最近在群里聊天,遇到一个哥们描述的一个问题:
大家好,请教一个关于文件的问题。有几个进程打开了/dev/input 设备,都可以收到数据,又来了一个进程x,打开了这个设备,不知道采用了什么方式,其他的进程都收不到数据了,只有x可以收到,请问是怎么实现数据独占的呢?
对于这个问题,其实在之前的 input子系统 -- 05 数据上报
这篇文章中有过描述
input_sync() -> input_event() -> input_handle_event() -> input_pass_values()
static void input_pass_values(struct input_dev *dev,
struct input_value *vals, unsigned int count)
{
struct input_handle *handle;
struct input_value *v;
if (!count)
return;
rcu_read_lock();
handle = rcu_dereference(dev->grab);
if (handle) {
/* 处理独占事件 */
count = input_to_handler(handle, vals, count);
} else {
/* 非独占,所有应用程序都会收到 */
list_for_each_entry_rcu(handle, &dev->h_list, d_node)
if (handle->open) {
count = input_to_handler(handle, vals, count);
if (!count)
break;
}
}
...
}这里的grab的意思是设备被抓或者设备被独占的意思,通过EVIOCGRAB ioctl设置,设置后当前设备变成唯一的来自设备的所有输入事件的接收者。
对于独占功能是如何配置的,我也是第一次使用,现在看一下内核驱动独占功能代码的实现
文件 drivers/input/evdev.c
static long evdev_do_ioctl(struct file *file, unsigned int cmd,
void __user *p, int compat_mode)
{
struct evdev_client *client = file->private_data;
struct evdev *evdev = client->evdev;
struct input_dev *dev = evdev->handle.dev;
struct input_absinfo abs;
struct input_mask mask;
struct ff_effect effect;
int __user *ip = (int __user *)p;
unsigned int i, t, u, v;
unsigned int size;
int error;
/* First we check for fixed-length commands */
switch (cmd) {
....
case EVIOCGRAB:
if (p)
/* 设置独占 */
return evdev_grab(evdev, client);
else
/* 取消独占 */
return evdev_ungrab(evdev, client);
....
}这部分代码可以看出,是否设置独占是根据p值设置的,而这个p值是应用程序传递下来的
那么应用程序可以这样写
int fd;
fd = open("/dev/input/event0", O_RDWR);
/* enable grab */
ioctl(fd, EVIOCGRAB, (void *)1);
/* disable grab */
ioctl(fd, EVIOCGRAB, (void *)0);编写应用代码测试
#include <stdio.h>
#include <linux/input.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <errno.h>
#define EVENT_NUM 4
#define DEV_EVENTX "/dev/input/event"
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int fd[EVENT_NUM];
int maxnum = 0;
int select_r;
fd_set fds, fds_init;
struct input_event ev;
int i = 0;
char event_path[32];
int enable_grab = 0;
if (argc > 1) {
if (*argv[1] == '1')
enable_grab = 1;
}
FD_ZERO(&fds_init);
for (i = 0; i < EVENT_NUM; i++) {
memset(event_path, 0, sizeof(event_path));
sprintf(event_path, "%s%d", DEV_EVENTX, i);
fd[i] = open(event_path, O_RDWR);
if (fd[i] < 0) {
printf("Open %s failed!\n", event_path);
} else {
if (fd[i] > maxnum) {
maxnum = fd[i];
}
FD_SET(fd[i], &fds_init);
if (enable_grab)
ret = ioctl(fd[i], EVIOCGRAB, (void*)1);
if (ret < 0)
printf("error: %d\n", errno);
}
}
while(1) {
fds = fds_init;
select_r = select(maxnum+1, &fds, NULL, NULL, NULL);
if (select_r < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "select error!\n");
break;
}
for(i = 0; i < EVENT_NUM; i++) {
if (FD_ISSET(fd[i], &fds)) {
read(fd[i], &ev, sizeof(struct input_event));
if (ev.type != EV_SYN)
printf("type: %d, code: %d, value: %d\n", ev.type, ev.code, ev.value);
}
}
}
实际运行测试结果如下:

可以看到当使能独占的时候,其他的应用就会收不到input的上报信息了
这里拓展一下如果,再有一个应用程序使能独占的话,会发生什么?
内核代码中可以看到
static int evdev_grab(struct evdev *evdev, struct evdev_client *client)
{
int error;
if (evdev->grab)
return -EBUSY;
error = input_grab_device(&evdev->handle);
if (error)
return error;
rcu_assign_pointer(evdev->grab, client);
return 0;
}
应该是返回-EBUSY
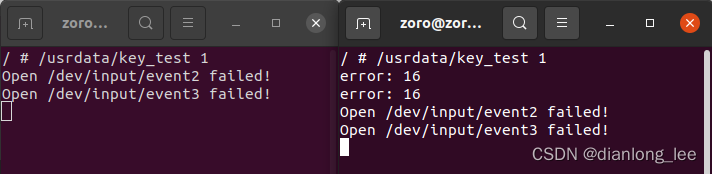
和之前分析的一样!