文章目录
- 核心原理
- 数据写
- 写操作
- UPSERT写流程
- INSERT写流程
- INSERT OVERWRIT写流程
- Key 生成策略
- 删除策略
- 写流程归纳
- 数据读
- 集成Spark使用
- 环境准备
- spark-shell使用
- 启动
- 插入数据
- 查询数据
- 更新数据
- 时间旅行查询
- 增量查询
- 指定时间点查询
- 删除数据
- 覆盖数据
- spark-sql使用
- 启动
- 创建表
- 插入数据
- 时间旅行查询
- 更新数据
- 删除数据
- 覆盖数据
- 其他
核心原理
数据写
写操作
- UPSERT:默认行为,数据先通过 index 打标(INSERT/UPDATE),有一些启发式算法决定消息的组织以优化文件的大小 => CDC 导入。
- INSERT:跳过 index,写入效率更高 => Log Deduplication。
- BULK_INSERT:写排序,对大数据量的 Hudi 表初始化友好,是对文件大小的限制最好效果(写 HFile)。
UPSERT写流程
- Copy On Write (COW)
- 先对 records 按照 record key 去重。
- 首先对这批数据创建索引 (HoodieKey => HoodieRecordLocation);通过索引区分哪些 records 是 update,哪些 records 是 insert(key 第一次写入)。
- 对于 update 消息,会直接找到对应 key 所在的最新 FileSlice 的 base 文件,并做 merge 后写新的 base file (新的 FileSlice)。
- 对于 insert 消息,会扫描当前 partition 的所有 SmallFile(小于一定大小的 base file),然后 merge 写新的 FileSlice;如果没有 SmallFile,直接写新的 FileGroup + FileSlice。
- Merge On Read (MOR)
- 先对 records 按照 record key 去重(可选)。
- 首先对这批数据创建索引 (HoodieKey => HoodieRecordLocation);通过索引区分哪些 records 是 update,哪些 records 是 insert(key 第一次写入)。
- 如果是 insert 消息,如果 log file 不可建索引(默认),会尝试 merge 分区内最小的 base file (不包含 log file 的 FileSlice),生成新的 FileSlice;如果没有 base file 就新写一个 FileGroup + FileSlice + base file;如果 log file 可建索引,尝试 append 小的 log file,如果没有就新写一个 FileGroup + FileSlice + base file。
- 如果是 update 消息,写对应的 file group + file slice,直接 append 最新的 log file(如果碰巧是当前最小的小文件,会 merge base file,生成新的 file slice)。
- log file 大小达到阈值会 roll over 一个新的。
INSERT写流程
- Copy On Write
- 先对 records 按照 record key 去重(可选)。
- 不会创建 Index。
- 如果有小的 base file 文件,merge base file,生成新的 FileSlice + base file,否则直接写新的 FileSlice + base file。
- Merge On Read
- 先对 records 按照 record key 去重(可选)。
- 不会创建 Index。
- 如果 log file 可索引,并且有小的 FileSlice,尝试追加或写最新的 log file;如果 log file 不可索引,写一个新的 FileSlice + base file。
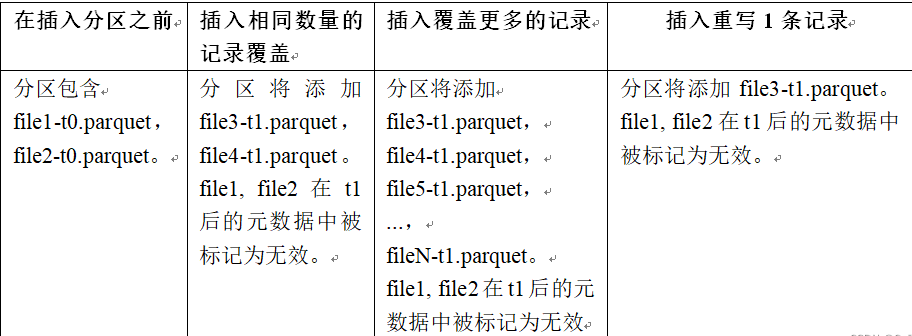
INSERT OVERWRIT写流程
在同一分区中创建新的文件组集,现有的文件组被标记为 “删除”,根据新记录的数量创建新的文件组。
COW流程如下
MOR流程如下
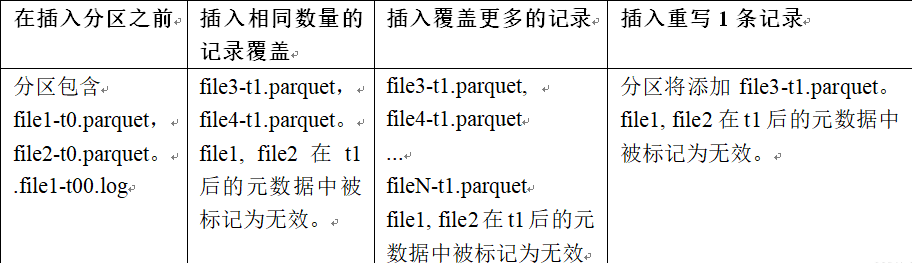
- 优点
- COW和MOR在执行方面非常相似。不干扰MOR的compaction。
- 减少parquet文件大小。
- 不需要更新关键路径中的外部索引。索引实现可以检查文件组是否无效(类似于在HBaseIndex中检查commit是否无效的方式)。
- 可以扩展清理策略,在一定的时间窗口后删除旧文件组。
- 缺点
- 需要转发以前提交的元数据。
- 在t1,比如file1被标记为无效,我们在t1.commit中存储 “invalidFiles=file1”(或者在MOR中存储deltacommit)。
- 在t2,比如file2也被标记为无效。我们转发之前的文件,并在t2.commit中标记 “invalidFiles=file1, file2”(或MOR的deltacommit)。
- 忽略磁盘中存在的parquet文件也是Hudi的一个新行为, 可能容易出错,我们必须认识到新的行为,并更新文件系统的所有视图来忽略它们。这一点可能会在实现其他功能时造成问题。
Key 生成策略
用来生成 HoodieKey(record key + partition path),目前支持以下策略:
- 支持多个字段组合 record keys。
- 支持多个字段组合的 parition path (可定制时间格式,Hive style path name)。
- 非分区表
删除策略
- 逻辑删:将 value 字段全部标记为 null。
- 物理删:
- 通过 OPERATION_OPT_KEY 删除所有的输入记录。
- 配置 PAYLOAD_CLASS_OPT_KEY = org.apache.hudi.EmptyHoodieRecordPayload 删除所有的输入记录。
- 在输入记录添加字段:_hoodie_is_deleted。
写流程归纳
通过对写流程的梳理可以了解到 Apache Hudi 相对于其他数据湖方案的核心优势:
- 写入过程充分优化了文件存储的小文件问题,Copy On Write 写会一直将一个 bucket (FileGroup)的 base 文件写到设定的阈值大小才会划分新的 bucket;Merge On Read 写在同一个 bucket 中,log file 也是一直 append 直到大小超过设定的阈值 roll over。
- 对 UPDATE 和 DELETE 的支持非常高效,一条 record 的整个生命周期操作都发生在同一个 bucket,不仅减少小文件数量,也提升了数据读取的效率(不必要的 join 和 merge)。
数据读
- Snapshot 读:读取所有 partiiton 下每个 FileGroup 最新的 FileSlice 中的文件,Copy On Write 表读 parquet 文件,Merge On Read 表读 parquet + log 文件。
- Incremantal读:当前的 Spark data source 可以指定消费的起始和结束 commit 时间,读取 commit 增量的数据集。但是内部的实现不够高效:拉取每个 commit 的全部目标文件再按照系统字段 hoodie_commit_time apply 过滤条件。
- Streaming读:0.8.0 版本的 HUDI Flink writer 支持实时的增量订阅,可用于同步 CDC 数据,日常的数据同步 ETL pipeline。Flink 的 streaming 读做到了真正的流式读取,source 定期监控新增的改动文件,将读取任务下派给读 task。
- Compaction 合并
- 没有 base file:走 copy on write insert 流程,直接 merge 所有的 log file 并写 base file。
- 有 base file:走 copy on write upsert 流程,先读 log file 建 index,再读 base file,最后读 log file 写新的 base file。
- Flink 和 Spark streaming 的 writer 都可以 apply 异步的 compaction 策略,按照间隔 commits 数或者时间来触发 compaction 任务,在独立的 pipeline 中执行。
集成Spark使用
环境准备
- 安装Spark
Hudi使用Spark-2.4.3+和Spark 3。x版本。Hudi支持的Spark版本如下:
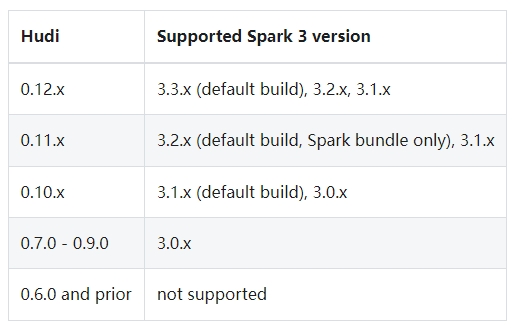
解压spark-3.3.0-bin-hadoop3.tgz,配置Spark环境变量
vim /etc/profile
export SPARK_HOME=/home/commons/spark-3.3.0-bin-hadoop3
export PATH=$SPARK_HOME/bin:$PATH
source /etc/profile
然后将前面编译的hudi-spark3.3-bundle_2.12-0.12.1.jar(在hudi的根目录下packaging/hudi-spark-bundle/target/,至于如何编译请看前面的内容)拷贝到Spark根目录下Jars目录。
- 启动hadoop(详细看前面关于hadoop的文章)
spark-shell使用
启动
不同版本(Spark 3.3、Spark 3.2、Spark 3.1、Spark 2.4)的spark-shell启动命令有所不同,下面以Spark 3.3来操作演示。
spark-shell \
--packages org.apache.hudi:hudi-spark3.3-bundle_2.12:0.12.1 \
--conf 'spark.serializer=org.apache.spark.serializer.KryoSerializer' \
--conf 'spark.sql.catalog.spark_catalog=org.apache.spark.sql.hudi.catalog.HoodieCatalog' \
--conf 'spark.sql.extensions=org.apache.spark.sql.hudi.HoodieSparkSessionExtension'
接下来设置表名、基本路径和数据生成器
import org.apache.hudi.QuickstartUtils._
import scala.collection.JavaConversions._
import org.apache.spark.sql.SaveMode._
import org.apache.hudi.DataSourceReadOptions._
import org.apache.hudi.DataSourceWriteOptions._
import org.apache.hudi.config.HoodieWriteConfig._
import org.apache.hudi.common.model.HoodieRecord
val tableName = "hudi_trips_cow"
val basePath = "file:///tmp/hudi_trips_cow"
val dataGen = new DataGenerator
DataGenerator可以根据旅行应用生成相应的样例数据插入和更新;spark中不需要单独的create table命令如果表不存在,第一批写入操作将创建该表。
插入数据
接下来通过DataGenerator生成一些新的行程数据,将它们加载到DataFrame中,并将DataFrame写入Hudi表中。
val inserts = convertToStringList(dataGen.generateInserts(10))
val df = spark.read.json(spark.sparkContext.parallelize(inserts, 2))
df.write.format("hudi").
options(getQuickstartWriteConfigs).
option(PRECOMBINE_FIELD_OPT_KEY, "ts").
option(RECORDKEY_FIELD_OPT_KEY, "uuid").
option(PARTITIONPATH_FIELD_OPT_KEY, "partitionpath").
option(TABLE_NAME, tableName).
mode(Overwrite).
save(basePath)
mode为Overwrite如果表存在则覆盖重新创建表。可以从basePath = “file:///tmp/hudi_trips_cow” 配置的本地文件目录查看hoodie的元数据和数据的变化。
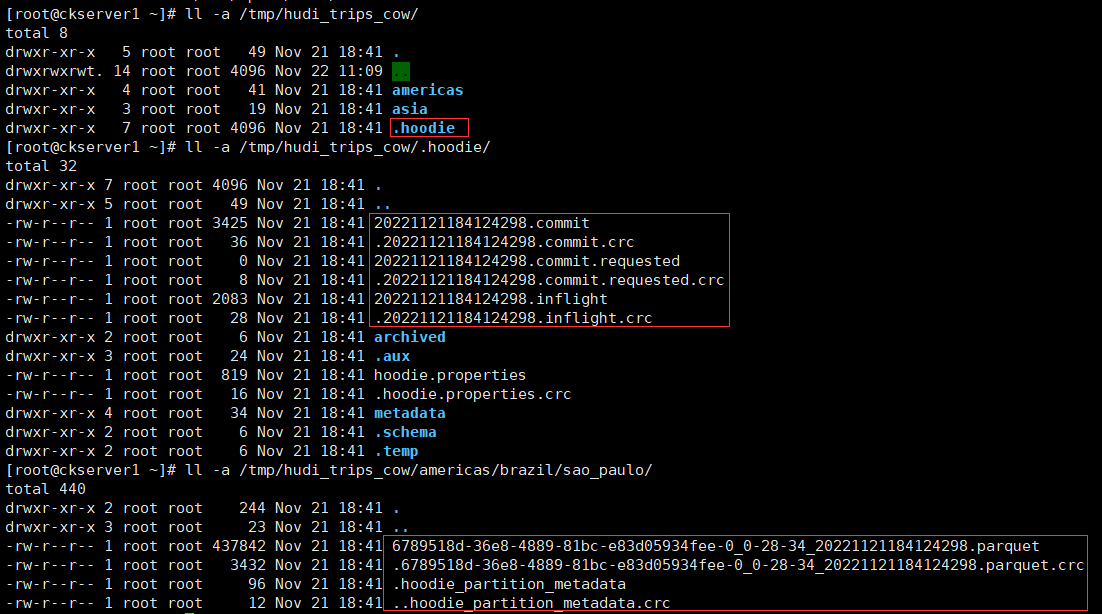
还可以通过外部化配置文件,可以在配置文件Hudi -default.conf中集中设置配置,而不是直接将配置设置传递给每个Hudi作业。
查询数据
先转成spark的df,然后再执行spark sql的查询
val tripsSnapshotDF = spark.
read.
format("hudi").
load(basePath)
tripsSnapshotDF.createOrReplaceTempView("hudi_trips_snapshot")
spark.sql("select fare, begin_lon, begin_lat, ts from hudi_trips_snapshot where fare > 20.0").show()
spark.sql("select _hoodie_commit_time, _hoodie_record_key, _hoodie_partition_path, rider, driver, fare from hudi_trips_snapshot").show()
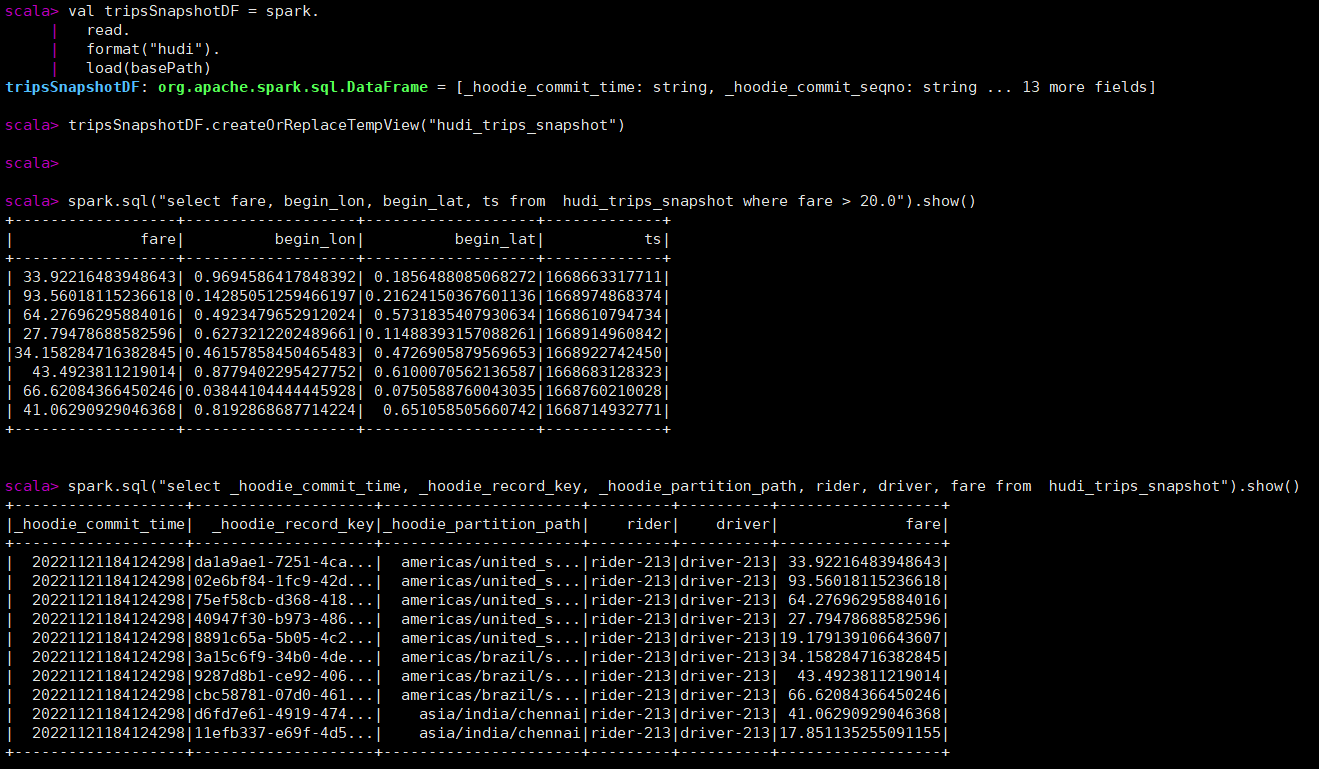
每个hoodie表固定加了如下的五个字段,hoodie提交时间、hoodie提交序号、hoodie记录键、hoodie分区路径、hoodie文件名。
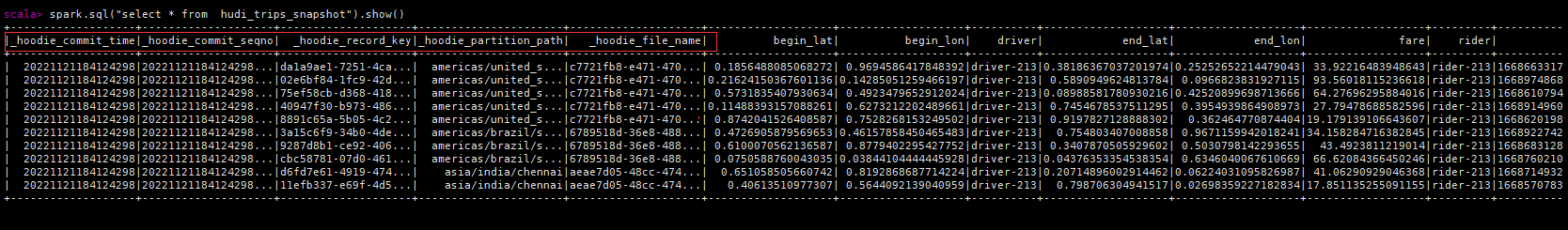
更新数据
类似于插入新数据,同样使用数据生成器生成新的行程的数据,加载到DataFrame中,并将DataFrame写入hudi表。
val updates = convertToStringList(dataGen.generateUpdates(10))
val df = spark.read.json(spark.sparkContext.parallelize(updates, 2))
df.write.format("hudi").
options(getQuickstartWriteConfigs).
option(PRECOMBINE_FIELD_OPT_KEY, "ts").
option(RECORDKEY_FIELD_OPT_KEY, "uuid").
option(PARTITIONPATH_FIELD_OPT_KEY, "partitionpath").
option(TABLE_NAME, tableName).
mode(Append).
save(basePath)
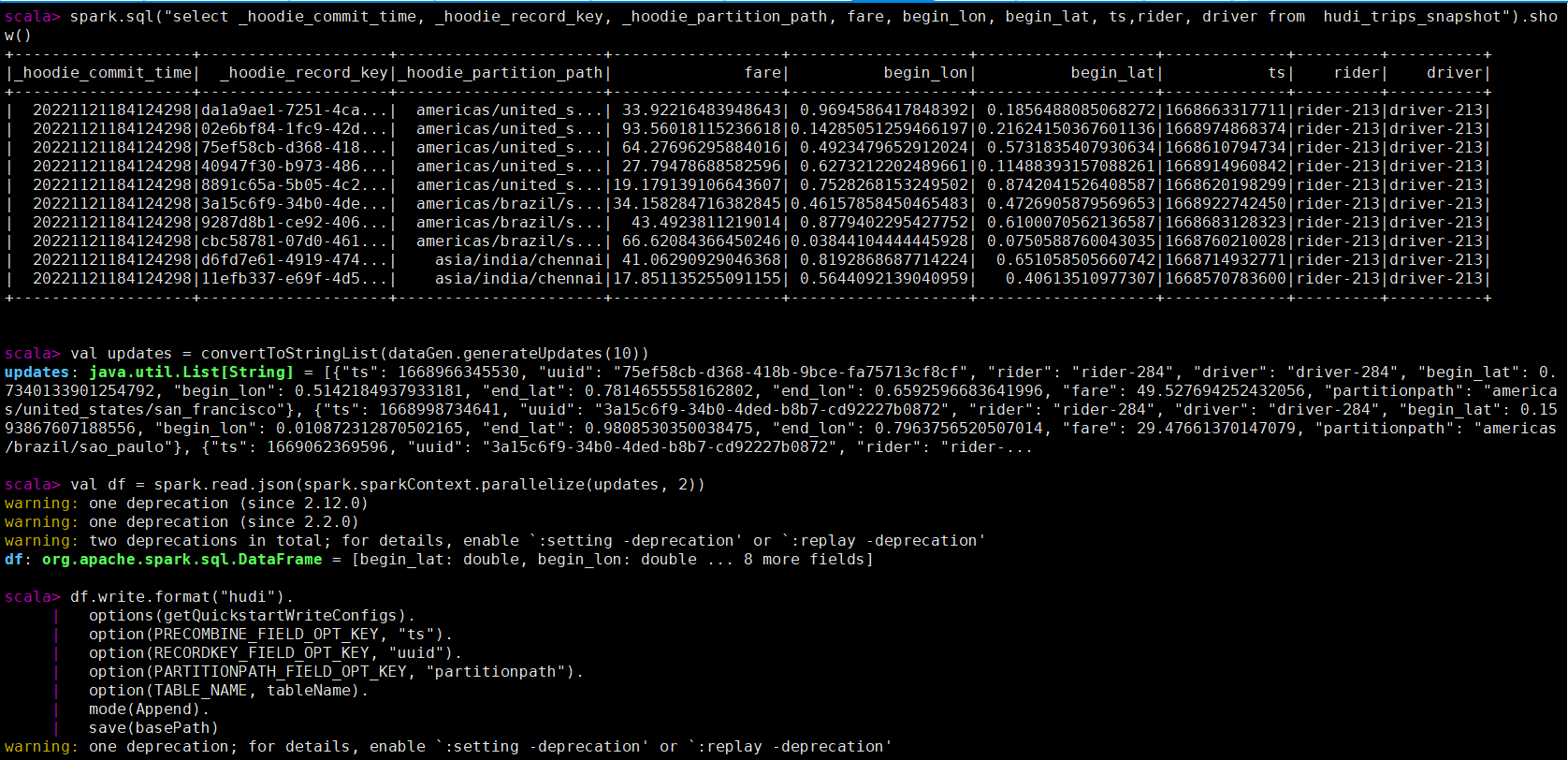
注意,现在保存模式是追加。通常,总是使用追加模式,除非您试图第一次创建表。再次查询数据将显示更新的行程。每个写操作都会生成一个由时间戳表示的新提交。在之前的提交中寻找相同的_hoodie_record_keys的_hoodie_commit_time、rider、driver字段的变化。
val tripsSnapshotDF = spark.
read.
format("hudi").
load(basePath)
tripsSnapshotDF.createOrReplaceTempView("hudi_trips_snapshot")
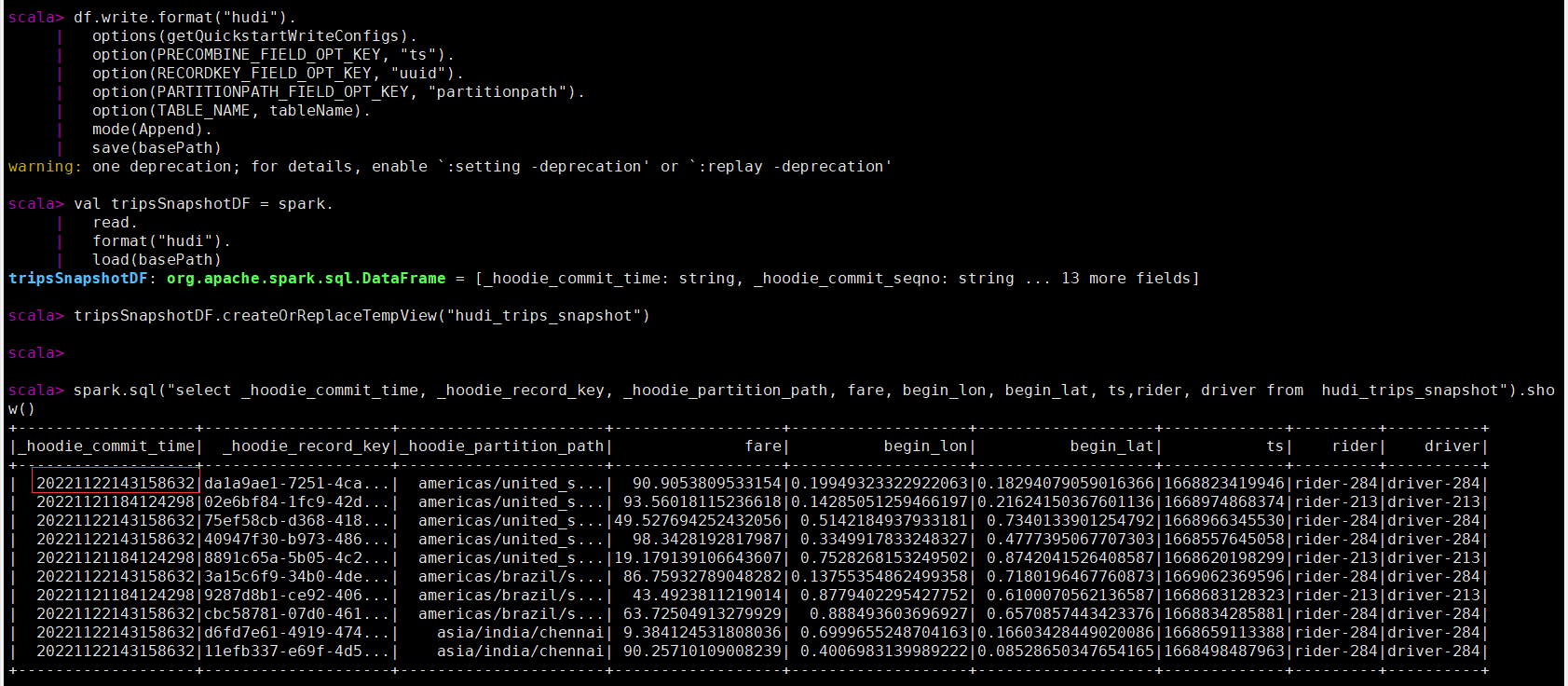
spark.sql("select _hoodie_commit_time, _hoodie_record_key, _hoodie_partition_path, fare, begin_lon, begin_lat, ts,rider, driver from hudi_trips_snapshot").show()
查询更新后的数据,已经有部分未更新后的数据,提交时间也有其他的值,记录数还是10条。
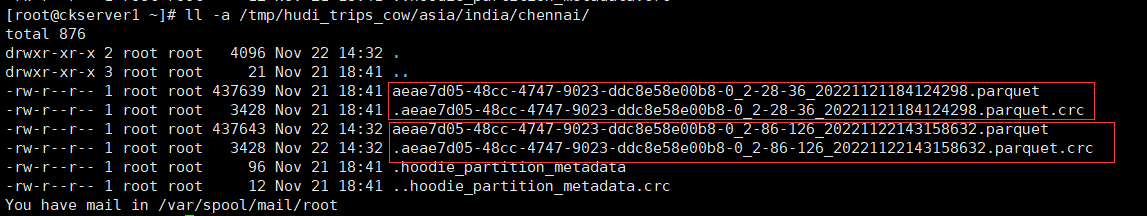
查看hoodie目录下已经多个一个版本文件
时间旅行查询
从0.9.0开始支持时间旅行查询。目前支持三种查询时间格式,如下所示
val tripsSnapshotDF = spark.read.
format("hudi").
option("as.of.instant", "20221122143158632").
load(basePath)
spark.read.
format("hudi").
option("as.of.instant", "2022-11-22 14:31:58.632").
load(basePath)
// 等价于"as.of.instant = 2022-11-22 00:00:00"
spark.read.
format("hudi").
option("as.of.instant", "2022-11-22").
load(basePath)
使用第一种示例如下:
val tripsSnapshotDF1 = spark.read.
format("hudi").
option("as.of.instant", "20221121184124298").
load(basePath)
tripsSnapshotDF1.createOrReplaceTempView("hudi_trips_snapshot1")
spark.sql("select _hoodie_commit_time, _hoodie_record_key, _hoodie_partition_path, fare, begin_lon, begin_lat, ts,rider, driver from hudi_trips_snapshot1").show()

增量查询
Hudi还提供了获取自给定提交时间戳以来更改的记录流的功能。这可以通过使用Hudi的增量查询来实现,并提供需要流化更改的开始时间。如果希望在给定的提交之后进行所有更改(通常是这样),则不需要指定endTime。这将给出在beginTime提交后发生的所有更改,过滤器为fare > 20.0。该特性的独特之处在于,它现在允许您在批处理数据上编写流管道。利用增量管道可以在批处理数据上创建增量管道。
先将上面的更新数据多执行几次,产生多个版本的数据
spark.
read.
format("hudi").
load(basePath).
createOrReplaceTempView("hudi_trips_snapshot")
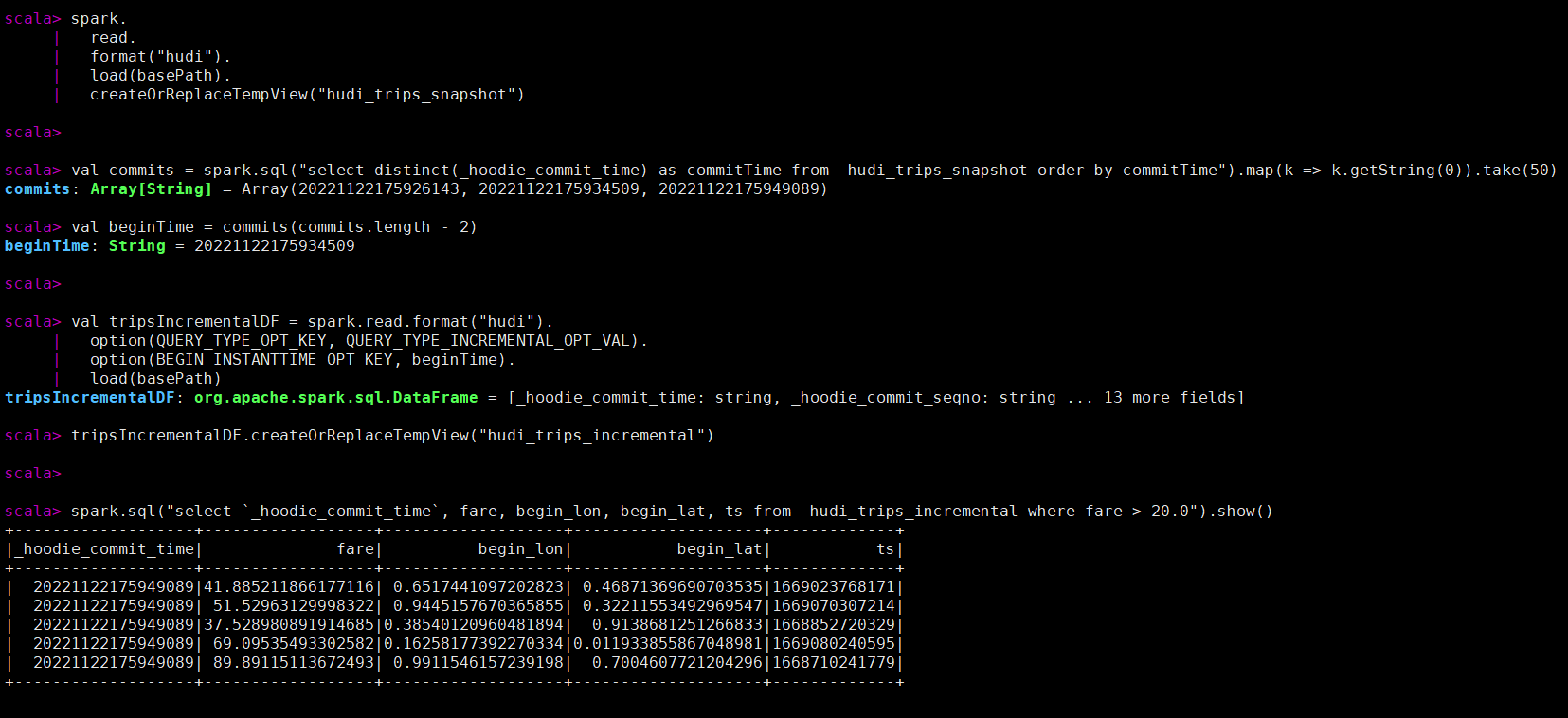
val commits = spark.sql("select distinct(_hoodie_commit_time) as commitTime from hudi_trips_snapshot order by commitTime").map(k => k.getString(0)).take(50)
val beginTime = commits(commits.length - 2)
val tripsIncrementalDF = spark.read.format("hudi").
option(QUERY_TYPE_OPT_KEY, QUERY_TYPE_INCREMENTAL_OPT_VAL).
option(BEGIN_INSTANTTIME_OPT_KEY, beginTime).
load(basePath)
tripsIncrementalDF.createOrReplaceTempView("hudi_trips_incremental")
spark.sql("select `_hoodie_commit_time`, fare, begin_lon, begin_lat, ts from hudi_trips_incremental where fare > 20.0").show()
指定时间点查询
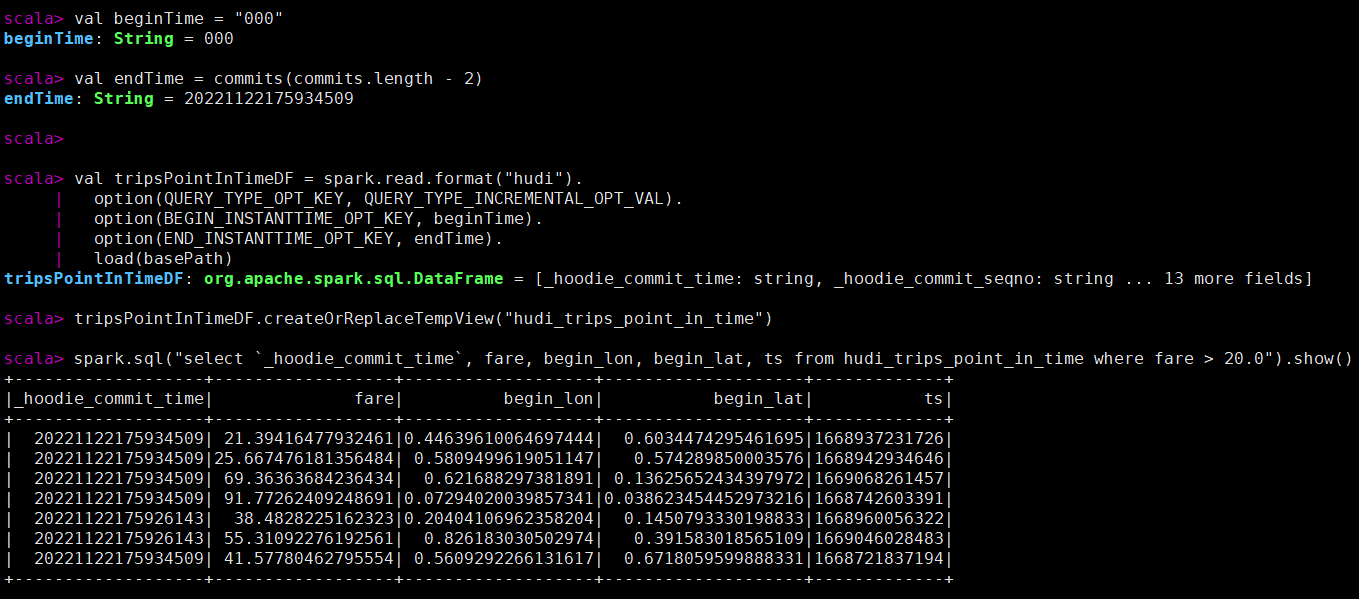
时间可以通过将endTime指向特定的提交时间,将beginTime指向“000”(表示尽可能早的提交时间)来表示。
val beginTime = "000"
val endTime = commits(commits.length - 2)
val tripsPointInTimeDF = spark.read.format("hudi").
option(QUERY_TYPE_OPT_KEY, QUERY_TYPE_INCREMENTAL_OPT_VAL).
option(BEGIN_INSTANTTIME_OPT_KEY, beginTime).
option(END_INSTANTTIME_OPT_KEY, endTime).
load(basePath)
tripsPointInTimeDF.createOrReplaceTempView("hudi_trips_point_in_time")
spark.sql("select `_hoodie_commit_time`, fare, begin_lon, begin_lat, ts from hudi_trips_point_in_time where fare > 20.0").show()
删除数据
Apache Hudi支持两种类型的删除:
- 软删除:保留记录键,只清除所有其他字段的值(软删除中为空的记录始终保存在存储中,而不会删除)。注意,保存模式是追加。
先查询当前记录数
spark.
read.
format("hudi").
load(basePath).
createOrReplaceTempView("hudi_trips_snapshot")
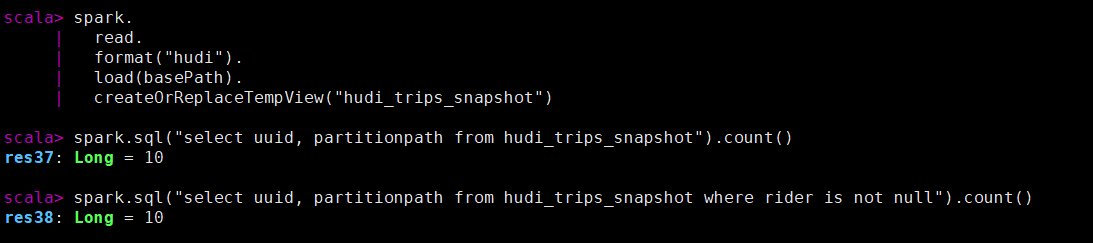
spark.sql("select uuid, partitionpath from hudi_trips_snapshot").count()
spark.sql("select uuid, partitionpath from hudi_trips_snapshot where rider is not null").count()
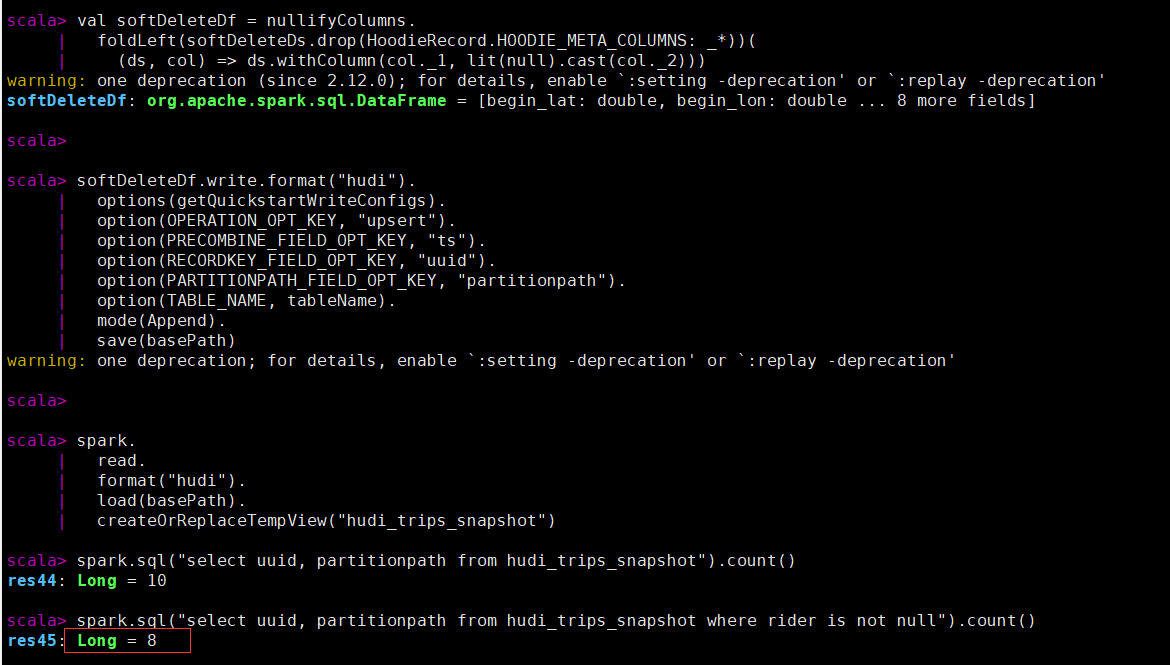
执行软删除后查看记录数,有两条被置为空。
val softDeleteDs = spark.sql("select * from hudi_trips_snapshot").limit(2)
val nullifyColumns = softDeleteDs.schema.fields.
map(field => (field.name, field.dataType.typeName)).
filter(pair => (!HoodieRecord.HOODIE_META_COLUMNS.contains(pair._1)
&& !Array("ts", "uuid", "partitionpath").contains(pair._1)))
val softDeleteDf = nullifyColumns.
foldLeft(softDeleteDs.drop(HoodieRecord.HOODIE_META_COLUMNS: _*))(
(ds, col) => ds.withColumn(col._1, lit(null).cast(col._2)))
softDeleteDf.write.format("hudi").
options(getQuickstartWriteConfigs).
option(OPERATION_OPT_KEY, "upsert").
option(PRECOMBINE_FIELD_OPT_KEY, "ts").
option(RECORDKEY_FIELD_OPT_KEY, "uuid").
option(PARTITIONPATH_FIELD_OPT_KEY, "partitionpath").
option(TABLE_NAME, tableName).
mode(Append).
save(basePath)
spark.
read.
format("hudi").
load(basePath).
createOrReplaceTempView("hudi_trips_snapshot")
spark.sql("select uuid, partitionpath from hudi_trips_snapshot").count()
spark.sql("select uuid, partitionpath from hudi_trips_snapshot where rider is not null").count()
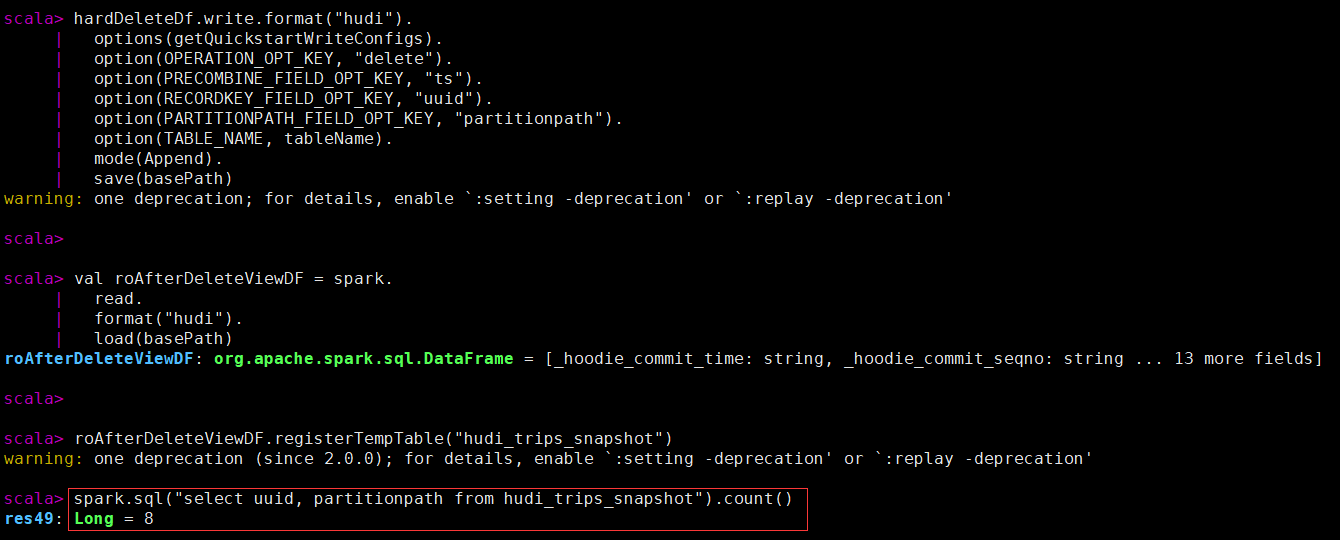
- 硬删除:从表中物理删除记录的任何痕迹。
删除传进来的hoodiekey记录,删除操作只支持“追加”模式。
spark.sql("select uuid, partitionpath from hudi_trips_snapshot").count()
val ds = spark.sql("select uuid, partitionpath from hudi_trips_snapshot").limit(2)
val deletes = dataGen.generateDeletes(ds.collectAsList())
val hardDeleteDf = spark.read.json(spark.sparkContext.parallelize(deletes, 2))
hardDeleteDf.write.format("hudi").
options(getQuickstartWriteConfigs).
option(OPERATION_OPT_KEY, "delete").
option(PRECOMBINE_FIELD_OPT_KEY, "ts").
option(RECORDKEY_FIELD_OPT_KEY, "uuid").
option(PARTITIONPATH_FIELD_OPT_KEY, "partitionpath").
option(TABLE_NAME, tableName).
mode(Append).
save(basePath)
val roAfterDeleteViewDF = spark.
read.
format("hudi").
load(basePath)
roAfterDeleteViewDF.registerTempTable("hudi_trips_snapshot")
spark.sql("select uuid, partitionpath from hudi_trips_snapshot").count()
覆盖数据
生成一些新的行程数据,覆盖输入中出现的所有分区。对于批处理ETL作业,此操作比upsert快,批处理ETL作业一次重新计算整个目标分区(与增量更新目标表相反)。这是由于能够完全绕过索引、预合并和upsert写路径中的其他重分区步骤。
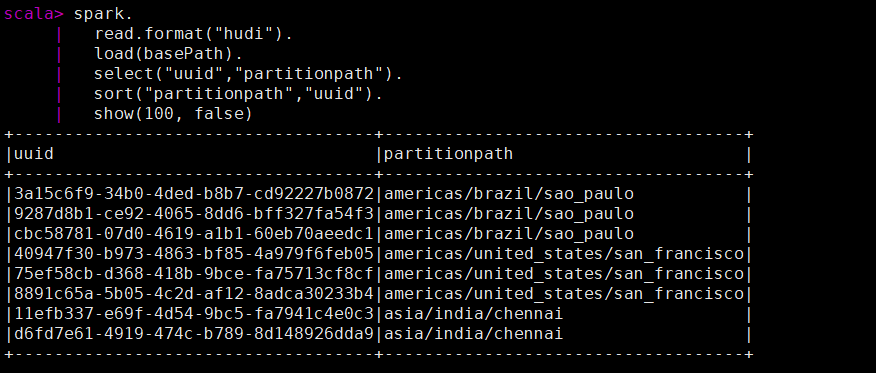
先查看当前的key数据
spark.
read.format("hudi").
load(basePath).
select("uuid","partitionpath").
sort("partitionpath","uuid").
show(100, false)
执行覆盖数据操作(类似hive的insert overwrite的功能)后查看key的数据。
val inserts = convertToStringList(dataGen.generateInserts(10))
val df = spark.
read.json(spark.sparkContext.parallelize(inserts, 2)).
filter("partitionpath = 'americas/united_states/san_francisco'")
df.write.format("hudi").
options(getQuickstartWriteConfigs).
option(OPERATION.key(),"insert_overwrite").
option(PRECOMBINE_FIELD.key(), "ts").
option(RECORDKEY_FIELD.key(), "uuid").
option(PARTITIONPATH_FIELD.key(), "partitionpath").
option(TBL_NAME.key(), tableName).
mode(Append).
save(basePath)
spark.
read.format("hudi").
load(basePath).
select("uuid","partitionpath").
sort("partitionpath","uuid").
show(100, false)
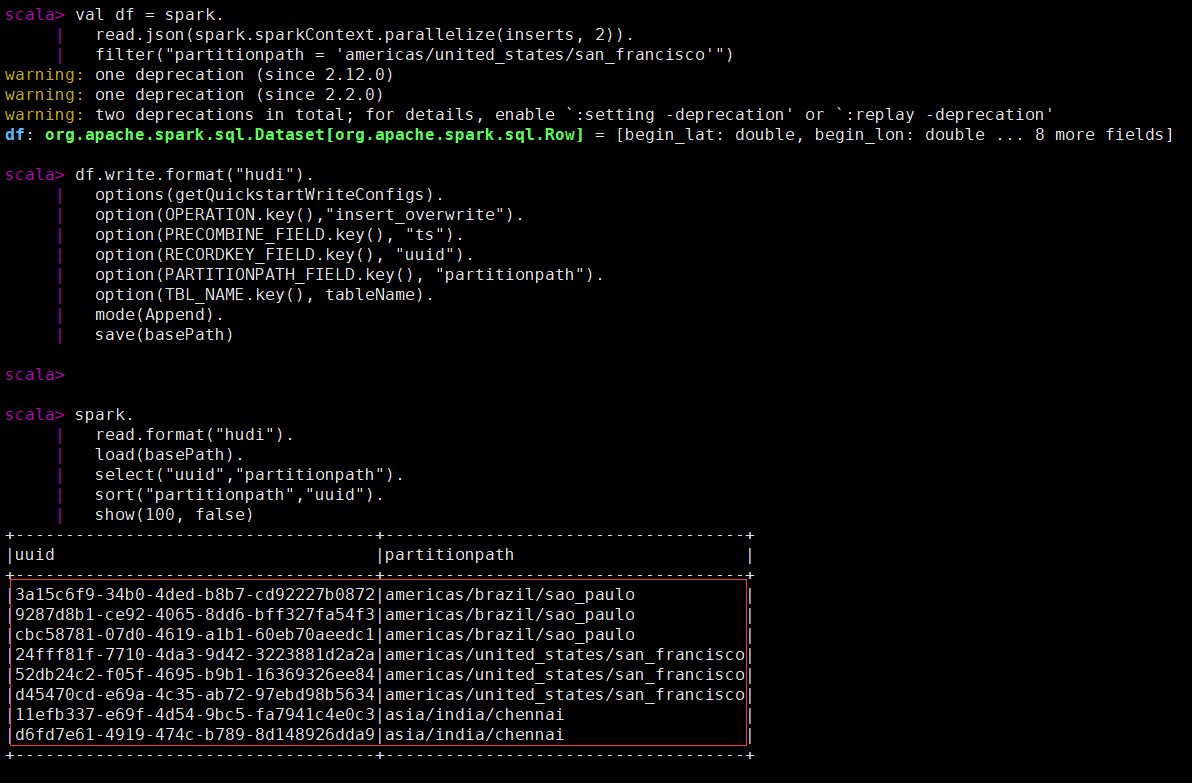
spark-sql使用
启动
Hudi支持使用Spark SQL与HoodieSparkSessionExtension SQL扩展写和读数据。在解压的目录下运行Spark SQL和Hudi:
- 启动hive的元数据服务
nohup hive --service metastore &
- 启动spark-sql,如果没有配置hive的环境变量,拷贝hive-site.xml到spark的conf目录。不同版本(Spark 3.3、Spark 3.2、Spark 3.1、Spark 2.4)的spark-sql启动命令有所不同,下面以Spark 3.3来操作演示
spark-sql --packages org.apache.hudi:hudi-spark3.3-bundle_2.12:0.12.1 \
--conf 'spark.serializer=org.apache.spark.serializer.KryoSerializer' \
--conf 'spark.sql.extensions=org.apache.spark.sql.hudi.HoodieSparkSessionExtension' \
--conf 'spark.sql.catalog.spark_catalog=org.apache.spark.sql.hudi.catalog.HoodieCatalog'
创建表
Spark SQL需要一个显式的create table命令。
- Hudi的两种表类型:即写时复制(COW)和读时合并(MOR),都可以使用Spark SQL创建。在创建表时,可以使用type选项指定表的类型:type = 'cow’或type = ‘mor’。
- 分区表和非分区表:用户可以在Spark SQL中创建分区表或非分区表。要创建分区表,需要使用partitioned by语句指定分区列以创建分区表。当没有使用create table命令进行分区的语句时,该表被认为是一个非分区表。
- 内部管理表和外部表:通常,Spark SQL支持两种表,即托管表和外部表。如果使用location语句或使用create external table显式地创建表来指定一个位置,则它是一个外部表,否则它被认为是一个内部管理表。
接下来通过实际sql演示如何创建不同的表。
-
创建一个非分区表
- 创建一个cow表,默认primaryKey ‘uuid’,不提供preCombineField。
create database hudi_spark; use hudi_spark; create table hudi_cow_nonpcf_tbl ( uuid int, name string, price double ) using hudi;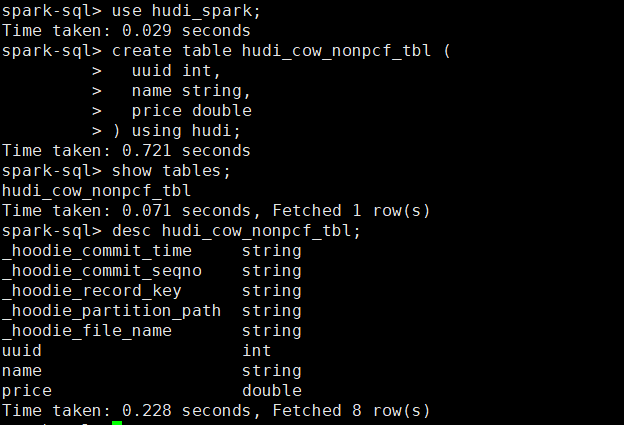
- 创建一个提供preCombineField的mor非分区表
create table hudi_mor_tbl ( id int, name string, price double, ts bigint ) using hudi tblproperties ( type = 'mor', primaryKey = 'id', preCombineField = 'ts' ); -
创建外部COW分区表
create table hudi_cow_pt_tbl (
id bigint,
name string,
ts bigint,
dt string,
hh string
) using hudi
tblproperties (
type = 'cow',
primaryKey = 'id',
preCombineField = 'ts'
)
partitioned by (dt, hh)
location '/tmp/hudi/hudi_cow_pt_tbl';
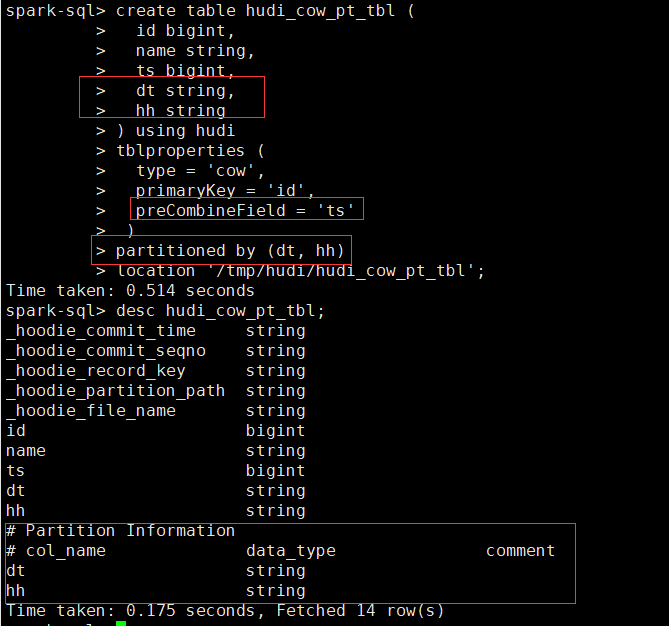
- 为已有的Hudi Table创建Table,可以在现有的hudi表上创建一个表(用spark-shell或deltastreamer创建)。这对于对已有的hudi表进行读写非常有用。
create table hudi_existing_tbl using hudi
location '/tmp/hudi/hudi_cow_pt_tbl';
-
CTAS,Hudi 支持在Spark SQL使用CTAS (Create Table As Select)
- 创建一个不带preCombineField的非分区cow表
create table hudi_ctas_cow_nonpcf_tbl using hudi tblproperties (primaryKey = 'id') as select 1 as id, 'a1' as name, 10 as price;- 使用实例创建一个分区的主键COW表。
create table hudi_ctas_cow_pt_tbl using hudi tblproperties (type = 'cow', primaryKey = 'id', preCombineField = 'ts') partitioned by (dt) as select 1 as id, 'a1' as name, 10 as price, 1000 as ts, '2021-12-01' as dt;
- 通过CTAS从另一个表加载数据,file://代表本地文件目录
create table parquet_mngd using parquet location 'file:///tmp/parquet_dataset/*.parquet';
create table hudi_ctas_cow_pt_tbl2 using hudi location 'file:/tmp/hudi/hudi_tbl/' options (
type = 'cow',
primaryKey = 'id',
preCombineField = 'ts'
)
partitioned by (datestr) as select * from parquet_mngd;
创建表属性可以在创建hudi表时设置表属性,关键选项如下:
- primaryKey:表的主键名,多个字段用逗号分隔。与hoodie.datasource.write.recordkey.field相同,默认为uuid。
- preCombineField:表的预合并字段,与hoodie.datasource.write.precombine.field相同。
- type:创建的表类型,type = 'cow’表示COPY-ON-WRITE表,而type = 'mor’表示MERGE-ON-READ表。与hoodie.datasource.write.table.type相同。
插入数据
-- 插入非分区表
insert into hudi_cow_nonpcf_tbl select 1, 'a1', 20;
insert into hudi_mor_tbl select 1, 'a1', 20, 1000;
-- 插入动态分区
insert into hudi_cow_pt_tbl partition (dt, hh)
select 1 as id, 'a1' as name, 1000 as ts, '2021-12-09' as dt, '10' as hh;
-- 插入静态分区
insert into hudi_cow_pt_tbl partition(dt = '2021-12-09', hh='11') select 2, 'a2', 1000;
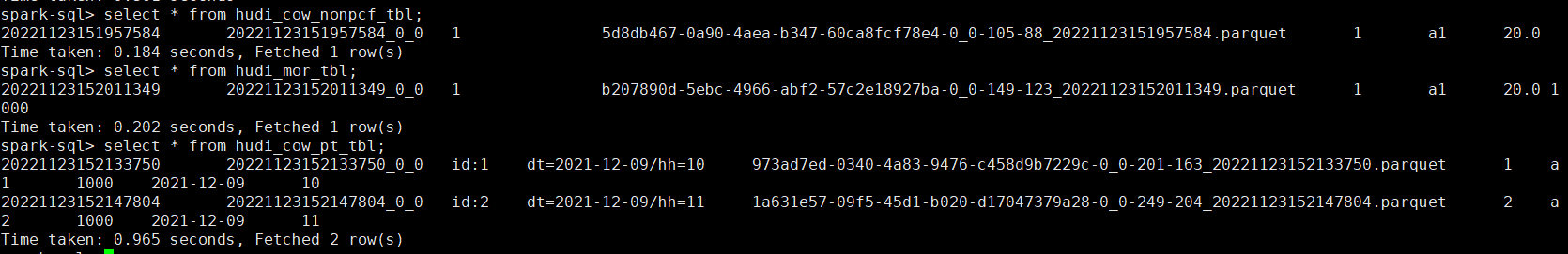
-- precombinefield提供的表的upsert模式
insert into hudi_mor_tbl select 1, 'a1_1', 20, 1001;
select id, name, price, ts from hudi_mor_tbl;
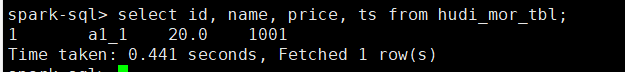
-- bulk_insert模式用于precombinefield提供的表
set hoodie.sql.bulk.insert.enable=true;
set hoodie.sql.insert.mode=non-strict;
insert into hudi_mor_tbl select 1, 'a1_2', 20, 1002;
select id, name, price, ts from hudi_mor_tbl;
时间旅行查询
create table hudi_cow_pt_tbl (
id bigint,
name string,
ts bigint,
dt string,
hh string
) using hudi
tblproperties (
type = 'cow',
primaryKey = 'id',
preCombineField = 'ts'
)
partitioned by (dt, hh)
location '/tmp/hudi/hudi_cow_pt_tbl';
insert into hudi_cow_pt_tbl select 3, 'c0', 1000, '2022-11-23', '10';
select * from hudi_cow_pt_tbl;
-- 记录id=3 修改 `name`
insert into hudi_cow_pt_tbl select 3, 'c1', 1001, '2022-11-23', '10';
select * from hudi_cow_pt_tbl;
-- 基于第一次提交时间的时间旅行,假设 `20220307091628793`
select * from hudi_cow_pt_tbl timestamp as of '20221123153135498' where id = 3;
-- 基于不同时间戳格式的时间旅行
select * from hudi_cow_pt_tbl timestamp as of '2022-11-23 15:31:35.498' where id = 3;
select * from hudi_cow_pt_tbl timestamp as of '2022-11-23' where id = 3;

更新数据
update hudi_mor_tbl set price = price * 2, ts = 1111 where id = 1;
update hudi_cow_pt_tbl set name = 'a1_1', ts = 1001 where id = 1;
update hudi_cow_pt_tbl set ts = 1005 where name = 'a1_1';
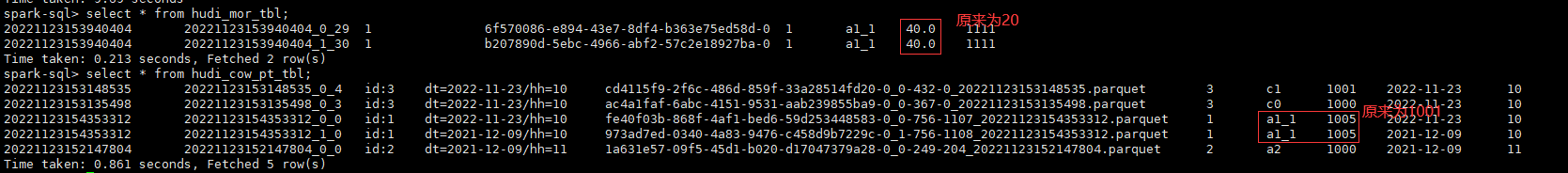
- 使用hudi测试合并到非分区表的源表
create table merge_source (id int, name string, price double, ts bigint) using hudi
tblproperties (primaryKey = 'id', preCombineField = 'ts');
insert into merge_source values (1, "old_a1", 22.22, 900), (2, "new_a2", 33.33, 2000), (3, "new_a3", 44.44, 2000);
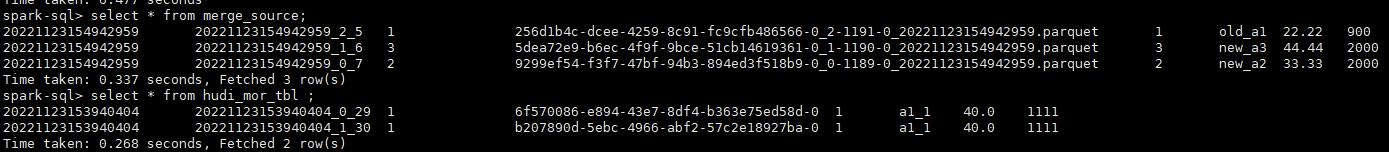
merge into hudi_mor_tbl as target
using merge_source as source
on target.id = source.id
when matched then update set *
when not matched then insert *
;
select * from hudi_mor_tbl ;

- 源表使用拼花测试合并到分区表
create table merge_source2 (id int, name string, flag string, dt string, hh string) using parquet;
insert into merge_source2 values (1, "new_a1", 'update', '2022-11-23', '10'), (2, "new_a2", 'delete', '2022-11-23', '11'), (3, "new_a3", 'insert', '2022-11-23', '12');
merge into hudi_cow_pt_tbl as target
using (
select id, name, '1000' as ts, flag, dt, hh from merge_source2
) source
on target.id = source.id
when matched and flag != 'delete' then
update set id = source.id, name = source.name, ts = source.ts, dt = source.dt, hh = source.hh
when matched and flag = 'delete' then delete
when not matched then
insert (id, name, ts, dt, hh) values(source.id, source.name, source.ts, source.dt, source.hh)
;
删除数据
delete from hudi_cow_nonpcf_tbl where uuid = 1;
delete from hudi_mor_tbl where id % 2 = 0;
delete from hudi_cow_pt_tbl where name = 'a1';
覆盖数据
insert覆盖分区表使用INSERT_OVERWRITE_TABLE类型的写操作,而非分区表使用INSERT_OVERWRITE_TABLE类型的写操作。
-- 插入覆盖非分区表
insert overwrite hudi_mor_tbl select 99, 'a99', 20.0, 900;
insert overwrite hudi_cow_nonpcf_tbl select 99, 'a99', 20.0;
-- 用动态分区插入覆盖分区表
insert overwrite table hudi_cow_pt_tbl select 10, 'a10', 1100, '2021-12-09', '10';
-- 用静态分区插入覆盖分区表
insert overwrite hudi_cow_pt_tbl partition(dt = '2021-12-09', hh='12') select 13, 'a13', 1100;
其他
-- 改表名
ALTER TABLE hudi_cow_nonpcf_tbl RENAME TO hudi_cow_nonpcf_tbl2;
-- 添加列
ALTER TABLE hudi_cow_nonpcf_tbl2 add columns(remark string);
-- 修改列
ALTER TABLE hudi_cow_nonpcf_tbl2 change column uuid uuid bigint;
-- 设置表属性
alter table hudi_cow_nonpcf_tbl2 set tblproperties (hoodie.keep.max.commits = '10');
-- 显示分区
show partitions hudi_cow_pt_tbl;
-- 删除分区
alter table hudi_cow_pt_tbl drop partition (dt='2022-11-23', hh='10');
本人博客网站IT小神 www.itxiaoshen.com