针对带有 HTTPS 访问的 Elasticsearch 集群来说,在我之前的很多文章,我都习惯于使用集群的证书来访问 Elasticsearch。你可以参考我之前的文章 “Elastic Stack 8.0 安装 - 保护你的 Elastic Stack 现在比以往任何时候都简单”。这是一种非常简便的方法。好处是,我们可以随时使用在安装过程中的证书来访问 Elasticsearch。一个很大的缺点就是,我们必须拷贝证书,并把它放到 Beats 或者 Logstash 可以访问的位置进行配置。这个在使用的过程中非常不方便。相反,我们可以使用 fingerprint 来进行配置 Beats 及 Logstash。Fingerprint 的好处是它不用带路径。在配置的时候,我们所需要做的就是把 fingerprint 的值拷贝进来就可以了,而无须去配置路径。
如何得到 fingerprint ?
我们可以通过如下的几种方法来得到 Elasticsearch 集群的 fingerprint。
第一次 Elasticsearch 启动时的输出
针对 Elastic Stack 8.x 的安装来说,在我们第一次启动的时候,我们就可以看到 fingerprint 的输出:

从上面的输出中我们可以看到 fingerprint 的输出。
从 Kibana 的配置中得到
在很多的时候,我们没有记下 Elasticsearch 第一次启动时的 fingerprint 的输出。那我们该怎么办呢?另外一种方法就是从 Kibana 的配置文件中,我们可以得到这个信息。我们打开 config/kibana.yml 文件,并查看最后的一行:
config/kibana.yml

很显然,我们在上面的文件中查看到 fingerprint 的值。
通过证书来获得
我们可以在 Elasticsearch 的安装目录中查看到证书所在的位置:
$ pwd
/Users/liuxg/elastic/elasticsearch-8.6.1
$ ls config/certs/
http.p12 http_ca.crt transport.p12从上面的显示中,我们可以看到在安装过程中,Elasticsearch 生成的三个证书文件。我们使用如下的命令来获得 fingerprint:
openssl x509 -fingerprint -sha256 -in config/certs/http_ca.crt
在实际的使用中,我们需要使用到没有冒号的 fingerprint。我们可以使用如下的命令来进行生成:
openssl x509 -in config/certs/http_ca.crt -sha256 -fingerprint | grep sha256 | sed 's/://g'$ pwd
/Users/liuxg/elastic/elasticsearch-8.6.1
$ openssl x509 -in config/certs/http_ca.crt -sha256 -fingerprint | grep sha256 | sed 's/://g'
sha256 Fingerprint=F8FA6EA4326C13224D952C5E0B2D36AFB18135A505EF41FC25490EBB5A652122上面的输出结果显示的是没有冒号的 fingerprint。
配置 Beats
一旦得到 Elasticsearch 集群证书的 fingerprint,我们可以通过如下的方式来配置 Beats,比如 Metricbeat。我们可以编辑 Metricbeat 的配置文件 metricbeat.yml 文件:
output.elasticsearch:
# Array of hosts to connect to.
hosts: ["localhost:9200"]
# Protocol - either `http` (default) or `https`.
protocol: "https"
# Authentication credentials - either API key or username/password.
#api_key: "id:api_key"
username: "elastic"
password: "gV4pgxNCTi5y*80GmoqN"
ssl:
enabled: true
ca_trusted_fingerprint: "F8FA6EA4326C13224D952C5E0B2D36AFB18135A505EF41FC25490EBB5A652122"如上所示,我们配置 ssl 项,并把从上面获得的 fingerprint 填入:

我们可以打入如下的命令来进行测试:
$ pwd
/Users/liuxg/elastic/metricbeat-8.6.1-darwin-aarch64
$ ./metricbeat test config
Config OK
$ ./metricbeat test output
elasticsearch: https://localhost:9200...
parse url... OK
connection...
parse host... OK
dns lookup... OK
addresses: ::1, 127.0.0.1
dial up... OK
TLS...
security: server's certificate chain verification is enabled
handshake... OK
TLS version: TLSv1.3
dial up... OK
talk to server... OK
version: 8.6.1上面表明我们的 fingerprint 的配置是成功的。它可以连接到 Elasticsearch。我们可以通过如下的命令来生成相应的 Dashboard:
$ pwd
/Users/liuxg/elastic/metricbeat-8.6.1-darwin-aarch64
$ ./metricbeat setup
Overwriting ILM policy is disabled. Set `setup.ilm.overwrite: true` for enabling.
Index setup finished.
Loading dashboards (Kibana must be running and reachable)
Loaded dashboards上面显示我们已经成功地上传了 Dashboard。我们可以通过如下的命令来启动 Metricbeat:

我们可以在 Kibana 中查看 System 模块的 Dashbord:


 从上面我们可以看到 HOST 机器的指标信息。
从上面我们可以看到 HOST 机器的指标信息。
Logstash 连接
同样地,我们也可以在 Logstash 的配置中使用 fingerprint。我们可以参照文档 Elasticsearch output plugin | Logstash Reference [8.6] | Elastic。我们使用如下的配置文件:
logstash.conf
input {
generator {
message => '{"id":2,"timestamp":"2019-08-11T17:55:56Z","paymentType":"Visa","name":"Darby Dacks","gender":"Female","ip_address":"77.72.239.47","purpose":"Shoes","country":"Poland","age":55}'
count => 1
}
}
filter {
json {
source => "message"
}
if [paymentType] == "Mastercard" {
drop {}
}
mutate {
remove_field => ["message", "@timestamp", "path", "host", "@version", "log", "event"]
}
}
output {
stdout {
codec => rubydebug
}
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["https://localhost:9200"]
index => "data-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"
user => "elastic"
password => "gV4pgxNCTi5y*80GmoqN"
ssl => true
ca_trusted_fingerprint => "F8FA6EA4326C13224D952C5E0B2D36AFB18135A505EF41FC25490EBB5A652122"
}
}我们使用如下的命令来启动 Logstash:
$ pwd
/Users/liuxg/elastic/logstash-8.6.1
$ ./bin/logstash -f logstash.conf

上面显示我们已经成功地写入一条文档到 Elasticsearch 中去了。我们到 Kibana 中进行查看:
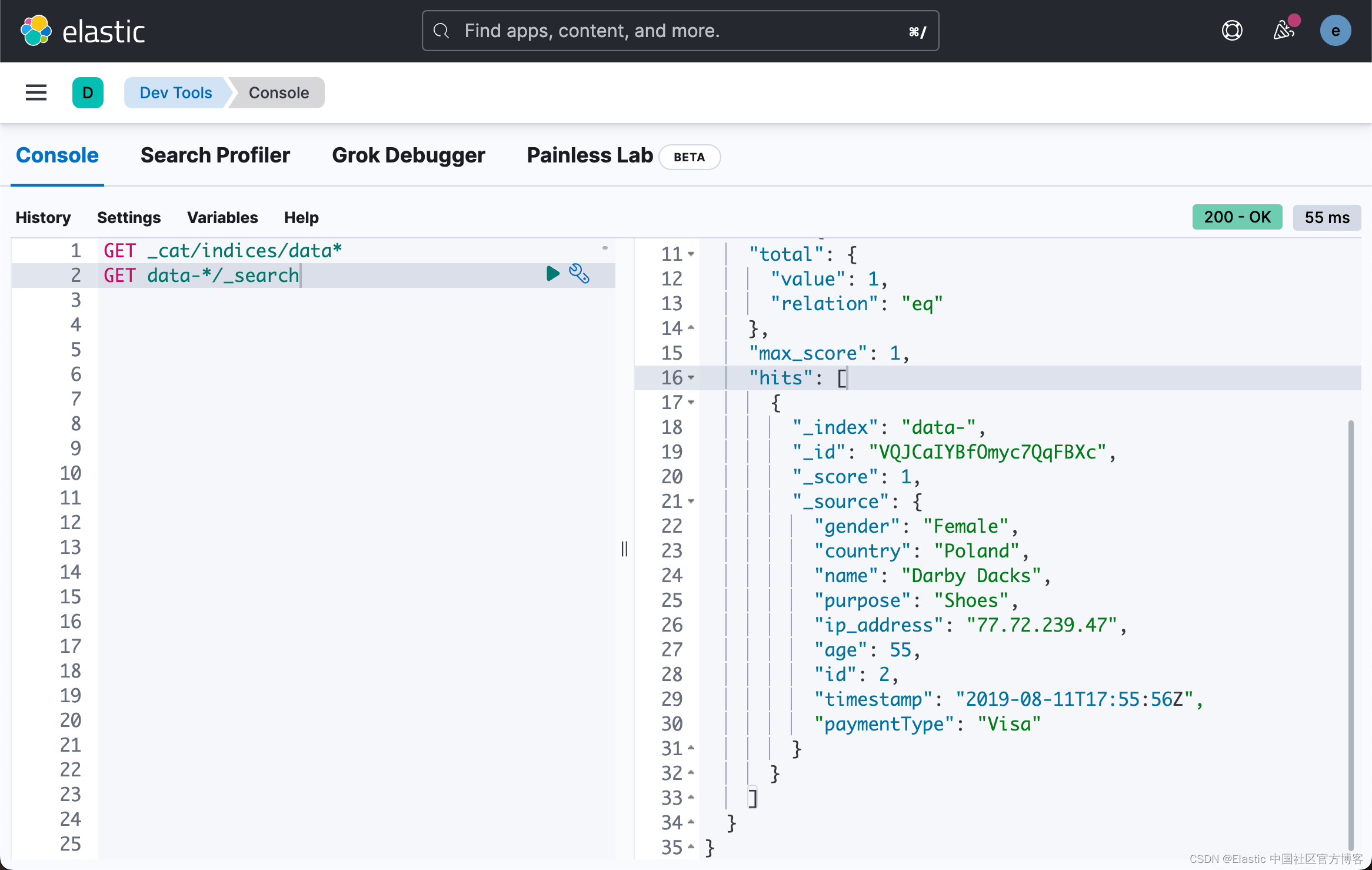
从上面,我们可以看出来,文档已经被成功地写入到 Elasticsearch 中去了。
好了,今天的分享就到这里。祝大家学习愉快!




![[软件工程导论(第六版)]第4章 形式化说明技术(复习笔记)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/286b5369cb3e437fb0720205c53cae97.png)