Spring反射内置工具类ReflectionUtils
- 前言
- 反射
- 1,什么是反射
- 2,反射的实现
- 2.1获取class对象的三种实现
- 2.1.1Object ——> getClass();
- 2.1.2 任何数据对象(包括数据基本类型)都有一个静态的class属性
- 通过Class类的静态方法:forName(String className)(常用)
- 例子 获取类中hashMap的值
- 1.1 通过JDK实现
- 1.2 通过org.springframework.util.ReflectionUtils
- 对属性的操作
- public static Field findField(Class<?> clazz, String name) 在类中查找指定属性
- public static Field findField(Class<?> clazz, @Nullable String name, @Nullable Class<?> type) 更精确的在类中查找指定属性,可以在指定属性的类型
- public static Object getField(Field field, @Nullable Object target) 获取对象的值
- void setField(Field field, Object target, Object value),可以设置 target 对象的 field 属性值,值为 value。
- void makeAccessible(Field field),取消java的权限控制检查,方便private私有访问权限的操作。
- 对方法的操作
- Method findMethod(Class clazz, String name),在类中查找指定名字方法
- Method findMethod(Class clazz, String name, Class... paramTypes),有的时候同一个类可能会有多个方法名相同,形参数不同的重载方法,可以使用这个方法更精确的在类中找到指定方法;
- Method[] getAllDeclaredMethods(Class leafClass),获得类中所有方法,包括继承而来的。
- 执行方法
前言
最近在搞通过sentinel熔断后,触发数据库代理ShardingSphere 代理直连DB的时候,这里需要通过反射获取sentinel熔断的规则map。原先是通过jdk反射机制,发现一堆异常处理,特别的不友好,代码整洁度和可阅读性也不是很好,后面发现spring给我们提供了一个ReflectionUtils。简直不要太香了。
反射
1,什么是反射
java反射机制在运行状态中,对于任何一个类,都能够知道这个类的所有属性和方法;对于任意一个对象,都能够调用它的任意一个方法和属性。这种动态的获取信息以及动态的调用对象的方法的功能我们称之为java的反射机制
eg:类的class声明(class对象),变量(field),方法(method)等等信息,利用反射技术可以对一个类进行解剖,动态获取信息进行处理。
2,反射的实现
2.1获取class对象的三种实现
2.1.1Object ——> getClass();
Demo demo = new Demo();
Class<? extends Demo> clazz = demo.getClass();
2.1.2 任何数据对象(包括数据基本类型)都有一个静态的class属性
Class<Demo> clazz = Demo.class;
通过Class类的静态方法:forName(String className)(常用)
Class clazz = Class.forName("com.demo.Demo");
例子 获取类中hashMap的值
获取com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.degrade.DegradeRuleManager 实体类中hashMap的数据,从以下JDK和spring的封装类中,我们能明显的感受到易用行。
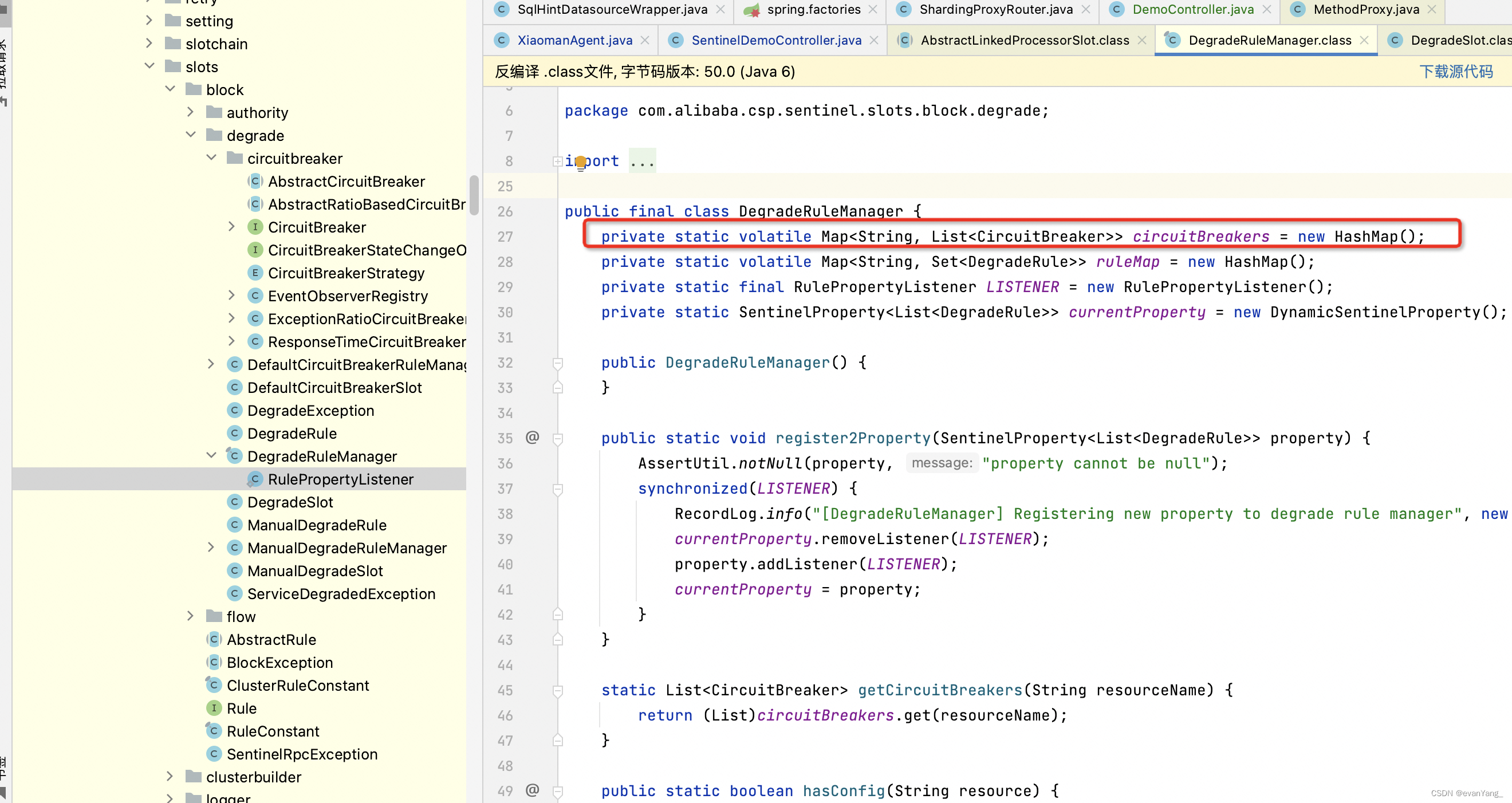
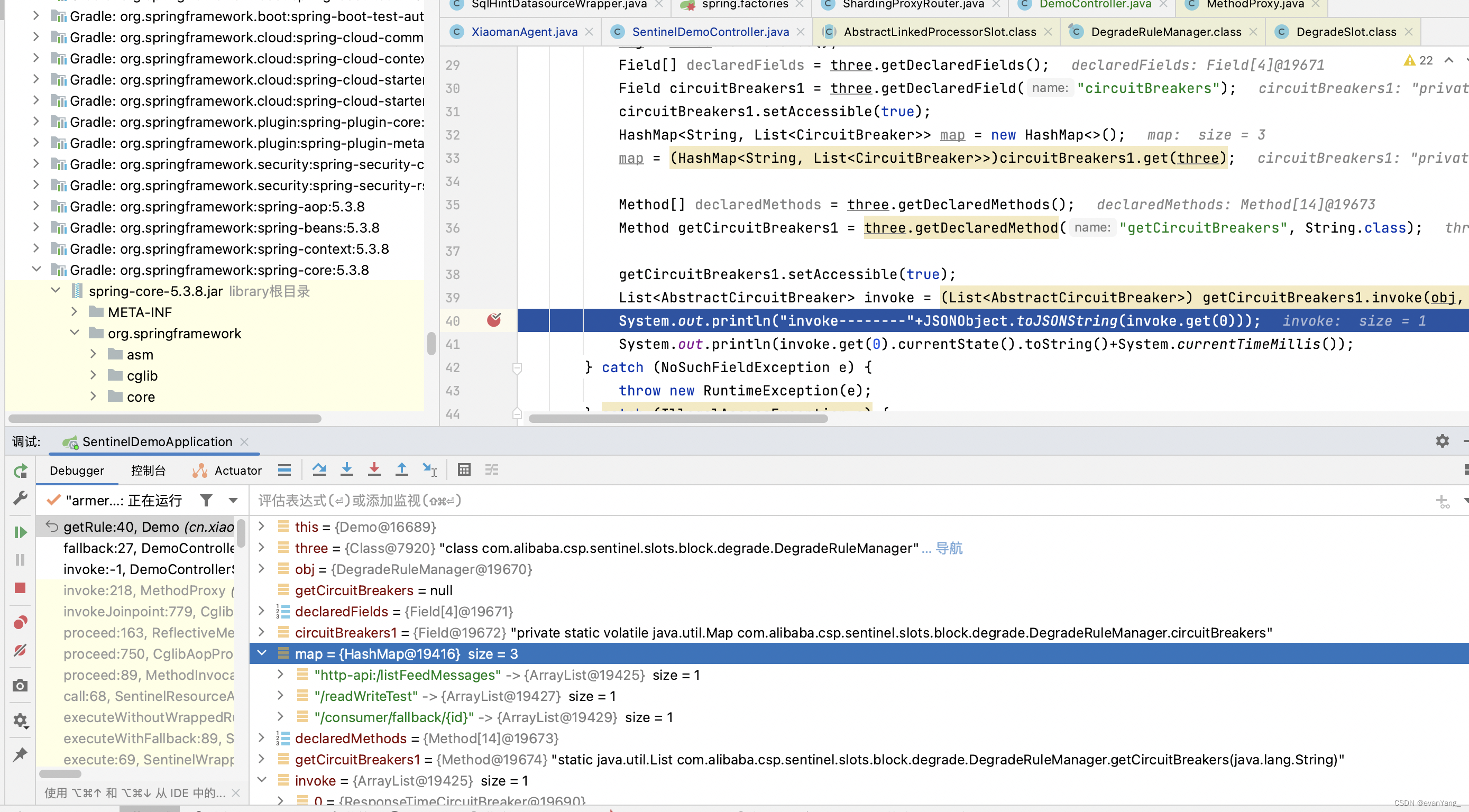
1.1 通过JDK实现
public void getRule() {
Class three = null;
Object obj = null;
Method getCircuitBreakers = null;
try {
three = Class.forName("com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.degrade.DegradeRuleManager");
obj = three.newInstance();
Field[] declaredFields = three.getDeclaredFields();
Field circuitBreakers1 = three.getDeclaredField("circuitBreakers");
circuitBreakers1.setAccessible(true);
HashMap<String, List<CircuitBreaker>> map = new HashMap<>();
map = (HashMap<String, List<CircuitBreaker>>)circuitBreakers1.get(three);
Method[] declaredMethods = three.getDeclaredMethods();
Method getCircuitBreakers1 = three.getDeclaredMethod("getCircuitBreakers", String.class);
getCircuitBreakers1.setAccessible(true);
List<AbstractCircuitBreaker> invoke = (List<AbstractCircuitBreaker>) getCircuitBreakers1.invoke(obj, "http-api:/listFeedMessages");
System.out.println("invoke--------"+JSONObject.toJSONString(invoke.get(0)));
System.out.println(invoke.get(0).currentState().toString()+System.currentTimeMillis());
} catch (NoSuchFieldException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
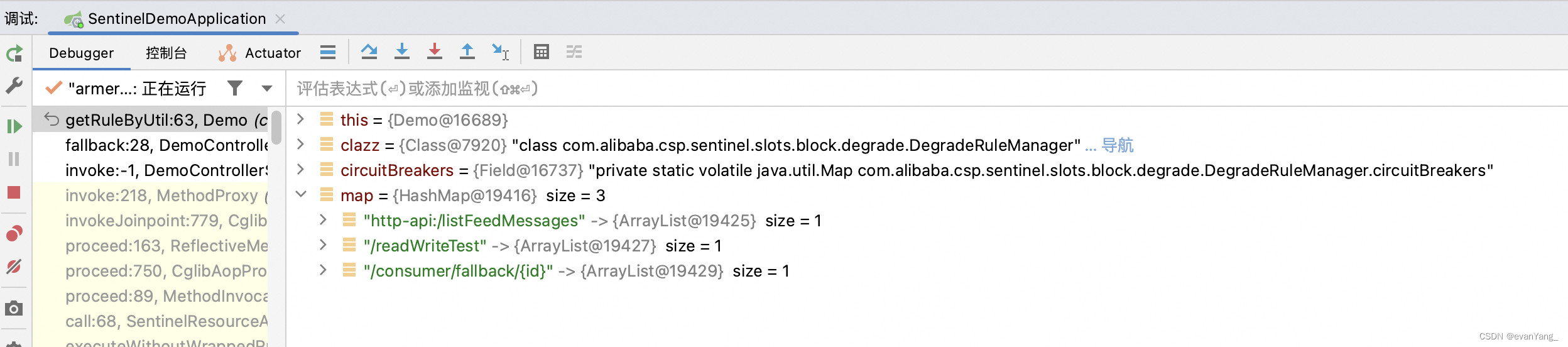
1.2 通过org.springframework.util.ReflectionUtils
public void getRuleByUtil() {
try {
Class clazz=Class.forName("com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.degrade.DegradeRuleManager");
Field circuitBreakers = ReflectionUtils.findField(clazz, "circuitBreakers");
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(circuitBreakers);
HashMap<String, List<CircuitBreaker>> map= (HashMap<String, List<CircuitBreaker>>) ReflectionUtils.getField(circuitBreakers,clazz);
System.out.println(map);
}catch (ClassNotFoundException e){
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
对属性的操作
public static Field findField(Class<?> clazz, String name) 在类中查找指定属性
public void getRuleByUtil() {
try {
Class clazz=Class.forName("com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.degrade.DegradeRuleManager");
Field circuitBreakers = ReflectionUtils.findField(clazz, "circuitBreakers");
}catch (ClassNotFoundException e){
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public static Field findField(Class<?> clazz, @Nullable String name, @Nullable Class<?> type) 更精确的在类中查找指定属性,可以在指定属性的类型
public void getRuleByUtil() {
try {
Class clazz=Class.forName("com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.degrade.DegradeRuleManager");
Field circuitBreakers = ReflectionUtils.findField(clazz, "circuitBreakers",Map.class);
}catch (ClassNotFoundException e){
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public static Object getField(Field field, @Nullable Object target) 获取对象的值
public void getRuleByUtil() {
try {
Class clazz=Class.forName("com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.degrade.DegradeRuleManager");
Field circuitBreakers = ReflectionUtils.findField(clazz, "circuitBreakers");
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(circuitBreakers);
HashMap<String, List<CircuitBreaker>> map= (HashMap<String, List<CircuitBreaker>>) ReflectionUtils.getField(circuitBreakers,clazz);
System.out.println(map);
}catch (ClassNotFoundException e){
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
void setField(Field field, Object target, Object value),可以设置 target 对象的 field 属性值,值为 value。
public void getRuleByUtil() {
try {
Class clazz=Class.forName("com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.degrade.DegradeRuleManager");
Field circuitBreakers = ReflectionUtils.findField(clazz, "circuitBreakers");
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(circuitBreakers);
HashMap<String, List<CircuitBreaker>> map= (HashMap<String, List<CircuitBreaker>>) ReflectionUtils.setField(circuitBreakers,clazz,Lists.newArrayList());
System.out.println(map);
}catch (ClassNotFoundException e){
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
void makeAccessible(Field field),取消java的权限控制检查,方便private私有访问权限的操作。
对方法的操作
Method findMethod(Class clazz, String name),在类中查找指定名字方法
Method findMethod(Class clazz, String name, Class… paramTypes),有的时候同一个类可能会有多个方法名相同,形参数不同的重载方法,可以使用这个方法更精确的在类中找到指定方法;
Method[] getAllDeclaredMethods(Class leafClass),获得类中所有方法,包括继承而来的。
执行方法
Object invokeMethod(Method method, Object target),执行无参数的方法;
Object invokeMethod(Method method, Object target, Object… args),执行有参数的方法
void makeAccessible(Method method),如果是私有方法,可以取消 Java 权限检查,以便后续执行该私有方法


![[WTL/ATL]_[初级]_[TreeView控件如何显示ToolTip]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/e6bafa1613b24008923ef65bb38e52b3.png#pic_center)