文章目录
- 1. jsx父子传值
- 2. provide和inject
- 3. v-memo指令
- 4. Teleport内置组件
- 5. KeepAlive缓存组件
- 6. transition过渡组件
1. jsx父子传值
父组件:
<template>
<div>
<child :title="title" :setTitle="setTitle" />
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { ref } from 'vue'
// 如果你用的是.jsx或.tsx,则引入时,扩展名不要写
import child from './components/child'
export default {
components: { child },
setup() {
let title = ref('测试')
const setTitle = titleStr => (title.value = titleStr)
return { title, setTitle }
}
}
</script>
<style lang="scss" scoped></style>
子组件:
// const Child = props => {
// return (
// <div>
// <h3>jsx -- {props.title}</h3>
// <button onClick={() => props.setTitle(Date.now() + '')}>jsx</button>
// </div>
// )
// }
// 解构写法
const Child = ({ title, setTitle }) => {
return (
<div>
<h3>jsx -- {title}</h3>
<button onClick={() => setTitle(Date.now() + '')}>jsx</button>
{/* <button onClick={() => changeTitle(setTitle)}>jsx</button> */}
</div>
)
}
export default Child

2. provide和inject
我们想要在组件内实现很方便的通信,却又想要与外界隔绝,这时候就需要用到 provide/inject。
父组件:
<template>
<div>
<child />
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { ref, provide } from 'vue'
import child from './components/child.vue'
export default {
components: { child },
setup() {
let title = ref('测试')
// 在祖先组件中发布了一个数据
// 如果你发布的数据它是一个响应式对象,则provide它就是一个响应式,如果是一个普通值和对象,则不是响应式
provide('title', title)
// 这种方式可以将会使发布的数据变为普通对象,无法响应
// provide('title', title.value)
return { title }
}
}
</script>
<style lang="scss" scoped></style>
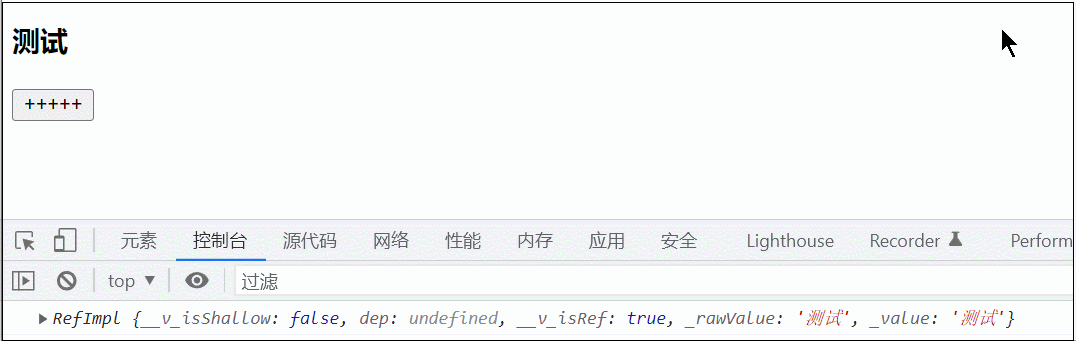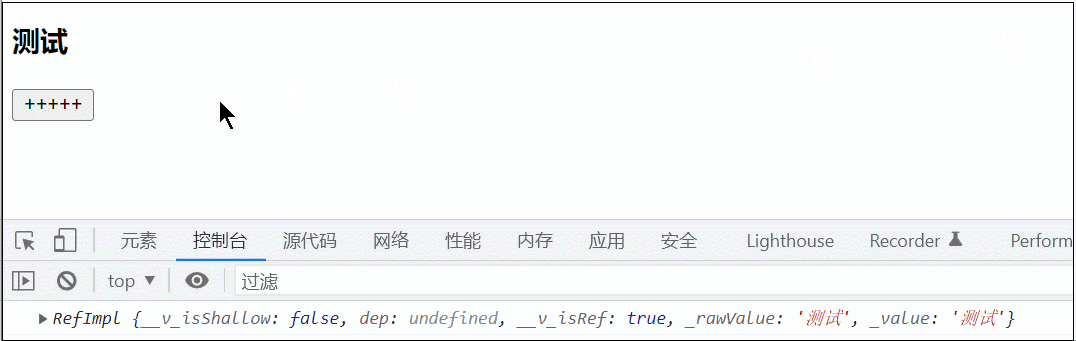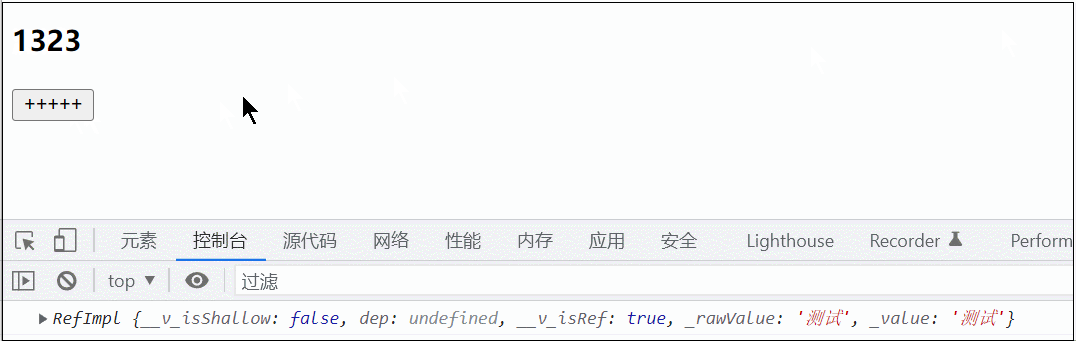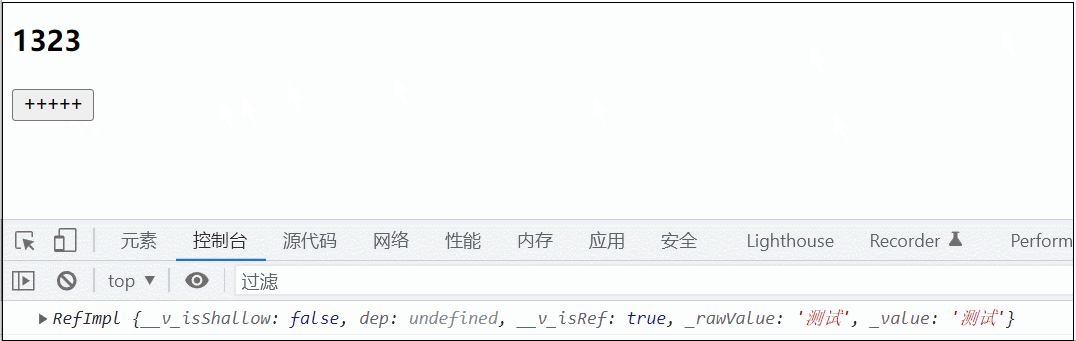
子组件:
<template>
<div>
<h3>{{ title }}</h3>
<button @click="title = 1323">+++++</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { inject } from 'vue'
export default {
setup() {
let title = inject('title')
console.log(title)
return { title }
}
}
</script>
<style lang="scss" scoped></style>
3. v-memo指令
只要 v-memo 的依赖项没有发生改变,那它的子元素就不会重新渲染,这是一种优化手段。
<template>
<div>
<!-- v-memo它依赖项没有发生改变,则它子元素不会重新渲染,优化 -->
<!-- <div v-memo="[names.length]"> -->
<div v-memo="[num]">
<ul v-for="item of names" :key="item">
<li> {{ item }}</li>
</ul>
</div>
<button @click="addNames">++++</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { ref, watch } from 'vue'
export default {
setup() {
let num = ref(0)
let names = ref(['乐乐', '英子', '小森', '亮亮'])
// 这里只是让names变量发生了变化,而v-memo的依赖项为num,所以这时候视图并不会重新渲染
const addNames = () => names.value.push(Date.now())
watch(
// 只要names属性发生了变化,就修改num的值
names,
n => {
num.value = n.length
},
{ deep: true, immediate: true }
)
return { num, names, addNames }
}
}
</script>
<style lang="scss" scoped>
</style>

4. Teleport内置组件
<Teleport> 是一个内置组件,它可以将一个组件内部的一部分模板“传送”到该组件的 DOM 结构外层的位置去。
举个例子,当我们利用 v-if 显示和隐藏某些元素的时候,可能会导致整个页面(当前 app 节点) html 结构的变化,从而导致元素样式的变化,这时候我们就可以将这个元素挂载到其他节点中去,于是就可以使用 Teleport 来包裹元素实现。
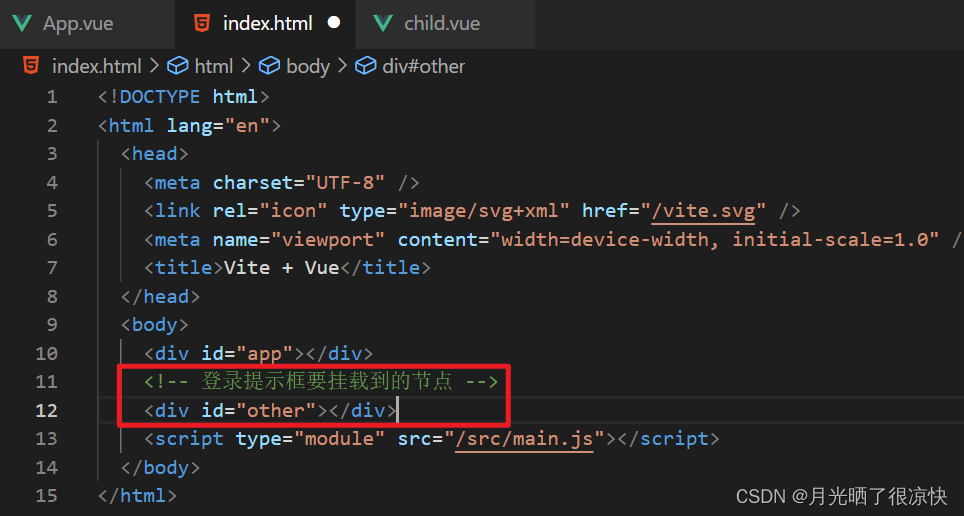
首先我们在根目录的 index.html 中添加一个新的挂载点:
父组件:
<template>
<div>
<button @click="isShow = !isShow">点击显示</button>
<Teleport to="#other">
<div v-if="isShow" class="modal">
<h3>提示框</h3>
<div>欢迎登录页面</div>
</div>
</Teleport>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { ref } from 'vue'
export default {
setup() {
let isShow = ref(false)
return { isShow }
}
}
</script>
<style lang="scss" scoped></style>

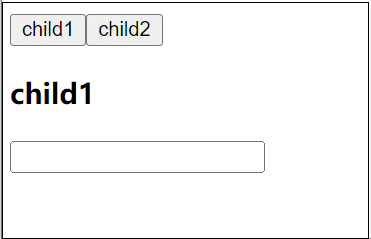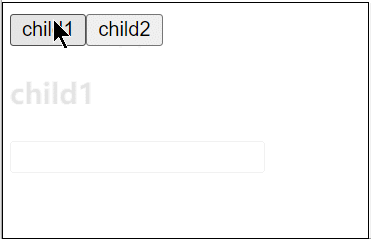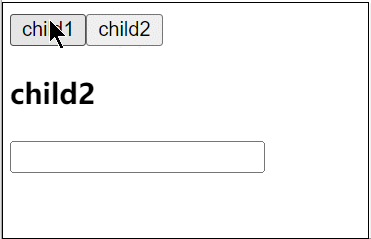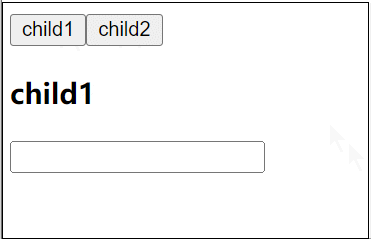
5. KeepAlive缓存组件
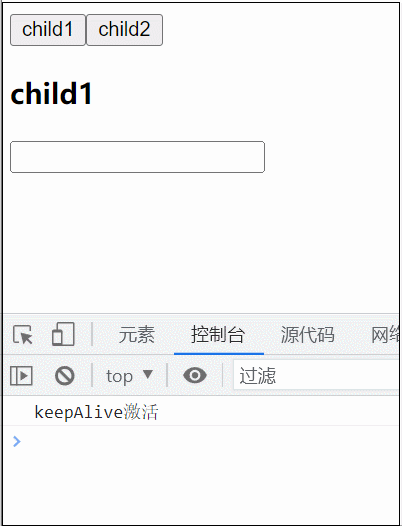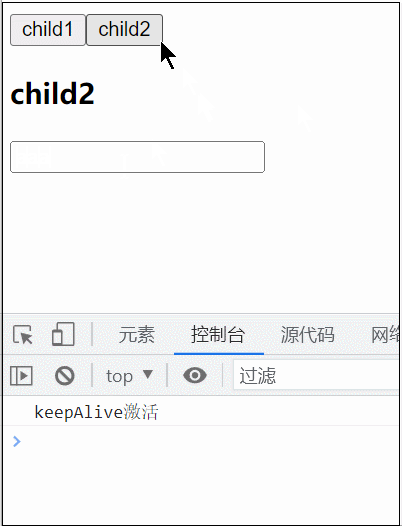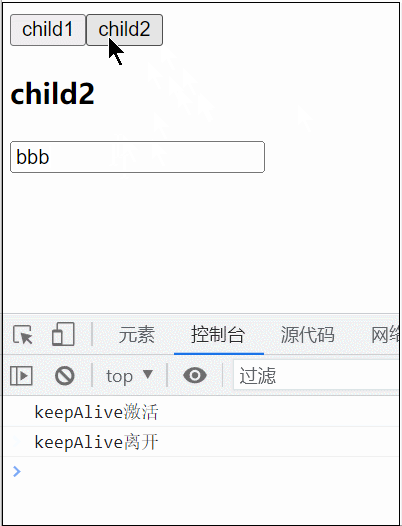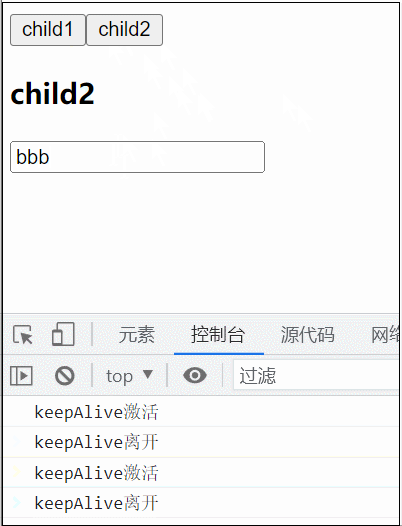
<KeepAlive> 是一个内置组件,它的功能是在多个组件间动态切换时缓存被移除的组件实例。
<template>
<div>
<button @click="cmp = 'child1'">child1</button>
<button @click="cmp = 'child2'">child2</button>
<!-- 只缓存 child2 中的内容 -->
<!-- <KeepAlive :include="['child1']"> -->
<!-- 如果是字符串,则一定不能有多余空格,多个以逗号隔开 -->
<!-- <KeepAlive include="child1"> -->
<!-- 使用正则匹配 -->
<KeepAlive :include="/child/">
<component :is="cmp"></component>
</KeepAlive>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { ref } from 'vue'
import child1 from './components/child1.vue'
import child2 from './components/child2.vue'
export default {
components: {
child1,
child2
},
setup() {
let cmp = ref('child1')
return { cmp }
}
}
</script>
<style lang="scss" scoped></style>
6. transition过渡组件
利用过渡组件实现元素的显示与隐藏:
<template>
<div>
<button @click="isShow = !isShow">点击显示</button>
<!-- 样式前缀,以v-开头 -->
<Transition name="v">
<div v-if="isShow" class="modal">
<h3>提示框</h3>
<div>欢迎登录页面</div>
</div>
</Transition>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { ref } from 'vue'
export default {
setup() {
let isShow = ref(false)
return { isShow }
}
}
</script>
<style lang="scss" scoped>
// enter 进场
// leave 出场
/* 在进场和退场的过程中,进行透明度的变化 */
.v-enter-active,
.v-leave-active {
transition: opacity 0.6s ease;
}
/* 进场开始和退场的结束 */
.v-enter-from,
.v-leave-to {
opacity: 0;
}
</style>

利用过渡组件和动态组件实现在组件间的切换:
<template>
<div>
<button @click="activeComponent = 'child1'">child1</button>
<button @click="activeComponent = 'child2'">child2</button>
<!-- 模式:先进入后退出 -->
<!-- <Transition name="v" mode="in-out"> -->
<!-- 模式:先退出后进入 -->
<Transition name="v" mode="out-in">
<component :is="activeComponent"></component>
</Transition>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { ref } from 'vue'
import child1 from './components/child1.vue'
import child2 from './components/child2.vue'
export default {
components: {
child1,
child2
},
setup() {
let isShow = ref(true)
let activeComponent = ref('child1')
return { isShow, activeComponent }
}
}
</script>
<style lang="scss" scoped>
// enter 进场
// leave 出场
/* 在进场和退场的过程中,进行透明度的变化 */
.v-enter-active,
.v-leave-active {
transition: opacity 0.3s ease;
}
/* 进场开始和退场的结束 */
.v-enter-from,
.v-leave-to {
opacity: 0;
}
</style>