线和在线特征的同步,保证模型训练与模型服务数据的一致性
feast-spark与数据处理和机器学习的关系可以参考如下的架构图:
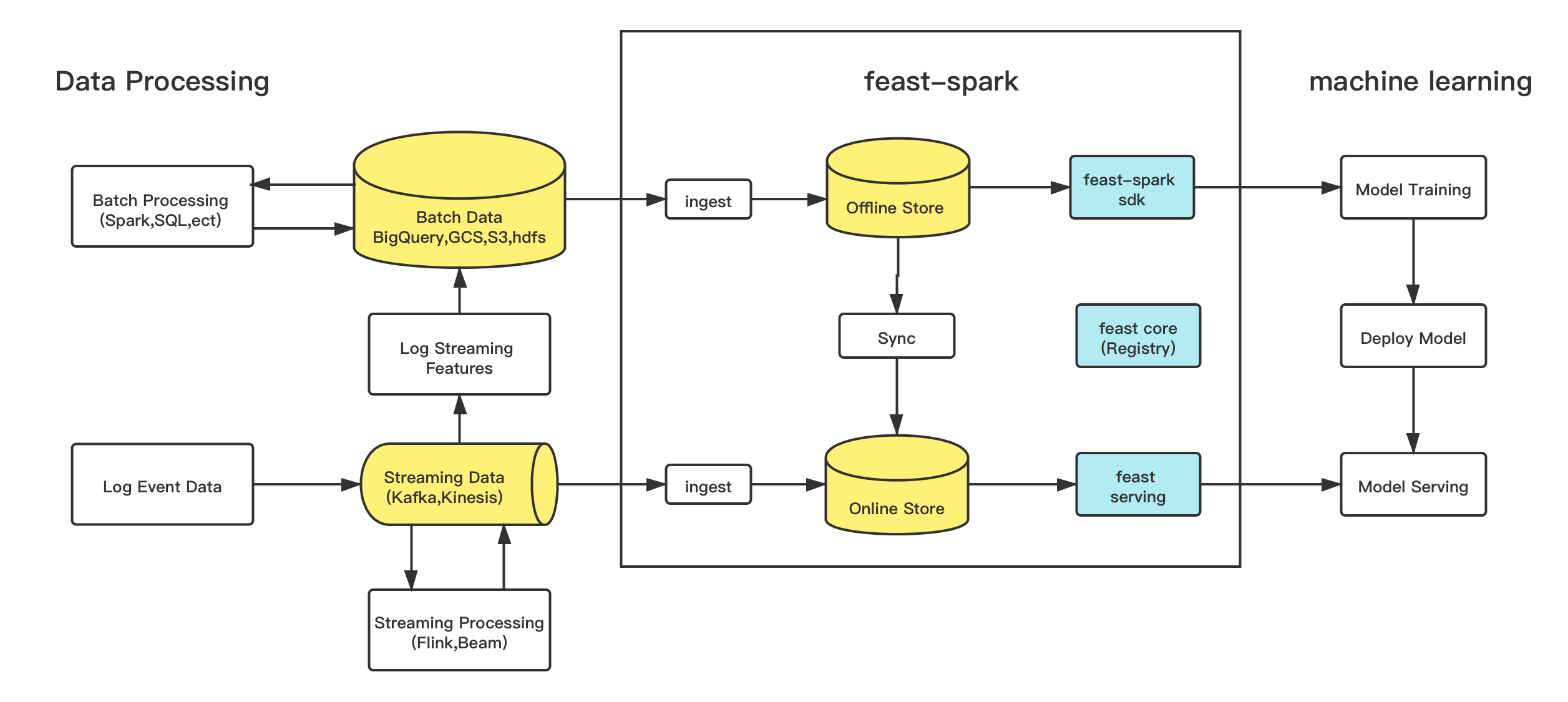
具体功能的实现细节:
1.注册特征表元数据
sdk通过grpc请求,将特征表结构元数据注册到feast core注册中心:
def _apply_feature_table(self, project: str, feature_table: FeatureTable):
"""
Registers a single feature table with Feast
Args:
feature_table: Feature table that will be registered
"""
feature_table.is_valid()
feature_table_proto = feature_table.to_spec_proto()
# Convert the feature table to a request and send to Feast Core
try:
apply_feature_table_response = self._core_service.ApplyFeatureTable(
ApplyFeatureTableRequest(project=project, table_spec=feature_table_proto), # type: ignore
timeout=self._config.getint(opt.GRPC_CONNECTION_TIMEOUT),
metadata=self._get_grpc_metadata(),
) # type: ApplyFeatureTableResponse
except grpc.RpcError as e:
raise grpc.RpcError(e.details())
feast core注册中心接口:
@Override
public void applyFeatureTable(
ApplyFeatureTableRequest request,
StreamObserver<ApplyFeatureTableResponse> responseObserver) {
String projectName = SpecService.resolveProjectName(request.getProject());
String tableName = request.getTableSpec().getName();
try {
// Check if user has authorization to apply feature table
authorizationService.authorizeRequest(SecurityContextHolder.getContext(), projectName);
ApplyFeatureTableResponse response = specService.applyFeatureTable(request);
responseObserver.onNext(response);
responseObserver.onCompleted();
} catch (AccessDeniedException e) {
log.info(
String.format(
"ApplyFeatureTable: Not authorized to access project to apply: %s", projectName));
responseObserver.onError(
Status.PERMISSION_DENIED
.withDescription(e.getMessage())
.withCause(e)
.asRuntimeException());
}
/**
* Applies the given FeatureTable to the FeatureTable registry. Creates the FeatureTable if does
* not exist, otherwise updates the existing FeatureTable. Applies FeatureTable in project if
* specified, otherwise in default project.
*
* @param request Contains FeatureTable spec and project parameters used to create or update a
* FeatureTable.
* @throws NoSuchElementException projects and entities referenced in request do not exist.
* @return response containing the applied FeatureTable spec.
*/
@Transactional
public ApplyFeatureTableResponse applyFeatureTable(ApplyFeatureTableRequest request) {
String projectName = resolveProjectName(request.getProject());
// Check that specification provided is valid
FeatureTableSpec applySpec = request.getTableSpec();
FeatureTableValidator.validateSpec(applySpec);
// Prevent apply if the project is archived.
Project project = projectRepository.findById(projectName).orElse(new Project(projectName));
if (project.isArchived()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
String.format(
"Cannot apply Feature Table to archived Project: (table: %s, project: %s)",
applySpec.getName(), projectName));
}
// Create or update depending on whether there is an existing Feature Table
Optional<FeatureTable> existingTable =
tableRepository.findFeatureTableByNameAndProject_Name(applySpec.getName(), projectName);
FeatureTable table = FeatureTable.fromProto(projectName, applySpec, entityRepository);
if (existingTable.isPresent() && table.equals(existingTable.get())) {
// Skip update if no change is detected
return ApplyFeatureTableResponse.newBuilder().setTable(existingTable.get().toProto()).build();
}
if (existingTable.isPresent()) {
existingTable.get().updateFromProto(projectName, applySpec, entityRepository);
table = existingTable.get();
}
// Commit FeatureTable to database and return applied FeatureTable
tableRepository.saveAndFlush(table);
return ApplyFeatureTableResponse.newBuilder().setTable(table.toProto()).build();
}
2.拽取批数据到离线特征仓库
将批特征数据,拽取到特征表关联的离线特征存地址,实现大致分为如下3个步骤:
a. 对拽取的数据格式做判断(目前只支持parquet格式的批数据)
# Check 1) Only parquet file format for FeatureTable batch source is supported
if (
feature_table.batch_source
and issubclass(type(feature_table.batch_source), FileSource)
and isinstance(
type(feature_table.batch_source.file_options.file_format), ParquetFormat
)
):
raise Exception(
f"No suitable batch source found for FeatureTable, {name}."
f"Only BATCH_FILE source with parquet format is supported for batch ingestion."
)
# read raw data from local, we will support hdfs data later
pyarrow_table, column_names = _read_table_from_source(source)
b. 以特征表为参照系,对拽取的数据作字段校验
# Check 2) Check if FeatureTable batch source field mappings can be found in provided source table
_check_field_mappings(
column_names,
name,
feature_table.batch_source.event_timestamp_column,
feature_table.batch_source.field_mapping,
)
c. 将批数据,拽取到特征表关联的离线特征存储地址
def _upload_to_file_source(
file_url: str, with_partitions: bool, dest_path: str, config: Config
) -> None:
"""
Uploads data into a FileSource. Currently supports GCS, S3, HDFS and Local FS.
Args:
file_url: file url of FileSource defined for FeatureTable
with_partitions: whether to treat dest_path as dir with partitioned table
dest_path: path to file or dir to be uploaded
config: Config instance to configure FileSource
"""
from urllib.parse import urlparse
uri = urlparse(file_url)
staging_client = get_staging_client(uri.scheme, config)
# supported offline storage middleware
storage_clients = {
GS: _gcs_client,
S3: _s3_client,
S3A: _s3a_client,
AZURE_SCHEME: _azure_blob_client,
LOCAL_FILE: _local_fs_client,
HDFS_FILE: _hdfs_fs_client
}
3.流数据拽取到在线仓库
由于目前只实现了redis作在线特征仓库,下面的实现也只以redis为例,实现大致分为如下3个步骤:
a. 取流式队列的消息数据(以kafka为例)
val input = config.source match {
case source: KafkaSource =>
sparkSession.readStream
.format("kafka")
.option("kafka.bootstrap.servers", source.bootstrapServers)
.option("subscribe", source.topic)
.load()
case source: MemoryStreamingSource =>
source.read
}
val parsed = config.source.asInstanceOf[StreamingSource].format match {
case ProtoFormat(classPath) =>
val parser = protoParser(sparkSession, classPath)
input.withColumn("features", parser($"value"))
case AvroFormat(schemaJson) =>
input.select(from_avro($"value", schemaJson).alias("features"))
case _ =>
val columns = input.columns.map(input(_))
input.select(struct(columns: _*).alias("features"))
}
val projected = parsed
.select("features.*")
.select(projection: _*)
b.对消息队列字段做校验
val query = projected.writeStream
.foreachBatch { (batchDF: DataFrame, batchID: Long) =>
val rowsAfterValidation = if (validationUDF.nonEmpty) {
val columns = batchDF.columns.map(batchDF(_))
batchDF.withColumn(
"_isValid",
rowValidator.allChecks && validationUDF.get(struct(columns: _*))
)
} else {
batchDF.withColumn("_isValid", rowValidator.allChecks)
}
rowsAfterValidation.persist()
implicit def rowEncoder: Encoder[Row] = RowEncoder(rowsAfterValidation.schema)
c.消息数据写到在线仓库
目前在线仓库是redis,特征数据的key都是经过加密处理;通过timestamp更新key对应的数据,保证特征数据是最新版本
rowsAfterValidation
.map(metrics.incrementRead)
.filter(if (config.doNotIngestInvalidRows) expr("_isValid") else rowValidator.allChecks)
.write
.format("feast.ingestion.stores.redis")
.option("entity_columns", featureTable.entities.map(_.name).mkString(","))
.option("namespace", featureTable.name)
.option("project_name", featureTable.project)
.option("timestamp_column", config.source.eventTimestampColumn)
.option("max_age", config.featureTable.maxAge.getOrElse(0L))
.save()
override def insert(data: DataFrame, overwrite: Boolean): Unit = {
// repartition for deduplication
val dataToStore =
if (config.repartitionByEntity && data.rdd.getNumPartitions > 1)
data
.repartition(data.rdd.getNumPartitions, config.entityColumns.map(col): _*)
.localCheckpoint()
else data
dataToStore.foreachPartition { partition: Iterator[Row] =>
// grouped iterator to only allocate memory for a portion of rows
partition.grouped(config.iteratorGroupingSize).foreach { batch =>
4.获取离线特征数据
目前离线特征仓库没有版本功能,离线仓库采用的是一种近似关联的处理策略:能获取entity对应的最新离线特征数据
获取离线特征数据,分为如下几步:
a. 从特征表批数据存放地址读取数据
feature_tables = [_feature_table_from_dict(dct) for dct in feature_tables_conf]
feature_tables_sources = [
_source_from_dict(dct) for dct in feature_tables_sources_conf
]
entity_source = _source_from_dict(entity_source_conf)
entity_df = _read_and_verify_entity_df_from_source(spark, entity_source)
feature_table_dfs = [
_read_and_verify_feature_table_df_from_source(spark, feature_table, source,)
for feature_table, source in zip(feature_tables, feature_tables_sources)
]
b.筛选出时间范围内的数据
def _filter_feature_table_by_time_range(
feature_table_df: DataFrame,
feature_table: FeatureTable,
feature_event_timestamp_column: str,
entity_df: DataFrame,
entity_event_timestamp_column: str,
):
entity_max_timestamp = entity_df.agg(
{entity_event_timestamp_column: "max"}
).collect()[0][0]
entity_min_timestamp = entity_df.agg(
{entity_event_timestamp_column: "min"}
).collect()[0][0]
feature_table_timestamp_filter = (
col(feature_event_timestamp_column).between(
entity_min_timestamp - timedelta(seconds=feature_table.max_age),
entity_max_timestamp,
)
if feature_table.max_age
else col(feature_event_timestamp_column) <= entity_max_timestamp
)
time_range_filtered_df = feature_table_df.filter(feature_table_timestamp_filter)
return time_range_filtered_df
c.近似特征表关联
近似特征表关联操作,是获取离线特征数据的核心部分,能保证关联的特征字段数据为当前最新数据
用户在定义特征表字段max_age为特征作用时间范围容忍度(近似偏差的范围)
entity_with_id = entity_df.withColumn("_row_nr", monotonically_increasing_id())
feature_event_timestamp_column_with_prefix = (
f"{feature_table.name}__{EVENT_TIMESTAMP_ALIAS}"
)
feature_created_timestamp_column_with_prefix = (
f"{feature_table.name}__{CREATED_TIMESTAMP_ALIAS}"
)
projection = [
col(col_name).alias(f"{feature_table.name}__{col_name}")
for col_name in feature_table_df.columns
]
aliased_feature_table_df = feature_table_df.select(projection)
join_cond = (
entity_with_id[entity_event_timestamp_column]
>= aliased_feature_table_df[feature_event_timestamp_column_with_prefix]
)
if feature_table.max_age:
join_cond = join_cond & (
aliased_feature_table_df[feature_event_timestamp_column_with_prefix]
>= entity_with_id[entity_event_timestamp_column]
- expr(f"INTERVAL {feature_table.max_age} seconds")
)
for key in feature_table.entity_names:
join_cond = join_cond & (
entity_with_id[key]
== aliased_feature_table_df[f"{feature_table.name}__{key}"]
)
conditional_join = entity_with_id.join(
aliased_feature_table_df, join_cond, "leftOuter"
)
for key in feature_table.entity_names:
conditional_join = conditional_join.drop(
aliased_feature_table_df[f"{feature_table.name}__{key}"]
)
window = Window.partitionBy("_row_nr", *feature_table.entity_names).orderBy(
col(feature_event_timestamp_column_with_prefix).desc(),
col(feature_created_timestamp_column_with_prefix).desc(),
)
filter_most_recent_feature_timestamp = conditional_join.withColumn(
"_rank", row_number().over(window)
).filter(col("_rank") == 1)
return filter_most_recent_feature_timestamp.select(
entity_df.columns
+ [
f"{feature_table.name}__{feature}"
for feature in feature_table.feature_names
]
)
5.离线特征同步到在线特征仓库
将特征从离线仓库同步到在线仓库,实现大致分为如下3个步骤:
a. 读取特征表的离线特征
val input = config.source match {
case source: BQSource =>
BigQueryReader.createBatchSource(
sparkSession.sqlContext,
source,
config.startTime,
config.endTime
)
case source: FileSource =>
FileReader.createBatchSource(
sparkSession.sqlContext,
source,
config.startTime,
config.endTime
)
}
val projected = input.select(projection: _*).cache()
b.离线特征数据作数据校验
implicit def rowEncoder: Encoder[Row] = RowEncoder(projected.schema)
TypeCheck.allTypesMatch(projected.schema, featureTable) match {
case Some(error) =>
throw new RuntimeException(s"Dataframe columns don't match expected feature types: $error")
case _ => ()
}
c.离线特征数据存储到在线仓库
val validRows = projected
.map(metrics.incrementRead)
.filter(rowValidator.allChecks)
validRows.write
.format("feast.ingestion.stores.redis")
.option("entity_columns", featureTable.entities.map(_.name).mkString(","))
.option("namespace", featureTable.name)
.option("project_name", featureTable.project)
.option("timestamp_column", config.source.eventTimestampColumn)
.option("max_age", config.featureTable.maxAge.getOrElse(0L))
.save()
6.获取在线特征数据
TODO
demo实操
原生feast-spark仅支持local、k8s、gcp模式下的spark,在我的分支中已经实现了on yarn的模式,下例中的配置皆适用于on yarn模式
通过一个简单的python案例,介绍仓库使用的全流程:
初始化连接到feast
from feast import Client, Feature, Entity, ValueType, FeatureTable
import feast_spark
from feast.data_source import FileSource, KafkaSource
from feast.data_format import ParquetFormat, AvroFormat
# 连接到feast的组件:core、serving、redis
feast_client = Client(
project="wbliu_august_eleven", # 特征分组
core_url="feast-release-feast-core.ume-feast:6565", # 实体、特征表元数据注册中心
serving_url="feast-release-feast-serving.ume-feast:6566", # 特征服务中心
# 使用feast额外的配置
options={"spark_staging_location": "hdfs://xxx/home/jovyan/spark_staging_location",
"spark_launcher": "yarn",
"spark_home": "/usr/hdp/current/spark3-client/",
"redis_host": "feast-release-feast-redis.ume-feast",
"redis_port": 6380}
)
# 使用feast-spark做批量特征的操作
client = feast_spark.Client(feast_client)
使用feast查看历史元数据信息
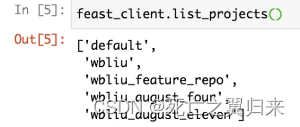
1.查看历史特征分组信息
feast_client.list_projects()
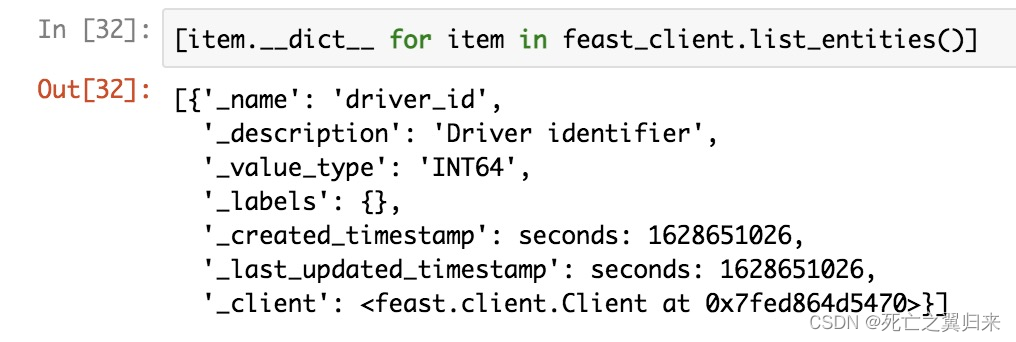
2.查看当前分组entity信息
feast_client.list_entities()
3.查看当前分组特征表信息
feast_client.list_feature_tables()

定义、注册entity和特征表到feast
1.定义entity
entity为特征表作表关联使用的主键
driver_id = Entity(name="driver_id", description="Driver identifier", value_type=ValueType.INT64)
2.定义特征
# Daily updated features
acc_rate = Feature("acc_rate", ValueType.FLOAT)
conv_rate = Feature("conv_rate", ValueType.FLOAT)
avg_daily_trips = Feature("avg_daily_trips", ValueType.INT32)
# Real-time updated features
trips_today = Feature("trips_today", ValueType.INT32)
3.定义特征表
driver_statistics = FeatureTable(
name="driver_statistics", # 特征表名
entities=["driver_id"], # 实体名
features=[ # 特征对象
acc_rate,
conv_rate,
avg_daily_trips
],
batch_source=FileSource( # 特征表关联的批数据源信息
event_timestamp_column="datetime", # 1.特征发生时间(必须有)
created_timestamp_column="created", # 2.特征产生时间 (必须有)
file_format=ParquetFormat(), # 批数据存储格式
file_url="hdfs://xxxx/home/jovyan/test_data/driver_statistics", # 批数据存储地址
date_partition_column="date" # 批数据存储划分partion的列
)
)
driver_trips = FeatureTable(
name="driver_trips",
entities=["driver_id"],
features=[
trips_today
],
batch_source=FileSource(
event_timestamp_column="datetime",
created_timestamp_column="created",
file_format=ParquetFormat(),
file_url="hdfs://xxx/home/jovyan/test_data/driver_trips",
date_partition_column="date"
)
)
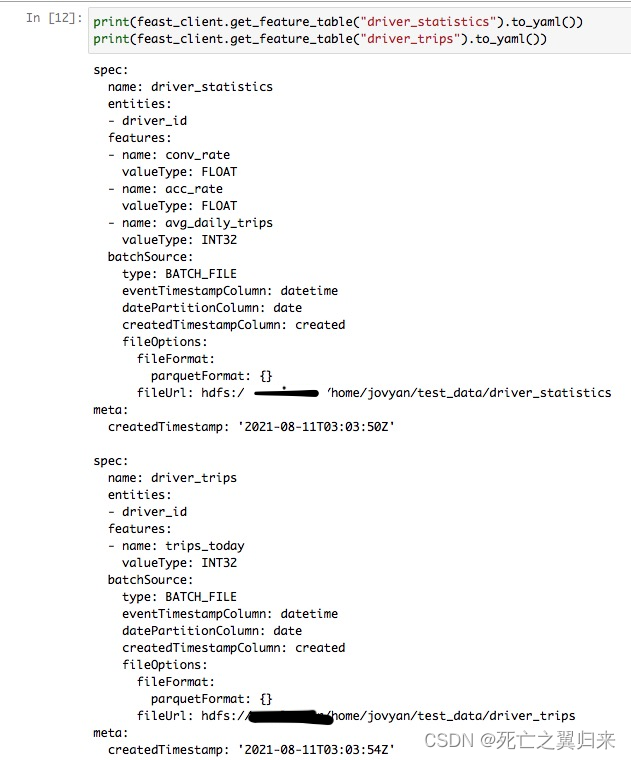
4.注册特征表、entity到feast
# Registering entities and feature tables in Feast Core
feast_client.apply(driver_id)
feast_client.apply(driver_statistics)
feast_client.apply(driver_trips)
5.准备特征数据
一般特征数据在特征处理之后生成,这个例子没有提前准备特征数据,所以临时生成一份特征数据:
def generate_entities():
return np.random.choice(999999, size=100, replace=False)
def generate_trips(entities):
df = pd.DataFrame(columns=["driver_id", "trips_today", "datetime", "created"])
df['driver_id'] = entities
df['trips_today'] = np.random.randint(0, 1000, size=100).astype(np.int32)
df['datetime'] = pd.to_datetime(
np.random.randint(
datetime(2020, 10, 10).timestamp(),
datetime(2020, 10, 20).timestamp(),
size=100),
unit="s"
)
df['created'] = pd.to_datetime(datetime.now())
return df
def generate_stats(entities):
df = pd.DataFrame(columns=["driver_id", "conv_rate", "acc_rate", "avg_daily_trips", "datetime", "created"])
df['driver_id'] = entities
df['conv_rate'] = np.random.random(size=100).astype(np.float32)
df['acc_rate'] = np.random.random(size=100).astype(np.float32)
df['avg_daily_trips'] = np.random.randint(0, 1000, size=100).astype(np.int32)
df['datetime'] = pd.to_datetime(
np.random.randint(
datetime(2020, 10, 10).timestamp(),
datetime(2020, 10, 20).timestamp(),
size=100),
unit="s"
)
df['created'] = pd.to_datetime(datetime.now())
return df
entities = generate_entities()
stats_df = generate_stats(entities)
trips_df = generate_trips(entities)
拽取特征数据,到对应的特征表批数据源地址
feast_client.ingest(driver_statistics, stats_df)
feast_client.ingest(driver_trips, trips_df)

获取离线训练特征数据
# Historical Retrieval For Training
# 准备需要抽取数据的范围
entities_with_timestamp = pd.DataFrame(columns=['driver_id', 'event_timestamp'])
entities_with_timestamp['driver_id'] = np.random.choice(entities, 10, replace=False)
entities_with_timestamp['event_timestamp'] = pd.to_datetime(np.random.randint(
datetime(2020, 10, 18).timestamp(),
datetime(2020, 10, 20).timestamp(),
size=10), unit='s')
# get_historical_features will return immediately once the Spark job has been submitted succesfully.
job = client.get_historical_features(
feature_refs=[# 需要使用的特征表和特征字段
"driver_statistics:avg_daily_trips",
"driver_statistics:conv_rate",
"driver_statistics:acc_rate",
"driver_trips:trips_today"
],
entity_source=entities_with_timestamp, # 需要抽取的数据范围
output_location="hdfs://xxx/home/jovyan/historical_feature_output" # 抽取的特征数据存放地址
)
离线特征数据同步到在线仓库
# offline to online ingestion
job = client.start_offline_to_online_ingestion(
driver_statistics, # 需要同步的特征表
datetime(2020, 10, 10), # 同步特征的事件时间范围
datetime(2020, 10, 20)
拽取流数据到在线仓库
这个例子没有提前准备流特征数据,临时构建一份kafka数据:
def send_avro_record_to_kafka(topic, record):
value_schema = avro.schema.parse(avro_schema_json)
writer = DatumWriter(value_schema)
bytes_writer = io.BytesIO()
encoder = BinaryEncoder(bytes_writer)
writer.write(record, encoder)
producer = Producer({
"bootstrap.servers": KAFKA_BROKER,
})
producer.produce(topic=topic, value=bytes_writer.getvalue())
producer.flush()
# Note: depending on the Kafka configuration you may need to create the Kafka topic first, like below:
# from confluent_kafka.admin import AdminClient, NewTopic
# admin = AdminClient({'bootstrap.servers': KAFKA_BROKER})
# new_topic = NewTopic('driver_trips', num_partitions=1, replication_factor=3)
# admin.create_topics(new_topic)
for record in trips_df.drop(columns=['created']).to_dict('record'):
record["datetime"] = (
record["datetime"].to_pydatetime().replace(tzinfo=pytz.utc)
)
send_avro_record_to_kafka(topic="driver_trips", record=record)
添加流数据源到特征表,更新特征表元数据:
# ingest from streaming source
# Change this to any Kafka broker addresses which is accessible by the spark cluster
KAFKA_BROKER = os.getenv("DEMO_KAFKA_BROKERS", "kafka:9092")
avro_schema_json = json.dumps({
"type": "record",
"name": "DriverTrips",
"fields": [
{"name": "driver_id", "type": "long"},
{"name": "trips_today", "type": "int"},
{
"name": "datetime",
"type": {"type": "long", "logicalType": "timestamp-micros"},
},
],
})
driver_trips.stream_source = KafkaSource(
event_timestamp_column="datetime",
created_timestamp_column="datetime",
bootstrap_servers=KAFKA_BROKER,
topic="driver_trips",
message_format=AvroFormat(avro_schema_json)
)
client.apply(driver_trips)
拽取流数据到在线仓库:
# Start the streaming job and send avro record to Kafka
job = client.start_stream_to_online_ingestion(
driver_trips
)
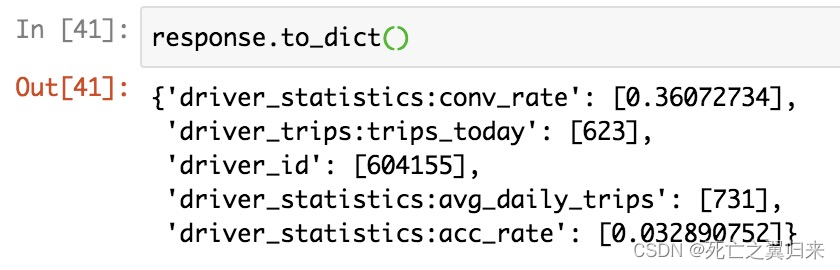
获取在线特征
response = feast_client.get_online_features(feature_refs=[ # 需要获取的特征列
"driver_statistics:avg_daily_trips",
"driver_statistics:conv_rate",
"driver_statistics:acc_rate",
"driver_trips:trips_today"
],
entity_rows=[{"driver_id": 604155}], # 特征数据的主键
project='wbliu')
response.to_dict()
目前还存在的问题
feast-spark虽然解决了一部分特征数据管理的问题,但是仍存在一些问题:
- 目前并未对离线、在线仓库做版本控制(和仓库的构建思路有一定关系)
- 特征的发现只能靠用户主动触发、需要用户具有一定的特征先验知识
- feast的使用、部署、环境等都有比较严苛的要求
展望
在feast 0.10+版本将会更轻量(对python开发者更友好)
使用方能继承实现更多个性化的特征仓库数据类型,帮助数据提供方(数仓)和数据使用方(算法)协作碰撞出更多火花
抛弃feast core、jobservice、serving等重组件,元数据可以采取本地(需要自己实现同步)或云的形式存储
参考:https://docs.feast.dev/project/feast-0.9-vs-feast-0.10+