二叉树
- 1.二叉树的递归遍历
- 144.二叉树的前序遍历
- 145.二叉树的后序遍历
- 94.二叉树的中序遍历
- 2.二叉树的迭代遍历
- 144.二叉树的前序遍历
- 145.二叉树的后序遍历
- 94.二叉树的中序遍历
- 3.二叉树的层序遍历
- 102.二叉树的层序遍历
- 107.二叉树的层序遍历||
- 199.二叉树的右视图
- 637.二叉树的层平均值
- 429.N叉树的层序遍历
- 515.在每个树行中找最大值
- 116.填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针
- 117.填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针||
- 104.二叉树的最大深度
- 111.二叉树的最小深度
- 4.翻转二叉树
- 226.翻转二叉树
- 5.对称二叉树
- 101.对称二叉树
- 572.另一棵树的子树
- 6.二叉树的最大深度
- 104.二叉树的最大深度
- 559.N叉树的最大深度
- 111.二叉树的最小深度
- 7.完全二叉树的节点个数
- 222.完全二叉树的节点个数
- 8.平衡二叉树
- 110.平衡二叉树
- 9.二叉树的所有路径
- 257.二叉树的所有路径
- 10.左叶子之和
- 404.左叶子之和
- 11.找树左下角的值
- 513.找树左下角的值
- 12.路径总和
- 112.路径总和
- 113.路径总和||
- 13.从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
- 106.从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
- 105.从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
- 14.最大二叉树
- 654.最大二叉树
- 15.合并二叉树
- 617.合并二叉树
- 16.二叉搜索树中的搜索
- 700.二叉搜索树中的搜索
- 17.验证二叉搜索树
- 98.验证二叉搜索树
- 18.二叉搜索树的最小绝对差
- 530.二叉搜索树的最小绝对差
- 19.二叉搜索树中的众数
- 501.二叉搜索树中的众数
- 20.二叉树的最近公共祖先
- 236.二叉树的最近公共祖先
- 21.二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
- 235.二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
- 22.二叉搜索树中的插入操作
- 701.二叉搜索树中的插入操作
- 23.删除二叉搜索树中的节点
- 450.删除二叉搜索树中的节点
- 24.修剪二叉搜索树
- 669.修剪二叉搜索树
- 25.将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树
- 33.把二叉树转换为累加树
- 538.把二叉搜索树转换为累加树
1.二叉树的递归遍历
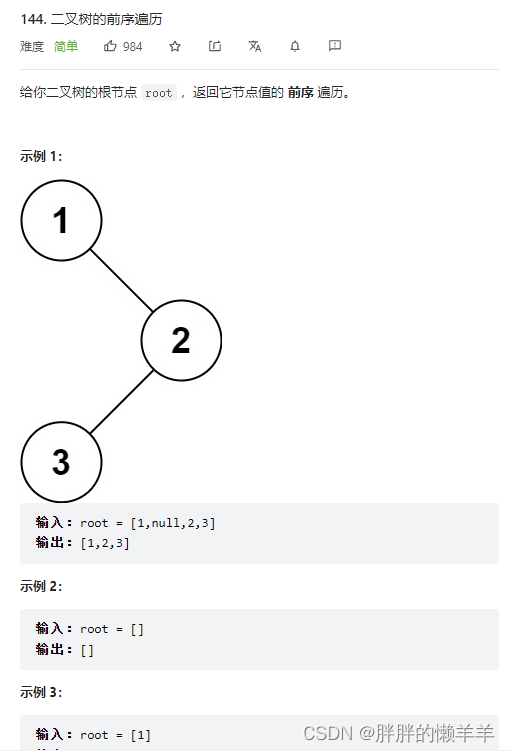
144.二叉树的前序遍历
思路:
前序遍历的顺序是,根节点,左孩子,右孩子
终止条件是当前节点为空。
class Solution {
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> result=new ArrayList<Integer>();
preorder(root,result);
return result;
}
public void preorder(TreeNode root,List<Integer> result) {
if(root==null) {
return ;
}
result.add(root.val);
preorder(root.left,result);
preorder(root.right,result);
}
}
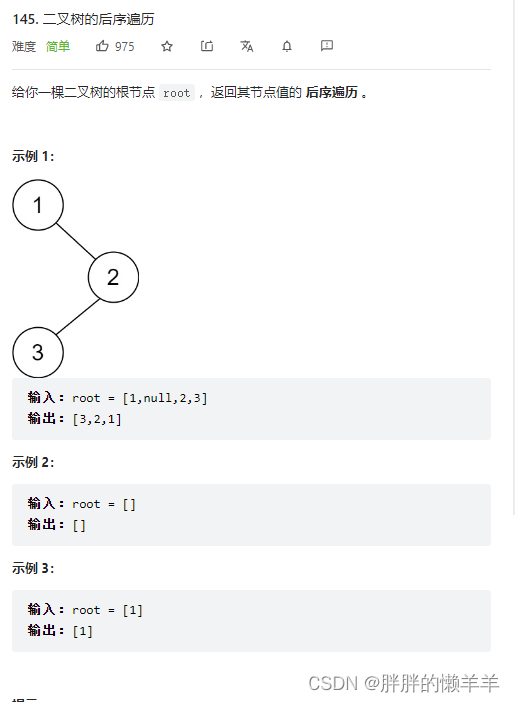
145.二叉树的后序遍历
思路:
后续遍历就是最后遍历根节点。递归函数里传入左孩子和右孩子即可。
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> result=new ArrayList<Integer>();
postorder(root, result);
return result;
}
public void postorder(TreeNode root,List<Integer> result) {
if(root==null) {
return ;
}
postorder(root.left,result);
postorder(root.right,result);
result.add(root.val);
}
94.二叉树的中序遍历
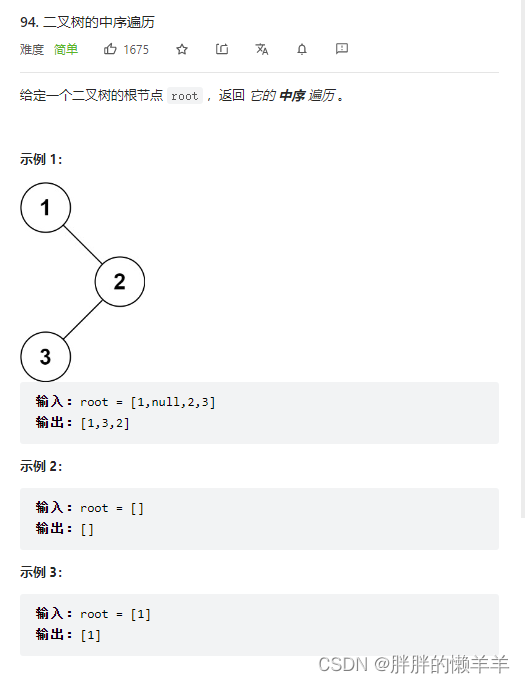
思路:
二叉树的中序遍历就是在中间遍历根节点。
class Solution {
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> result=new ArrayList<Integer>();
inorder(root, result);
return result;
}
public void inorder(TreeNode root,List<Integer> result) {
if(root==null) {
return ;
}
inorder(root.left,result);
result.add(root.val);
inorder(root.right,result);
}
}
2.二叉树的迭代遍历
144.二叉树的前序遍历
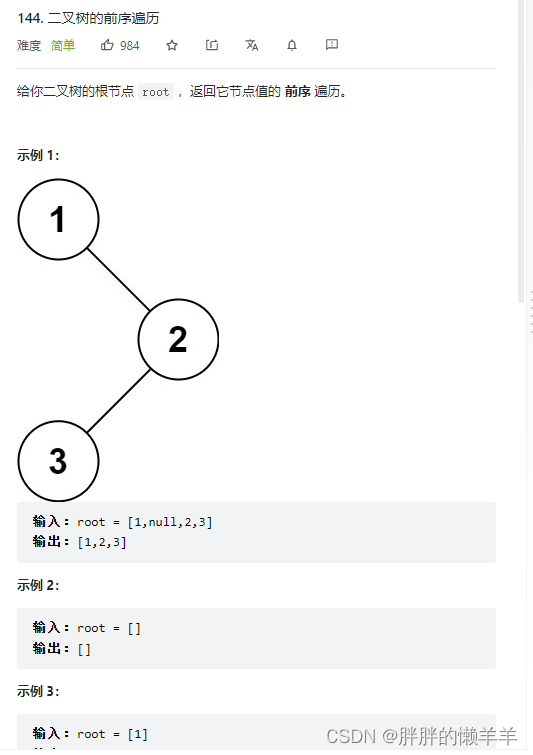
思路:
因为递归都是通过栈来实现的,所以我们这里也用栈来实现。
先序遍历的顺序是 中,左,右。
所以我们先让根节点进去,然后操作这个node节点,让它弹出来。然后再让右子节点进去,这样它就会后出来。这样一步步来处理。
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> result=new ArrayList<>();
Stack<TreeNode> stack=new Stack<>();
if(root==null) {
return result;
}
//先在栈中放入根节点
stack.push(root);
//当栈不为空时
while(!stack.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node=stack.pop();
result.add(node.val);
//先放右节点,因为先进的会压在栈底
if(node.right!=null) {
stack.push(node.right);
}
if(node.left!=null) {
stack.push(node.left);
}
}
return result;
}
145.二叉树的后序遍历
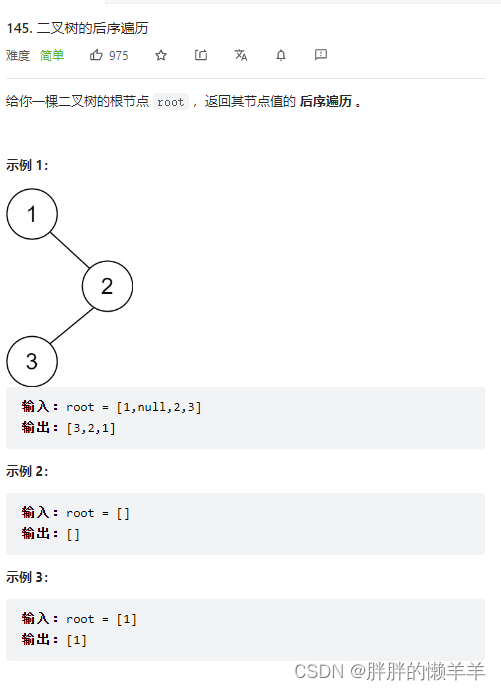
思路:
后续遍历的顺序是,左,右,中
所以可以通过先序遍历的代码,迭代改一下。
因为进栈的顺序是中,左,右,进入result的顺序就是中,右,左,所以再逆转result数组就可以实现左右中。
94.二叉树的中序遍历
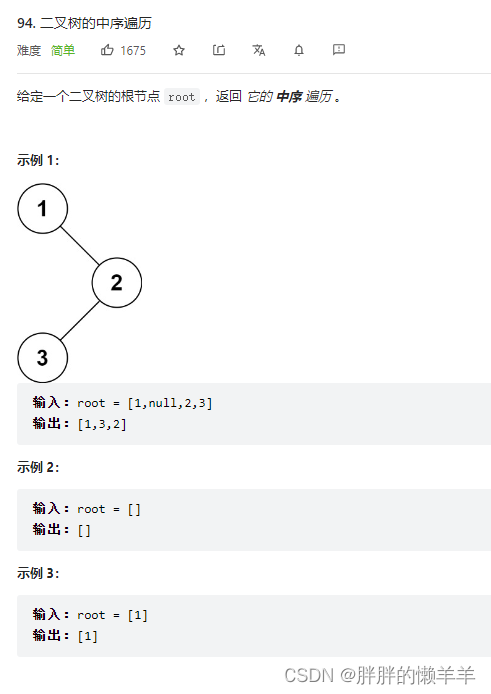
思路:
因为加入栈的节点和要处理的节点不一样,所以我们用一个指针来控制。
让指针一直遍历左节点,然后把遍历过的节点加入栈。
当节点是空的时候,栈中弹出元素,并且操作这个元素。让指针指向右节点,看他有没有孩子。
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> result=new ArrayList<>();
Stack<TreeNode> stack=new Stack<>();
if(root==null) {
return result;
}
TreeNode cur=root;
while(cur!=null||!stack.isEmpty()) {
if(cur!=null) {
//找到最左边的节点,把遍历过的节点加入栈中
stack.push(cur);
cur=cur.left;
}else {
cur=stack.pop();
result.add(cur.val);
cur=cur.right;
}
}
return result;
}
3.二叉树的层序遍历
102.二叉树的层序遍历
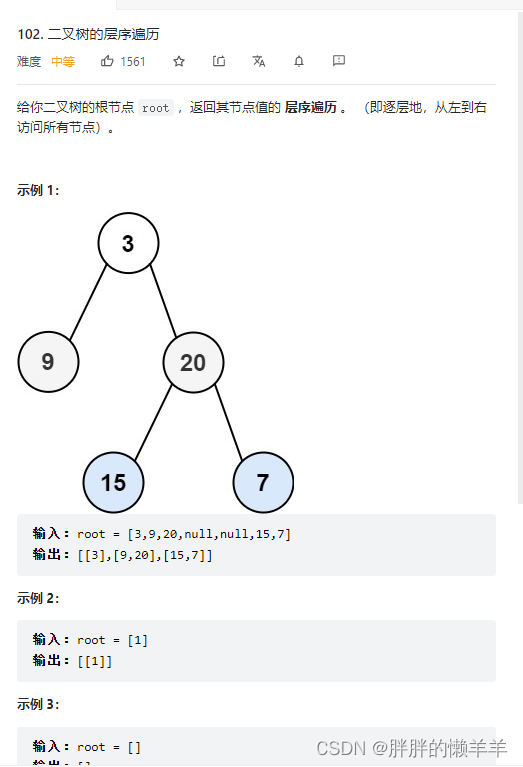
思路:
层序遍历用队列这中数据结构来实现,先将根节点放入队列中,记录此时层数的值。然后弹出一个节点时,把这个节点的左右孩子加入到队列中。层数的元素个数来判断进入每层的节点。
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
Deque<TreeNode > deque=new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
List<List<Integer>> result=new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
if(root!=null) {
deque.offer(root);
}
while(!deque.isEmpty()) {
List<Integer> index=new ArrayList<Integer>();//用来记录每一层的元素
int len=deque.size();//len用来记录每一层的元素个数
while(len-->0) {
TreeNode node =deque.poll();
index.add(node.val);
if(node.left!=null) {
deque.add(node.left);
}
if(node.right!=null) {
deque.add(node.right);
}
}
result.add(index);
}
return result;
}
}
107.二叉树的层序遍历||
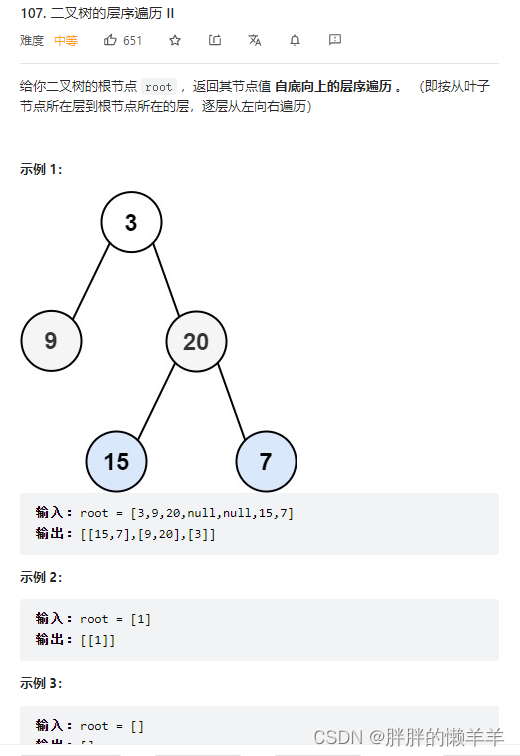
思路:
将正序遍历的结果逆转一下就行。
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrderBottom(TreeNode root) {
Deque<TreeNode > deque=new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
List<List<Integer>> result=new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
if(root!=null) {
deque.offer(root);
}
while(!deque.isEmpty()) {
List<Integer> index=new ArrayList<Integer>();//用来记录每一层的元素
int len=deque.size();//len用来记录每一层的元素个数
while(len-->0) {
TreeNode node =deque.poll();
index.add(node.val);
if(node.left!=null) {
deque.add(node.left);
}
if(node.right!=null) {
deque.add(node.right);
}
}
result.add(index);
}
Collections.reverse(result);
return result;
}
}
199.二叉树的右视图
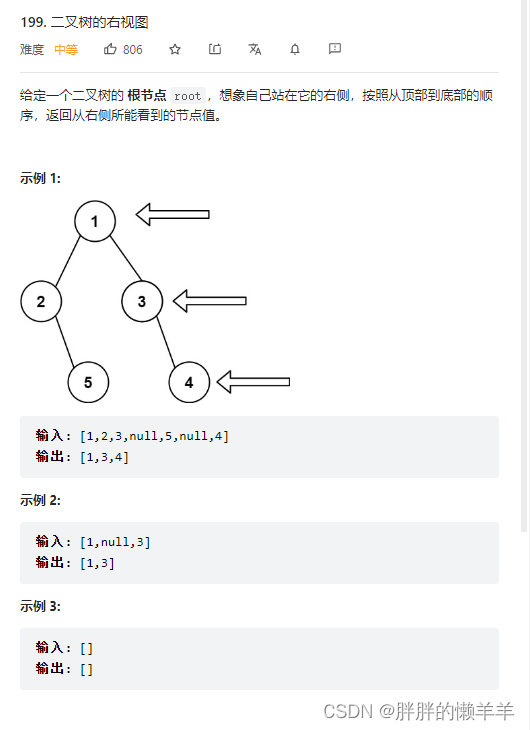
思路:
和前边一样一次遍历每个节点,当遍历到最后一个节点时,再把这个节点加入到结果中。
public List<Integer> rightSideView(TreeNode root) {
Deque<TreeNode > deque=new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
List<Integer> result=new ArrayList<Integer>();
if(root!=null) {
deque.offer(root);
}
while(!deque.isEmpty()) {
int len=deque.size();//len用来记录每一层的元素个数
while(len-->0) {
TreeNode node =deque.poll();
if(node.left!=null) {
deque.add(node.left);
}
if(node.right!=null) {
deque.add(node.right);
}
if(len==1) {
result.add(node.val);
}
}
}
return result;
}
637.二叉树的层平均值
思路:
将每层二叉树的和除以每层二叉树的元素个数即可。
class Solution {
public List<Double> averageOfLevels(TreeNode root) {
Deque<TreeNode > deque=new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
List<Double> result=new ArrayList<Double>();
if(root!=null) {
deque.offer(root);
}
while(!deque.isEmpty()) {
List<Integer> index=new ArrayList<Integer>();//用来记录每一层的元素
Double sum=0.0;
int len=deque.size();//len用来记录每一层的元素个数
int levelsize=deque.size();
while(len-->0) {
TreeNode node =deque.poll();
index.add(node.val);
if(node.left!=null) {
deque.add(node.left);
}
if(node.right!=null) {
deque.add(node.right);
}
index.add(node.val);
sum+=node.val;
}
result.add(sum/levelsize);
}
return result;
}
}
429.N叉树的层序遍历
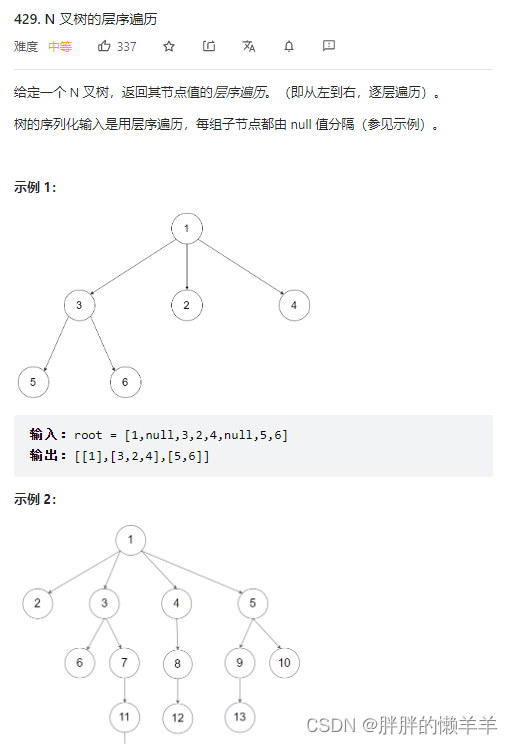
思路:
把以前的左右孩子节点换成一个数组来遍历,当遇到空节点时就算停止。
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(Node root) {
Deque<Node > deque=new LinkedList<Node>();
List<List<Integer>> result=new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
if(root!=null) {
deque.offer(root);
}
while(!deque.isEmpty()) {
List<Integer> index=new ArrayList<Integer>();//用来记录每一层的元素
int len=deque.size();//len用来记录每一层的元素个数
while(len-->0) {
Node node =deque.poll();
index.add(node.val);
List<Node> childern=node.children;
for(Node node1:childern) {
if(node1!=null) {
deque.add(node1);
}
}
}
result.add(index);
}
return result;
}
515.在每个树行中找最大值
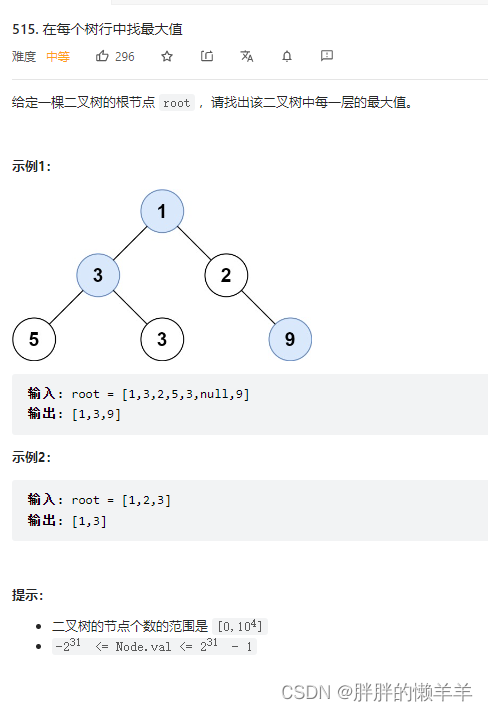
思路:
注意此时的max值要用Integer.MIN_VALUE来设置,因为可能出现比0小的情况。
public List<Integer> largestValues(TreeNode root) {
Deque<TreeNode > deque=new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
List<Integer> result=new ArrayList<Integer>();
if(root!=null) {
deque.offer(root);
}
while(!deque.isEmpty()) {
int len=deque.size();//len用来记录每一层的元素个数
int max=Integer.MIN_VALUE;
while(len-->0) {
TreeNode node =deque.poll();
max=node.val>max?node.val:max;
if(node.left!=null) {
deque.add(node.left);
}
if(node.right!=null) {
deque.add(node.right);
}
}
result.add(max);
}
return result;
}
116.填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针
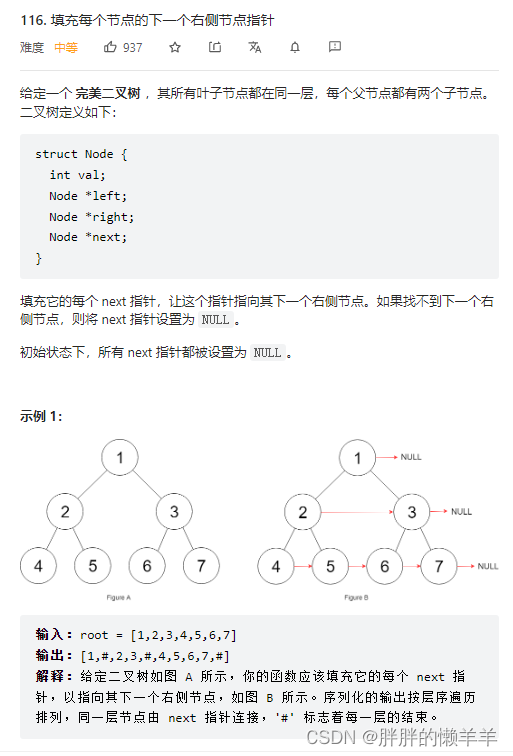
思路:
遍历每一层的时候,先保留第一个节点,然后将这个top指针保留住,每次更新下一个节点就行。
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(Node root) {
Deque<Node > deque=new LinkedList<Node>();
List<List<Integer>> result=new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
if(root!=null) {
deque.offer(root);
}
while(!deque.isEmpty()) {
List<Integer> index=new ArrayList<Integer>();//用来记录每一层的元素
int len=deque.size();//len用来记录每一层的元素个数
while(len-->0) {
Node node =deque.poll();
index.add(node.val);
List<Node> childern=node.children;
for(Node node1:childern) {
if(node1!=null) {
deque.add(node1);
}
}
}
result.add(index);
}
return result;
}
117.填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针||
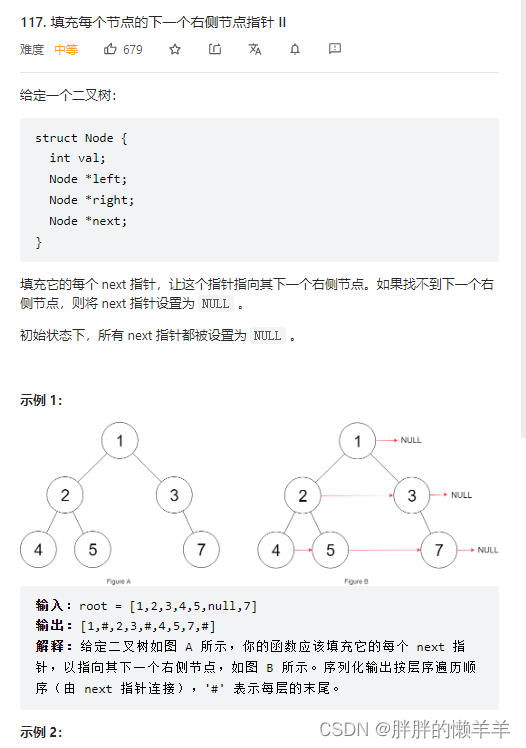
思路:
和上边没有任何差别,思路一样。
public Node connect(Node root) {
Deque<Node > deque=new LinkedList<Node>();
List<Integer> result=new ArrayList<Integer>();
if(root!=null) {
deque.offer(root);
}
while(!deque.isEmpty()) {
int len=deque.size();//len用来记录每一层的元素个数
Node top=deque.pop();//将每层的头节点记录下来
if(top.left!=null) {
deque.add(top.left);
}
if(top.right!=null) {
deque.add(top.right);
}
while(len-->1) {
Node next =deque.poll();
if(next.left!=null) {
deque.add(next.left);
}
if(next.right!=null) {
deque.add(next.right);
}
top.next=next;//将top节点指向下一个节点
top=next;//自己变成top节点
}
}
return root;
}
104.二叉树的最大深度
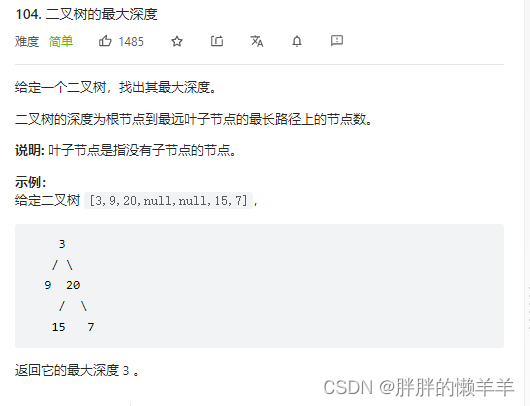
思路:每层遍历了多少个就是一共有几层。
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
Deque<TreeNode > deque=new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
List<Integer> result=new ArrayList<Integer>();
if(root!=null) {
deque.offer(root);
}
int dept=0;
while(!deque.isEmpty()) {
dept++;
int len=deque.size();//len用来记录每一层的元素个数
int max=Integer.MIN_VALUE;
while(len-->0) {
TreeNode node =deque.poll();
max=node.val>max?node.val:max;
if(node.left!=null) {
deque.add(node.left);
}
if(node.right!=null) {
deque.add(node.right);
}
}
result.add(max);
}
return dept;
}
111.二叉树的最小深度
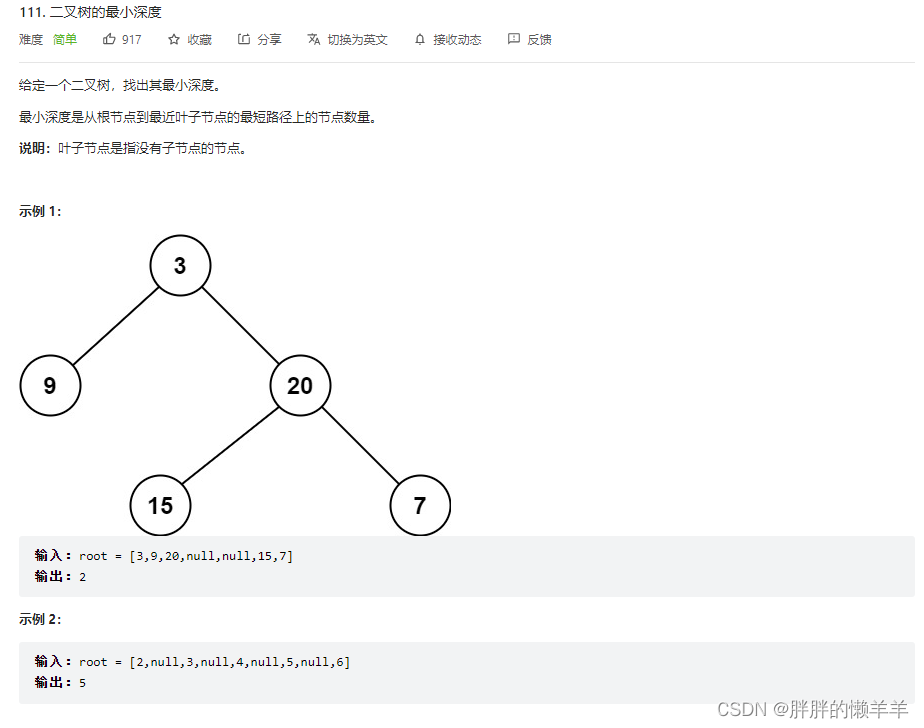
思路:
当节点的左右节点都为空时,就代表这个节点为空了。
class Solution {
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
Deque<TreeNode > deque=new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
List<Integer> result=new ArrayList<Integer>();
if(root!=null) {
deque.offer(root);
}
int dept=0;
while(!deque.isEmpty()) {
dept++;
int len=deque.size();//len用来记录每一层的元素个数
while(len-->0) {
TreeNode node =deque.poll();
if(node.left!=null) {
deque.add(node.left);
}
if(node.right!=null) {
deque.add(node.right);
}
if(node.left==null&&node.right==null) {
return dept;
}
}
}
return dept;
}
}
4.翻转二叉树
226.翻转二叉树
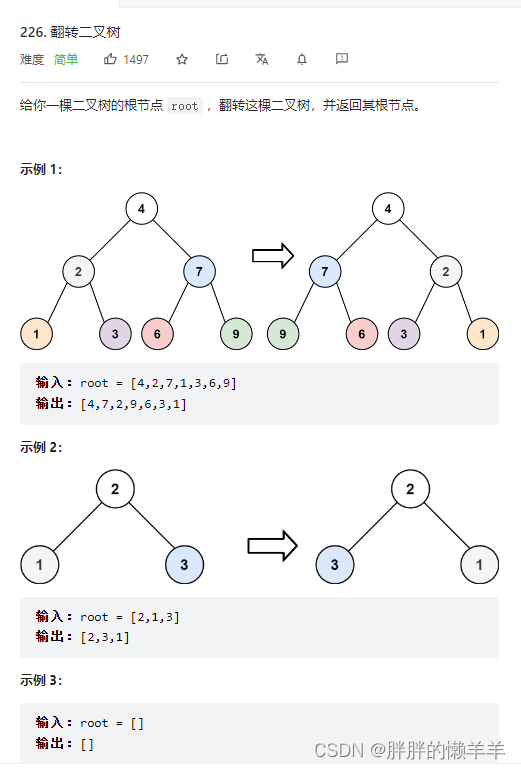
思路:
判断终止条件,结束条件就行,函数体中是翻转两个节点的左右孩子,可以先序遍历,也可以后序遍历。中序遍历则不行。
class Solution {
public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null) {
return null;
}
invertTree(root.left);
invertTree(root.right);
swap(root);
return root;
}
public void swap(TreeNode root) {
TreeNode temp=root.left;
root.left=root.right;
root.right=temp;
}
}
5.对称二叉树
101.对称二叉树
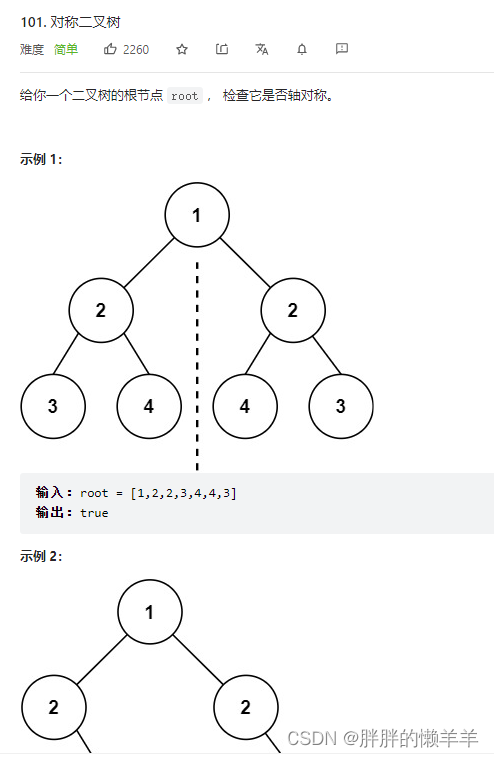
思路:
用递归的方式来进行比较,比较根节点的左右两个子树,判断出终止条件,当两边的值或者有一方为空节点时,都返回false。
运用后序遍历法,先比较外侧节点,再比较内侧节点。最后比较中间节点。
class Solution {
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
return compare(root.left,root.right);
}
public boolean compare(TreeNode left,TreeNode right) {
if(left==null&&right!=null) {
return false;
}else if(left!=null&&right==null) {
return false;
}else if(left==null&&right==null) {
return true;
}else if(left.val!=right.val) {
return false;
}
boolean outSide=compare(left.left,right.right);
boolean inSide=compare(left.right,right.left);
return outSide&&inSide;
}
}
572.另一棵树的子树
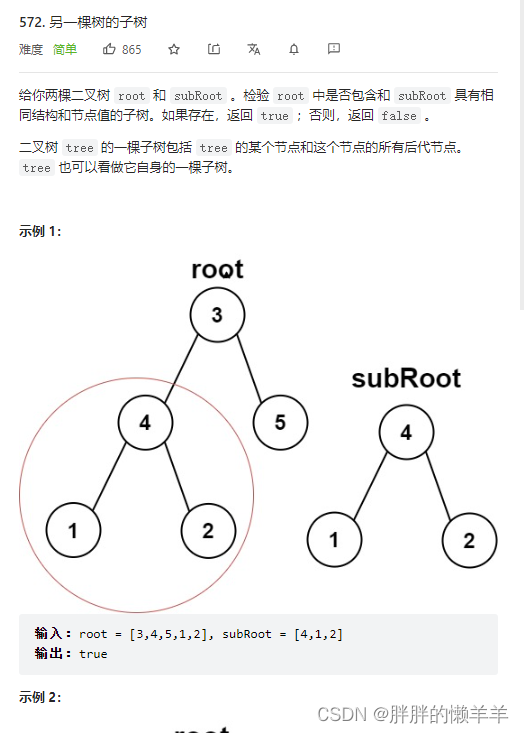
思路:
运用递归法判断,要判断好终止条件,然后写出比较两个子树是否一样的函数。判断,这棵树和比较的树是否一样,或者这颗树的左右子树和比较的树是否一样。这三个条件满足其中一个即可。
class Solution {
public boolean compare(TreeNode left,TreeNode right) {
if(left==null&&right!=null) {
return false;
}else if(left!=null&&right==null) {
return false;
}else if(left==null&&right==null) {
return true;
}else if(left.val!=right.val) {
return false;
}
boolean outSide=compare(left.left,right.left);
boolean inSide=compare(left.right,right.right);
return outSide&&inSide;
}
public boolean isSubtree(TreeNode root, TreeNode subRoot) {
if(subRoot==null) {
return true;
}
if(root==null) {
return false;
}
return isSubtree(root.left,subRoot)||isSubtree(root.right,subRoot)||compare(root,subRoot);
}
}
6.二叉树的最大深度
104.二叉树的最大深度
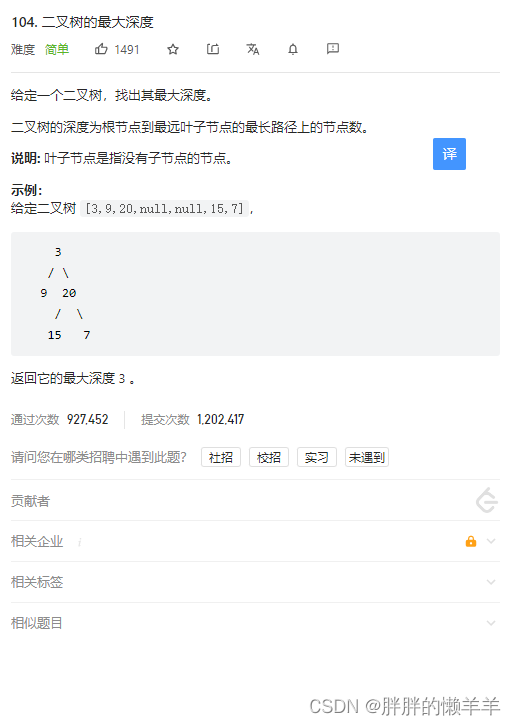
思路:
深度是从根节点往下属。而高度则是从下往上数。
所以,深度是先序遍历,中左右。
高度是后序遍历,左右中。
这里我们求出了根节点的高度,也就求出了二叉树的深度。
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null) {
return 0;
}
return 1+Math.max(maxDepth(root.left), maxDepth(root.right));
}
559.N叉树的最大深度
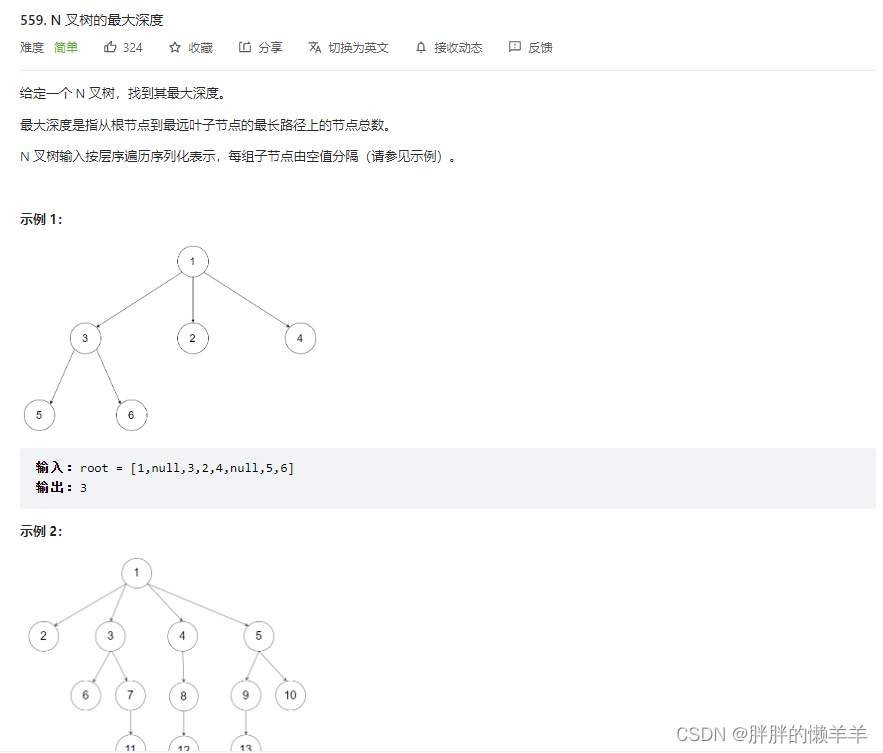
思路:
递归思路,当遇到空节点时,深度为0。
然后每一次的最大节点就是当前层的孩子的最大节点。
最后return 1+max(children)。
public int maxDepth(Node root) {
if(root==null) {
return 0;
}
List<Node> children=root.children;
int max=0;
for(Node node:children) {
max=Math.max(max,maxDepth(node));
}
return 1+max;
}
111.二叉树的最小深度
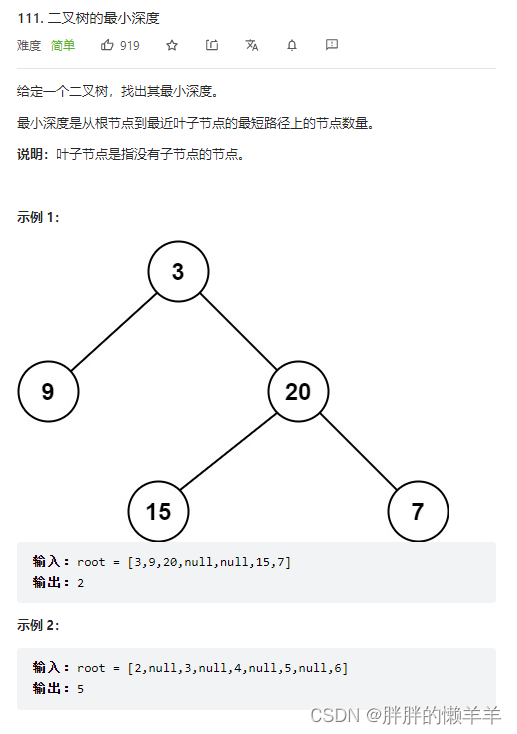
思路:
这里的最小深度是一个节点的子树的最小深度,如果一个节点还有左节点或者右节点,那么此时它就不能称为一个最小节点。因为它有叶子节点就不能称为一个叶子。所以判断条件上,要分别判断,左子树为空右子树不为空,或左子树不为空,右子树为空,或者左右子树都不为空的情况。
class Solution {
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null) {
return 0;
}
int leftDepth=minDepth(root.left);
int rightDepth=minDepth(root.right);
if(root.left==null&&root.right!=null) {
return 1+rightDepth;
}
if(root.left!=null&&root.right==null) {
return 1+leftDepth;
}
return 1+Math.min(leftDepth, rightDepth);
}
}
7.完全二叉树的节点个数
222.完全二叉树的节点个数
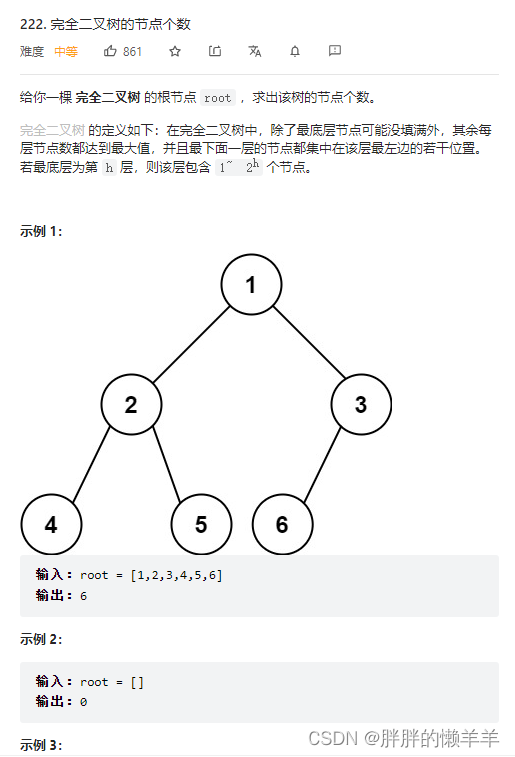
思路:
普通解法:运动递归。
class Solution {
public int countNodes(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null) {
return 0;
}
return countNodes(root.left)+countNodes(root.right)+1;
}
}
公式解法:
完全二叉树的满二叉树节点个数是2^n-1。
所以这时候当遇到的节点是满二叉树时,直接用公式求解。
public int countNodes(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null) {
return 0;
}
TreeNode left=root.left;
TreeNode right=root.right;
int leftDept=0;
int rightDept=0;
while(left!=null) {
left=left.left;
leftDept++;
}
while(right!=null) {
right=right.right;
rightDept++;
}
if(leftDept==rightDept) {
return (2<<leftDept)-1;
}
return countNodes(root.left)+countNodes(root.right)+1;
}
8.平衡二叉树
110.平衡二叉树
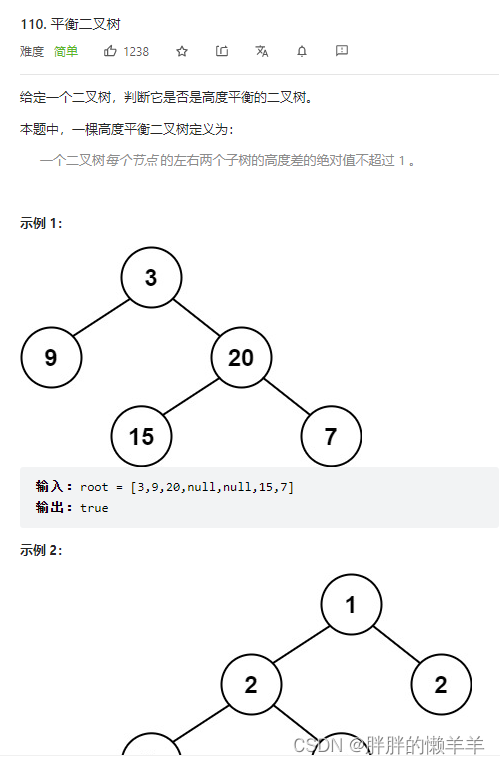
思路:
判断左右子树的高度。判断左子树是不是平衡二叉树,如果不是,返回-1.
判断右子树是不是平衡二叉树,如果不是,返回-1.
如果两棵子树的高度差超过1,直接返回-1.
class Solution {
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
if(depth(root)==-1) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
public int depth(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null) {
return 0;
}
//求左子树的高度
int leftdepth=depth(root.left);
if(leftdepth==-1) {
return -1;
}
int rightdepth=depth(root.right);
if(rightdepth==-1) {
return -1;
}
int result;
if(Math.abs(leftdepth-rightdepth)>1) {
return -1;
}else {
return 1+Math.max(leftdepth, rightdepth);
}
}
}
9.二叉树的所有路径
257.二叉树的所有路径
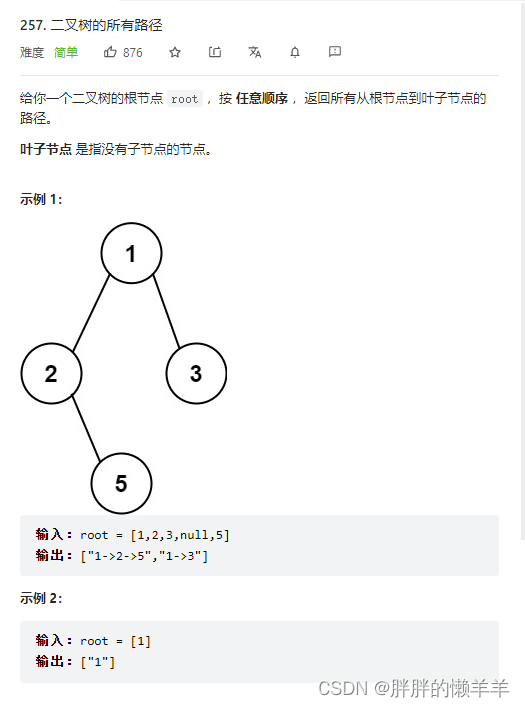
思路:
递归法,先序遍历,中左右。
每次碰到一个节点,把它放入路径中。
如果这个是叶子节点,就可以输入了。
如果不是叶子节点,就继续去递归,递归完之后把最后一个元素弄出来。这就是回溯法。
class Solution {
public List<String> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode root) {
List<String> result=new ArrayList<String>();
if(root==null) {
return result;
}
List<Integer> paths=new ArrayList<Integer>();
traversal(root,paths,result);
return result;
}
public void traversal(TreeNode root,List<Integer>paths,List<String> result) {
paths.add(root.val);
//如果遇到了叶子节点,就要考虑输出了。
if(root.left==null&&root.right==null) {
StringBuilder path=new StringBuilder();
for(int i=0;i<paths.size()-1;i++) {
path.append(paths.get(i)).append("->");
}
path.append(paths.get(paths.size()-1));
result.add(path.toString());
return ;
}
//如果左节点不为空
if(root.left!=null) {
traversal(root.left,paths,result);
//进行回溯操作,把最后一个节点弹出去
paths.remove(paths.size()-1);
}
//如果右节点不为空
if(root.right!=null) {
traversal(root.right,paths,result);
paths.remove(paths.size()-1);
}
}
}
10.左叶子之和
404.左叶子之和
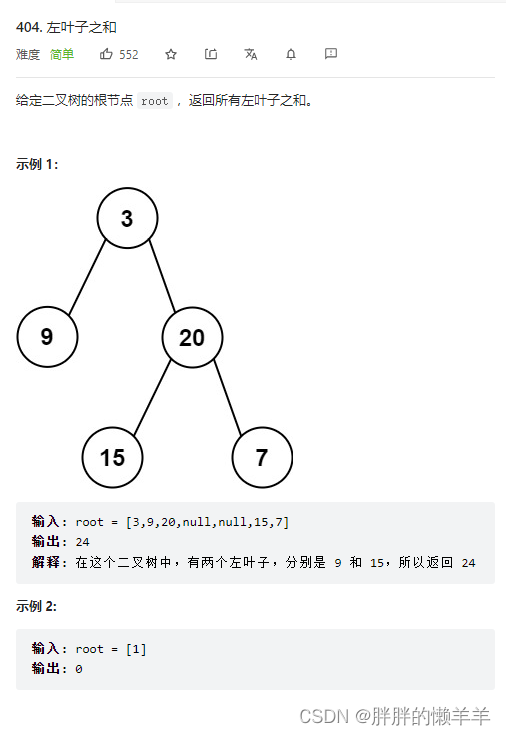
思路:
如果遇到空节点,返回null。
总和是左子树的左节点之和加上右子树的左节点之和。
判断左节点时要从它的父节点找,当父节点有左节点时并且左节点没有左右孩子节点。就可以了。
class Solution {
public int sumOfLeftLeaves(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null) {
return 0;
}
int leftSum=sumOfLeftLeaves(root.left);
int rightSum=sumOfLeftLeaves(root.right);
int middle=0;
if(root.left!=null&&root.left.left==null&&root.left.right==null) {
middle=root.left.val;
}
return middle+leftSum+rightSum;
}
}
11.找树左下角的值
513.找树左下角的值
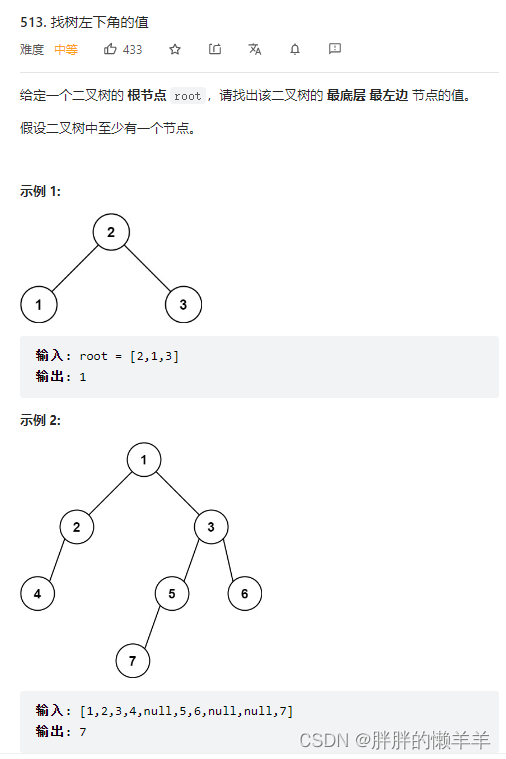
思路:
用迭代法比较简单。
这里使用递归法。用一个额外变量记录最大深度。用额外变量记录result。当找到叶子节点时,判断此时是不是最大深度,如果是,更新value值,因为是先进行左节点遍历,所以会先找到最大层数的左节点。
class Solution {
private int Deep = -1;
private int value = 0;
public int findBottomLeftValue(TreeNode root) {
value=root.val;
findLeftValue(root,0);
return value;
}
public void findLeftValue(TreeNode root,int dept) {
if(root==null) {
return ;
}
//找到叶子节点
if(root.left==null&&root.right==null) {
if(dept>Deep) {
Deep=dept;
value=root.val;
}
}
//先找左节点
if(root.left!=null) {
dept++;
findLeftValue(root.left,dept);
dept--;//用到了回溯找完左节点再退回去找右节点
}
if(root.right!=null) {
dept++;
findLeftValue(root.right,dept);
dept--;
}
}
}
12.路径总和
112.路径总和
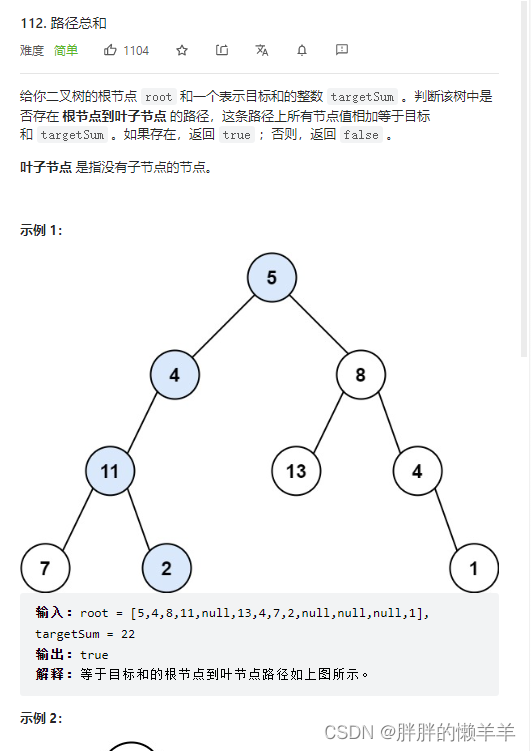
思路:
这道题只是判断有没有对应的路径满足条件,所以不需要做输出处理。
当遍历到一个节点时,需要减去这个节点的值,最后当遍历到叶子节点时,判断数值是不是0即可。
public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
if(root==null) {
return false;
}
//当弹出去的时候就相当于了回溯的过程
targetSum-=root.val;
if(root.left==null&&root.right==null) {
return targetSum==0;
}
if(root.left!=null) {
boolean left=hasPathSum(root.left,targetSum);
//当判断左子树满足条件时,才会直接返回true,所以当是false的时候不会直接终止函数
if(left) {
return true;
}
}
if(root.right!=null) {
boolean right=hasPathSum(root.right,targetSum);
if(right) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
113.路径总和||
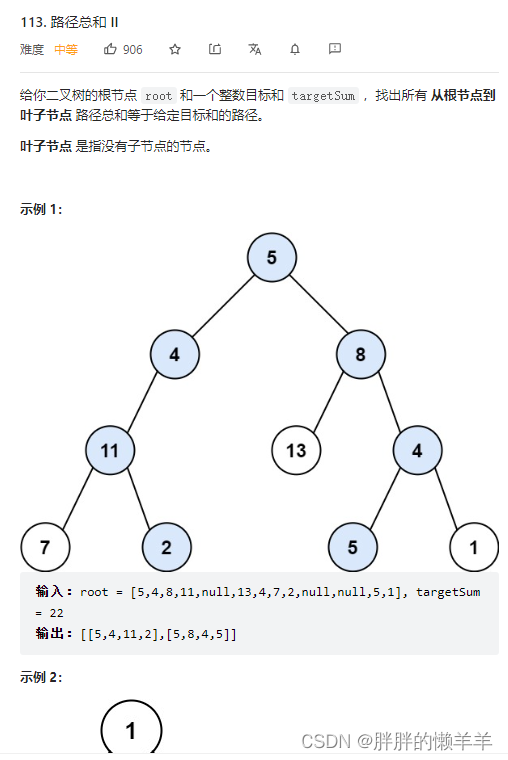
思路:
把所有的路径都遍历一遍,就是不需要返回值,把结果数组放入res里面即可。注意要有回溯操作。
public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
List<List<Integer>> res=new ArrayList<>();
if(root==null) return res;
List<Integer> path=new LinkedList<>();
preorderdfs(root,targetSum,res,path);
return res;
}
public void preorderdfs(TreeNode root, int targetsum, List<List<Integer>> res, List<Integer> path) {
path.add(root.val);
//遇到了叶子节点
if(root.left==null&&root.right==null) {
//找到了和为targetSum的路径
if(targetsum-root.val==0) {
res.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
}
return ;
}
if(root.left!=null) {
preorderdfs(root.left, targetsum-root.val, res, path);
//回溯
path.remove(path.size()-1);
}
if(root.right!=null) {
preorderdfs(root.right,targetsum-root.val,res,path);
path.remove(path.size()-1);
}
}
13.从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
106.从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
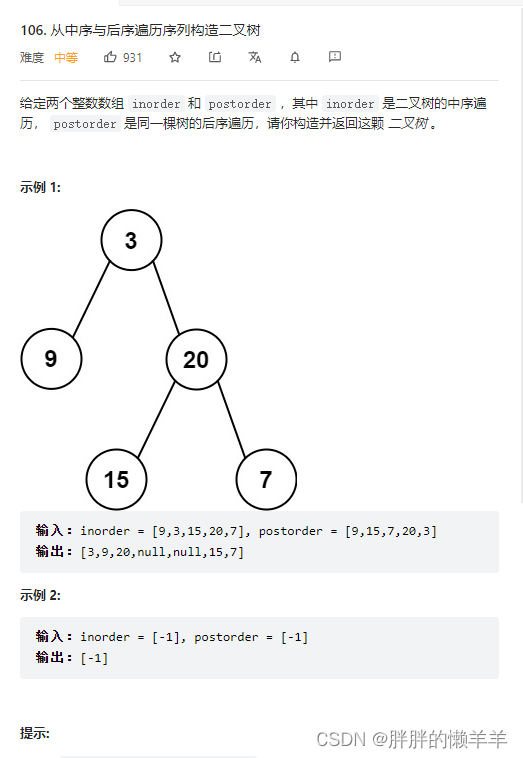
思路:
1.找到后序遍历的最后一个节点就是根节点。
2.根据根节点去切割中序遍历,可以找到左子树和右子树的范围。
3.根据中序遍历中左子树和右子树的范围,可以找到后序遍历中的左子树和右子树。
4.然后再进行递归求解,中序遍历的左子树和后序遍历的左子树这又是一个新的条件。所以可以继续求解。
Map<Integer,Integer> map;
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] inorder, int[] postorder) {
map=new HashMap<>();
for(int i=0;i<inorder.length;i++) {//用map保存中序序列的数值对应位置
map.put(inorder[i], i);
}
return findNode(inorder,0,inorder.length,postorder,0,postorder.length);
}
public TreeNode findNode(int[] inorder, int inBegin, int inEnd, int[] postorder, int postBegin, int postEnd) {
if(inBegin>=inEnd||postBegin>=postEnd) {
return null;
}
//找到中序遍历中根节点的位置
int rootIndex=map.get(postorder[postEnd-1]);
TreeNode root=new TreeNode(inorder[rootIndex]);
//根据根节点的位置确定中序遍历总左子树的数量
int lengthofLeft=rootIndex-inBegin;
root.left=findNode(inorder,inBegin,rootIndex,postorder,postBegin,postBegin+lengthofLeft);//左子树分别在中序和后序的位置
root.right=findNode(inorder,rootIndex+1,inEnd,postorder,postBegin+lengthofLeft,postEnd-1);//右子树分别在中序和后序的位置
return root;
}
105.从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
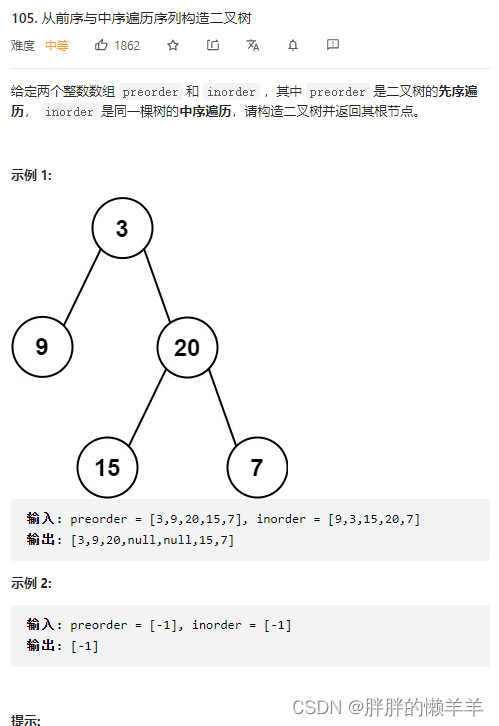
思路:
和后序中序生成二叉树一样。
依靠先序第一个节点找到根节点。然后再根据根节点在中序上找,找到位置就可以分出左子树和右子树。
这样两种遍历方式的左右子树都分出来了。最后就递归生成即可。
Map<Integer,Integer>map;
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
map=new HashMap<>();
//把中序遍历中每个元素出现的位置存起来
for(int i=0;i<inorder.length;i++) {
map.put(inorder[i],i);
}
return findNode(preorder,0,preorder.length,inorder,0,inorder.length);
}
public TreeNode findNode(int[] preorder,int preBegin,int preEnd,int[] inorder, int inBegin, int inEnd) {
//参数范围都是前闭后开
if(preBegin>=preEnd||inBegin>=inEnd) {
return null;
}
int rootIndex=map.get(preorder[preBegin]);//找到根节点在中序遍历的位置
TreeNode root=new TreeNode(inorder[rootIndex]);
//找到左子树的数量
int lengthOfLeft=rootIndex-inBegin;
root.left=findNode(preorder,preBegin+1,preBegin+1+lengthOfLeft,inorder,inBegin,inBegin+lengthOfLeft);
root.right=findNode(preorder,preBegin+1+lengthOfLeft,preEnd,inorder,rootIndex+1,inEnd);
return root;
}
14.最大二叉树
654.最大二叉树
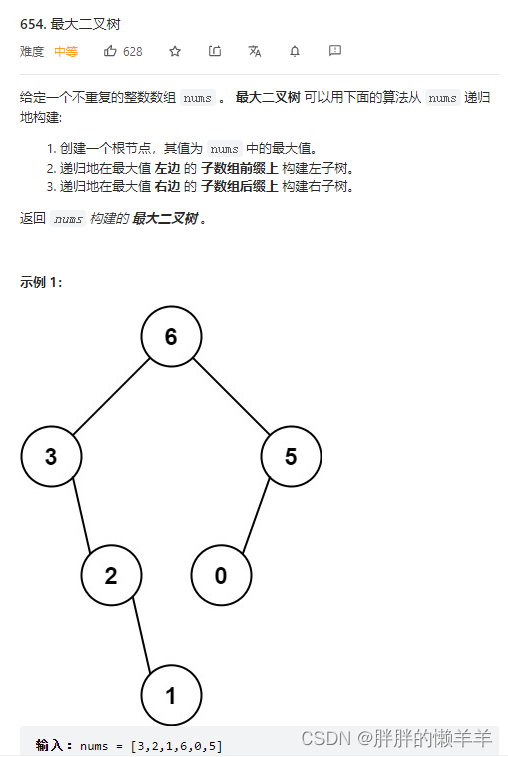
思路:
递归函数里要确定终止条件。
1.当区间里没有元素时,直接返回null。
2.当区间里只有一个元素时,直接构造一个节点。
3.找到这个区间里的最大值和最大元素下标。
4.用最大值创建一个节点。根据最大元素下标去切分剩下的数组。来生成左子树和右子树。
public TreeNode constructMaximumBinaryTree(int[] nums) {
return constructMaximumBinaryTree1(nums,0,nums.length);
}
public TreeNode constructMaximumBinaryTree1(int[] nums,int leftIndex,int rightIndex) {
//判断终止条件,如果区间里边没有元素了直接返回
if(leftIndex>=rightIndex) {
return null;
}
//如果区间里边只有一个元素,那么直接返回这个节点
if((rightIndex-leftIndex)==1) {
return new TreeNode(nums[leftIndex]);
}
//找到区间里最大的元素和下标。找最大的元素构造根节点,找到下标用来切分数组
int maxValue=nums[leftIndex];
int maxIndex=leftIndex;
for(int i=leftIndex+1;i<rightIndex;i++) {
if(nums[i]>maxValue) {
maxValue=nums[i];
maxIndex=i;
}
}
//用这个最大的元素来构造根节点
TreeNode root=new TreeNode(maxValue);
//递归去找左子树
root.left=constructMaximumBinaryTree1(nums,leftIndex,maxIndex);
root.right=constructMaximumBinaryTree1(nums,maxIndex+1,rightIndex);
return root;
}
15.合并二叉树
617.合并二叉树
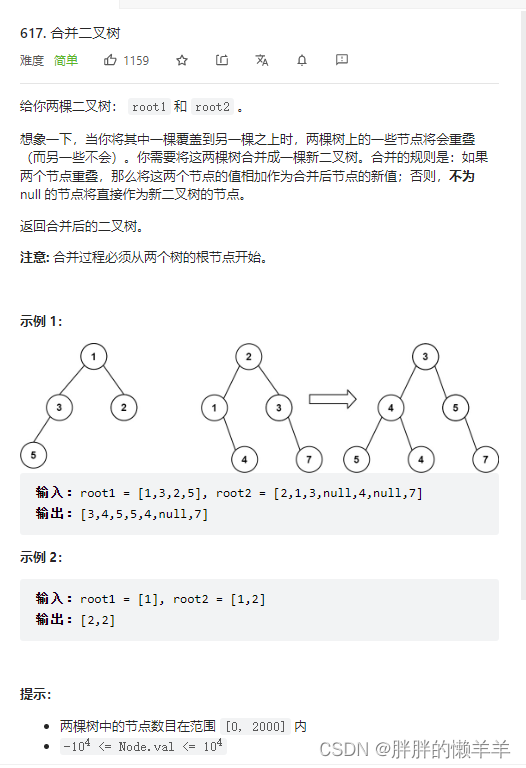
思路:
用递归来做,当左子树是空时,返回右子树。
当右子树是空时,返回左子树。
然后合并之后的树等于左子树和右子树两个数的继续合并。
public TreeNode mergeTrees(TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2) {
if(root1==null) {
return root2;
}
if(root2==null) {
return root1;
}
root1.val+=root2.val;
root1.left=mergeTrees(root1.left,root2.left);
root1.right=mergeTrees(root1.right,root2.right);
return root1;
}
16.二叉搜索树中的搜索
700.二叉搜索树中的搜索
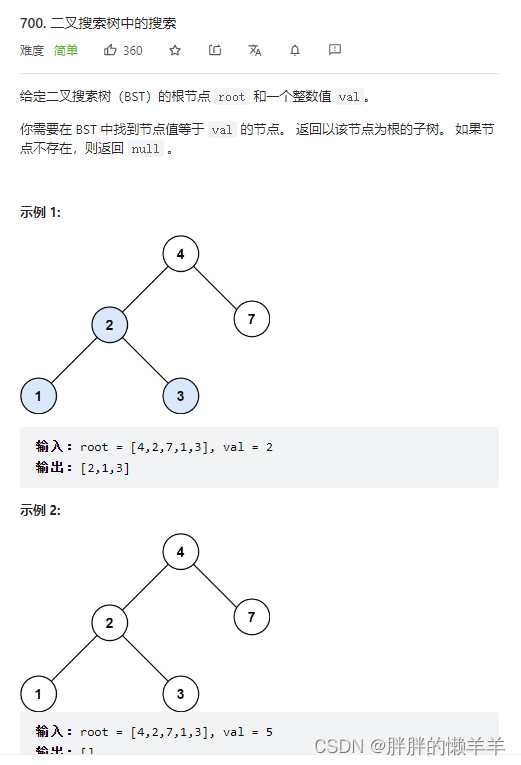
思路:
终止条件:当遇到的节点是空时,或者遇到的节点的值等于目标值时,返回这个节点。
根据二叉搜索树的特点,
递归里的逻辑:当节点的值比目标值小时,向右子树查找。当节点的值比目标值大时,向左子树查找。
public TreeNode searchBST(TreeNode root, int val) {
//终止条件
if(root==null||root.val==val) {
return root;
}
//递归里的逻辑
TreeNode node=null;
if(root.val>val) {
node=searchBST(root.left,val);
}else if(root.val<val) {
node=searchBST(root.right,val);
}
return node;
}
17.验证二叉搜索树
98.验证二叉搜索树
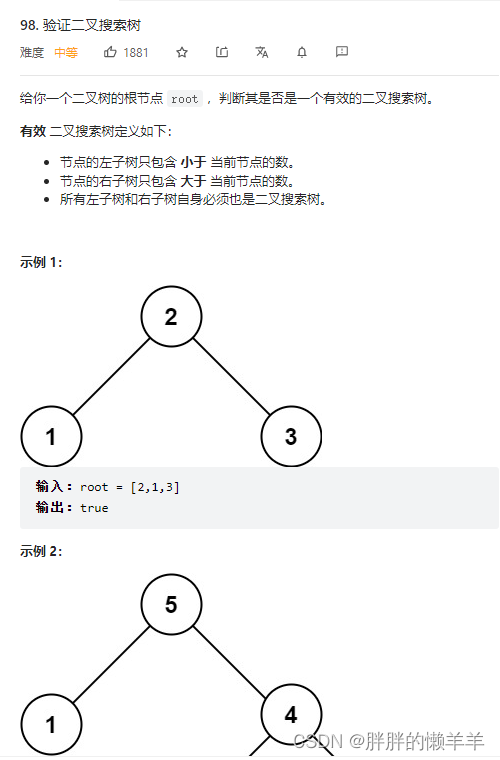
思路:
用一个指针去记录左边的节点,当这个节点不等于null并且数值大于等于中间的节点的时候,就判断出了它不是二叉搜索树。返回false。
public TreeNode pre;
public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {
//当节点为空的时候
if(root==null) {
return true;
}
//判断左边是不是二叉搜索树
boolean left=isValidBST(root.left);
if(!left) {
return false; }
//判断中间是不是二叉搜索树
if(pre!=null&&pre.val>=root.val) {
return false;
}
pre=root;
boolean right=isValidBST(root.right);
return left&&right;
}
18.二叉搜索树的最小绝对差
530.二叉搜索树的最小绝对差
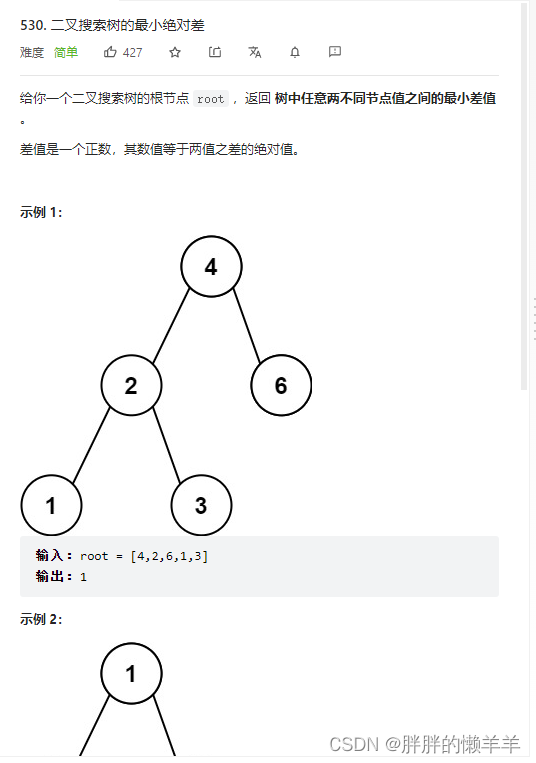
思路:
定义两个指针,一个前指针,一个后指针,两个指针一步一步的走,采用中序遍历的方式,如果一步一步的走,将每次最小的差值记录下来。
class Solution {
public int result=Integer.MAX_VALUE;
TreeNode pre1;
public int getMinimumDifference(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null) return 0;
traversal(root);
return result;
}
public void traversal(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null) {
return ;
}
//采用中序遍历
traversal(root.left);
if(pre1!=null) {
result=(root.val-pre1.val)<result?(root.val-pre1.val):result;
}
pre1=root;
traversal(root.right);
}
}
19.二叉搜索树中的众数
501.二叉搜索树中的众数

思路:
有一个maxcount变量来记录出现最大的次数。count记录当前数字出现的数。如果前指针和后指针不相等时,count等于1,代表出现一次。然后每次相等的时候count++。
当count=maxcount的时候,把结果更新进去,如果count大于maxcount了只需要清空结果集里的元素然后把后面的元素加进去即可。
List<Integer> res=new ArrayList<Integer>();
int maxCount=0;
int count=0;
TreeNode pre2=null;
public int[] findMode(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null) {
return res.stream().mapToInt(x->x).toArray() ;
}
findMode(root.left);
if(pre==null||root.val!=pre.val) {
count=1;
}else {
count++;
}
//更新结果以及maxCount
if(count>maxCount) {
res.clear();
res.add(root.val);
maxCount=count;
}else if(count==maxCount) {
res.add(root.val);
}
pre=root;
findMode(root.right);
return res.stream().mapToInt(x->x).toArray() ;
}
20.二叉树的最近公共祖先
236.二叉树的最近公共祖先
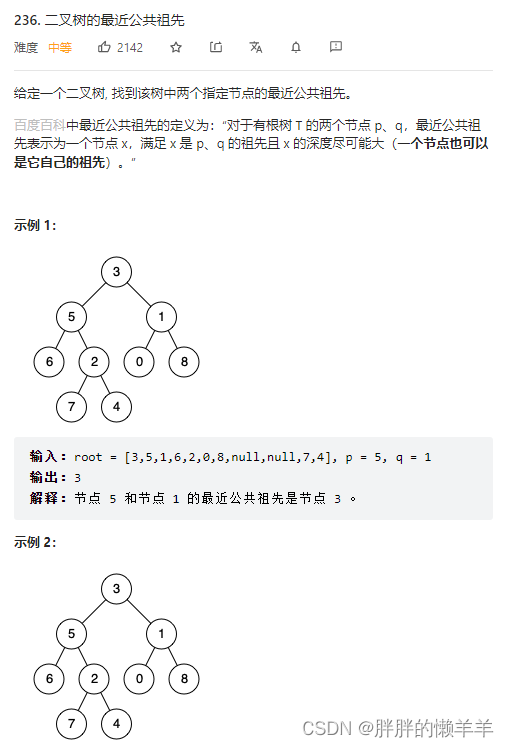
思路:
终止条件:当节点为空时或者左节点找到了目标节点,或者右节点找到了目标节点。
采用后序遍历的方法。
先看左子树有没有目标值,再看右子树有没有目标值。
如果左子树和右子树都有了目标值,直接返回root。
如果两个子树中仅有一个有目标值,返回这个子树即可。
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(root==null||root==p||root==q) {
//递归条件结束,当有一个节点找到p或q时,递归结束
return root;
}
//采用后序遍历
TreeNode left=lowestCommonAncestor(root.left,p,q);
TreeNode right=lowestCommonAncestor(root.right,p,q);
//当两个节点都没找到时
if(left==null&&right==null) {
return null;
}else if(left==null&&right!=null) {//当右节点找到一个目标值时,左节点没有找到,返回右节点
return right;
}else if(left!=null&&right==null) {//当左节点找到一个目标值时,右节点没有找到,返回左节点
return left;
}else {
return root;//当两个节点都找到了目标值,直接返回root
}
}
21.二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
235.二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
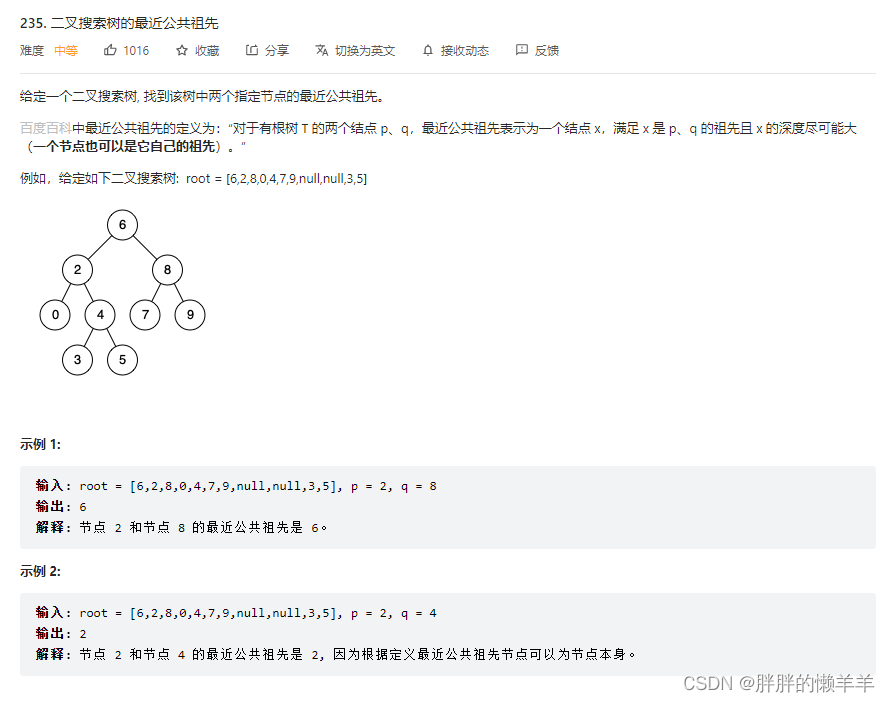
思路:
当根节点为空时返回null。
当根节点的数值大于目标节点的数值时。往左子树查找,如果左子树不为空,直接返回左子树即可。
当根节点的数值小于目标节点的数值时。往右子树查找,如果右子树不为空,直接返回右子树即可。
如果根节点的数值在两个节点之间。那么返回这个节点即可。
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor2(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
//二叉搜索树因为知道了节点大小,所以搜索起来会方便很多。
if(root==null) {
return null;
}
if(root.val>p.val&&root.val>q.val) {//说明根节点的数值比两个目标值大,所以结果在左边
TreeNode left=lowestCommonAncestor2(root.left,p,q);
if(left!=null) {//如果左节点不等于null,直接返回即可
return left;
}
}
if(root.val<p.val&&root.val<q.val) {//说明根节点的数值比两个目标值小,所以结果在右边
TreeNode right=lowestCommonAncestor2(root.right,p,q);
if(right!=null) {//如果右节点不等于null,直接返回即可。
return right;
}
}
return root;
}
22.二叉搜索树中的插入操作
701.二叉搜索树中的插入操作
思路:用递归法,当遇到空节点时,直接生成节点,然后返回这个节点。这样递归函数返回到上一层时,让左子树的节点指向这个节点。
public TreeNode insertIntoBST(TreeNode root, int val) {
//当遇到的节点为空时,构造新的节点
if(root==null) {
TreeNode children=new TreeNode(val);
return children;
}
//如果节点的值比目标值大,往左子树去插
if(root.val>val) {
root.left=insertIntoBST(root.left,val);
}
//如果节点的值比目标值小,往右子树去插
if(root.val<val) {
root.right=insertIntoBST(root.right,val);
}
return root;
}
23.删除二叉搜索树中的节点
450.删除二叉搜索树中的节点
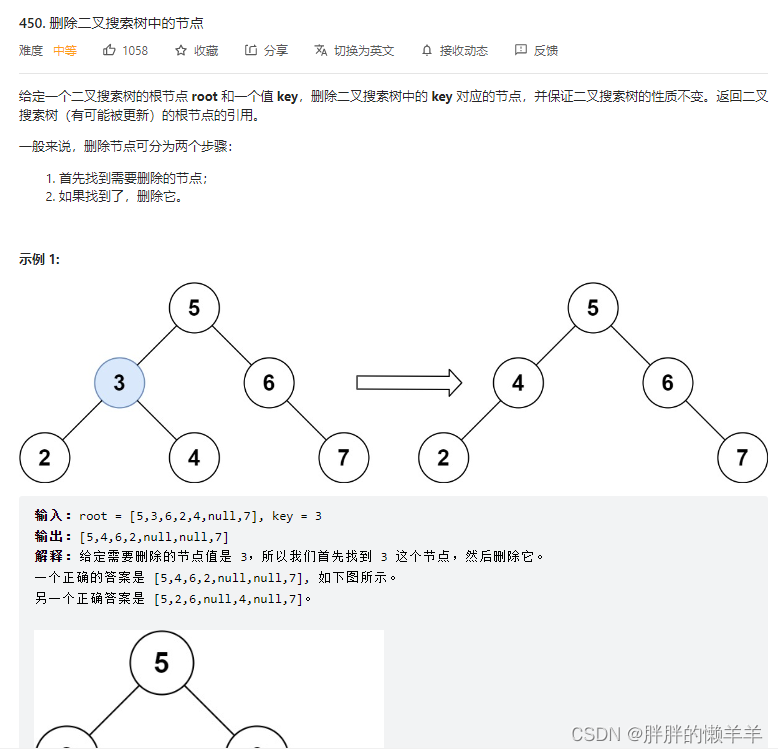
思路:
把5种情况理清楚就可以了。
public TreeNode deleteNode(TreeNode root, int key) {
/**
* 分为五种情况,key没有找到
* 删除叶子节点
* 删除节点有左子树,直接让它指向左子树即可
* 删除节点有右子树,直接让它指向右子树即可
* 删除节点左右子树都有,找到右子树的最小节点的值,然后让这个子树的左节点指向它即可。
*/
if(root==null) {
return null;
}
if(root.val==key) {
//找到了节点
if(root.left==null&&root.right==null) {//删除叶子节点
return null;
}else if(root.left!=null&&root.right==null) {//删除节点有左子树
return root.left;
}else if(root.left==null&&root.right!=null) {//删除节点有右子树
return root.right;
}else {
TreeNode cur=root.right;
//找到右子树的最左边的节点
while(cur.left!=null) {
cur=cur.left;
}
cur.left=root.left;
return root.right;
}
}
//告诉节点规则,让它在哪个方向去找Key
if(root.val>key) {
root.left=deleteNode(root.left,key);
}else if(root.val<key) {
root.right=deleteNode(root.right,key);
}
return root;
}
24.修剪二叉搜索树
669.修剪二叉搜索树
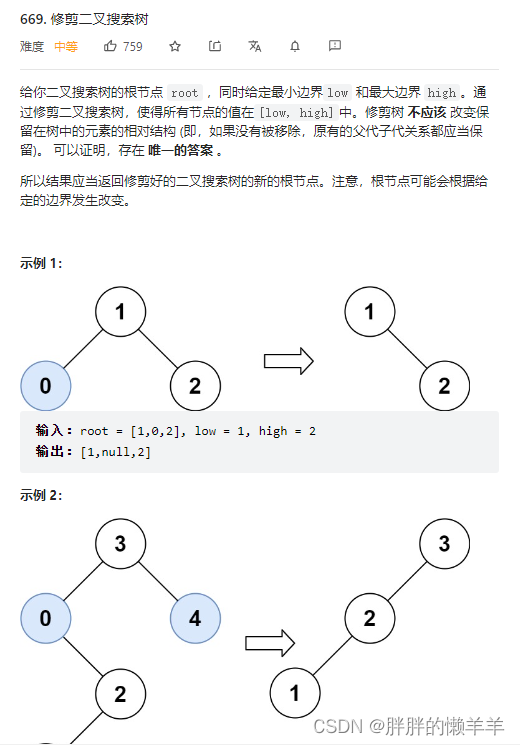
思路:
当修剪到叶子节点时,节点比左边界要小,返回这个节点修剪后的右子树给上一个节点。节点比右边界要大,返回这个节点修剪后的左子树给上一个节点。如果这个节点恰好在两个中间,那么直接返回这个节点即可。
public TreeNode trimBST(TreeNode root, int low, int high) {
//当遇到空节点,返回null
if(root==null) {
return null;
}
//当遇见的节点比左边界的值要小,让右子树去剪枝,返回右子树
if(root.val<low) {
TreeNode right=trimBST(root.right,low,high);
return right;
}
//当遇见的节点比右边界的值要大,让左子树去剪枝,返回左子树
if(root.val>high) {
TreeNode left=trimBST(root.left,low,high);
return left;
}
//当遇见的节点在两个边界点之间。分别对左右两个子树减枝即可
root.left=trimBST(root.left,low,high);
root.right=trimBST(root.right,low,high);
return root;
}
25.将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树
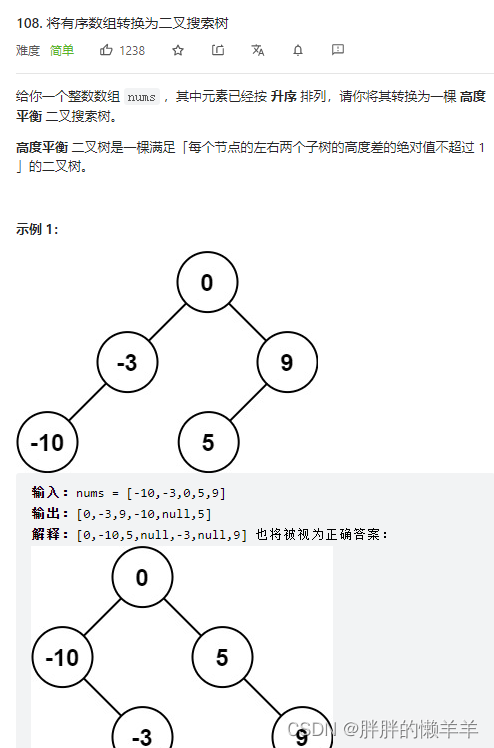
思路:
用递归的方式,找到中间节点,然后生成这个节点,递归去遍历左右区间。
public TreeNode sortedArrayToBST(int[] nums) {
return sortedArray(nums,0,nums.length-1);
}
public TreeNode sortedArray(int[]nums,int left,int right) {
//运用中节点,递归去处理,采用左闭右闭区间
if(left>right) {
return null;
}
int mid=(left+right)/2;
TreeNode root=new TreeNode(nums[mid]);
root.left=sortedArray(nums,left,mid-1);
root.right=sortedArray(nums,mid+1,right);
return root;
}
33.把二叉树转换为累加树
538.把二叉搜索树转换为累加树
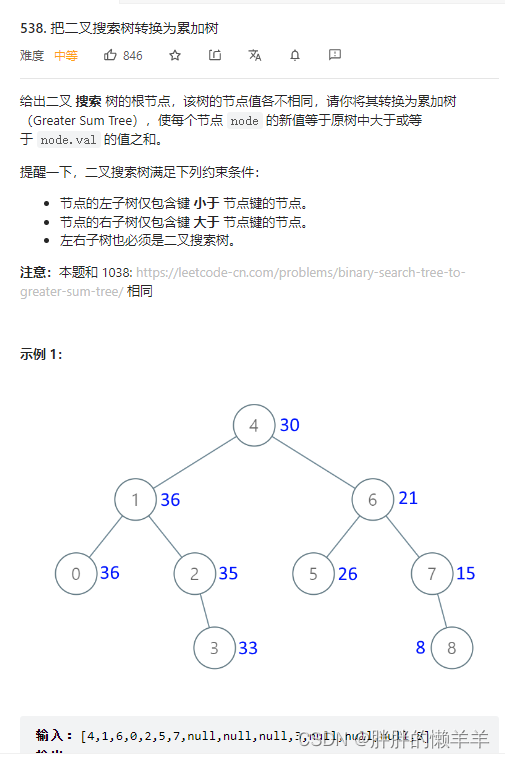
思路:
用右中左的顺序去遍历,把前一个节点的值记录好,然后顺序更新即可。
int pre3=0;
public TreeNode convertBST(TreeNode root) {
//右中左的顺序去遍历,然后每次更新pre的树枝即可.
if(root==null) {
return null;
}
convertBST(root.right);
//中间节点的逻辑
root.val+=pre3;
pre3=root.val;
convertBST(root.left);
return root;
}



![[MySQL]初识数据库](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/ddc48061334f9d94dacbb94df155a73c.gif)