需要源码和环境搭建请点赞关注收藏后评论区留下QQ~~~
一、Q-Learning算法
Q-Learning算法中动作值函数Q的更新方向是最优动作值函数q,而与Agent所遵循的行为策略无关,在评估动作值函数Q时,更新目标为最优动作值函数q的直接近似,故需要遍历当前状态的所有动作,在所有状态都能被无限次访问的前提下,Q-Learning算法能以1的概率收敛到最优动作值函数和最优策略
下图是估算最优策略的Q-Learning算法流程图
Q-Learning虽然是异策略,但是从值函数更新迭代式中可以看出,它并没有使用到重要性采样。

使用Q-Learning算法解决确定环境中的扫地机器人问题 参数设置与之前相同 使用贪心策略
机器人背景及环境搭建
输出如下
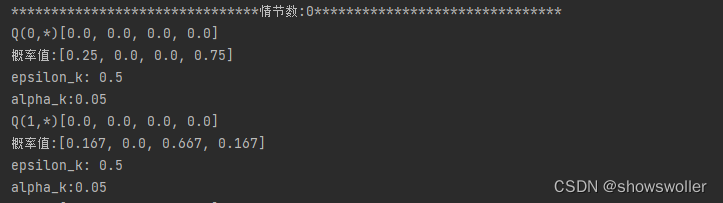
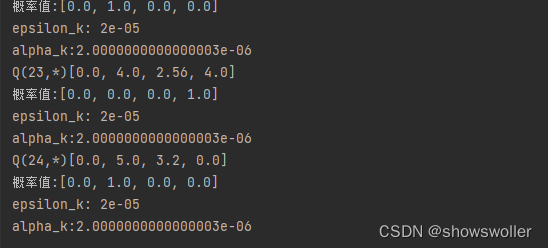
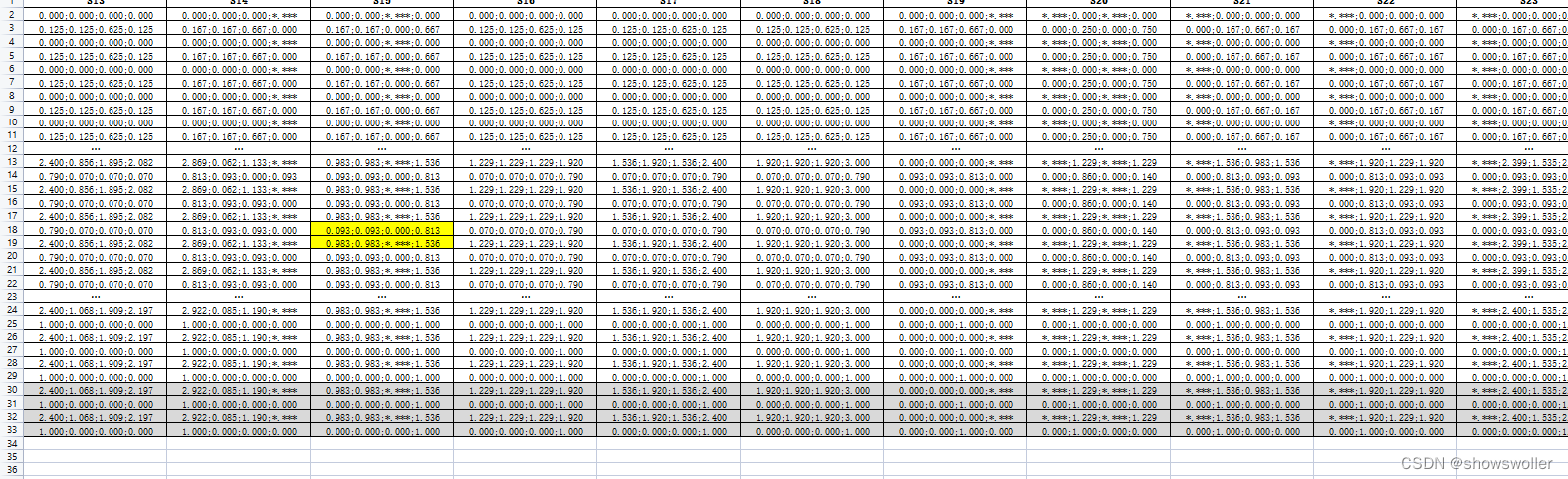
代码如下
#Q-learning算法
from 扫地机器人gym环境 import GridWorldEnv
import numpy as np
np.random.seed(1)
env = GridWorldEnv()
#有效动作空间
def vilid_action_space(s):
action_sacpe = []
if s % 5 != 0:#左
action_sacpe.append(0)
if s % 5 != 4:#右
action_sacpe.append(1)
if s <= 19:#上
action_sacpe.append(2)
if s >= 5:#下
action_sacpe.append(3)
return action_sacpe
def policy_epsilon_greedy(s, Q, epsilon):
Q_s = Q[s]
action = vilid_action_space(s)
if np.random.rand() < epsilon:
a = np.random.choice(action)
else:
index_a = np.argmax([Q_s[i] for i in action])
a = action[index_a]
return a
def trans1(Q_S):
new_Q = []
new_Q.append(Q_S[2])
new_Q.append(Q_S[3])
new_Q.append(Q_S[0])
new_Q.append(Q_S[1])
return new_Q
def trans(Q_S):
new_Q = []
new_Q.append(round(Q_S[2],3))
new_Q.append(round(Q_S[3],3))
new_Q.append(round(Q_S[0],3))
new_Q.append(round(Q_S[1],3))
return new_Q
def print_dd(s, a, next_s, print_len, episode_i, Q,e_k,a_k):
for i in range(2):
if episode_i == int(print_len * (0.1 * i + 1)):
if s == 15 and a == 3 and next_s == 10:
print("*********************************单步的计算过程***************************************")
print("alpha:"+str(a_k))
print("epsilon:"+str(e_k))
print("state:" + str(int(print_len * (0.1 * i + 1))))
print("Q(%d,%d)"%(s,a))
print(Q[s][a])
print("Q(%d,*)"%(next_s))
print(trans1(Q[next_s]))
print('output:'+str(Q[s][a] + a_k * (0.8 * np.max(Q[next_s]) - Q[s, a])))
def print_ff(list_q, Q, episode_i,epsilon_k,alpha_k):
list_s = range(0,25)
for em in list_q:
if em == episode_i:
print("*******************************情节数:%s*******************************"%(str(em)))
for state in list_s:
print("Q(%d,*)"%(state) + str(trans(Q[state])))
action = vilid_action_space(state)
len_a = len(action)
e_p = epsilon_k / float(len_a)
max_a = np.argmax(Q[state])
prob = []
index_a = np.argmax([Q[state][i] for i in action])
for i in range(4):#计算epsilon
if i not in action:
prob.append(0.0)
else:
if i == action[index_a]:
prob.append(1 - epsilon_k + e_p)
else:
prob.append(e_p)
print('概率值:' + str(trans(prob)))
print("epsilon_k: {}".format(epsilon_k))
print("alpha_k:{}".format(alpha_k))
def Attenuation(epsilon,alpha,episode_sum,episode):
epsilon = (float(episode_sum) - float(episode)) / float(episode_sum) * epsilon
alpha = (float(episode_sum) - float(episode)) / float(episode_sum) * alpha
return epsilon, alpha
while not done:
a = policy_epsilon_greedy(s, Q, epsilon_k)
next_s, r, done, _ = env.step(a)
print_dd(s, a, next_s, 10000, episode_i, Q, epsilon_k, alpha_k)
Q[s, a] += alpha_k * (r + gamma * np.max(Q[next_s]) - Q[s, a])
s = next_s
return Q
Q = Q_Learning(env, 25000, 0.05, 0.8, 0.5)二、期望Sarsa算法
通过对Sarsa算法进行改进,得到一种异策略TD算法,该算法考虑当前策略下所有动作的可能性,利用动作值函数的期望值取代某一特定动作值函数来更新估计值,该算法称为期望Sarsa算法。
相比于Sarsa算法,期望Sarsa算法计算更为复杂,但通过计算能够有效地消除银随机选择而产生的方差,因此通常情况下,期望Sarsa算法明显优于Sarsa算法,另外期望Sarsa算法还可以使用异策略方法,将Q-Learning进行推广并提升性能
下面利用期望Sarsa算法解决确定环境扫地机器人问题 背景与前面相同 不再赘述
迭代到20000次后基本Q值已经收敛
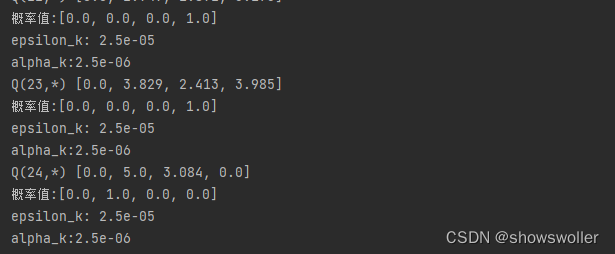
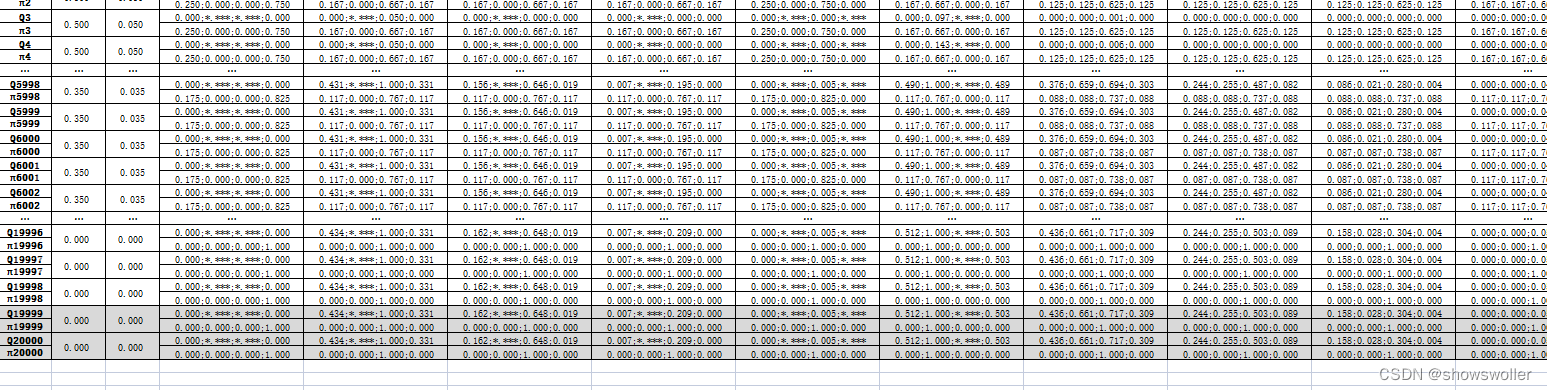
代码如下
# 期望Sarsa算法
from 扫地机器人gym环境 import GridWorldEnv
import numpy as np
from queue import Queue
np.random.seed(1)
env = GridWorldEnv()
# 有效动作空间
def vilid_action_space(s):
action_sacpe = []
if s % 5 != 0: # 左
action_sacpe.append(0)
if s % 5 != 4: # 右
action_sacpe.append(1)
if s <= 19: # 上
action_sacpe.append(2)
if s >= 5: # 下
action_sacpe.append(3)
return action_sacpe
def policy_epsilon_greedy(s, Q, epsilon):
Q_s = Q[s]
action = vilid_action_space(s)
if np.random.rand() < epsilon:
a = np.random.choice(action)
else:
index_a = np.argmax([Q_s[i] for i in action])
a = action[index_a]
return a
def compute_epsion(s, Q, epsilon):
max_a = np.argmax(Q[s])
action = vilid_action_space(s)
len_all_a = len(action)
prob_l = [0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0]
for index_a in action:
if index_a == max_a:
prob_l[index_a] = 1.0 - epsilon + (epsilon / len_all_a)
else:
prob_l[index_a] = epsilon / len_all_a
return prob_l
def compute_e_q(prob, q_n):
sum = 0.0
for i in range(4):
sum += prob[i] * q_n[i]
return sum
def trans1(Q_S):
new_Q = []
new_Q.append(Q_S[2])
new_Q.append(Q_S[3])
new_Q.append(Q_S[0])
new_Q.append(Q_S[1])
return new_Q
def print_dd(s, a, next_s, print_len, episode_i, Q, e_k, a_k):
for i in range(50):
if episode_i == int(print_len * ((0.02 * i) + 1)):
if s == 15 and a == 3 and next_s == 10:
print("*****************************单步计算过程****************************************")
print("alpha:" + str(a_k))
print("epsilon:" + str(e_k))
print("state:" + str(int(print_len * (1 + (0.02 * i)))))
print("Q(%d,%d)" % (s, a))
print(Q[s][a])
print("Q(%d,*)" % (next_s))
print(trans1(Q[next_s]))
prob_l = compute_epsion(next_s, Q, e_k)
print('概率' + str(trans1(prob_l)))
Q_e = compute_e_q(prob_l, Q[next_s])
print('update:' + str(Q[s, a] + a_k * (0.8 * Q_e - Q[s, a])))
def trans(Q_S):
new_Q = []
new_Q.append(round(Q_S[2], 3))
new_Q.append(round(Q_S[3], 3))
new_Q.append(round(Q_S[0], 3))
new_Q.append(round(Q_S[1], 3))
return new_Q
def print_ff(list_q, Q, episode_i, epsilon_k, alpha_k):
list_s = range(0, 25)
for em in list_q:
if em == episode_i:
print("*******************************情节数:%s*******************************" % (str(em)))
for state in list_s:
print("Q(%d,*) " % (state) + str(trans(Q[state])))
action = vilid_action_space(state)
len_a = len(action)
e_p = epsilon_k / float(len_a)
prob = []
index_a = np.argmax([Q[state][i] for i in action])
for i in range(4): # 计算epsilon
if i not in action:
prob.append(0.0)
else:
if i == action[index_a]:
prob.append(1 - epsilon_k + e_p)
else:
prob.append(e_p)
print('概率值:' + str(trans(prob)))
print("epsilon_k: {}".format(epsilon_k))
print("alpha_k:{}".format(alpha_k))
def Attenuation(epsilon, alpha, episode_sum, episode):
epsilon = (float(episode_sum) - float(episode)) / float(episode_sum) * epsilon
alpha = (float(episode_sum) - float(episode)) / float(episode_sum) * alpha
return epsilon, alpha
def Expectation_sarsa(env, episode_num, alpha, gamma, epsilon):
Q = np.zeros((env.n_width * env.n_height, env.action_space.n))
Q_queue = Queue(maxsize=11)
lon_k, alpha_k)
prob_l = compute_epsion(next_s, Q, epsilon_k)
Q_e = compute_e_q(prob_l, Q[next_s])
Q[s, a] += alpha_k * (r + gamma * Q_e - Q[s, a])
s = next_s
return Q
Q = Expectation_sarsa(env, 20000, 0.05, 0.8, 0.5)创作不易 觉得有帮助请点赞关注收藏~~~