如何检测一个障碍物呢?
视觉、雷达?
可视化效果如何?
机器人所装备的传感器例如感知设备,主要负责环境的获取和识别。
然后,结果发送给电机控制运动,在环境中自主、智能决策和规划。
需要先简单看一下仿真可视化效果。
书中给出两幅图:
ROS2机器人Gazebo是一个专门为机器人应用开发的三维模拟器,它可以帮助机器人开发人员更快、更容易地设计和调试机器人应用。Gazebo提供了一个可视化的环境,可以模拟真实世界的物理环境,并且可以通过ROS2接口与其他机器人应用进行通信。使用Gazebo,可以更快、更容易地开发机器人应用,并且可以在实际环境中更好地测试和调试机器人应用。
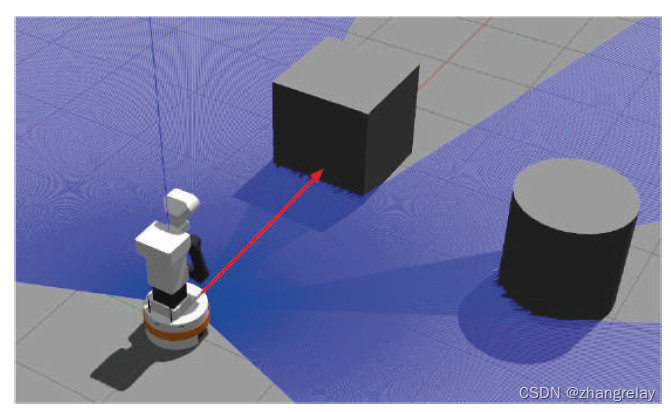
机器人Tiago用激光传感器探测障碍物。红色箭头突出显示检测到障碍物的中心读数。
ROS2机器人Rviz2是一个可视化工具,用于显示机器人环境中的消息,提供3D视角来查看机器人的状态和活动。它可以帮助开发者更好地理解机器人当前的状态和活动,以及其他可视化消息。Rviz2提供了一系列的可视化工具,可以帮助开发者更好地理解机器人的状态和活动,比如可视化坐标系、激光扫描消息、点云消息、机器人模型等等。使用Rviz2,可以轻松地查看和调试机器人系统,从而更好地实现机器人目标。
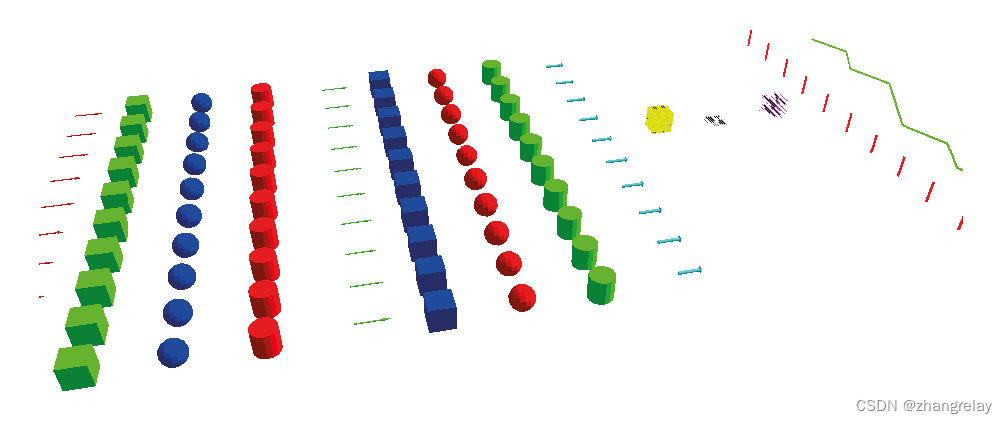
可用于视觉调试的视觉标记
可以用turtlebot复现一下。
打开一个空白的环境:
ros2 launch turtlebot3_gazebo empty_world.launch.py
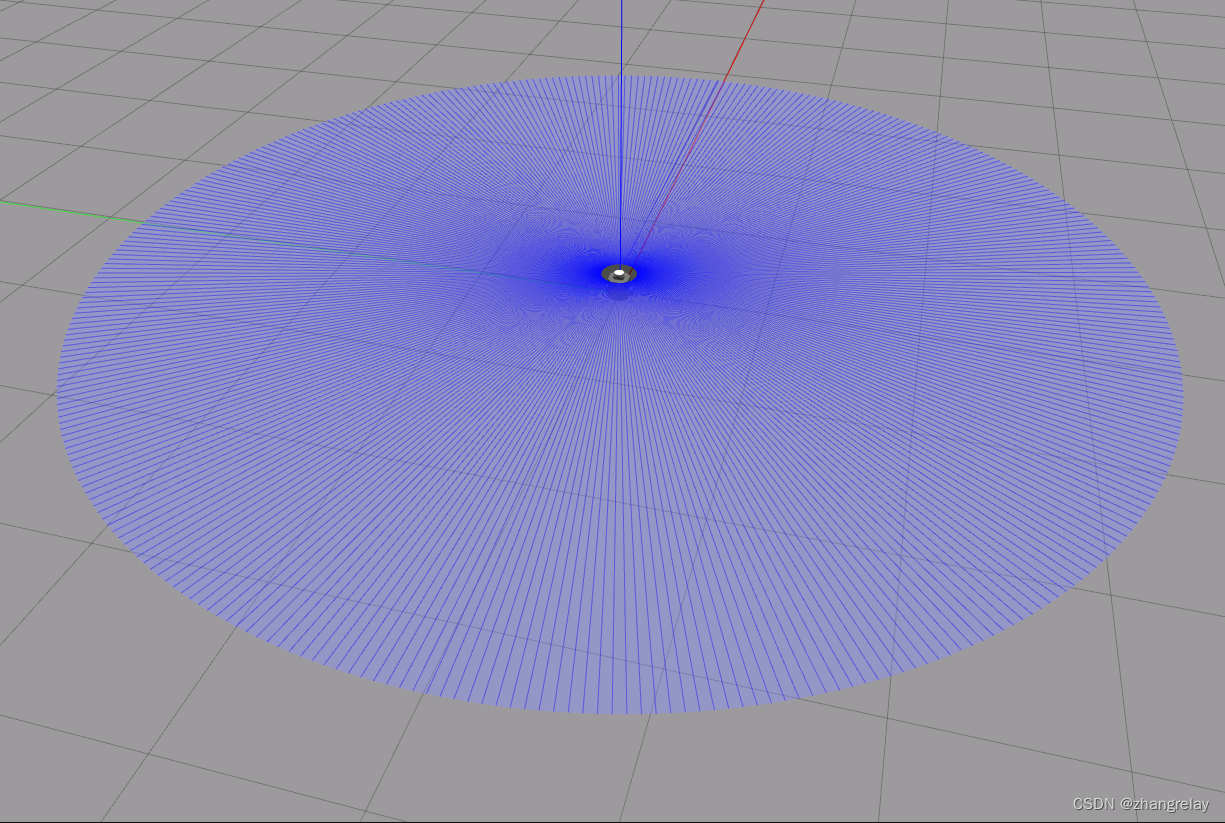
这时候,如果用topic查看数据可以得到:
网络中,所有计算机和机器人节点都能正常通信,支持windows、linux。
其中/scan
数据太多只看一组:
---
header:
stamp:
sec: 140
nanosec: 162000000
frame_id: base_scan
angle_min: 0.0
angle_max: 6.28000020980835
angle_increment: 0.01749303564429283
time_increment: 0.0
scan_time: 0.0
range_min: 0.11999999731779099
range_max: 3.5
ranges:
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- '...'
intensities:
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- 0.0
- '...'
---其中,.inf代表此时传感器最大量程中,没有检测到障碍物。
各类障碍物有典型特征。如下分别举例。
机器人正前方有方形障碍物。
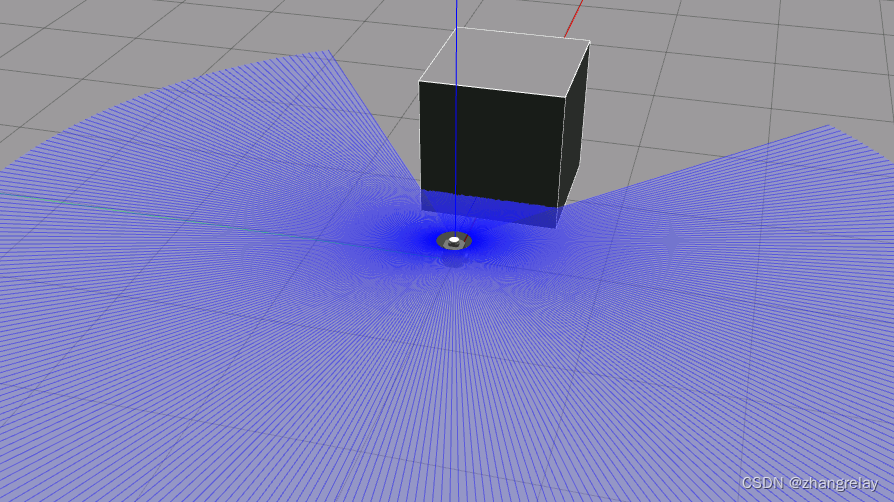
数据:
header:
stamp:
sec: 266
nanosec: 306000000
frame_id: base_scan
angle_min: 0.0
angle_max: 6.28000020980835
angle_increment: 0.01749303564429283
time_increment: 0.0
scan_time: 0.0
range_min: 0.11999999731779099
range_max: 3.5
ranges:
- 0.631385326385498
- 0.6107633709907532
- 0.6275626420974731
- 0.6091671586036682
- 0.6179323196411133
- 0.629402220249176
- 0.6138762831687927
- 0.6203798055648804
- 0.6130021810531616
- 0.6370837688446045
- 0.6302768588066101
- 0.6479257345199585
- 0.6441364288330078
- 0.6394597887992859
- 0.6609111428260803
- 0.6480688452720642
- 0.6676570773124695
- 0.6556036472320557
- 0.6597179770469666
- 0.6508679389953613
- 0.6702691912651062
- 0.671261727809906
- 0.6567016243934631
- 0.6737935543060303
- 0.6872966289520264
- 0.6952883005142212
- 0.7050795555114746
- 0.6851144433021545
- 0.7049869298934937
- 0.6912679076194763
- 0.7239711284637451
- 0.7069382071495056
- 0.7477790713310242
- 0.7354172468185425
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf圆柱体:
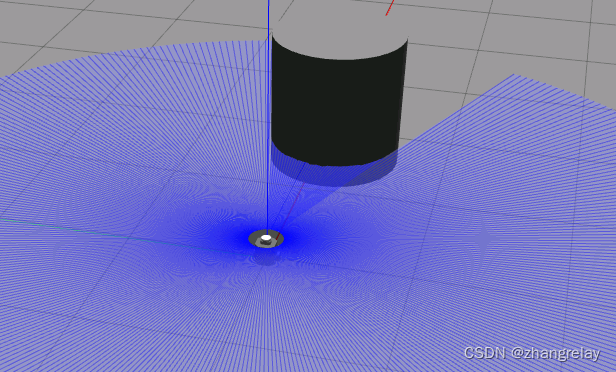
数据:
header:
stamp:
sec: 408
nanosec: 739000000
frame_id: base_scan
angle_min: 0.0
angle_max: 6.28000020980835
angle_increment: 0.01749303564429283
time_increment: 0.0
scan_time: 0.0
range_min: 0.11999999731779099
range_max: 3.5
ranges:
- 1.1339192390441895
- 1.1576037406921387
- 1.1470191478729248
- 1.1520755290985107
- 1.1525921821594238
- 1.1922894716262817
- 1.1875109672546387
- 1.1898000240325928
- 1.2374821901321411
- 1.2563176155090332
- 1.27926504611969
- 1.31011164188385
- 1.366029143333435
- 1.4372227191925049
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
- .inf
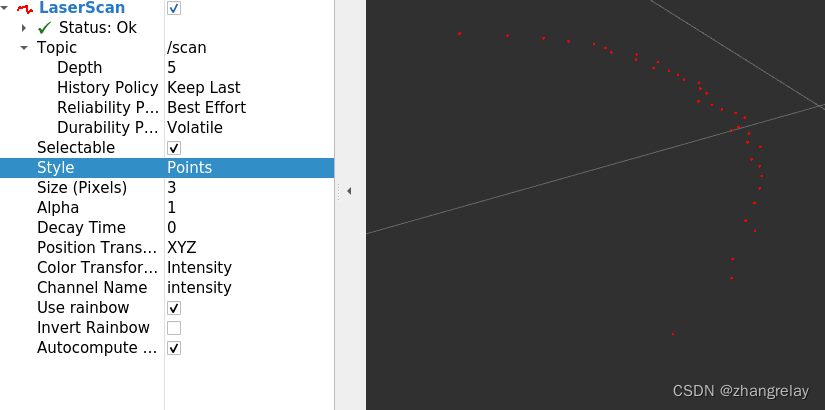
- .inf这样数据不便于分析和查看,rviz2可以可视化此类数据。
点:
球:
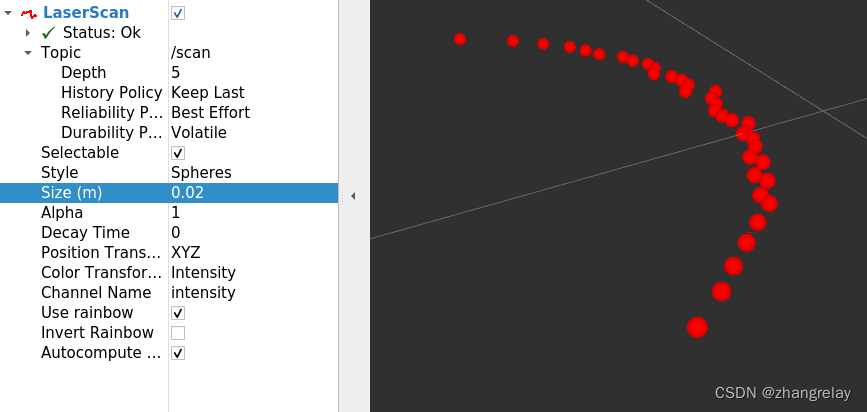
此部分内容需要全面掌握好的。
比如坐标角度与仿真不同?
调整一下
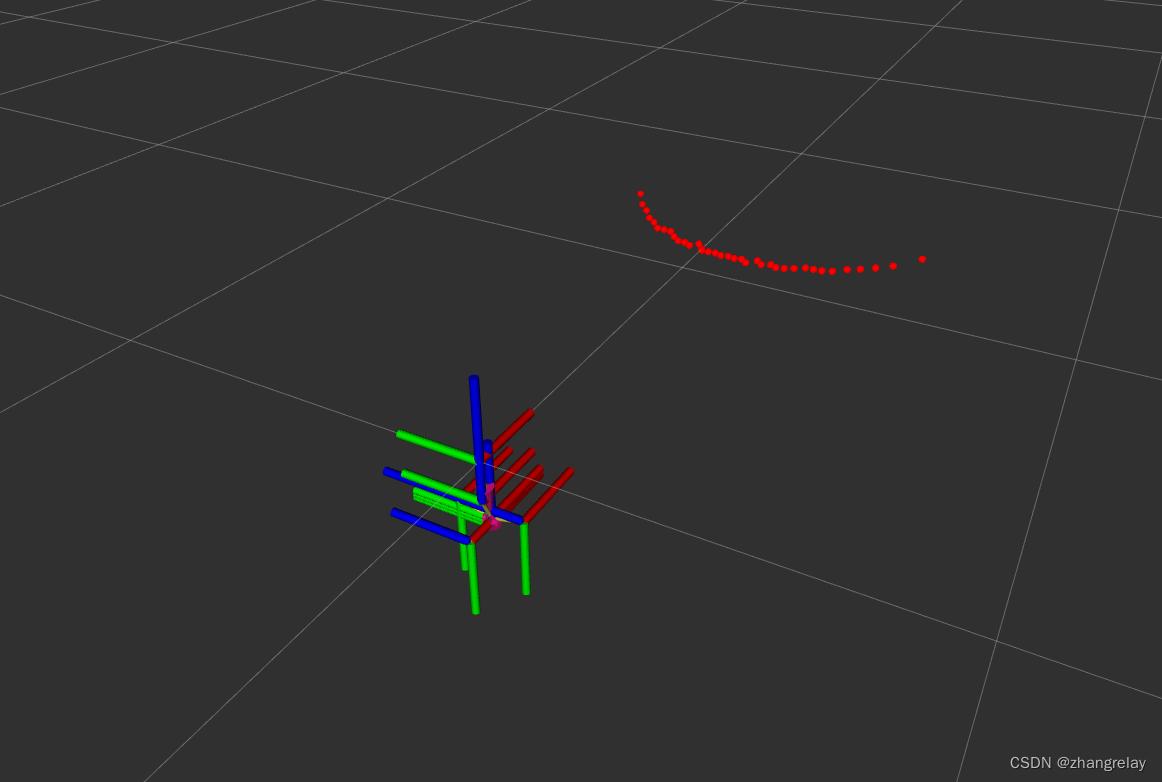
完全对应:
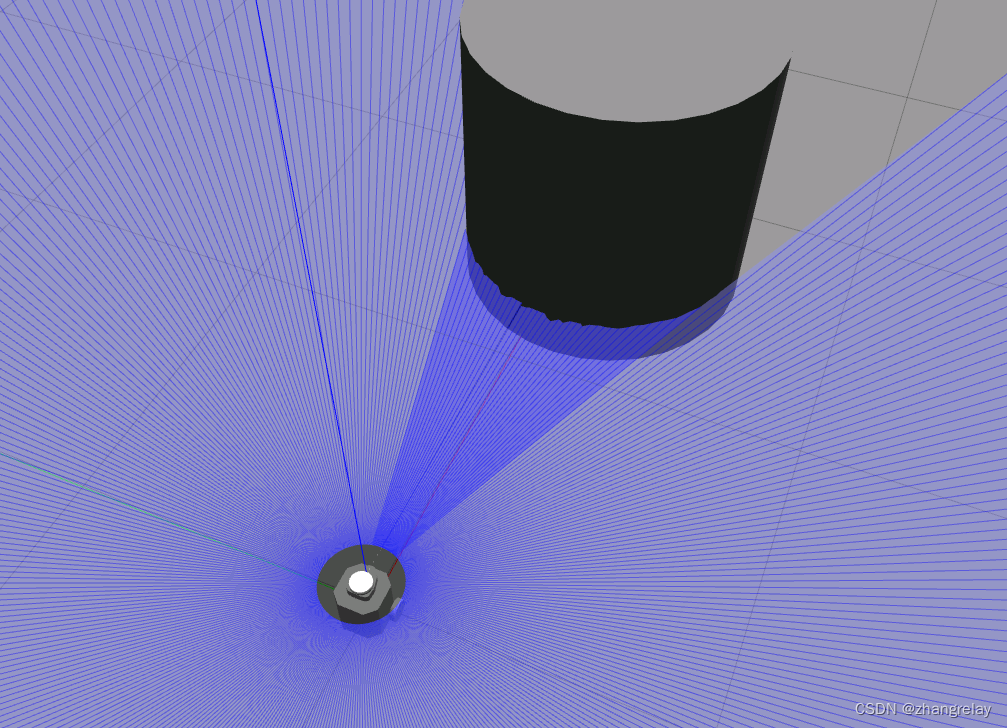
这一章主要内容后续会将障碍物与TF做一个案例。
书中给出的检测转TF代码:
// Copyright 2021 Intelligent Robotics Lab
//
// Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
// you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
// You may obtain a copy of the License at
//
// http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
//
// Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
// distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
// WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
// See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
// limitations under the License.
#include <memory>
#include "br2_tf2_detector/ObstacleDetectorNode.hpp"
#include "sensor_msgs/msg/laser_scan.hpp"
#include "geometry_msgs/msg/transform_stamped.hpp"
#include "rclcpp/rclcpp.hpp"
namespace br2_tf2_detector
{
using std::placeholders::_1;
ObstacleDetectorNode::ObstacleDetectorNode()
: Node("obstacle_detector")
{
scan_sub_ = create_subscription<sensor_msgs::msg::LaserScan>(
"input_scan", rclcpp::SensorDataQoS(),
std::bind(&ObstacleDetectorNode::scan_callback, this, _1));
tf_broadcaster_ = std::make_shared<tf2_ros::StaticTransformBroadcaster>(*this);
}
void
ObstacleDetectorNode::scan_callback(sensor_msgs::msg::LaserScan::UniquePtr msg)
{
double dist = msg->ranges[msg->ranges.size() / 2];
if (!std::isinf(dist)) {
geometry_msgs::msg::TransformStamped detection_tf;
detection_tf.header = msg->header;
detection_tf.child_frame_id = "detected_obstacle";
detection_tf.transform.translation.x = msg->ranges[msg->ranges.size() / 2];
tf_broadcaster_->sendTransform(detection_tf);
}
}
} // namespace br2_tf2_detector









![[MySQL教程①] - MySQL的安装](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/ff64db4e0a02450603a0f9d06ab781f5.png)