动态规划算法通常用于求解具有某种最优性质的问题。在这类问题中,可能会有许多可行解。每一个解都对应于一个值,我们希望找到具有最优值的解。动态规划算法与分治法类似,其基本思想也是将待求解问题分解成若干个子问题,先求解子问题,然后从这些子问题的解得到原问题的解。动态规划算法在算法思想中是极为重要的,需要重点掌握。
动态规划相关题目
递归和动态规划都是将原问题拆成多个子问题然后求解,他们之间最本质的区别是,动态规划保存了子问题的解,避免重复计算。
斐波那契数列
爬楼梯
70. Climbing Stairs (Easy)
题目描述: 有 N 阶楼梯,每次可以上一阶或者两阶,求有多少种上楼梯的方法。
定义一个数组 dp 存储上楼梯的方法数(为了方便讨论,数组下标从 1 开始),dp[i] 表示走到第 i 个楼梯的方法数目。
第 i 个楼梯可以从第 i-1 和 i-2 个楼梯再走一步到达,走到第 i 个楼梯的方法数为走到第 i-1 和第 i-2 个楼梯的方法数之和。
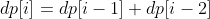
考虑到 dp[i] 只与 dp[i - 1] 和 dp[i - 2] 有关,因此可以只用两个变量来存储 dp[i - 1] 和 dp[i - 2],使得原来的 O(N) 空间复杂度优化为 O(1) 复杂度。
public int climbStairs(int n) {
if (n <= 2) {
return n;
}
int pre2 = 1, pre1 = 2;
for (int i = 2; i < n; i++) {
int cur = pre1 + pre2;
pre2 = pre1;
pre1 = cur;
}
return pre1;
}强盗抢劫
198. House Robber (Easy)
题目描述: 抢劫一排住户,但是不能抢邻近的住户,求最大抢劫量。
定义 dp 数组用来存储最大的抢劫量,其中 dp[i] 表示抢到第 i 个住户时的最大抢劫量。
由于不能抢劫邻近住户,因此如果抢劫了第 i 个住户那么只能抢劫 i - 2 或者 i - 3 的住户,所以
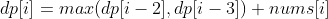
public int rob(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
if (n == 0) {
return 0;
}
if (n == 1) {
return nums[0];
}
int pre3 = 0, pre2 = 0, pre1 = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int cur = Math.max(pre2, pre3) + nums[i];
pre3 = pre2;
pre2 = pre1;
pre1 = cur;
}
return Math.max(pre1, pre2);
}强盗在环形街区抢劫
213. House Robber II (Medium)
public int rob(int[] nums) {
if (nums == null || nums.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
int n = nums.length;
if (n == 1) {
return nums[0];
}
return Math.max(rob(nums, 0, n - 2), rob(nums, 1, n - 1));
}
private int rob(int[] nums, int first, int last) {
int pre3 = 0, pre2 = 0, pre1 = 0;
for (int i = first; i <= last; i++) {
int cur = Math.max(pre3, pre2) + nums[i];
pre3 = pre2;
pre2 = pre1;
pre1 = cur;
}
return Math.max(pre2, pre1);
}信件错排
题目描述: 有 N 个 信 和 信封,它们被打乱,求错误装信方式的数量。
定义一个数组 dp 存储错误方式数量,dp[i] 表示前 i 个信和信封的错误方式数量。假设第 i 个信装到第 j 个信封里面,而第 j 个信装到第 k 个信封里面。根据 i 和 k 是否相等,有两种情况:
i==k,交换 i 和 k 的信后,它们的信和信封在正确的位置,但是其余 i-2 封信有 dp[i-2] 种错误装信的方式。由于 j 有 i-1 种取值,因此共有 (i-1)*dp[i-2] 种错误装信方式。
i != k,交换 i 和 j 的信后,第 i 个信和信封在正确的位置,其余 i-1 封信有 dp[i-1] 种错误装信方式。由于 j 有 i-1 种取值,因此共有 (i-1)*dp[i-1] 种错误装信方式。
综上所述,错误装信数量方式数量为:
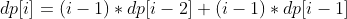
母牛生产
题目描述: 假设农场中成熟的母牛每年都会生 1 头小母牛,并且永远不会死。第一年有 1 只小母牛,从第二年开始,母牛开始生小母牛。每只小母牛 3 年之后成熟又可以生小母牛。给定整数 N,求 N 年后牛的数量。
第 i 年成熟的牛的数量为:
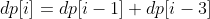
矩阵路径
矩阵的最小路径和
64. Minimum Path Sum (Medium)
[[1,3,1],
[1,5,1],
[4,2,1]]
Given the above grid map, return 7. Because the path 1→3→1→1→1 minimizes the sum.题目描述: 求从矩阵的左上角到右下角的最小路径和,每次只能向右和向下移动。
public int minPathSum(int[][] grid) {
if (grid.length == 0 || grid[0].length == 0) {
return 0;
}
int m = grid.length, n = grid[0].length;
int[] dp = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (i == 0) {
dp[j] = dp[j - 1];
} else {
dp[j] = Math.min(dp[j - 1], dp[j]);
}
dp[j] += grid[i][j];
}
}
return dp[n - 1];
}矩阵的总路径数
62. Unique Paths (Medium)
题目描述: 统计从矩阵左上角到右下角的路径总数,每次只能向右或者向下移动。
public int uniquePaths(int m, int n) {
int[] dp = new int[n];
Arrays.fill(dp, 1);
for (int i = 1; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < n; j++) {
dp[j] = dp[j] + dp[j - 1];
}
}
return dp[n - 1];
}也可以直接用数学公式求解,这是一个组合问题。机器人总共移动的次数 S=m+n-2,向下移动的次数 D=m-1,那么问题可以看成从 S 从取出 D 个位置的组合数量,这个问题的解为 C(S, D)。
public int uniquePaths(int m, int n) {
int S = m + n - 2; // 总共的移动次数
int D = m - 1; // 向下的移动次数
long ret = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= D; i++) {
ret = ret * (S - D + i) / i;
}
return (int) ret;
}数组区间
数组区间和
303. Range Sum Query - Immutable (Easy)
Given nums = [-2, 0, 3, -5, 2, -1]
sumRange(0, 2) -> 1
sumRange(2, 5) -> -1
sumRange(0, 5) -> -3求区间 i ~ j 的和,可以转换为 sum[j] - sum[i-1],其中 sum[i] 为 0 ~ i 的和。
class NumArray {
private int[] sums;
public NumArray(int[] nums) {
sums = new int[nums.length + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= nums.length; i++) {
sums[i] = sums[i - 1] + nums[i - 1];
}
}
public int sumRange(int i, int j) {
return sums[j + 1] - sums[i];
}
}子数组最大的和
53. Maximum Subarray (Easy)
For example, given the array [-2,1,-3,4,-1,2,1,-5,4],
the contiguous subarray [4,-1,2,1] has the largest sum = 6.public int maxSubArray(int[] nums) {
if (nums == null || nums.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
int preSum = nums[0];
int maxSum = preSum;
for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
preSum = preSum > 0 ? preSum + nums[i] : nums[i];
maxSum = Math.max(maxSum, preSum);
}
return maxSum;
}数组中等差递增子区间的个数
413. Arithmetic Slices (Medium)
A = [1, 2, 3, 4]
return: 3, for 3 arithmetic slices in A: [1, 2, 3], [2, 3, 4] and [1, 2, 3, 4] itself.dp[i] 表示以 A[i] 为结尾的等差递增子区间的个数。
在 A[i] - A[i - 1] == A[i - 1] - A[i - 2] 的条件下,{A[i - 2], A[i - 1], A[i]} 是一个等差递增子区间。如果 {A[i - 3], A[i - 2], A[i - 1]} 是一个等差递增子区间,那么 {A[i - 3], A[i - 2], A[i - 1], A[i]} 也是等差递增子区间,dp[i] = dp[i-1] + 1。
public int numberOfArithmeticSlices(int[] A) {
if (A == null || A.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
int n = A.length;
int[] dp = new int[n];
for (int i = 2; i < n; i++) {
if (A[i] - A[i - 1] == A[i - 1] - A[i - 2]) {
dp[i] = dp[i - 1] + 1;
}
}
int total = 0;
for (int cnt : dp) {
total += cnt;
}
return total;
}分割整数
分割整数的最大乘积
343. Integer Break (Medim)
题目描述: For example, given n = 2, return 1 (2 = 1 + 1); given n = 10, return 36 (10 = 3 + 3 + 4).
public int integerBreak(int n) {
int[] dp = new int[n + 1];
dp[1] = 1;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= i - 1; j++) {
dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i], Math.max(j * dp[i - j], j * (i - j)));
}
}
return dp[n];
}按平方数来分割整数
279. Perfect Squares(Medium)
题目描述: For example, given n = 12, return 3 because 12 = 4 + 4 + 4; given n = 13, return 2 because 13 = 4 + 9.
public int numSquares(int n) {
List<Integer> squareList = generateSquareList(n);
int[] dp = new int[n + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int square : squareList) {
if (square > i) {
break;
}
min = Math.min(min, dp[i - square] + 1);
}
dp[i] = min;
}
return dp[n];
}
private List<Integer> generateSquareList(int n) {
List<Integer> squareList = new ArrayList<>();
int diff = 3;
int square = 1;
while (square <= n) {
squareList.add(square);
square += diff;
diff += 2;
}
return squareList;
}分割整数构成字母字符串
91. Decode Ways (Medium)
题目描述: Given encoded message "12", it could be decoded as "AB" (1 2) or "L" (12).
public int numDecodings(String s) {
if (s == null || s.length() == 0) {
return 0;
}
int n = s.length();
int[] dp = new int[n + 1];
dp[0] = 1;
dp[1] = s.charAt(0) == '0' ? 0 : 1;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
int one = Integer.valueOf(s.substring(i - 1, i));
if (one != 0) {
dp[i] += dp[i - 1];
}
if (s.charAt(i - 2) == '0') {
continue;
}
int two = Integer.valueOf(s.substring(i - 2, i));
if (two <= 26) {
dp[i] += dp[i - 2];
}
}
return dp[n];
}最长递增子序列
已知一个序列 {S1, S2,...,Sn},取出若干数组成新的序列 {Si1, Si2,..., Sim},其中 i1、i2 ... im 保持递增,即新序列中各个数仍然保持原数列中的先后顺序,称新序列为原序列的一个 子序列 。
如果在子序列中,当下标 ix > iy 时,Six > Siy,称子序列为原序列的一个 递增子序列 。
定义一个数组 dp 存储最长递增子序列的长度,dp[n] 表示以 Sn 结尾的序列的最长递增子序列长度。对于一个递增子序列 {Si1, Si2,...,Sim},如果 im < n 并且 Sim < Sn,此时 {Si1, Si2,..., Sim, Sn} 为一个递增子序列,递增子序列的长度增加 1。满足上述条件的递增子序列中,长度最长的那个递增子序列就是要找的,在长度最长的递增子序列上加上 Sn 就构成了以 Sn 为结尾的最长递增子序列。因此 dp[n] = max{ dp[i]+1 | Si < Sn && i < n} 。
因为在求 dp[n] 时可能无法找到一个满足条件的递增子序列,此时 {Sn} 就构成了递增子序列,需要对前面的求解方程做修改,令 dp[n] 最小为 1,即:

对于一个长度为 N 的序列,最长递增子序列并不一定会以 SN 为结尾,因此 dp[N] 不是序列的最长递增子序列的长度,需要遍历 dp 数组找出最大值才是所要的结果,max{ dp[i] | 1 <= i <= N} 即为所求。
最长递增子序列
300. Longest Increasing Subsequence (Medium)
public int lengthOfLIS(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
int[] dp = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int max = 1;
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
if (nums[i] > nums[j]) {
max = Math.max(max, dp[j] + 1);
}
}
dp[i] = max;
}
return Arrays.stream(dp).max().orElse(0);
}使用 Stream 求最大值会导致运行时间过长,可以改成以下形式:
int ret = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
ret = Math.max(ret, dp[i]);
}
return ret;以上解法的时间复杂度为 O(N2),可以使用二分查找将时间复杂度降低为 O(NlogN)。
定义一个 tails 数组,其中 tails[i] 存储长度为 i + 1 的最长递增子序列的最后一个元素。对于一个元素 x,
如果它大于 tails 数组所有的值,那么把它添加到 tails 后面,表示最长递增子序列长度加 1;
如果 tails[i-1] < x <= tails[i],那么更新 tails[i-1] = x。
例如对于数组 [4,3,6,5],有:
tails len num
[] 0 4
[4] 1 3
[3] 1 6
[3,6] 2 5
[3,5] 2 null可以看出 tails 数组保持有序,因此在查找 Si 位于 tails 数组的位置时就可以使用二分查找。
public int lengthOfLIS(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
int[] tails = new int[n];
int len = 0;
for (int num : nums) {
int index = binarySearch(tails, len, num);
tails[index] = num;
if (index == len) {
len++;
}
}
return len;
}
private int binarySearch(int[] tails, int len, int key) {
int l = 0, h = len;
while (l < h) {
int mid = l + (h - l) / 2;
if (tails[mid] == key) {
return mid;
} else if (tails[mid] > key) {
h = mid;
} else {
l = mid + 1;
}
}
return l;
}一组整数对能够构成的最长链
646. Maximum Length of Pair Chain (Medium)
Input: [[1,2], [2,3], [3,4]]
Output: 2
Explanation: The longest chain is [1,2] -> [3,4]题目描述: 对于 (a, b) 和 (c, d) ,如果 b < c,则它们可以构成一条链。
public int findLongestChain(int[][] pairs) {
if (pairs == null || pairs.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
Arrays.sort(pairs, (a, b) -> (a[0] - b[0]));
int n = pairs.length;
int[] dp = new int[n];
Arrays.fill(dp, 1);
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
if (pairs[j][1] < pairs[i][0]) {
dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i], dp[j] + 1);
}
}
}
return Arrays.stream(dp).max().orElse(0);
}最长摆动子序列
376. Wiggle Subsequence (Medium)
Input: [1,7,4,9,2,5]
Output: 6
The entire sequence is a wiggle sequence.
Input: [1,17,5,10,13,15,10,5,16,8]
Output: 7
There are several subsequences that achieve this length. One is [1,17,10,13,10,16,8].
Input: [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9]
Output: 2要求: 使用 O(N) 时间复杂度求解。
public int wiggleMaxLength(int[] nums) {
if (nums == null || nums.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
int up = 1, down = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (nums[i] > nums[i - 1]) {
up = down + 1;
} else if (nums[i] < nums[i - 1]) {
down = up + 1;
}
}
return Math.max(up, down);
}最长公共子序列
对于两个子序列 S1 和 S2,找出它们最长的公共子序列。
定义一个二维数组 dp 用来存储最长公共子序列的长度,其中 dp[i][j] 表示 S1 的前 i 个字符与 S2 的前 j 个字符最长公共子序列的长度。考虑 S1i 与 S2j 值是否相等,分为两种情况:
当 S1i==S2j 时,那么就能在 S1 的前 i-1 个字符与 S2 的前 j-1 个字符最长公共子序列的基础上再加上 S1i 这个值,最长公共子序列长度加 1,即 dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1] + 1。
当 S1i != S2j 时,此时最长公共子序列为 S1 的前 i-1 个字符和 S2 的前 j 个字符最长公共子序列,或者 S1 的前 i 个字符和 S2 的前 j-1 个字符最长公共子序列,取它们的最大者,即 dp[i][j] = max{ dp[i-1][j], dp[i][j-1] }。
综上,最长公共子序列的状态转移方程为:

对于长度为 N 的序列 S1 和长度为 M 的序列 S2,dp[N][M] 就是序列 S1 和序列 S2 的最长公共子序列长度。
与最长递增子序列相比,最长公共子序列有以下不同点:
针对的是两个序列,求它们的最长公共子序列。
在最长递增子序列中,dp[i] 表示以 Si 为结尾的最长递增子序列长度,子序列必须包含 Si ;在最长公共子序列中,dp[i][j] 表示 S1 中前 i 个字符与 S2 中前 j 个字符的最长公共子序列长度,不一定包含 S1i 和 S2j。
在求最终解时,最长公共子序列中 dp[N][M] 就是最终解,而最长递增子序列中 dp[N] 不是最终解,因为以 SN 为结尾的最长递增子序列不一定是整个序列最长递增子序列,需要遍历一遍 dp 数组找到最大者。
public int lengthOfLCS(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {
int n1 = nums1.length, n2 = nums2.length;
int[][] dp = new int[n1 + 1][n2 + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= n1; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n2; j++) {
if (nums1[i - 1] == nums2[j - 1]) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 1;
} else {
dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]);
}
}
}
return dp[n1][n2];
}0-1 背包
有一个容量为 N 的背包,要用这个背包装下物品的价值最大,这些物品有两个属性: 体积 w 和价值 v。
定义一个二维数组 dp 存储最大价值,其中 dp[i][j] 表示前 i 件物品体积不超过 j 的情况下能达到的最大价值。设第 i 件物品体积为 w,价值为 v,根据第 i 件物品是否添加到背包中,可以分两种情况讨论:
第 i 件物品没添加到背包,总体积不超过 j 的前 i 件物品的最大价值就是总体积不超过 j 的前 i-1 件物品的最大价值,dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j]。
第 i 件物品添加到背包中,dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-w] + v。
第 i 件物品可添加也可以不添加,取决于哪种情况下最大价值更大。因此,0-1 背包的状态转移方程为:
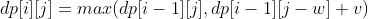
public int knapsack(int W, int N, int[] weights, int[] values) {
int[][] dp = new int[N + 1][W + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
int w = weights[i - 1], v = values[i - 1];
for (int j = 1; j <= W; j++) {
if (j >= w) {
dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i - 1][j - w] + v);
} else {
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j];
}
}
}
return dp[N][W];
}空间优化
在程序实现时可以对 0-1 背包做优化。观察状态转移方程可以知道,前 i 件物品的状态仅与前 i-1 件物品的状态有关,因此可以将 dp 定义为一维数组,其中 dp[j] 既可以表示 dp[i-1][j] 也可以表示 dp[i][j]。此时,
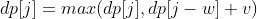
因为 dp[j-w] 表示 dp[i-1][j-w],因此不能先求 dp[i][j-w],以防将 dp[i-1][j-w] 覆盖。也就是说要先计算 dp[i][j] 再计算 dp[i][j-w],在程序实现时需要按倒序来循环求解。
public int knapsack(int W, int N, int[] weights, int[] values) {
int[] dp = new int[W + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
int w = weights[i - 1], v = values[i - 1];
for (int j = W; j >= 1; j--) {
if (j >= w) {
dp[j] = Math.max(dp[j], dp[j - w] + v);
}
}
}
return dp[W];
}无法使用贪心算法的解释
0-1 背包问题无法使用贪心算法来求解,也就是说不能按照先添加性价比最高的物品来达到最优,这是因为这种方式可能造成背包空间的浪费,从而无法达到最优。考虑下面的物品和一个容量为 5 的背包,如果先添加物品 0 再添加物品 1,那么只能存放的价值为 16,浪费了大小为 2 的空间。最优的方式是存放物品 1 和物品 2,价值为 22.
id | w | v | v/w |
0 | 1 | 6 | 6 |
1 | 2 | 10 | 5 |
2 | 3 | 12 | 4 |
变种
完全背包: 物品数量为无限个
多重背包: 物品数量有限制
多维费用背包: 物品不仅有重量,还有体积,同时考虑这两种限制
其它: 物品之间相互约束或者依赖
划分数组为和相等的两部分
416. Partition Equal Subset Sum (Medium)
Input: [1, 5, 11, 5]
Output: true
Explanation: The array can be partitioned as [1, 5, 5] and [11].可以看成一个背包大小为 sum/2 的 0-1 背包问题。
public boolean canPartition(int[] nums) {
int sum = computeArraySum(nums);
if (sum % 2 != 0) {
return false;
}
int W = sum / 2;
boolean[] dp = new boolean[W + 1];
dp[0] = true;
Arrays.sort(nums);
for (int num : nums) { // 0-1 背包一个物品只能用一次
for (int i = W; i >= num; i--) { // 从后往前,先计算 dp[i] 再计算 dp[i-num]
dp[i] = dp[i] || dp[i - num];
}
}
return dp[W];
}
private int computeArraySum(int[] nums) {
int sum = 0;
for (int num : nums) {
sum += num;
}
return sum;
}改变一组数的正负号使得它们的和为一给定数
494. Target Sum (Medium)
Input: nums is [1, 1, 1, 1, 1], S is 3.
Output: 5
Explanation:
-1+1+1+1+1 = 3
+1-1+1+1+1 = 3
+1+1-1+1+1 = 3
+1+1+1-1+1 = 3
+1+1+1+1-1 = 3
There are 5 ways to assign symbols to make the sum of nums be target 3.该问题可以转换为 Subset Sum 问题,从而使用 0-1 背包的方法来求解。
可以将这组数看成两部分,P 和 N,其中 P 使用正号,N 使用负号,有以下推导:
sum(P) - sum(N) = target
sum(P) + sum(N) + sum(P) - sum(N) = target + sum(P) + sum(N)
2 * sum(P) = target + sum(nums)因此只要找到一个子集,令它们都取正号,并且和等于 (target + sum(nums))/2,就证明存在解。
public int findTargetSumWays(int[] nums, int S) {
int sum = computeArraySum(nums);
if (sum < S || (sum + S) % 2 == 1) {
return 0;
}
int W = (sum + S) / 2;
int[] dp = new int[W + 1];
dp[0] = 1;
Arrays.sort(nums);
for (int num : nums) {
for (int i = W; i >= num; i--) {
dp[i] = dp[i] + dp[i - num];
}
}
return dp[W];
}
private int computeArraySum(int[] nums) {
int sum = 0;
for (int num : nums) {
sum += num;
}
return sum;
}DFS 解法:
public int findTargetSumWays(int[] nums, int S) {
return findTargetSumWays(nums, 0, S);
}
private int findTargetSumWays(int[] nums, int start, int S) {
if (start == nums.length) {
return S == 0 ? 1 : 0;
}
return findTargetSumWays(nums, start + 1, S + nums[start])
+ findTargetSumWays(nums, start + 1, S - nums[start]);
}字符串按单词列表分割
139. Word Break (Medium)
s = "leetcode",
dict = ["leet", "code"].
Return true because "leetcode" can be segmented as "leet code".dict 中的单词没有使用次数的限制,因此这是一个完全背包问题。
0-1 背包和完全背包在实现上的不同之处是,0-1 背包对物品的迭代是在最外层,而完全背包对物品的迭代是在最里层。
public boolean wordBreak(String s, List<String> wordDict) {
int n = s.length();
boolean[] dp = new boolean[n + 1];
dp[0] = true;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (String word : wordDict) { // 完全一个物品可以使用多次
int len = word.length();
if (len <= i && word.equals(s.substring(i - len, i))) {
dp[i] = dp[i] || dp[i - len];
}
}
}
return dp[n];
}01 字符构成最多的字符串
474. Ones and Zeroes (Medium)
Input: Array = {"10", "0001", "111001", "1", "0"}, m = 5, n = 3
Output: 4
Explanation: There are totally 4 strings can be formed by the using of 5 0s and 3 1s, which are "10","0001","1","0"这是一个多维费用的 0-1 背包问题,有两个背包大小,0 的数量和 1 的数量。
public int findMaxForm(String[] strs, int m, int n) {
if (strs == null || strs.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
int[][] dp = new int[m + 1][n + 1];
for (String s : strs) { // 每个字符串只能用一次
int ones = 0, zeros = 0;
for (char c : s.toCharArray()) {
if (c == '0') {
zeros++;
} else {
ones++;
}
}
for (int i = m; i >= zeros; i--) {
for (int j = n; j >= ones; j--) {
dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i][j], dp[i - zeros][j - ones] + 1);
}
}
}
return dp[m][n];
}找零钱的最少硬币数
322. Coin Change (Medium)
Example 1:
coins = [1, 2, 5], amount = 11
return 3 (11 = 5 + 5 + 1)
Example 2:
coins = [2], amount = 3
return -1.题目描述: 给一些面额的硬币,要求用这些硬币来组成给定面额的钱数,并且使得硬币数量最少。硬币可以重复使用。
物品: 硬币
物品大小: 面额
物品价值: 数量
因为硬币可以重复使用,因此这是一个完全背包问题。
public int coinChange(int[] coins, int amount) {
if (coins == null || coins.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
int[] minimum = new int[amount + 1];
Arrays.fill(minimum, amount + 1);
minimum[0] = 0;
Arrays.sort(coins);
for (int i = 1; i <= amount; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < coins.length && coins[j] <= i; j++) {
minimum[i] = Math.min(minimum[i], minimum[i - coins[j]] + 1);
}
}
return minimum[amount] > amount ? -1 : minimum[amount];
}组合总和
377. Combination Sum IV (Medium)
nums = [1, 2, 3]
target = 4
The possible combination ways are:
(1, 1, 1, 1)
(1, 1, 2)
(1, 2, 1)
(1, 3)
(2, 1, 1)
(2, 2)
(3, 1)
Note that different sequences are counted as different combinations.
Therefore the output is 7.完全背包。
public int combinationSum4(int[] nums, int target) {
if (nums == null || nums.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
int[] maximum = new int[target + 1];
maximum[0] = 1;
Arrays.sort(nums);
for (int i = 1; i <= target; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < nums.length && nums[j] <= i; j++) {
maximum[i] += maximum[i - nums[j]];
}
}
return maximum[target];
}股票交易
需要冷却期的股票交易
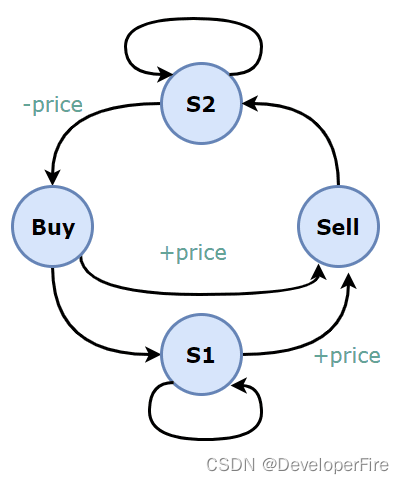
309. Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock with Cooldown(Medium)
题目描述: 交易之后需要有一天的冷却时间。
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
if (prices == null || prices.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
int N = prices.length;
int[] buy = new int[N];
int[] s1 = new int[N];
int[] sell = new int[N];
int[] s2 = new int[N];
s1[0] = buy[0] = -prices[0];
sell[0] = s2[0] = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < N; i++) {
buy[i] = s2[i - 1] - prices[i];
s1[i] = Math.max(buy[i - 1], s1[i - 1]);
sell[i] = Math.max(buy[i - 1], s1[i - 1]) + prices[i];
s2[i] = Math.max(s2[i - 1], sell[i - 1]);
}
return Math.max(sell[N - 1], s2[N - 1]);
}需要交易费用的股票交易
714. Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock with Transaction Fee (Medium)
Input: prices = [1, 3, 2, 8, 4, 9], fee = 2
Output: 8
Explanation: The maximum profit can be achieved by:
Buying at prices[0] = 1
Selling at prices[3] = 8
Buying at prices[4] = 4
Selling at prices[5] = 9
The total profit is ((8 - 1) - 2) + ((9 - 4) - 2) = 8.题目描述: 每交易一次,都要支付一定的费用。
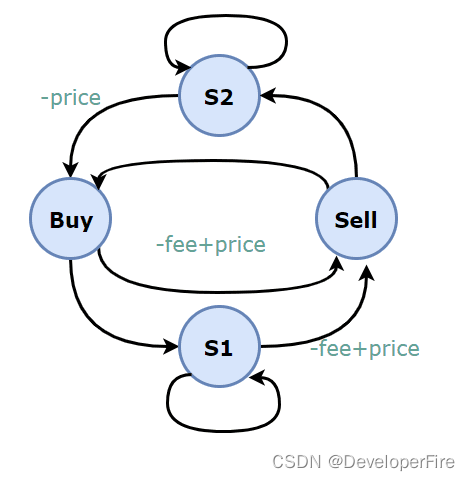
public int maxProfit(int[] prices, int fee) {
int N = prices.length;
int[] buy = new int[N];
int[] s1 = new int[N];
int[] sell = new int[N];
int[] s2 = new int[N];
s1[0] = buy[0] = -prices[0];
sell[0] = s2[0] = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < N; i++) {
buy[i] = Math.max(sell[i - 1], s2[i - 1]) - prices[i];
s1[i] = Math.max(buy[i - 1], s1[i - 1]);
sell[i] = Math.max(buy[i - 1], s1[i - 1]) - fee + prices[i];
s2[i] = Math.max(s2[i - 1], sell[i - 1]);
}
return Math.max(sell[N - 1], s2[N - 1]);
}买入和售出股票最大的收益
121. Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock (Easy)
题目描述: 只进行一次交易。
只要记录前面的最小价格,将这个最小价格作为买入价格,然后将当前的价格作为售出价格,查看当前收益是不是最大收益。
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
int n = prices.length;
if (n == 0) return 0;
int soFarMin = prices[0];
int max = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (soFarMin > prices[i]) soFarMin = prices[i];
else max = Math.max(max, prices[i] - soFarMin);
}
return max;
}只能进行两次的股票交易
123. Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock III (Hard)
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
int firstBuy = Integer.MIN_VALUE, firstSell = 0;
int secondBuy = Integer.MIN_VALUE, secondSell = 0;
for (int curPrice : prices) {
if (firstBuy < -curPrice) {
firstBuy = -curPrice;
}
if (firstSell < firstBuy + curPrice) {
firstSell = firstBuy + curPrice;
}
if (secondBuy < firstSell - curPrice) {
secondBuy = firstSell - curPrice;
}
if (secondSell < secondBuy + curPrice) {
secondSell = secondBuy + curPrice;
}
}
return secondSell;
}只能进行 k 次的股票交易
188. Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock IV (Hard)
public int maxProfit(int k, int[] prices) {
int n = prices.length;
if (k >= n / 2) { // 这种情况下该问题退化为普通的股票交易问题
int maxProfit = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (prices[i] > prices[i - 1]) {
maxProfit += prices[i] - prices[i - 1];
}
}
return maxProfit;
}
int[][] maxProfit = new int[k + 1][n];
for (int i = 1; i <= k; i++) {
int localMax = maxProfit[i - 1][0] - prices[0];
for (int j = 1; j < n; j++) {
maxProfit[i][j] = Math.max(maxProfit[i][j - 1], prices[j] + localMax);
localMax = Math.max(localMax, maxProfit[i - 1][j] - prices[j]);
}
}
return maxProfit[k][n - 1];
}字符串编辑
删除两个字符串的字符使它们相等
583. Delete Operation for Two Strings (Medium)
Input: "sea", "eat"
Output: 2
Explanation: You need one step to make "sea" to "ea" and another step to make "eat" to "ea".可以转换为求两个字符串的最长公共子序列问题。
public int minDistance(String word1, String word2) {
int m = word1.length(), n = word2.length();
int[][] dp = new int[m + 1][n + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
if (word1.charAt(i - 1) == word2.charAt(j - 1)) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 1;
} else {
dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i][j - 1], dp[i - 1][j]);
}
}
}
return m + n - 2 * dp[m][n];
}编辑距离
72. Edit Distance (Hard)
Example 1:
Input: word1 = "horse", word2 = "ros"
Output: 3
Explanation:
horse -> rorse (replace 'h' with 'r')
rorse -> rose (remove 'r')
rose -> ros (remove 'e')
Example 2:
Input: word1 = "intention", word2 = "execution"
Output: 5
Explanation:
intention -> inention (remove 't')
inention -> enention (replace 'i' with 'e')
enention -> exention (replace 'n' with 'x')
exention -> exection (replace 'n' with 'c')
exection -> execution (insert 'u')题目描述: 修改一个字符串成为另一个字符串,使得修改次数最少。一次修改操作包括: 插入一个字符、删除一个字符、替换一个字符。
public int minDistance(String word1, String word2) {
if (word1 == null || word2 == null) {
return 0;
}
int m = word1.length(), n = word2.length();
int[][] dp = new int[m + 1][n + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
dp[i][0] = i;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
dp[0][i] = i;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
if (word1.charAt(i - 1) == word2.charAt(j - 1)) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1];
} else {
dp[i][j] = Math.min(dp[i - 1][j - 1], Math.min(dp[i][j - 1], dp[i - 1][j])) + 1;
}
}
}
return dp[m][n];
}复制粘贴字符
650. 2 Keys Keyboard (Medium)
题目描述: 最开始只有一个字符 A,问需要多少次操作能够得到 n 个字符 A,每次操作可以复制当前所有的字符,或者粘贴。
Input: 3
Output: 3
Explanation:
Intitally, we have one character 'A'.
In step 1, we use Copy All operation.
In step 2, we use Paste operation to get 'AA'.
In step 3, we use Paste operation to get 'AAA'.public int minSteps(int n) {
if (n == 1) return 0;
for (int i = 2; i <= Math.sqrt(n); i++) {
if (n % i == 0) return i + minSteps(n / i);
}
return n;
}public int minSteps(int n) {
int[] dp = new int[n + 1];
int h = (int) Math.sqrt(n);
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
dp[i] = i;
for (int j = 2; j <= h; j++) {
if (i % j == 0) {
dp[i] = dp[j] + dp[i / j];
break;
}
}
}
return dp[n];
}




![[架构之路-107]-《软考-系统架构设计师》-0-系统分析师与系统架构设计师简介与官网介绍](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/d29ed2ba5ee03869c50fc9328c60b447.png)