目录
15.重载运算符
15.1 eg.Person
15.2 eg.MyString
15.3 智能指针
15.重载运算符
-
定义:给原有的运算符赋予新的意义。
-
为什么重载<<或>>一定要用友元?
如果是重载双目操作符(即为类的成员函数),就只要设置一个参数作为右侧运算量,而左侧运算量就是对象本身。
而 >> 或<< 左侧运算量是
cin或cout而不是对象本身,所以不满足左侧运算量就是对象本身的特点。所以要申明为友元函数。如果一定要声明为成员函数,只能成为如下的形式:
ostream & operator<<(ostream &output){ return output; }所以在运用这个<<运算符时就变为:
data<<cout;不符合习惯。
15.1 eg.Person
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Person {
private:
string name;
int age;
float weight;
public:
Person();
Person(string, int, float);
~Person();
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, Person& ob);
friend istream& operator>>(istream& in, Person& ob);
friend Person operator+(Person& ob1, Person& ob2);
friend Person operator-(Person& ob1, Person& ob2);
friend Person operator*(Person& ob1, Person& ob2);
friend Person operator/(Person& ob1, Person& ob2);
friend Person operator++(Person& ob);//前置++
friend Person operator++(Person& ob,int t);//后置++
friend Person operator--(Person& ob);//前置--
friend Person operator--(Person& ob,int t);//后置--
friend bool operator==(Person& ob1, Person& ob2);
};
Person::Person() {
name = "YY";
age = 19;
weight = 55.5;
}
Person::Person(string _name, int _age, float _weight) {
name = _name;
age = _age;
weight = _weight;
}
Person::~Person() {
//cout << "~Person" << endl;
}
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, Person& ob) {
cout << "name:" << ob.name <<" "
<<"age:" <<ob.age<<" "
<<"weight:"<<ob.weight<< endl;
return out;
}
istream& operator>>(istream& in, Person& ob) {
Person(ob.name, ob.age, ob.weight);
return in;
}
Person operator+(Person& ob1, Person& ob2) {
Person ob3;
ob3.age=ob1.age + ob2.age;
ob3.weight = ob1.weight + ob2.weight;
ob3.name = ob1.name + ob2.name;
return ob3;
}
Person operator-(Person& ob1, Person& ob2) {
Person ob3;
ob3.age = ob1.age - ob2.age;
ob3.weight = ob1.weight - ob2.weight;
return ob3;
}
Person operator*(Person& ob1, Person& ob2) {
Person ob3;
ob3.age = ob1.age * ob2.age;
ob3.weight = ob1.weight * ob2.weight;
return ob3;
}
Person operator/(Person& ob1, Person& ob2) {
Person ob3;
ob3.age = ob1.age / ob2.age;
ob3.weight = ob1.weight / ob2.weight;
return ob3;
}
Person operator++(Person& ob) {
ob.age++;
ob.weight++;
ob.name += ob.name;
return ob;
}
Person operator++(Person& ob, int t) {
Person old = ob;
++ob;
return old;
}
Person operator--(Person& ob) {
ob.age--;
ob.weight--;
return ob;
}
Person operator--(Person& ob, int t) {
Person old = ob;
--ob;
return old;
}
bool operator==(Person& ob1, Person& ob2){
if (ob1.age == ob2.age && ob1.weight == ob2.weight) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
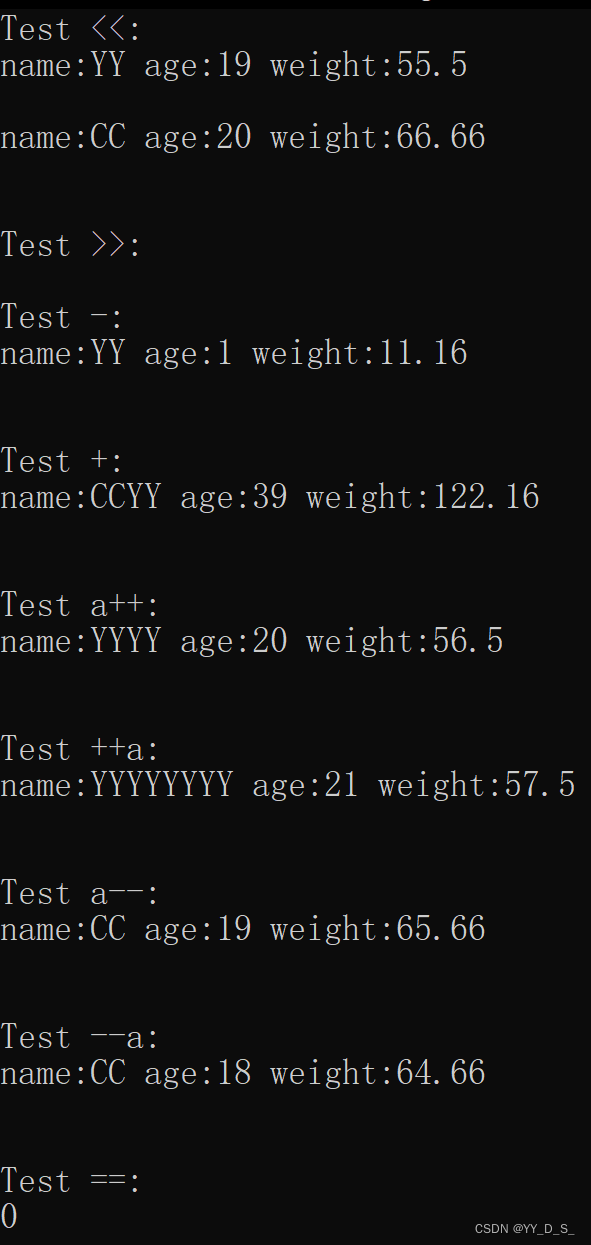
int main()
{
Person ob1;
Person ob2("CC", 20, 66.66);
Person temp;
cout << "Test <<:" << endl;
cout << ob1 << endl;
cout << ob2 << endl;
cout << "\nTest >>:" << endl;
cin >> temp ;
cout << "\nTest -:" << endl;
temp = ob2 - ob1;
cout << temp << endl;
cout << "\nTest +:" << endl;
temp = ob2 + ob1;
cout << temp << endl;
cout << "\nTest a++:" << endl;
ob1++;
cout<< ob1 << endl;
cout << "\nTest ++a:" << endl;
++ob1;
cout << ob1 << endl;
cout << "\nTest a--:" << endl;
ob2--;
cout << ob2 << endl;
cout << "\nTest --a:" << endl;
--ob2;
cout << ob2 << endl;
cout << "\nTest ==:" << endl;
bool f=(ob1==ob2);
cout << f << endl;
}
15.2 eg.MyString
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
class MyString {
private:
int size;
char* str;
public:
MyString();
MyString(const char*s); //一定要有const
~MyString();
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, MyString ob);
friend istream& operator>>(istream& in, MyString &ob);//一定要有&
MyString operator+(MyString ob);
MyString operator=(MyString ob);
bool operator>(MyString ob);
char &operator[](int i);//获取字符串中的一个字符
};
MyString::MyString() {
size = 0;
str = NULL;
}
MyString::MyString(const char* _str){
size = strlen(_str);
str = new char[size + 1];
strcpy(str, _str);
}
MyString::~MyString() {
//cout << "\n~MyString" << endl;
}
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, MyString ob) {
out << ob.str;
return out;
}
istream& operator>>(istream& in, MyString &ob) {
char temp[99];
cin >> temp;
if (ob.str != NULL) {
delete[]ob.str;
ob.str = NULL;
}
ob.size = strlen(temp);
ob.str = new char[ob.size + 1];
strcpy(ob.str, temp);
return in;
}
MyString MyString::operator+(MyString ob) {
MyString temp;
temp.size=size + ob.size;
temp = new char[temp.size + 1];
strcpy(temp.str, str);
strcat(temp.str, ob.str);
return temp;
}
MyString MyString::operator=(MyString ob) {
size = ob.size;
if (str != NULL) {
delete[]str;
str = NULL;
}
str = new char[size+1];
str = ob.str;
return *this;
}
bool MyString::operator>(MyString ob) {
if (strcmp(str, ob.str)) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
char& MyString::operator[](int i) {
return str[i];
}
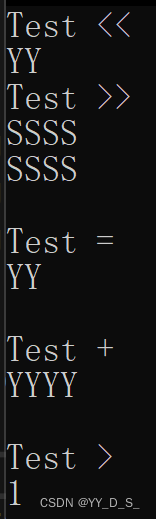
int main()
{
MyString ob1;
MyString ob2("YY");
MyString temp;
cout << "Test <<" << endl;
cout << ob2 << endl;
cout << "\nTest >>" << endl;
cin >> temp;
cout << temp << endl;
cout << "\nTest =" << endl;
ob1 = ob2;
cout << ob1 << endl;
cout << "\nTest +" << endl;
temp = ob1 + ob2;
cout << temp << endl;
cout << "\nTest >" << endl;
bool f=temp>ob1;
cout << f<< endl;
}
-
析构函数的调用顺序:
#include<iostream> #include<string> using namespace std; class MyString { private: int size; char* str; string name; public: MyString(); MyString(const char*s,string _name); //一定要有const ~MyString(); friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, MyString ob); friend istream& operator>>(istream& in, MyString &ob);//一定要有& MyString operator+(MyString ob); MyString operator=(MyString ob); bool operator>(MyString ob); char &operator[](int i);//获取字符串中的一个字符 }; MyString::MyString() { size = 0; str = NULL; } MyString::MyString(const char* _str,string _name){ cout << "Create:" << _name << endl; size = strlen(_str); str = new char[size + 1]; strcpy(str, _str); name = _name; } MyString::~MyString() { cout << "\n~MyString:"<<this->name << endl; } ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, MyString ob) { out << ob.str; return out; } istream& operator>>(istream& in, MyString &ob) { char temp[99]; cin >> temp; if (ob.str != NULL) { delete[]ob.str; ob.str = NULL; } ob.size = strlen(temp); ob.str = new char[ob.size + 1]; strcpy(ob.str, temp); return in; } MyString MyString::operator+(MyString ob) { MyString temp; temp.size=this->size + ob.size; temp.str = new char[temp.size+1]; strcpy(temp.str, this->str); strcat(temp.str, ob.str); return temp; } MyString MyString::operator=(MyString ob) { size = ob.size; if (str != NULL) { delete[]str; str = NULL; } str = new char[size+1]; str = ob.str; return *this; } bool MyString::operator>(MyString ob) { if (strcmp(str, ob.str)) { return true; } return false; } char& MyString::operator[](int i) { return str[i]; } int main() { MyString ob1("S","ob1"); MyString ob2("YY","ob2"); MyString temp("T","temp"); cout << "Test <<" << endl; cout << ob2 << endl; cout << "Test >>" << endl; cin >> temp; cout << temp << endl; cout << "Test =" << endl; ob1 = ob2; cout << ob1 << endl; cout << "Test +" << endl; temp = ob1 + ob2; cout << temp << endl; cout << "Test >" << endl; bool f=temp>ob1; cout << f<< endl; }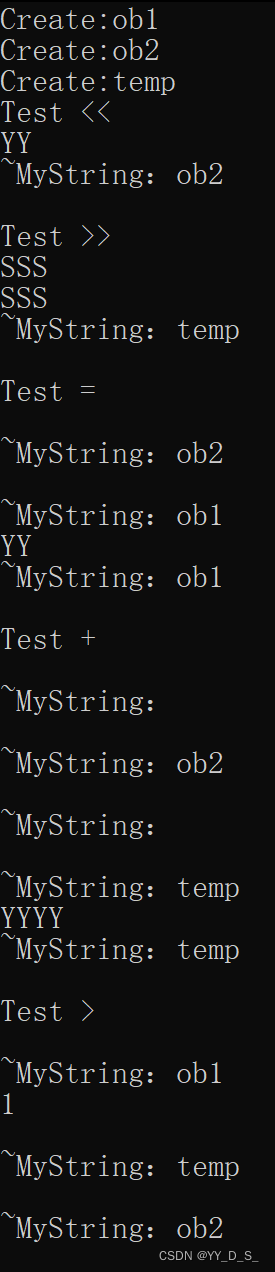
15.3 智能指针
(指针运算(*、->)重载)
-
作用:解决 堆区空间的对象 释放问题。(手动怕忘)
智能指针就是帮我们C++程序员管理动态分配的内存的,它会帮助我们自动释放new出来的内存,从而避免内存泄漏!
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Data {
private:
int a;
public:
Data();
Data(int);
~Data();
void Datafuc();
};
class smartpoint {
private:
Data* p;
public:
smartpoint();
smartpoint(Data* p);
~smartpoint();
Data* operator->();
Data& operator*();
};
Data::Data() {}
Data::Data(int _a) {
a = _a;
}
Data::~Data() {
cout << "~Data" << endl;
}
void Data::Datafuc() {
cout << "smartpoint调用Datafuc" << endl;
}
smartpoint::smartpoint() {
*p = NULL;
}
smartpoint::smartpoint(Data* _p) {
p = _p;
}
smartpoint::~smartpoint() {
cout << "~smartpoint" << endl;
}
Data& smartpoint::operator*() {
cout << "重载运算符*" << endl;
return *p;
}
Data* smartpoint::operator->() {
cout << "重载运算符->" << endl;
return this->p;
}
int main()
{
Data da(5);
smartpoint sp(&da);
//重载运算符调用函数
sp->Datafuc();
(*sp).Datafuc();
}