概述
JobGraph 是 StreamGraph 优化后的产物,客户端会将优化后的 JobGraph 发送给 JM。接下来的文章涉及到一些前置知识点,没有看前几期的小伙伴最好看一下前几期:
- 【Flink】详解StreamGraph
- 【Flink】浅谈Flink架构和调度
- 【Flink】详解Flink的八种分区
Flink 在客户端将 StreamGraph 对象转换成 JobGraph 对象,这个转换的核心在于将多个符合条件的 StreamNode 节点合并在一起,形成一个 JobVertex 节点,这样的优化方式称之为算子链合并,这样做可以有效减少数据在节点间传递所需的序列化、反序列化操作。同一个算子链中的算子运行在同一个 TaskSlot 中,也可由理解为运行在一个线程中,这样可以显著降低线程切换的性能开销,并且能增大吞吐量和降低延迟。
源码分析
JobGraph 的构建
JobGraph 的相关代码主要在【flink-runtime】模块下的 org.apache.flink.runtime.JobGraph 中。其调用链路是 StreamGraph#getJobGraph → StreamingJobGraphGenerator#createJobGraph() →
/*------------------------ StreamGraph ---------------------------*/
// 构造入口
public JobGraph getJobGraph() {
return getJobGraph(null);
}
public JobGraph getJobGraph(@Nullable JobID jobID) {
return StreamingJobGraphGenerator.createJobGraph(this, jobID);
}
/*---------------------------------------------------------*/
/*--------------- StreamingJobGraphGenerator ------------------*/
public static JobGraph createJobGraph(StreamGraph streamGraph, @Nullable JobID jobID) {
return new StreamingJobGraphGenerator(streamGraph, jobID).createJobGraph();
}
private JobGraph createJobGraph() {
// 前置校验
preValidate();
// 获取StreamGraph的调度模式
// 设置JobGraph的调度模式
jobGraph.setJobType(streamGraph.getJobType());
// jobGraph设置是否启动本地近似恢复策略
jobGraph.enableApproximateLocalRecovery( streamGraph.getCheckpointConfig().isApproximateLocalRecoveryEnabled());
// 为每一个StreamNode生成一个确定的哈希值
defaultStreamGraphHasher.traverseStreamGraphAndGenerateHashes(streamGraph);
// 为兼容问题生成哈希值
List<Map<Integer, byte[]>> legacyHashes = new ArrayList<>(legacyStreamGraphHashers.size());
for (StreamGraphHasher hasher : legacyStreamGraphHashers) {
legacyHashes.add(hasher.traverseStreamGraphAndGenerateHashes(streamGraph));
}
// 这里是重点,JobGraph的顶点和边在这个方法中创建。
// 尝试将尽可能多的StreamNode聚合在一个JobGraph节点中。
// 判断算子chain,合并创建JobVertex,并生成JobEdge。
setChaining(hashes, legacyHashes);
// 设置物理边界
setPhysicalEdges();
// 设置jobGraph的SlotSharingGroup和CoLocationGroup
setSlotSharingAndCoLocation();
setManagedMemoryFraction(
Collections.unmodifiableMap(jobVertices),
Collections.unmodifiableMap(vertexConfigs),
Collections.unmodifiableMap(chainedConfigs),
id -> streamGraph.getStreamNode(id).getManagedMemoryOperatorScopeUseCaseWeights(),
id -> streamGraph.getStreamNode(id).getManagedMemorySlotScopeUseCases());
// 设置jobGraph的各个 JobVertex 的checkpoint 信息
// 比如说source JobVertex 需要trigger checkpoint
// 所有的JobVertex需要commit和ack checkpoint
configureCheckpointing();
// 设置保存点配置
jobGraph.setSavepointRestoreSettings(streamGraph.getSavepointRestoreSettings());
final Map<String, DistributedCache.DistributedCacheEntry> distributedCacheEntries =
JobGraphUtils.prepareUserArtifactEntries(
streamGraph.getUserArtifacts().stream()
.collect(Collectors.toMap(e -> e.f0, e -> e.f1)),
jobGraph.getJobID());
for (Map.Entry<String, DistributedCache.DistributedCacheEntry> entry :
distributedCacheEntries.entrySet()) {
jobGraph.addUserArtifact(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());
}
// 设置运行时配置信息
try {
jobGraph.setExecutionConfig(streamGraph.getExecutionConfig());
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new IllegalConfigurationException(
"Could not serialize the ExecutionConfig."
+ "This indicates that non-serializable types (like custom serializers) were registered");
}
// 返回JobGraph对象
return jobGraph;
}
/*---------------------------------------------------------*/
// 定义Flink-Job调度枚举类型
public enum JobType {
// 批处理模式
BATCH,
// 流处理模式
STREAMING
}
从上面的分析可以看出,由 StreamGraph 到 JobGraph 最重要的一步是创建算子链 setChaining(hashes, legacyHashes),这样做可以尽可能的多整合一些操作在同一个节点中完成,避免不必要的线程切换和网络通信。举一个简单一点的例子,DataStream.map(a -> a+1).filter(a -> a > 2),此时数据流有两个处理步骤,也就是两个算子组成,即 map 和 filter,这两个算子会组成不同的 StreamNode 对象和 Task 对象,如果这两个 Task 不在一个 TaskSlot 或者一个 TM 中,那么必然涉及到网络传输,这样的执行性能会很差,为了优化这一点,Flink 引入了算子链的概念,一个算子链代表一组可以在同一个 TaskSlot 中执行的算子串。
/*--------------- StreamingJobGraphGenerator ------------------*/
// 从StreamNode递归创建JobVertex对象
private void setChaining(Map<Integer, byte[]> hashes, List<Map<Integer, byte[]>> legacyHashes) {
final Map<Integer, OperatorChainInfo> chainEntryPoints =
buildChainedInputsAndGetHeadInputs(hashes, legacyHashes);
final Collection<OperatorChainInfo> initialEntryPoints =
chainEntryPoints.entrySet().stream()
.sorted(Comparator.comparing(Map.Entry::getKey))
.map(Map.Entry::getValue)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
// 创建算子链
for (OperatorChainInfo info : initialEntryPoints) {
createChain(
info.getStartNodeId(),
1, // 索引从1开始,0是Source
info,
chainEntryPoints);
}
}
// 创建算子链
private List<StreamEdge> createChain(
final Integer currentNodeId,
final int chainIndex,
final OperatorChainInfo chainInfo,
final Map<Integer, OperatorChainInfo> chainEntryPoints) {
// 获取起始Node-ID
Integer startNodeId = chainInfo.getStartNodeId();
// builtVertices用于存放已经进行构建的StreamNode ID,避免重复构造
if (!builtVertices.contains(startNodeId)) {
// transitiveOutEdges 存储整个算子链的出边
List<StreamEdge> transitiveOutEdges = new ArrayList<StreamEdge>();
// chainableOutputs 存储所有可以形成算子链的StreamEdge
List<StreamEdge> chainableOutputs = new ArrayList<StreamEdge>();
// nonChainableOutputs 存储不可以形成算子链的StreamEdge
List<StreamEdge> nonChainableOutputs = new ArrayList<StreamEdge>();
// 获取当前处理的SteamNode
StreamNode currentNode = streamGraph.getStreamNode(currentNodeId);
// 对所有的StreamEdge进行处理,分为可以形成算子链和不可以形成算子链两类
for (StreamEdge outEdge : currentNode.getOutEdges()) {
if (isChainable(outEdge, streamGraph)) {
chainableOutputs.add(outEdge);
} else {
nonChainableOutputs.add(outEdge);
}
}
// 如果是可以形成算子链的StreamEdge对象,递归调用createChain,并添加到transitiveOutEdges
// 递归结束条件:
// 1. 当前节点不再有出边;
// 2. 当前节点已经完成转换
for (StreamEdge chainable : chainableOutputs) {
transitiveOutEdges.addAll(
createChain(
chainable.getTargetId(),
chainIndex + 1,
chainInfo,
chainEntryPoints));
}
// 如果是不可被chain的StreamEdge,添加到transitiveOutEdges集合中
for (StreamEdge nonChainable : nonChainableOutputs) {
transitiveOutEdges.add(nonChainable);
createChain(
nonChainable.getTargetId(),
1, // operators start at position 1 because 0 is for chained source inputs
chainEntryPoints.computeIfAbsent(
nonChainable.getTargetId(),
(k) -> chainInfo.newChain(nonChainable.getTargetId())),
chainEntryPoints);
}
// 设置算子链名称
chainedNames.put(
currentNodeId,
createChainedName(
currentNodeId,
chainableOutputs,
Optional.ofNullable(chainEntryPoints.get(currentNodeId))));
// 设置算子链所需最小资源
chainedMinResources.put(
currentNodeId, createChainedMinResources(currentNodeId, chainableOutputs));
// 设置算子链所需最佳资源
chainedPreferredResources.put(
currentNodeId,
createChainedPreferredResources(currentNodeId, chainableOutputs));
//
OperatorID currentOperatorId =
chainInfo.addNodeToChain(currentNodeId, chainedNames.get(currentNodeId));
if (currentNode.getInputFormat() != null) {
getOrCreateFormatContainer(startNodeId)
.addInputFormat(currentOperatorId, currentNode.getInputFormat());
}
if (currentNode.getOutputFormat() != null) {
getOrCreateFormatContainer(startNodeId)
.addOutputFormat(currentOperatorId, currentNode.getOutputFormat());
}
// 如果currentNodeId和startNodeId相等,说明需要创建一个新的chain,会生成一个JobVertex
StreamConfig config =
currentNodeId.equals(startNodeId)
? createJobVertex(startNodeId, chainInfo)
: new StreamConfig(new Configuration());
// 设置的顶点属性到config中
setVertexConfig(
currentNodeId,
config,
chainableOutputs,
nonChainableOutputs,
chainInfo.getChainedSources());
if (currentNodeId.equals(startNodeId)) {
// 开始一个新的算子链的连接
config.setChainStart();
config.setChainIndex(chainIndex);
config.setOperatorName(streamGraph.getStreamNode(currentNodeId).getOperatorName());
// 对于每一个算子链,把它和指向下一个算子链的出边连接起来
for (StreamEdge edge : transitiveOutEdges) {
connect(startNodeId, edge);
}
//
config.setOutEdgesInOrder(transitiveOutEdges);
config.setTransitiveChainedTaskConfigs(chainedConfigs.get(startNodeId));
} else {
chainedConfigs.computeIfAbsent(
startNodeId, k -> new HashMap<Integer, StreamConfig>());
config.setChainIndex(chainIndex);
StreamNode node = streamGraph.getStreamNode(currentNodeId);
config.setOperatorName(node.getOperatorName());
chainedConfigs.get(startNodeId).put(currentNodeId, config);
}
config.setOperatorID(currentOperatorId);
if (chainableOutputs.isEmpty()) {
config.setChainEnd();
}
return transitiveOutEdges;
} else {
return new ArrayList<>();
}
}
// 判断是否可以形成算子链
public static boolean isChainable(StreamEdge edge, StreamGraph streamGraph) {
StreamNode downStreamVertex = streamGraph.getTargetVertex(edge);
return downStreamVertex.getInEdges().size() == 1 && isChainableInput(edge, streamGraph);
}
private static boolean isChainableInput(StreamEdge edge, StreamGraph streamGraph) {
StreamNode upStreamVertex = streamGraph.getSourceVertex(edge);
StreamNode downStreamVertex = streamGraph.getTargetVertex(edge);
if (!(upStreamVertex.isSameSlotSharingGroup(downStreamVertex)
&& areOperatorsChainable(upStreamVertex, downStreamVertex, streamGraph)
&& (edge.getPartitioner() instanceof ForwardPartitioner)
&& edge.getShuffleMode() != ShuffleMode.BATCH
&& upStreamVertex.getParallelism() == downStreamVertex.getParallelism()
&& streamGraph.isChainingEnabled())) {
return false;
}
for (StreamEdge inEdge : downStreamVertex.getInEdges()) {
if (inEdge != edge && inEdge.getTypeNumber() == edge.getTypeNumber()) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
public boolean isSameSlotSharingGroup(StreamNode downstreamVertex) {
return (slotSharingGroup == null && downstreamVertex.slotSharingGroup == null)
|| (slotSharingGroup != null
&& slotSharingGroup.equals(downstreamVertex.slotSharingGroup));
}
private Map<Integer, OperatorChainInfo> buildChainedInputsAndGetHeadInputs(
final Map<Integer, byte[]> hashes, final List<Map<Integer, byte[]>> legacyHashes) {
final Map<Integer, ChainedSourceInfo> chainedSources = new HashMap<>();
final Map<Integer, OperatorChainInfo> chainEntryPoints = new HashMap<>();
// 遍历所有的Source-StreamNode
for (Integer sourceNodeId : streamGraph.getSourceIDs()) {
// 根据ID获取StreamNode对象
final StreamNode sourceNode = streamGraph.getStreamNode(sourceNodeId);
if (sourceNode.getOperatorFactory() instanceof SourceOperatorFactory
&& sourceNode.getOutEdges().size() == 1) {
final StreamEdge sourceOutEdge = sourceNode.getOutEdges().get(0);
final StreamNode target = streamGraph.getStreamNode(sourceOutEdge.getTargetId());
final ChainingStrategy targetChainingStrategy =
target.getOperatorFactory().getChainingStrategy();
if (targetChainingStrategy == ChainingStrategy.HEAD_WITH_SOURCES
&& isChainableInput(sourceOutEdge, streamGraph)) {
final OperatorID opId = new OperatorID(hashes.get(sourceNodeId));
final StreamConfig.SourceInputConfig inputConfig =
new StreamConfig.SourceInputConfig(sourceOutEdge);
final StreamConfig operatorConfig = new StreamConfig(new Configuration());
setVertexConfig(
sourceNodeId,
operatorConfig,
Collections.emptyList(),
Collections.emptyList(),
Collections.emptyMap());
operatorConfig.setChainIndex(0); // sources are always first
operatorConfig.setOperatorID(opId);
operatorConfig.setOperatorName(sourceNode.getOperatorName());
chainedSources.put(
sourceNodeId, new ChainedSourceInfo(operatorConfig, inputConfig));
final SourceOperatorFactory<?> sourceOpFact =
(SourceOperatorFactory<?>) sourceNode.getOperatorFactory();
final OperatorCoordinator.Provider coord =
sourceOpFact.getCoordinatorProvider(sourceNode.getOperatorName(), opId);
final OperatorChainInfo chainInfo =
chainEntryPoints.computeIfAbsent(
sourceOutEdge.getTargetId(),
(k) ->
new OperatorChainInfo(
sourceOutEdge.getTargetId(),
hashes,
legacyHashes,
chainedSources,
streamGraph));
chainInfo.addCoordinatorProvider(coord);
continue;
}
}
// 将SourceID-OperatorChainInfo添加到HashMap中
chainEntryPoints.put(
sourceNodeId,
new OperatorChainInfo(
sourceNodeId, hashes, legacyHashes, chainedSources, streamGraph));
}
return chainEntryPoints;
}
/*---------------------------------------------------------*/
/*--------------- ChainingStrategy ------------------*/
public enum ChainingStrategy {
// 最大程度连接前后算子
ALWAYS,
// 算子不会连接前后的算子形成算子链
NEVER,
// 算子只会连接后面的算子但是不会连接前面的算子
HEAD,
// 头部算子,尽可能连接多个source算子
HEAD_WITH_SOURCES;
// 默认连接策略是【ALWAYS】
public static final ChainingStrategy DEFAULT_CHAINING_STRATEGY = ALWAYS;
}
/*--------------------------------------------------*/
简单总结一下 JobGraph 的构建过程,入口方法是 setChaining(),该方法会构造一个 Collection<OperatorChainInfo> 对象,该对象是所有 Source 节点的信息集合,遍历该集合调用 createChain() 方法,该方法会递归调用下游节点,构建算子链。在改方法中会对每一个 Operator 调用 isChainable 方法,将所有的出边分成两类:chainalbeOutputs 和 noChainableOutputs,递归遍历二者进行算子链的构建,同时将 StreamNode 的配置信息序列化到 StreamConfig 对象中,这里会有一个分支,如果当前节点是算子链的头结点,则会调用 createJobVertex 构建 JobVertex 对象和 JobEdge 对象相连;如果当前节点不是算子链的头节点,则构建一个新的 StreamConfig 对象。
能够形成算子链的依据是 isChainable 方法和 isChainableInput 方法,具体判断条件如下:
- 下游节点的前置节点只有一个;
- 分区器必须是ForwardPartitioner;
- Shuffle 模式必须是 Pipeline 模式;
- 上下游的并行度必须一致;
- StreamGraph 启用算子链优化;
- 上游算子的算子链策略必须是【ALWAYS | HEAD | HEAD_WITH_SOURCES】;
- 下游算子的算子链策略必须是【ALWAYS | 上游是 Source 算子的情况下 HEAD_WITH_SOURCES】;
- 上、下游算子都分配了 SlotSharingGroup 而且二者一致;
在 createJobVertex 方法中,首先创建一个 JobVertex 对象,然后调用 jobVertex.setInvokableClass() 设置执行类,然后设置运行资源和并行度。最后传递 JobVertex 对象的配置信息构建一个 StreamConfig 对象并返回。
遍历 transitiveOutEdges,调用 connect() 方法,在 connect 方法中,依据 StreamEdge 对象得到上下游 JobVertex 节点信息;通过 StreamEdge.getPartitioner() 方法得到 StreamPartitioner 属性,如果分区器的 isPointwise() 方法返回 True(ForwardPartitioner 和 RescalePartitioner 分区器都是由明确指向的),那么构建 DistributionPattern.POINTWISE 类型的 JobEdge 对象,其余的分区器构建 DistributionPattern.ALL_TO_ALL 类型的 JobEdge 对象,JobEdge 对象就是各个 JobVertex 之间的连接对象,也就是说在 connect 方法中就完成了 JobGraph 的各个节点之间的连接工作。
// connect方法
private void connect(Integer headOfChain, StreamEdge edge) {
physicalEdgesInOrder.add(edge);
Integer downStreamVertexID = edge.getTargetId();
// 获取算子链头JobVertex对象
JobVertex headVertex = jobVertices.get(headOfChain);
// 获取下游JobVertex对象
JobVertex downStreamVertex = jobVertices.get(downStreamVertexID);
StreamConfig downStreamConfig = new StreamConfig(downStreamVertex.getConfiguration());
downStreamConfig.setNumberOfNetworkInputs(downStreamConfig.getNumberOfNetworkInputs() + 1);
// 获取分区器
StreamPartitioner<?> partitioner = edge.getPartitioner();
// 获取结果分区类型
ResultPartitionType resultPartitionType;
switch (edge.getShuffleMode()) {
case PIPELINED:
resultPartitionType = ResultPartitionType.PIPELINED_BOUNDED;
break;
case BATCH:
resultPartitionType = ResultPartitionType.BLOCKING;
break;
case UNDEFINED:
resultPartitionType = determineResultPartitionType(partitioner);
break;
default:
throw new UnsupportedOperationException(
"Data exchange mode " + edge.getShuffleMode() + " is not supported yet.");
}
checkAndResetBufferTimeout(resultPartitionType, edge);
// 依据分区器的不同构建JobEdge对象
JobEdge jobEdge;
if (partitioner.isPointwise()) {
jobEdge =
downStreamVertex.connectNewDataSetAsInput(
headVertex, DistributionPattern.POINTWISE, resultPartitionType);
} else {
jobEdge =
downStreamVertex.connectNewDataSetAsInput(
headVertex, DistributionPattern.ALL_TO_ALL, resultPartitionType);
}
// 设置策略名称,这些都可以在Web上看到
jobEdge.setShipStrategyName(partitioner.toString());
jobEdge.setDownstreamSubtaskStateMapper(partitioner.getDownstreamSubtaskStateMapper());
jobEdge.setUpstreamSubtaskStateMapper(partitioner.getUpstreamSubtaskStateMapper());
// 打印日志【分区器名称】-【算子链头】->【下游VertexID】
if (LOG.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOG.debug(
"CONNECTED: {} - {} -> {}",
partitioner.getClass().getSimpleName(),
headOfChain,
downStreamVertexID);
}
}
物理边界的设置
setPhysicalEdges 方法用于设置 JobVertex 的物理边界,执行方法总结如下:
- 遍历 physicalEdgesInOrder 对象,该对象包含所有不能构成算子链的边,将边的目标节点的入边添加到一个 List 对象中;
- 遍历所有的 physicalInEdgesInOrder,经过上面的步骤,该对象的内部结构为不能构成算子链的边的下游节点 ID-入边集合,将该节点的入边结合都设置为实际物理边界。
// 设置物理边界
private void setPhysicalEdges() {
Map<Integer, List<StreamEdge>> physicalInEdgesInOrder =
new HashMap<Integer, List<StreamEdge>>();
for (StreamEdge edge : physicalEdgesInOrder) {
int target = edge.getTargetId();
List<StreamEdge> inEdges =
physicalInEdgesInOrder.computeIfAbsent(target, k -> new ArrayList<>());
inEdges.add(edge);
}
for (Map.Entry<Integer, List<StreamEdge>> inEdges : physicalInEdgesInOrder.entrySet()) {
int vertex = inEdges.getKey();
List<StreamEdge> edgeList = inEdges.getValue();
vertexConfigs.get(vertex).setInPhysicalEdges(edgeList);
}
}
最终完成物理边界划分的 JobGraph 如下图所示:
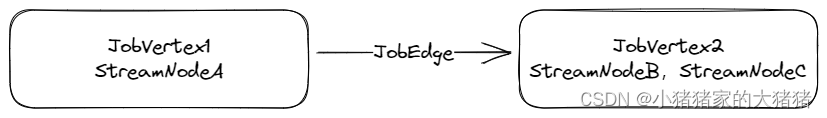
JobGraph 的提交
JobGraph 的相关行为由ClusterClient接口进行定义,该接口定义了封装程序提交到远程集群的方法,关键源码分析如下:
public interface ClusterClient<T> extends AutoCloseable {
// 返回集群ID
T getClusterId();
// 返回Flink设置
Configuration getFlinkConfiguration();
// 关闭客户端此时连接的集群
void shutDownCluster();
// 获取所有的正在运行和完成的作业
CompletableFuture<Collection<JobStatusMessage>> listJobs() throws Exception;
// 提交JobGraph给集群
CompletableFuture<JobID> submitJob(JobGraph jobGraph);
// 根据作业ID获取其运行状态
CompletableFuture<JobResult> requestJobResult(JobID jobId);
// 根据JobId触发保存点
CompletableFuture<String> triggerSavepoint(JobID jobId, @Nullable String savepointDirectory);
// 向协调器发出请求并接收回应
CompletableFuture<CoordinationResponse> sendCoordinationRequest(
JobID jobId, OperatorID operatorId, CoordinationRequest request);
// 根据JobID停止相关作业(仅适用于流式作业)
// 发送停止指令后本质上只是Source停止发送数据,整个程序停止还需要所有的TM处理完当前数据
// jobId:作业唯一标识符
// advanceToEndOfEventTime:表示Source是否注入最大水位线
CompletableFuture<String> stopWithSavepoint(
final JobID jobId,
final boolean advanceToEndOfEventTime,
@Nullable final String savepointDirectory);
// 根据JobID获取Job结果
CompletableFuture<JobResult> requestJobResult(JobID jobId);
// 根据JobID获取累加器
// jobId:作业唯一标识符
// loader:用于反序列化
CompletableFuture<Map<String, Object>> getAccumulators(JobID jobID, ClassLoader loader);
// 根据JobID撤销作业
CompletableFuture<Acknowledge> cancel(JobID jobId);
...
}
也就是说 JobGraph 对象最终会由 ClusterClient#submitJob() 发送给集群,由 JM 的 JobMaster 进行接收,之后的调用链路是 JobMaster#startJobExecution() → JobMaster#startScheduling() 开始进行任务调动。
往期回顾
- 【Flink】详解StreamGraph
- 【Flink】浅谈Flink架构和调度
- 【Flink】详解Flink的八种分区
- 【Flink】浅谈Flink背压问题(1)
- 【分布式】浅谈CAP、BASE理论(1)
文中难免会出现一些描述不当之处(尽管我已反复检查多次),欢迎在留言区指正,相关的知识点也可进行分享,希望大家都能有所收获!!







![[acwing周赛复盘] 第 90 场周赛20230211 补](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/1e8beba049654439996ef43e3f0f0886.png)