深度学习网络模型——ConvNeXt网络详解、ConvNeXt网络训练花分类数据集整体项目实现
- 1、介绍
- 2、设计方案
- 3、Macro design
- 4、ResNeXt-ify
- 5、Inverted Bottleneck
- 7、Large Kernel Sizes
- 8、Micro Design
- 9、ConvNeXt variants
- 10、ConvNeXt-T 结构图
- 11、网络代码实现:
ConvNeXt
论文名称:A ConvNet for the 2020s
论文下载链接:https://arxiv.org/abs/2201.03545
1、介绍
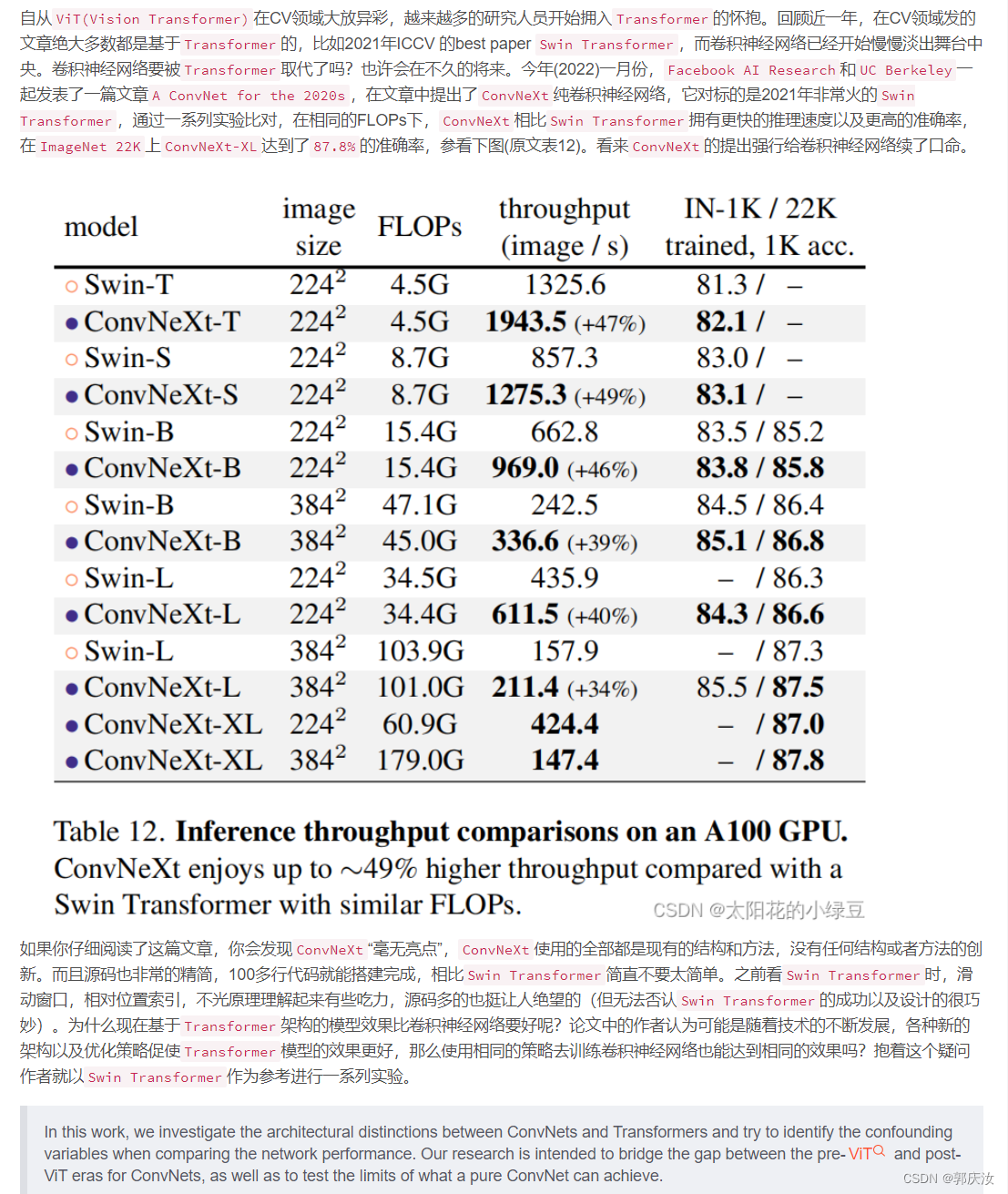
2、设计方案
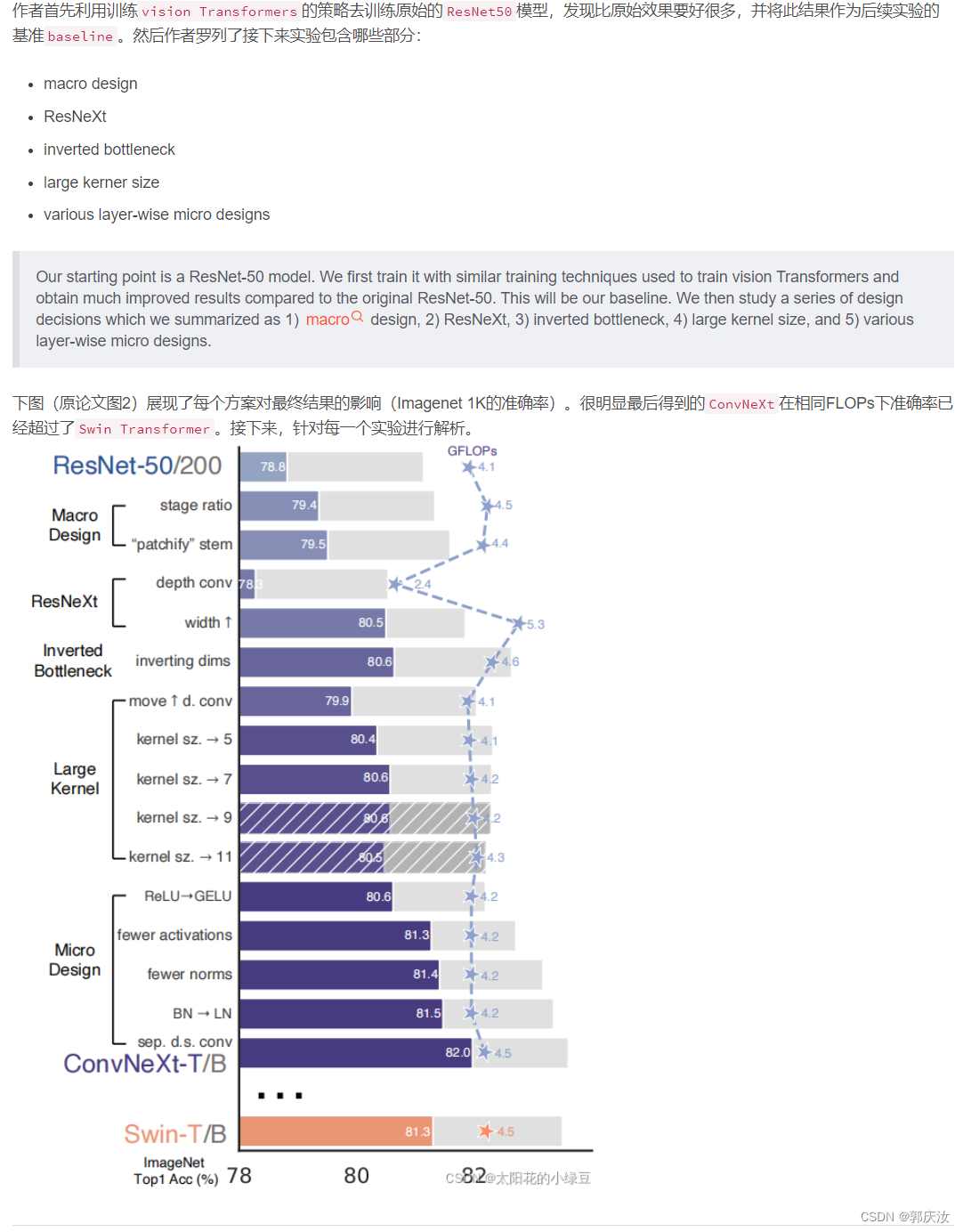
3、Macro design
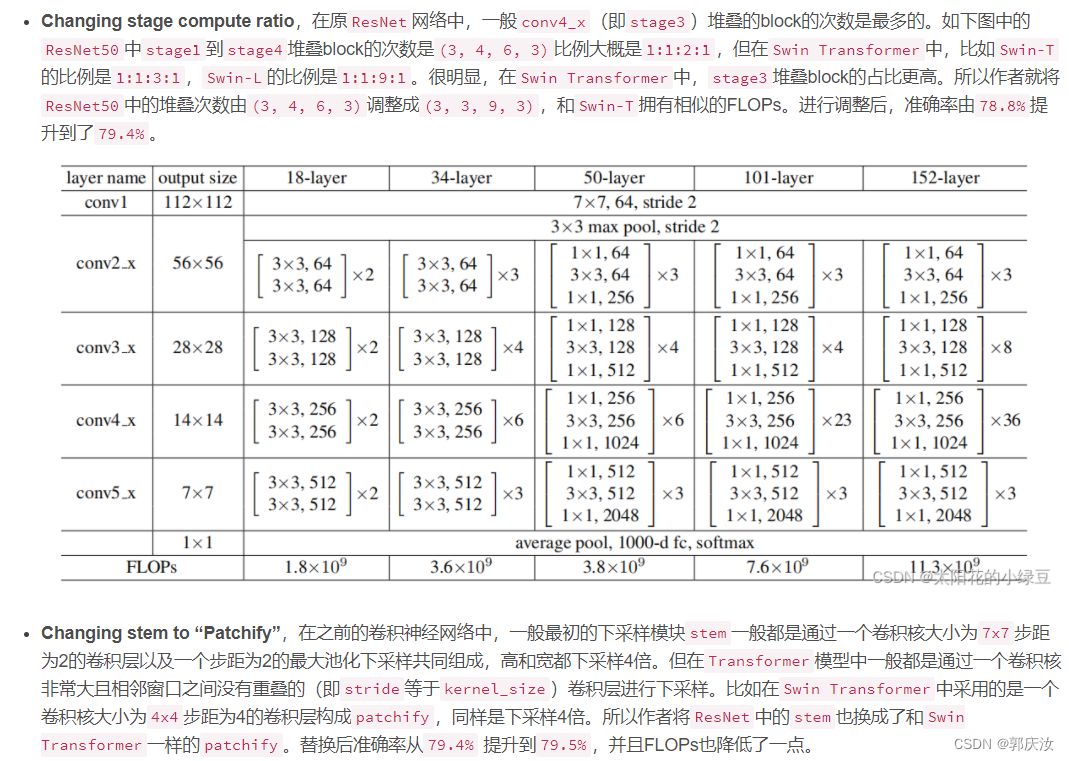
4、ResNeXt-ify
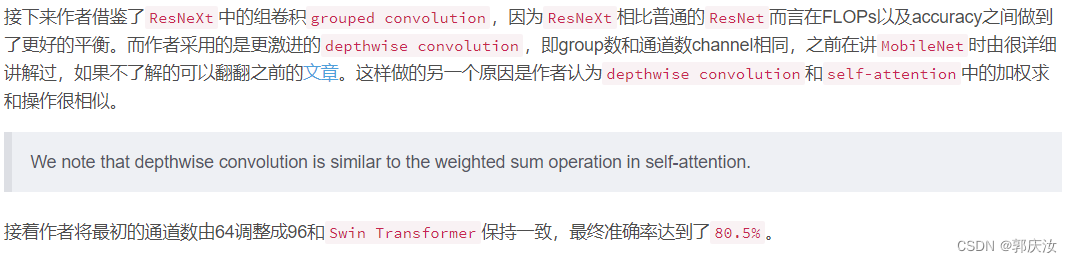
5、Inverted Bottleneck
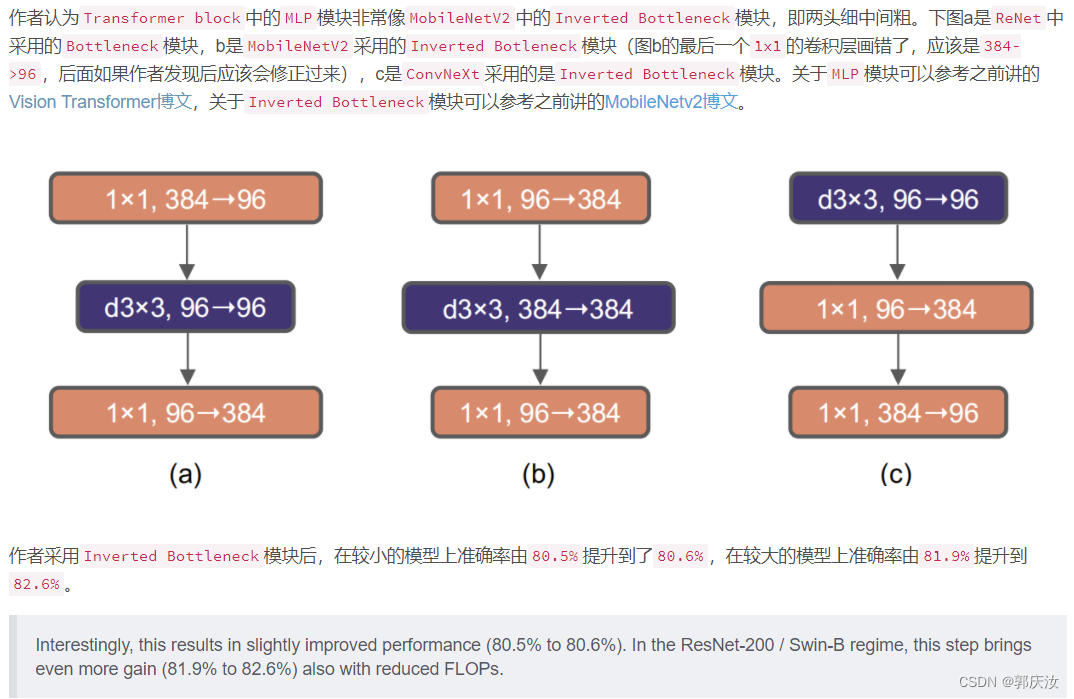
7、Large Kernel Sizes

8、Micro Design
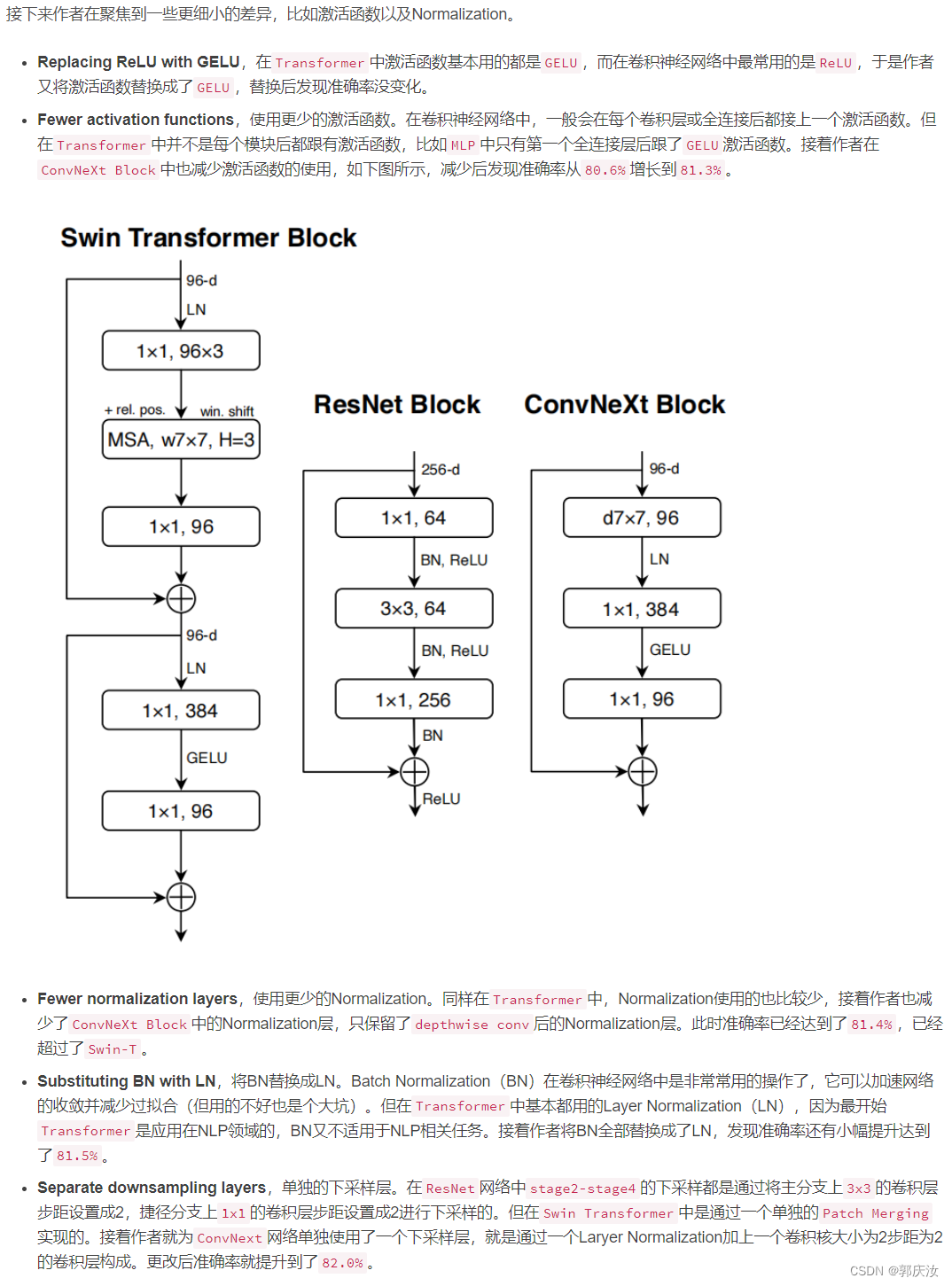
9、ConvNeXt variants

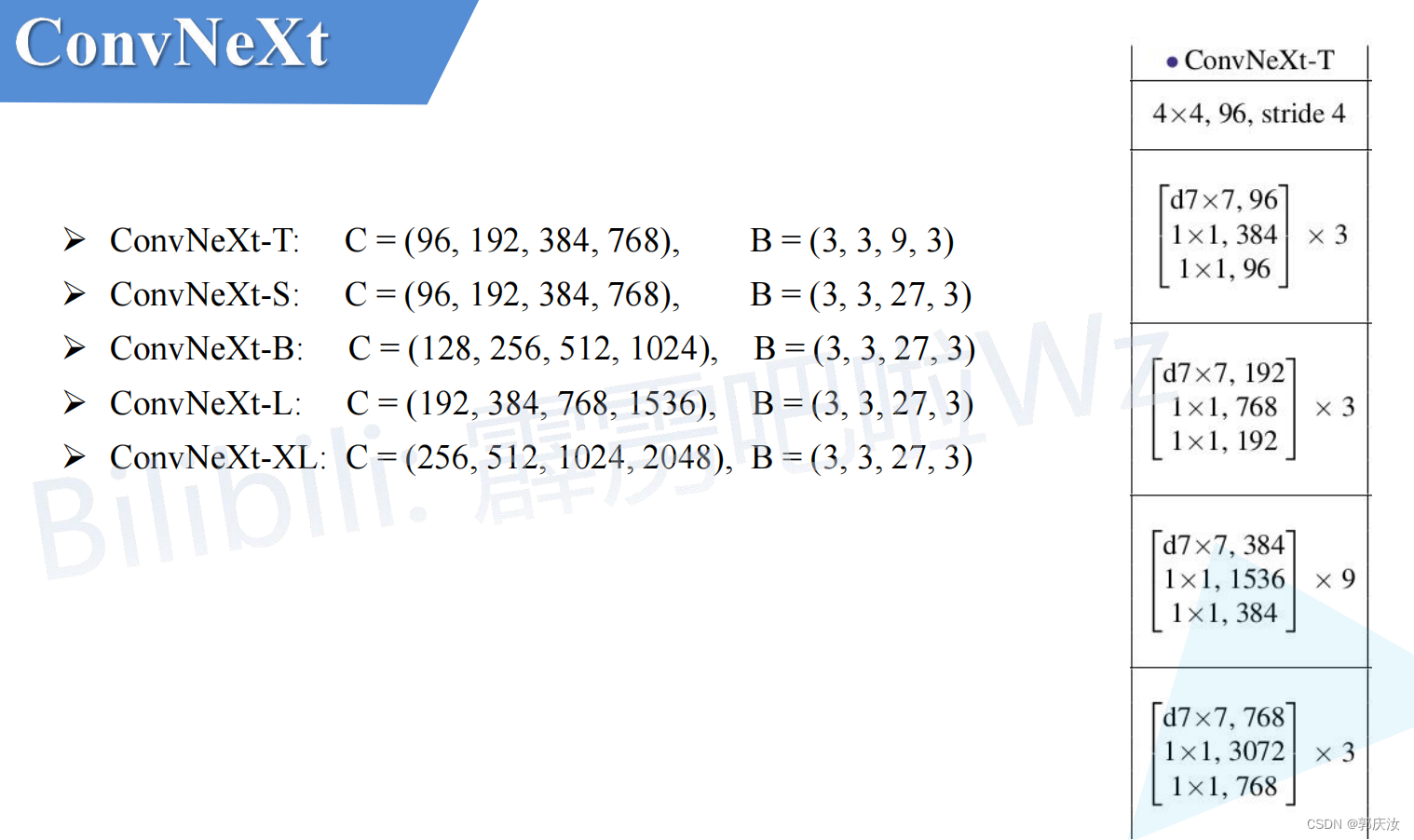
10、ConvNeXt-T 结构图

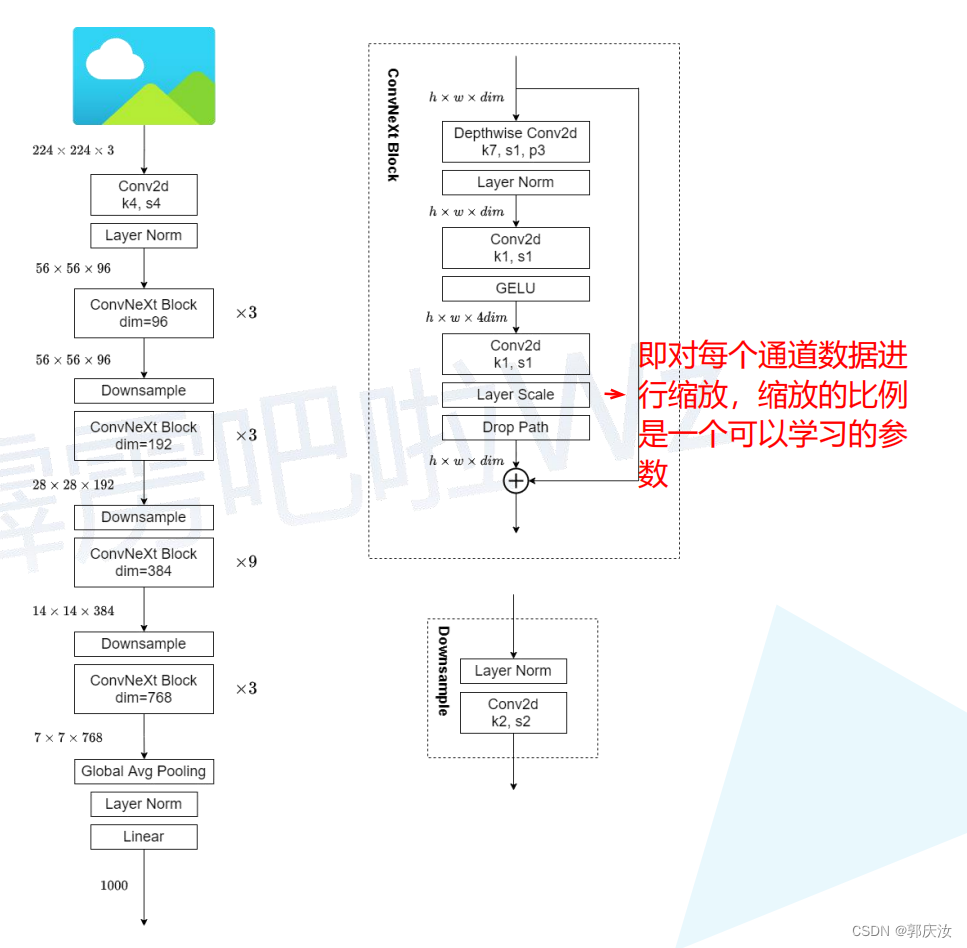
11、网络代码实现:
convnext_tiny
convnext_small
convnext_base
convnext_large
convnext_xlarge
model.py
"""
original code from facebook research:
https://github.com/facebookresearch/ConvNeXt
"""
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
def drop_path(x, drop_prob: float = 0., training: bool = False):
"""Drop paths (Stochastic Depth) per sample (when applied in main path of residual blocks).
This is the same as the DropConnect impl I created for EfficientNet, etc networks, however,
the original name is misleading as 'Drop Connect' is a different form of dropout in a separate paper...
See discussion: https://github.com/tensorflow/tpu/issues/494#issuecomment-532968956 ... I've opted for
changing the layer and argument names to 'drop path' rather than mix DropConnect as a layer name and use
'survival rate' as the argument.
"""
if drop_prob == 0. or not training:
return x
keep_prob = 1 - drop_prob
shape = (x.shape[0],) + (1,) * (x.ndim - 1) # work with diff dim tensors, not just 2D ConvNets
random_tensor = keep_prob + torch.rand(shape, dtype=x.dtype, device=x.device)
random_tensor.floor_() # binarize
output = x.div(keep_prob) * random_tensor
return output
class DropPath(nn.Module):
"""Drop paths (Stochastic Depth) per sample (when applied in main path of residual blocks).
"""
def __init__(self, drop_prob=None):
super(DropPath, self).__init__()
self.drop_prob = drop_prob
def forward(self, x):
return drop_path(x, self.drop_prob, self.training)
class LayerNorm(nn.Module):
r""" LayerNorm that supports two data formats: channels_last (default) or channels_first.
The ordering of the dimensions in the inputs. channels_last corresponds to inputs with
shape (batch_size, height, width, channels) while channels_first corresponds to inputs
with shape (batch_size, channels, height, width).
"""
def __init__(self, normalized_shape, eps=1e-6, data_format="channels_last"):
super().__init__()
self.weight = nn.Parameter(torch.ones(normalized_shape), requires_grad=True)
self.bias = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(normalized_shape), requires_grad=True)
self.eps = eps
self.data_format = data_format
if self.data_format not in ["channels_last", "channels_first"]:
raise ValueError(f"not support data format '{self.data_format}'")
self.normalized_shape = (normalized_shape,)
def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
if self.data_format == "channels_last":
return F.layer_norm(x, self.normalized_shape, self.weight, self.bias, self.eps)
elif self.data_format == "channels_first":
# [batch_size, channels, height, width]
mean = x.mean(1, keepdim=True)
var = (x - mean).pow(2).mean(1, keepdim=True) # 得到的是方差
x = (x - mean) / torch.sqrt(var + self.eps) # 减去均值除以标准差
x = self.weight[:, None, None] * x + self.bias[:, None, None]
return x
class Block(nn.Module):
r""" ConvNeXt Block. There are two equivalent implementations:
(1) DwConv -> LayerNorm (channels_first) -> 1x1 Conv -> GELU -> 1x1 Conv; all in (N, C, H, W)
(2) DwConv -> Permute to (N, H, W, C); LayerNorm (channels_last) -> Linear -> GELU -> Linear; Permute back
We use (2) as we find it slightly faster in PyTorch
Args:
dim (int): Number of input channels.
drop_rate (float): Stochastic depth rate. Default: 0.0
layer_scale_init_value (float): Init value for Layer Scale. Default: 1e-6.
"""
def __init__(self, dim, drop_rate=0., layer_scale_init_value=1e-6):
super().__init__()
self.dwconv = nn.Conv2d(dim, dim, kernel_size=7, padding=3, groups=dim) # depthwise conv 此处使用的是depthwise卷积
self.norm = LayerNorm(dim, eps=1e-6, data_format="channels_last")
self.pwconv1 = nn.Linear(dim, 4 * dim) # pointwise/1x1 convs, implemented with linear layers 此处使用的是全连接层,代替1x1的卷积层,效果一样
self.act = nn.GELU()
self.pwconv2 = nn.Linear(4 * dim, dim)
# 定义layer scale层的scale因子
self.gamma = nn.Parameter(layer_scale_init_value * torch.ones((dim,)),
requires_grad=True) if layer_scale_init_value > 0 else None # 其元素的个数与输入特征层channel的个数是一样的
self.drop_path = DropPath(drop_rate) if drop_rate > 0. else nn.Identity()
def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
shortcut = x
x = self.dwconv(x)
x = x.permute(0, 2, 3, 1) # [N, C, H, W] -> [N, H, W, C]
x = self.norm(x)
x = self.pwconv1(x)
x = self.act(x)
x = self.pwconv2(x)
if self.gamma is not None:
x = self.gamma * x # 对每个通道的数据进行缩放
x = x.permute(0, 3, 1, 2) # [N, H, W, C] -> [N, C, H, W]
x = shortcut + self.drop_path(x)
return x
class ConvNeXt(nn.Module):
r""" ConvNeXt
A PyTorch impl of : `A ConvNet for the 2020s` -
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2201.03545.pdf
Args:
in_chans (int): Number of input image channels. Default: 3
num_classes (int): Number of classes for classification head. Default: 1000
depths (tuple(int)): Number of blocks at each stage. Default: [3, 3, 9, 3]
dims (int): Feature dimension at each stage. Default: [96, 192, 384, 768]
drop_path_rate (float): Stochastic depth rate. Default: 0.
layer_scale_init_value (float): Init value for Layer Scale. Default: 1e-6.
head_init_scale (float): Init scaling value for classifier weights and biases. Default: 1.
"""
def __init__(self, in_chans: int = 3, num_classes: int = 1000, depths: list = None,
dims: list = None, drop_path_rate: float = 0., layer_scale_init_value: float = 1e-6,
head_init_scale: float = 1.):
super().__init__()
self.downsample_layers = nn.ModuleList() # stem and 3 intermediate downsampling conv layers # 最初的下采样部分
stem = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(in_chans, dims[0], kernel_size=4, stride=4),
LayerNorm(dims[0], eps=1e-6, data_format="channels_first"))
self.downsample_layers.append(stem)
# 对应stage2-stage4前的3个downsample
for i in range(3):
downsample_layer = nn.Sequential(LayerNorm(dims[i], eps=1e-6, data_format="channels_first"),
nn.Conv2d(dims[i], dims[i+1], kernel_size=2, stride=2))
self.downsample_layers.append(downsample_layer)
self.stages = nn.ModuleList() # 4 feature resolution stages, each consisting of multiple blocks
dp_rates = [x.item() for x in torch.linspace(0, drop_path_rate, sum(depths))] # 即表示每一个block会使用一个dropPathRate,并且其是递增的
cur = 0
# 构建每个stage中堆叠的block
for i in range(4):
stage = nn.Sequential(
*[Block(dim=dims[i], drop_rate=dp_rates[cur + j], layer_scale_init_value=layer_scale_init_value)
for j in range(depths[i])]
)
self.stages.append(stage)
cur += depths[i]
self.norm = nn.LayerNorm(dims[-1], eps=1e-6) # final norm layer
self.head = nn.Linear(dims[-1], num_classes)
self.apply(self._init_weights) # 调用父类的方法,初始化各层参数
self.head.weight.data.mul_(head_init_scale) # 对self.head层的weight乘上一个因子,此处因为为1,表示不进行任何缩放
self.head.bias.data.mul_(head_init_scale) # 对self.head层的bias乘上一个因子,此处因为为1,表示不进行任何缩放
def _init_weights(self, m):
if isinstance(m, (nn.Conv2d, nn.Linear)):
nn.init.trunc_normal_(m.weight, std=0.2)
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
def forward_features(self, x: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
for i in range(4):
x = self.downsample_layers[i](x)
x = self.stages[i](x)
return self.norm(x.mean([-2, -1])) # global average pooling, (N, C, H, W) -> (N, C) # 此处相当于做了一个globalAverage Pooling操作
def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
x = self.forward_features(x)
x = self.head(x)
return x
def convnext_tiny(num_classes: int):
# https://dl.fbaipublicfiles.com/convnext/convnext_tiny_1k_224_ema.pth
model = ConvNeXt(depths=[3, 3, 9, 3],
dims=[96, 192, 384, 768],
num_classes=num_classes)
return model
def convnext_small(num_classes: int):
# https://dl.fbaipublicfiles.com/convnext/convnext_small_1k_224_ema.pth
model = ConvNeXt(depths=[3, 3, 27, 3],
dims=[96, 192, 384, 768],
num_classes=num_classes)
return model
def convnext_base(num_classes: int):
# https://dl.fbaipublicfiles.com/convnext/convnext_base_1k_224_ema.pth
# https://dl.fbaipublicfiles.com/convnext/convnext_base_22k_224.pth
model = ConvNeXt(depths=[3, 3, 27, 3],
dims=[128, 256, 512, 1024],
num_classes=num_classes)
return model
def convnext_large(num_classes: int):
# https://dl.fbaipublicfiles.com/convnext/convnext_large_1k_224_ema.pth
# https://dl.fbaipublicfiles.com/convnext/convnext_large_22k_224.pth
model = ConvNeXt(depths=[3, 3, 27, 3],
dims=[192, 384, 768, 1536],
num_classes=num_classes)
return model
def convnext_xlarge(num_classes: int):
# https://dl.fbaipublicfiles.com/convnext/convnext_xlarge_22k_224.pth
model = ConvNeXt(depths=[3, 3, 27, 3],
dims=[256, 512, 1024, 2048],
num_classes=num_classes)
return model