Problem - 1455D - Codeforces

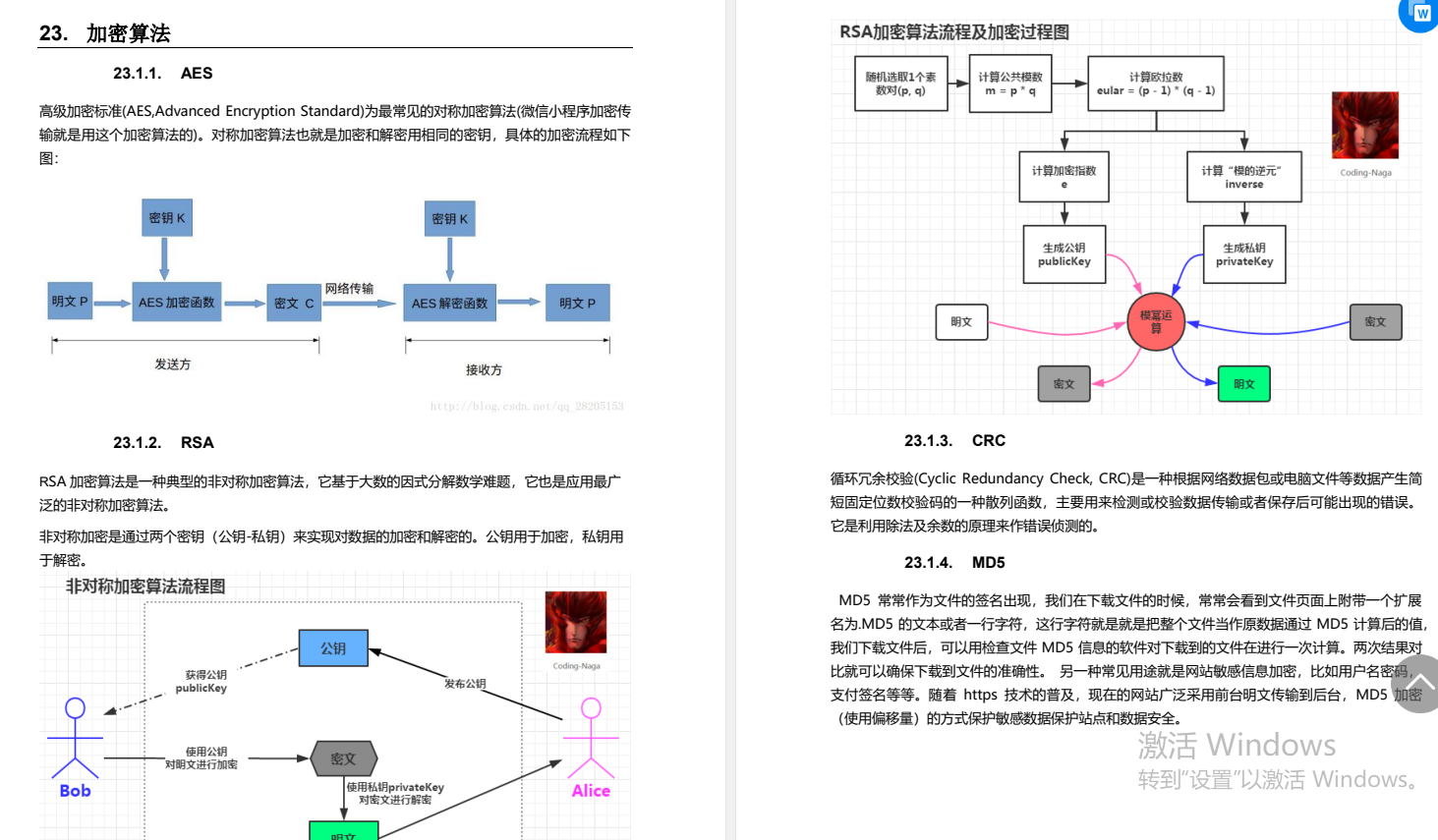
你的任务是使该序列排序(如果条件a1≤a2≤a3≤⋯≤an成立,它就被认为是排序的)。
为了使序列排序,你可以执行以下操作的任何次数(可能是零):选择一个整数i,使1≤i≤n且ai>x,并交换ai和x的值。
例如,如果a=[0,2,3,5,4],x=1,就可以进行以下操作序列。
选择i=2(这是可能的,因为a2>x),那么a=[0,1,3,5,4],x=2。
选择i=3(因为a3>x,所以有可能),然后a=[0,1,2,5,4],x=3。
选择i=4(因为a4>x,所以有可能),然后a=[0,1,2,3,4],x=5。
计算你必须执行的最小操作数,以使a成为排序的,或者报告说这是不可能的。
输入
第一行包含一个整数t(1≤t≤500)--测试案例的数量。
每个测试用例由两行组成。第一行包含两个整数n和x(1≤n≤500,0≤x≤500)--序列中元素的数量和x的初始值。
第二行包含n个整数a1,a2,...,an(0≤ai≤500)。
在输入的所有测试案例中,n的值之和不超过500。
输出
对于每个测试案例,打印一个整数--你必须执行的最小操作数,如果不可能,则打印-1。
例子
inputCopy
6
4 1
2 3 5 4
5 6
1 1 3 4 4
1 10
2
2 10
11 9
2 10
12 11
5 18
81 324 218 413 324
输出拷贝
3
0
0
-1
1
3
题解:
由于n的范围很小我们可以考虑暴力的方法,通过观察我们发现,如果出现a[i] > a[i+1]
如果可以修改结果就会变为a[i] = a[i-1] a[i-1] = a[i-2] .... a[i-k] = x
x = a[i]
x是在不断变大的,我们只需要模拟这个过程即可,并且每次check是否为非降序排列
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<string>
#include<map>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
int a[505];
int n,x;
int check()
{
for(int i = 2;i <= n;i++)
{
if(a[i] < a[i-1])
{
return 0;
}
}
return 1;
}
void solve()
{
// int n,x;
cin >> n >> x;
for(int i = 1;i <= n;i++)
{
cin >> a[i];
}
if(check())
{
cout<<"0\n";
return ;
}
int ans = 0;
for(int i = 1;i <= n;i ++)
{
if(a[i] > x)
{
swap(a[i],x);
ans++;
}
if(check())
{
cout<<ans<<"\n";
return ;
}
}
cout<<"-1\n";
}
signed main()
{
int t = 1;
cin >> t;
while(t--)
{
solve();
}
}