目录
一、CompletableFuture是什么
二、CompletableFuture用法
2.1、创建CompletableFuture
2.1.1、直接创建
2.1.2、创建一个使用指定数据作为结果的已结束的CompletableFuture
2.1.3、通过执行异步任务获取CompletableFuture
2.2、获取任务结果
2.3、消费结果
2.3.1、whenComplete
2.3.2、thenAccept
2.3.3、thenApply
2.3.4、thenRun
2.3.5、handle
2.3.6、exceptionally
2.4、多任务编排
2.4.1、 依赖(thenCompose)
2.4.2、 AND(thenCombine,thenAcceptBoth,runAfterBoth)
2.4.3、OR(applyToEither)
2.4.4、 并行(allOf,anyOf)
一、CompletableFuture是什么
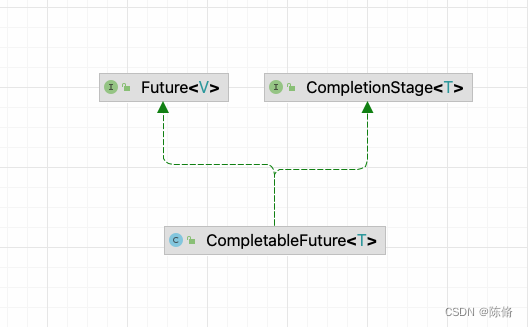
CompletableFuture是对Future的扩展和增强。CompletableFuture实现了Future接口和CompletionStage使其实现了对任务编排的能力。借助这项能力,可以轻松地组织不同任务的运行顺序、规则以及方式。
二、CompletableFuture用法
2.1、创建CompletableFuture
2.1.1、直接创建
CompletableFuture completableFuture=new CompletableFuture();2.1.2、创建一个使用指定数据作为结果的已结束的CompletableFuture
CompletableFuture<String> test1 = CompletableFuture.completedFuture("test");2.1.3、通过执行异步任务获取CompletableFuture
/**
* 使用默认线程池执行异步任务,有返回值
*/
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "hello CompletableFuture!");
/**
* 使用指定线程池执行异步任务,有返回值
*/
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "Hello CompletableFuture!", Executors.newCachedThreadPool());
/**
* 使用默认线程池执行异步任务,无返回值
*/
CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> System.out.println("Hello runAsync!"));
/**
* 使用指定线程池执行异步任务,无返回值
*/
CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> System.out.println("Hello RunAsync!"), Executors.newCachedThreadPool());2.2、获取任务结果
| 方法 | 是否阻塞 | 是否抛出检查异常 | 说明 |
| get() | 阻塞 | 抛出检查异常 | |
| getNow(V value) | 不阻塞 | 不抛出 | 如果任务没有结束就返回指定的默认值 |
| get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) | 阻塞指定时间 | 抛出 | |
| join() | 阻塞 | 不抛出 |
示例代码:
/**
* 获取任务结果,阻塞直到任务结束,会抛出检查异常
*/
String test = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "Hello").get();
/**
* 获取任务结果,如果超过等待之间任务未结束则抛出TimeoutException
*/
test = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "test").get(10, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
/**
* 如果任务结束则返回任务结果,如果任务未结束则返回指定的默认值
*/
test = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "test").getNow("default");
/**
* 阻塞获取任务结果,和get相似,但是不会抛出检查异常
*/
test = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "join").join();2.3、消费结果
2.3.1、whenComplete
whenComplete是当某个任务执行完成后执行的回调方法,不管任务异常还是正常结束都会执行该回调;该回调的入参是任务的执行结果和异常;
如果是正常执行则异常为null,回调方法对应的CompletableFuture的result和该任务一致,如果该任务正常执行,则get方法返回执行结果,如果是执行异常,则get方法抛出异常。
| 方法 | 说明 |
| whenComplete(BiConsumer<? super T, ? super Throwable> action ) | 在当前线程中同步执行回调操作 |
| whenCompleteAsync(BiConsumer<? super T, ? super Throwable> action ) | 在默认线程池中异步执行回调 |
| whenCompleteAsync(BiConsumer<? super T, ? super Throwable> action,Executor executor ) | 在指定线程池中异步执行回调 |
示例代码如下:
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("threadId: " + Thread.currentThread().getId() + ",threadName: " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
return "whenComplete";
}).whenComplete((a, e) ->
System.out.println("threadId: " + Thread.currentThread().getId() + ",threadName: " + Thread.currentThread().getName() + ", a: " + a)
);
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{throw new RuntimeException("");}).whenComplete((a,e)->System.out.println(e));执行结果如下:
threadId: 11,threadName: ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-9
threadId: 1,threadName: main, a: whenComplete
java.util.concurrent.CompletionException: java.lang.RuntimeException:
2.3.2、thenAccept
thenAccept只消费正常处理结束的结果,不消费异常同时没有返回值
| 方法 | 说明 |
| thenAccept(Consumer<? super T> action ) | 在当前线程中消费同步消费 |
| thenAcceptAsync(Consumer<? super T> action ) | 在默认线程池中异步消费 |
| thenAcceptAsync(Consumer<? super T> action, Executor executor ) | 在指定线程池中异步消费 |
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "thenAccept")
.thenAccept(str -> System.out.println("threadId: " + Thread.currentThread().getId() + ",threadName: " + Thread.currentThread().getName()+",str="+str));
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "thenAcceptAsync")
.thenAcceptAsync(str -> System.out.println("threadId: " + Thread.currentThread().getId() + ",threadName: " + Thread.currentThread().getName()+",str="+str));
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->"thenAcceptAsync")
.thenAcceptAsync(str-> System.out.println("threadId: " + Thread.currentThread().getId() + ",threadName: " + Thread.currentThread().getName()+",str="+str),Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor());
执行结果如下:
threadId: 1,threadName: main,str=thenAccept
threadId: 11,threadName: ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-9,str=thenAcceptAsync
threadId: 16,threadName: pool-6-thread-1,str=thenAcceptAsync2.3.3、thenApply
thenApply和thenAccept的相同点都是消费任务正常结束的结果,不同点就是thenAccept没有返回值而thenApply有返回值。
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "Dora")
.thenApply(str ->"Hello, "+str).thenAccept(System.out::println);
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "Dora")
.thenApplyAsync(str ->"Hello, "+str).thenAccept(System.out::println);
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->"Dora")
.thenApplyAsync(str ->"Hello, "+str).thenAccept(System.out::println);
执行结果如下:
Hello, Dora
Hello, Dora
Hello, Dora
2.3.4、thenRun
thenRun和thenAccept相似,都是在任务正常结束后执行且都没有返回值,两者的区别是thenAccept关心上一个任务的结果而thenRun不关心结果。
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "thenRun")
.thenRun(() -> System.out.println("threadId: " + Thread.currentThread().getId() + ",threadName: " + Thread.currentThread().getName()));
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "thenRunAsync")
.thenRunAsync(() -> System.out.println("threadId: " + Thread.currentThread().getId() + ",threadName: " + Thread.currentThread().getName()));
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->"thenRunAsync")
.thenRunAsync(()-> System.out.println("threadId: " + Thread.currentThread().getId() + ",threadName: " + Thread.currentThread().getName()),Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor());
2.3.5、handle
handle方法的使用和whenComplete类似
| handle | whenComplete | |
| 入参 | 任务的结果和异常 | 任务的结果和异常 |
| 触发阶段 | 任务结束后,不管正常结束还是异常结束 | 任务结束后,不管正常结束还是异常结束 |
| 返回值 | 有返回值 | Void |
2.3.6、exceptionally
exceptionally是当任务执行出现异常时的回调处理,否则不会触发该回调;可以使用whenComplete和handle方法替代该方法
//如果任务执行异常则返回"exception"
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{throw new RuntimeException("");}).exceptionally((e->"exception")).whenComplete((a,e)->System.out.println(a+" "+e));
执行结果如下:
exception null
2.4、多任务编排
2.4.1、 依赖(thenCompose)
thenCompose 是依赖前一个任务结果,前一个任务的结果作为当前任务的入参
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "hello").thenCompose(p -> CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> p + " world")).thenAccept(System.out::println);2.4.2、 AND(thenCombine,thenAcceptBoth,runAfterBoth)
thenCombine 是将两个任务的结果进行合并处理
String test = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
return "a";
}).thenCombineAsync(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
} catch (Exception e) {
}
return "b";
}), (a, b) -> a + "_" + b).join();结果是:
a_b
thenAcceptBoth和thenCombine比较类似,区别是thenCombine是有返回值,而thenAcceptBoth是消费前两个任务的结果没有返回值
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "hello").thenAcceptBoth(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "world"), (a, b) -> {
System.out.println(a + "—" + b);
});结果是:
a-b
runAfterBoth和thenCombine、thenAcceptBoth有所不同,它不关心前两个任务的结果,只要前两个任务都结束就会触发第三个任务执行
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "hello").runAfterBoth(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "world"), () -> {
System.out.println("end");
});结果是
end2.4.3、OR(applyToEither)
applyToEither从名字上就可以知道两个任务是或的关系,只要有一个任务结束就出发第三个任务执行。
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "first").applyToEither(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "second"), str ->
str + " end").thenAccept(System.out::println);结果是:
first end
acceptEither是只要有一个任务结束第三个任务就消费它
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "first").acceptEither(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "second"), str ->System.out.println(str+" end"));
2.4.4、 并行(allOf,anyOf)
allOf 是所有任务都必须执行结束,anyOf是有一个任务正常结束即可。
CompletableFuture.allOf(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->"a"),CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->"b")).join();


![【C++】重载运算符+-=>/*[]==++-- MyString 智能指针(* ->)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/71604cfea51243ed9fb573052c90645c.png)