文章目录
- 前言
- 一、环境
- 1、硬件
- 2、软件
- 二、YOLO模型
- 三、新建Qt项目
- 1、pro文件
- 2、main函数
- 四、YOLO 类封装
- 1、yolo.h
- 2、yolo.cpp
- 3、classes.txt
- 五、效果
前言
最近工作中需要用yolov5训练模型,然后在win10系统下,完成推理部署。本篇主要介绍使用opencv-dnn模块实现模型推理部署。
一、环境
1、硬件
Intel® Core i5-7400 CPU @ 3.00GHZ
Intel® HD Graphics 630 内存4G 核显
内存 8G
win10 64位系统
2、软件
opencv4.6.0
yolov5 6.2版本
二、YOLO模型
我使用的是onnx模型,如果没有训练过自己的模型,可以使用官方的yolov5s.pt模型,将其转化为yolov5s.onnx模型,转化方法如下:
python export.py
在yolov5-master目录下,可以看到yolov5s.onnx模型已生成。
三、新建Qt项目
1、pro文件
在pro文件中,添加opencv相关配置,内容如下:
#-------------------------------------------------
#
# Project created by QtCreator 2022-10-09T13:28:19
#
#-------------------------------------------------
QT += core gui
greaterThan(QT_MAJOR_VERSION, 4): QT += widgets
TARGET = untitled1
TEMPLATE = app
SOURCES += main.cpp\
mainwindow.cpp \
yolo.cpp
HEADERS += mainwindow.h \
yolo.h
FORMS += mainwindow.ui
INCLUDEPATH += C:/opencv4.6.0/build/include
C:/opencv4.6.0/build/include/opencv2
LIBS += -LC:/opencv4.6.0/build/x64/vc14/lib/ -lopencv_world460
2、main函数
#include "mainwindow.h"
#include <QApplication>
#include <QDebug>
#include "yolo.h"
#include <iomanip>
#include <QTime>
#include <QThread>
//const vector<Scalar> colors = { Scalar(255, 255, 0), Scalar(0, 255, 0), Scalar(0, 255, 255), Scalar(255, 0, 0) };
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
Mat frame;
VideoCapture capture("G:/1.mp4");//sample
if (!capture.isOpened())
{
std::cerr << "Error opening video file\n";
return -1;
}
cv::VideoWriter video("out.avi",cv::VideoWriter::fourcc('M','J','P','G'),10, cv::Size(1920,1080));
//
YOLO *yolov5 = new YOLO;
yolov5->init("F:/SVN-ZJKY/YiFeiShouJiRobot/yolov5-6.1/yolov5s.onnx");
//
std::vector<detect_result> output;
int total_frames = 0;
//
clock_t start_name = 0;
clock_t end_time = 0;
//
while ( true )
{
//
start_name = clock();
capture.read(frame);
if (frame.empty())
{
std::cout << "End of stream\n";
break;
}
//
total_frames++;
// auto start = std::chrono::system_clock::now();
// t = (double)cv::getTickCount();
yolov5->detect(frame,output);
// auto end = std::chrono::system_clock::now();
// auto detect_time =std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::milliseconds>(end - start).count();//ms
// std::cout<<detect_time<<":"<<total_frames<<":"<<output.size()<<std::endl;
//
// t = ((double)cv::getTickCount() - t) / cv::getTickFrequency();
// fps = 1.0 / t;
end_time=clock();//ms
auto text = "FPS: " + std::to_string(1 / ((double)(end_time - start_name) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC));
qDebug() << "Frame time(ms): " << (double)(end_time - start_name) /*/ CLOCKS_PER_SEC*/;
cv::putText(frame, text, cv::Point(3, 25), cv::FONT_ITALIC, 0.8, cv::Scalar(0, 0, 255), 2);
//
yolov5->draw_frame(frame,output);
imshow("output", frame);
video.write(frame);
if (waitKey(1) != -1)
{
std::cout << "finished by user\n";
break;
}
output.clear();
}
//
capture.release();
video.release();
cv::destroyAllWindows();
waitKey(0);
//std::cout << "Total frames: " << total_frames << "\n";
return 0;
}
四、YOLO 类封装
1、yolo.h
#include <fstream>
#include <sstream>
#include <iostream>
#include <opencv2/dnn.hpp>
#include <opencv2/imgproc.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui.hpp>
using namespace cv;
using namespace dnn;
using namespace std;
class detect_result
{
public:
int classId;
float confidence;
cv::Rect_<float> box;
};
class YOLO
{
public:
YOLO();
~YOLO();
void init(std::string onnxpath);
//Net loadNet(bool is_cuda);
//Mat format_yolov5(const Mat &source);
std::vector<std::string> classes_;
void detect(cv::Mat & frame, std::vector<detect_result> &result);
//void drawRect(Mat &image,vector<Detection> &output);
//std::vector<std::string> load_class_list();
void draw_frame(cv::Mat & frame, std::vector<detect_result> &results);
private:
cv::dnn::Net net;
//cv::dnn::Net m_net;
// const float INPUT_WIDTH = 640.0;
// const float INPUT_HEIGHT = 640.0;
// const float SCORE_THRESHOLD = 0.2;
// const float NMS_THRESHOLD = 0.4;
// const float CONFIDENCE_THRESHOLD = 0.4;
const float confidence_threshold_ =0.25f;
const float nms_threshold_ = 0.4f;
const int model_input_width_ = 640;
const int model_input_height_ = 640;
};
2、yolo.cpp
#include "yolo.h"
YOLO::YOLO()
{
//loadNet(false);
}
YOLO::~YOLO()
{
}
//std::vector<std::string> YOLO::load_class_list()
//{
// std::vector<std::string> class_list;
// std::ifstream ifs("G:/classes.txt");
// std::string line;
// while (getline(ifs, line))
// {
// class_list.push_back(line);
// }
// return class_list;
//}
//Net YOLO::loadNet(bool is_cuda)
//{
// //F:\SVN-ZJKY\YiFeiShouJiRobot\yolov5-master
// //m_net = readNet("F:\\SVN-ZJKY\\YiFeiShouJiRobot\\yolov5-master\\yolov5s.onnx");
// m_net = readNet("F:\\SVN-ZJKY\\YiFeiShouJiRobot\\demo\\yolov5-opencv-dnn-cpp-main\\QtDemo\\build-yolov5-opencv-dnn-cpp-main-Qt5_6_2_MSVC2015_64bit-Release\\release\\yolov5s.onnx");
// if (is_cuda)
// {
// cout << "Attempty to use CUDA\n";
// m_net.setPreferableBackend(DNN_BACKEND_CUDA);
// m_net.setPreferableTarget(DNN_TARGET_CUDA_FP16);
// }
// else
// {
// cout << "Running on CPU12\n";
// m_net.setPreferableBackend(DNN_BACKEND_OPENCV);
// m_net.setPreferableTarget(DNN_TARGET_CPU);
// }
// return m_net;
//}
//Mat YOLO::format_yolov5(const Mat &source)
//{
// int col = source.cols;
// int row = source.rows;
// int _max = MAX(col, row);
// Mat result = Mat::zeros(_max, _max, CV_8UC3);
// source.copyTo(result(Rect(0, 0, col, row)));
// return result;
//}
void YOLO::init(std::string onnxpath)
{
this->net = cv::dnn::readNetFromONNX(onnxpath);
std::string file="G:/classes.txt";
std::ifstream ifs(file);
if (!ifs.is_open())
CV_Error(cv::Error::StsError, "File " + file + " not found");
std::string line;
while (std::getline(ifs, line))
{
classes_.push_back(line);
}
}
void YOLO::detect(cv::Mat & frame, std::vector<detect_result> &results)
{
int w = frame.cols;
int h = frame.rows;
int _max = std::max(h, w);
cv::Mat image = cv::Mat::zeros(cv::Size(_max, _max), CV_8UC3);
cv::Rect roi(0, 0, w, h);
frame.copyTo(image(roi));
float x_factor = static_cast<float>(image.cols) / model_input_width_;
float y_factor = static_cast<float>(image.rows) / model_input_height_;
//std::cout<<x_factor<<std::endl;
//std::cout<<y_factor<<std::endl;
cv::Mat blob = cv::dnn::blobFromImage(image, 1 / 255.0, cv::Size(model_input_width_, model_input_height_), cv::Scalar(0, 0, 0), true, false);
this->net.setInput(blob);
cv::Mat preds = this->net.forward("output");//outputname
cv::Mat det_output(preds.size[1], preds.size[2], CV_32F, preds.ptr<float>());
std::vector<cv::Rect> boxes;
std::vector<int> classIds;
std::vector<float> confidences;
for (int i = 0; i < det_output.rows; i++)
{
float box_conf = det_output.at<float>(i, 4);
if (box_conf < nms_threshold_)
{
continue;
}
cv::Mat classes_confidences = det_output.row(i).colRange(5, 85);
cv::Point classIdPoint;
double cls_conf;
cv::minMaxLoc(classes_confidences, 0, &cls_conf, 0, &classIdPoint);
if (cls_conf > confidence_threshold_)
{
float cx = det_output.at<float>(i, 0);
float cy = det_output.at<float>(i, 1);
float ow = det_output.at<float>(i, 2);
float oh = det_output.at<float>(i, 3);
int x = static_cast<int>((cx - 0.5 * ow) * x_factor);
int y = static_cast<int>((cy - 0.5 * oh) * y_factor);
int width = static_cast<int>(ow * x_factor);
int height = static_cast<int>(oh * y_factor);
cv::Rect box;
box.x = x;
box.y = y;
box.width = width;
box.height = height;
boxes.push_back(box);
classIds.push_back(classIdPoint.x);
confidences.push_back(cls_conf * box_conf);
}
}
std::vector<int> indexes;
cv::dnn::NMSBoxes(boxes, confidences, confidence_threshold_, nms_threshold_, indexes);
for (size_t i = 0; i < indexes.size(); i++)
{
detect_result dr;
int index = indexes[i];
int idx = classIds[index];
dr.box = boxes[index];
dr.classId = idx;
dr.confidence = confidences[index];
results.push_back(dr);
}
}
void YOLO::draw_frame(cv::Mat & frame, std::vector<detect_result> &results)
{
for(auto dr : results)
{
cv::rectangle(frame, dr.box , cv::Scalar(0, 0, 255), 2, 8);
cv::rectangle(frame, cv::Point(dr.box .tl().x, dr.box .tl().y - 20), cv::Point(dr.box .br().x, dr.box .tl().y), cv::Scalar(255, 0, 0), -1);
std::string label = cv::format("%.2f", dr.confidence);
label = classes_[dr.classId ] + ":" + label;
cv::putText(frame, label, cv::Point(dr.box.x, dr.box.y + 6), 1, 2, cv::Scalar(0, 255, 0),2);
}
}
3、classes.txt
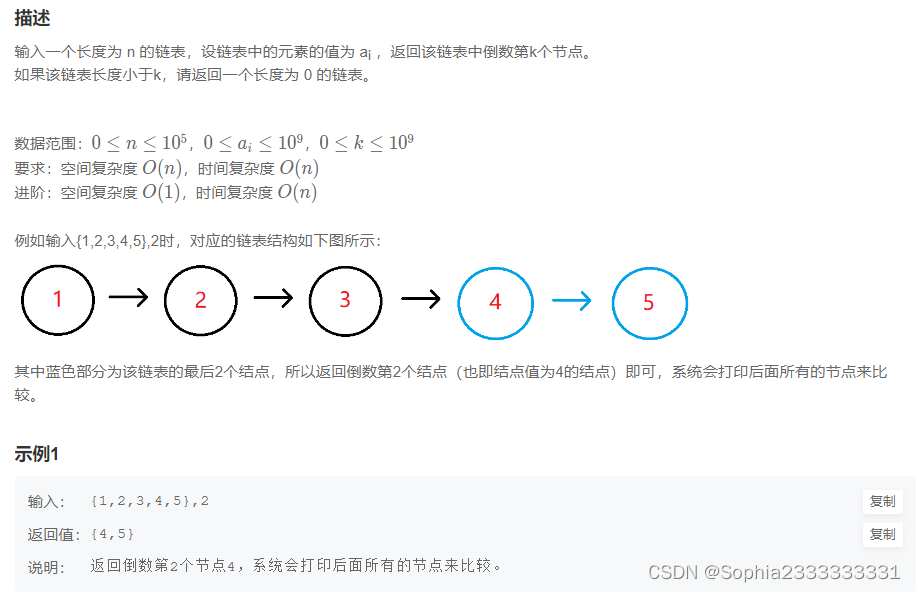
官方yolov5s.pt模型,能够识别80种物体,classes.txt文件记录的就是这80种物体类别名,如下:
person
bicycle
car
motorbike
aeroplane
bus
train
truck
boat
traffic light
fire hydrant
stop sign
parking meter
bench
bird
cat
dog
horse
sheep
cow
elephant
bear
zebra
giraffe
backpack
umbrella
handbag
tie
suitcase
frisbee
skis
snowboard
sports ball
kite
baseball bat
baseball glove
skateboard
surfboard
tennis racket
bottle
wine glass
cup
fork
knife
spoon
bowl
banana
apple
sandwich
orange
broccoli
carrot
hot dog
pizza
donut
cake
chair
sofa
pottedplant
bed
diningtable
toilet
tvmonitor
laptop
mouse
remote
keyboard
cell phone
microwave
oven
toaster
sink
refrigerator
book
clock
vase
scissors
teddy bear
hair drier
toothbrush
五、效果
以本地视频文件1.mp4为例,效果如下:

可以看到,在我的机器上,视频卡顿现象非常严重,FPS较小。