不要被事物的表面现象所迷惑~
- 🌳前言
- 🌳结构声明
- 🌳接口算法实现
- 🍎动态开辟&初始化【Init】
- 🍎尾插【PushBack】
- 🍎尾删【PopBack】
- 🍎头插【PushFront】
- 🍎头删【PopFront】
- 💻阶段测试一
- 🍌查找指定结点【FindNode】
- 🍌插入【Insert】
- 直接万用版
- 直接复用版
- 🍌删除【Erase】
- 直接万用版
- 直接复用版
- 💻阶段测试二
- 🍒打印【Print】
- 🍒判空【Empty】
- 🍒求解链表大小【Size】
- 🍒释放【Destroy】
- 🌳OJ题目实训
- 【LeetCode】138 - 复制带随机指针的链表
- 🌳整体代码展示
- 🌳总结与提炼
🌳前言
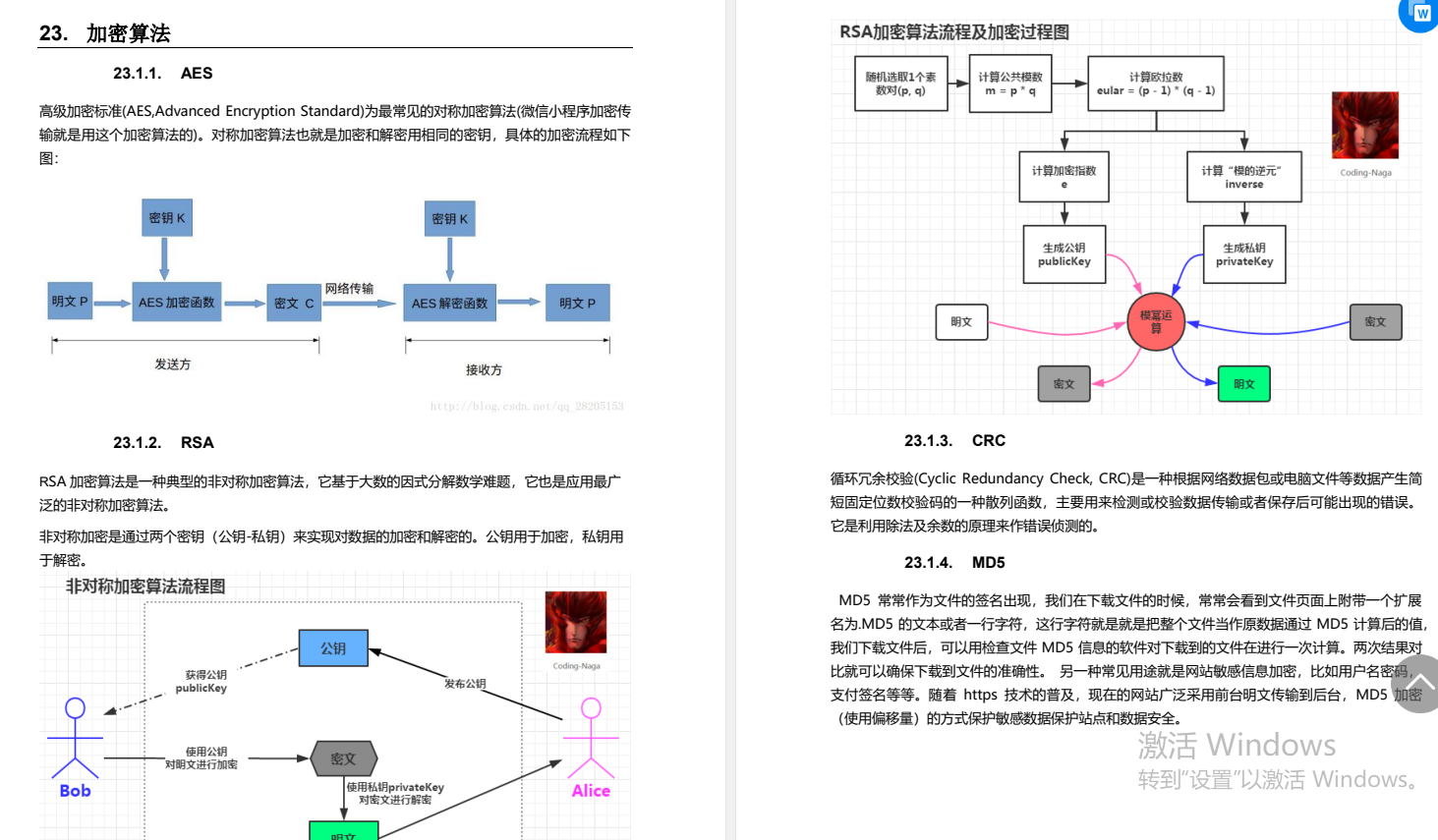
- 在上一文中,我们讲到了【单链表】,这种单链表的结构呢是所有链表之中最简单的,因为它不带头、是单向的,而且不循环,所以看起来非常得简洁,看过我这篇文章的小伙伴应该可以知晓。其各种算法结构实现起来确实非常麻烦,各种二级指针的传参以及各种边界条件的判断,都需要很熟练的指针把控技巧
- 但我们还是需要这种简单的结构,因为简洁的单链表一般可以作为其他复杂数据结构的子结构,比如说哈希桶、图的邻接表等等,这个我后续都会讲解到
- 那我们只学习这一种链表结构就可以了吗,答案是:不可以。因为单链表的结构虽然简单,但是缺陷太多,实现起来非常的繁琐,不利于企业中的开发,于是我们就需要学习另一种链表的数据结构叫做【双链表】,也就是本节所要介绍的内容,对于双链表,我要介绍的这种是最复杂的,也就是【带头双向循环链表】,可以看到,与单链表相比,它不带头但是我带头,它是单向我是双向,它不循环但是我循环
- 那有同学说,这完全就是一个极端呀,这么复杂的数据结构我能学的会吗😢,单链表已经复杂成这个样子,那它不是更加复杂了?
- 那我告诉你,其实这个结构并不复杂,只是它看起来比较复杂,但是实现起来却非常方便,先给你吃一个定心丸,接下去我们就好好来研究一下这个复杂的结构
🌳结构声明
- 首先来看一下它的结构声明是怎样的。可以看到,其具有一个data域和两个指针域,连个指针域分别是【prev】前驱指针以及【next】后继指针,分别指向前面和后面一个结点
typedef int DLDataType;
typedef struct DLinkList {
DLDataType data;
struct DLinkList* prev;
struct DLinkList* next;
}DList;
- 可以看到,其结构体是比单链表来得复杂,但是你要这么像,给你的条件多了,多了一个【prev】指针,从代码实现的角度来看何尝不是一件好事呢?你就可以很轻易地找到当前结点的前一个结点了,不需要再从头开始遍历
🌳接口算法实现
接下去我们来看看双链表的接口算法实现。内容还是和单链表基本一致,只是内部实现的算法逻辑需要做一个改动
🍎动态开辟&初始化【Init】
- 好,首先我们来说一说如何去进行初始化,因为是带头,所以其初始化就需要去将这个头结点进行一个处理,然后又因为是双向的,所以我们需要去处理两个指针,也就是【prev】和【next】,那要怎么进行一个初始化呢,我们又可以观察到,这是一个循环的链表,那对于一个只有头结点的循环链表,其【prev】和【next】都是指向它自己的,然后对于【data】域的话我们直接置为【-1】就好了,表示这是开始,因为不可以将这个头置空。
- 所以一开始的头结点初始化应该是下面这样的
- 我们来看一下代码
- 可以看到,这里的初始化结点,我使用的是一级指针,没有像单链表里面那样使用二级指针,其实不使用二级指针传参的话是改变不了这个链表的结构的,只是函数内部做了一个修改,但是我们知道,想对头结点做一个改动有以下是那种方法
①传二级指针 ②C++引用【&】传参 ③设置返回值 - 由于我的数据结构是使用纯C实现的,所以我没有使用C++中的引用,而是使用的第三种方法,也就是【设置返回值】,将我修改后的头结点做一个返回,然后外部使用一个结构体指针做一个接收,便可以获取到内部函数所修改的结点
/*初始化结点*/
DList* DlistInit()
{
DList* phead = DListBugNode(-1);
phead->prev = phead;
phead->next = phead;
return phead;
}
DList* phead = DlistInit();
- 然后是这个申请结点的代码,这个我在单链表中做过详细介绍,就不多讲了
/*开辟一个结点空间*/
DList* DListBugNode(DLDataType x)
{
DList* newnode = (DList*)malloc(sizeof(DList));
if (newnode == NULL) {
perror("fail malloc");
exit(-1);
}
newnode->data = x;
newnode->prev = NULL;
newnode->next = NULL;
return newnode;
}
🍎尾插【PushBack】
- 好,我们来说说尾插,不要紧张,没有你想得那么复杂
- 可以看到,我们在后面增加一个结点,此时我们只需要修改一下【prev】和【next】这两个指针即可
- 但是在这之前呢,因为你是要在最后一个结点之后新增一个结点,所以你要找到做好一个结点的地址才可以,那我们怎么去找呢,始终要牢记,这是一个双向循环链表,是循环的!!!最后一个结点指向头结点,那么头结点也就是保存着尾结点的地址,因此第一步我们就需要通过头来找到这个尾结点
//1、首先需要找到尾指针
DList* tail = phead->prev;
- 有了指向这个尾结点的结构体指针,就可以去修改其指针域了,
//2、修改指针域进行插入
tail->next = newnode;
newnode->prev = tail;
newnode->next = phead;
phead->prev = newnode;
那有同学说,真的就是这么简单吗?是的,真的就是这样。为什么不禁锢你的思维,我们再来看一种特殊的
- 可以看到,也就是下面这个直接在头结点之后进行的尾插,对照上面的代码你可以发现,一样适用,不需要做额外的判断
- 很清晰,很简略,很震撼
- 没错,这个链表的操作就是这么容易,其实这些指针的修改时很容易出错的,但是你在经历过【单链表】的地狱训练🎃后,就会觉得这个双链表也就那样。好,我么继续看下去,难点后面还是有的👇
🍎尾删【PopBack】
- 来看看尾删,对于尾删,也是一样,修改一下其指针域的指向接即可

- 首先,我们一样需要去找到这个尾结点,通过头结点去找
//1.先找到尾指针
DList* tail = phead->prev;
- 通过链表的学习我们可以知道,要删除一个结点,那就要找到它的前驱结点,因为只有这个前驱结点才是指向这个当前要删除结点的,需要删除当前这个结点,就是要修改其前驱结点的【next】指向。这个时候双向链表的优势就来了,只需要一个【prev】指针,便可以很轻易找到这个结点
//2.保存待删结点的上一个结点
DList* pre = tail->prev;
- 然后的话就是修改指针域即可
//3.修改指针域进行删除
pre->next = phead;
phead->prev = pre;
free(tail);
- 一样,我们再通过特殊情况做一个分析✍
- 找到当前待删的尾结点的上一个结点,也就是头结点,然后使头结点的【next】域指向头结点就是它自己,让头结点【prev】指向待删结点的上一二个结点,也就是头结点自己,那就可以看出,还原成我们初始化的那个样子了
- 其实善于观察的小伙伴已经可以得出结论了,这个【带头双向循环链表】是一个很完美的结构,无论是对于现在的尾插和尾删,对于头插和头删以及后续的操作,其实都依赖于这个结构的完整性
- 看我画的图是不是很工整呢😄
🍎头插【PushFront】
- 接下去我们继续看看头插,一样是通过普通示例和特殊示例来观察👀
- 刚才有忽略的一个点,就是插入结点的时候需要动态开辟,也就是我们的【BuyNode】,这个大家不要忘了
DList* newnode = DListBugNode(x);
- 从图中可以看出,对于这个即将插入的结点,我很明确地画出了这个指针域的修改过程,是存在顺序的;你要先去修改待插入结点和首结点的指针指向,若是你直接去修改头结点和待插入结点的指针指向,因为头结点的【next】域存放的是首结点的地址,若是随意修改,就找不到首结点了
- 所以应该按照这个顺序来🐟
//需要考虑顺序
newnode->next = phead->next;
phead->next->prev = newnode;
phead->next = newnode;
newnode->prev = phead;
- 当然,你也可以选择不考虑顺序,这样的话就需要先去保存一下头结点的下一个结点也就是首结点
DList* first = phead->next;
//无需考虑顺序
phead->next = newnode;
newnode->prev = phead;
newnode->next = first;
first->prev = newnode;
- 可以看到,以上这种是完全不需要考虑顺序的,直接修改即可
接下来看看特殊的插入
- 可以看到,对于头插和尾插,都是一样的,就是在头结点之后插入,而对于单链表而言则是不同
- 对照上面的代码可以发现,又是可以进行复用的,完全不需要进行特殊情况的判断
🍎头删【PopFront】
- 接着继续看头删
- 为了增加代码的可读性,我不会出现【cur->next->next】这样的代码,所以会定义一些变量来帮助大家理解
- 首先,为了进行头删,我需要先行保存待删结点的下一个结点,因为待删结点中就存有它的地址,之后修改一下指向,让首结点指向它即可
DList* cur = phead->next;
DList* nextNode = cur->next;
phead->next = nextNode;
nextNode->prev = phead;
free(cur);
- 主要再来看特殊情况。我们依旧可以使用尾插的图示来复用
- 对照代码,我们来看【cur】即为首结点,【nextNode】为cur的next,也及时头结点,然后执行【phead->next = nextNode】和【nextNode->prev = phead】,离奇般的又可以链接上了🔒
💻阶段测试一
- 好,我们进行一个小结:看完了尾删、尾删、头插、头删,你应该觉得双链表虽然看起来很复杂,但是其接口的算法实现却一点也不复杂,只需要修改一下指针的指向即可
- 接下去我们使用上面的代码进行一个阶段性的测试【测试代码后面统一给出】
🍌查找指定结点【FindNode】
- 对于查找,很简单,我们在单链表中也讲到过,因此不做细讲
/*查找*/
DList* DListFind(DList* phead, DLDataType x)
{
DList* cur = phead->next;
while (cur != phead)
{
if (cur->data == x)
return cur;
cur = cur->next;
}
}
🍌插入【Insert】
- 好,接下来我们再来说一说这个【insert】插入,这个值得是在给出的【pos】指针所指结点的前面插入一个结点
- 若是这个【pos】位置位于链表中间的某处,也是一样修改指针域的指向即可,但是要先找到【pos】所指结点的前一个结点
DList* pre = pos->prev;
- 找到了之后还是一样,无需考虑顺序,直接做修改即可
pre->next = newnode;
newnode->prev = pre;
newnode->next = pos;
pos->prev = newnode;
- 好,接下去我们一样去考虑一下极端的位置。可以看到,当【pos】位于头结点的下一个结点时,在其前面插入就是一个头插。如果你去试着写一下也可以发现依旧是可以实用的
- 那可以实现头插,一定可以实现尾插,那若是要实现尾插,这个【pos】该在何处呢,因为是要在尾结点后插入一个结点,那其实就是在头结点的前面插入一个结点,就像下面这样。因为这是一个带头的循环链表,头结点和尾结点之间是相互关联的
- 看完了上面的叙述,你应该明白了如何在【pos】所指结点的前一个位置插入结点了吧,我这里给出了两种形式,供你选择
直接万用版
- 这种是直接在这个【Insert】函数里做判断,就可以直接用,看清楚,参数是三个
/*插入 - 万能版*/
void DListInsert2(DList* phead, DList* pos, DLDataType x)
{
if (pos == phead->next)
DListPushFront(phead, x);
else if (pos == phead)
DListPushBack(phead, x);
else
{
DList* pre = pos->prev;
DList* newnode = DListBugNode(x);
pre->next = newnode;
newnode->prev = pre;
newnode->next = pos;
pos->prev = newnode;
}
}
直接复用版
- 这种是将头插和尾插的内核代码直接复用【Insert】,是将头结点,所以参数是两个
/*头插*/
DListInsert1(phead->next, x);
/*尾插*/
DListInsert1(phead, x);
/*插入 - 复用版*/
void DListInsert1(DList* pos, DLDataType x)
{
assert(pos);
DList* pre = pos->prev;
DList* newnode = DListBugNode(x);
pre->next = newnode;
newnode->prev = pre;
newnode->next = pos;
pos->prev = newnode;
}
🍌删除【Erase】
- 有插入(Insert),一定有删除(Erase)
- 但是对于删除,我们是删除当前【pos】位置所指结点,而不是上一个
- 想必,不用我说你都可以分析出来这也是可以复用的吧【你他喵就是懒得讲好吧o(=•ェ•=)m】
直接万用版
/*删除 - 万能版*/
void DListErase2(DList* phead, DList* pos)
{
assert(pos);
if (pos == phead->next)
DListPopFront(phead); //传入的是phead,不传pos,否则会出错
else if (pos == phead->prev)
DListPopBack(phead); //传入的是phead,不传pos,否则会出错
else
{
DList* pre = pos->prev;
DList* nextNode = pos->next;
free(pos);
pre->next = nextNode;
nextNode->prev = pre;
}
}
直接复用版
/*头删*/
DListErase1(phead->next);
/*尾删*/
DListErase1(phead->prev);
/*删除 - 复用版*/
void DListErase1(DList* pos)
{
assert(pos);
DList* pre = pos->prev;
DList* nextNode = pos->next;
free(pos);
pre->next = nextNode;
nextNode->prev = pre;
}
💻阶段测试二
- 好,我们对上面所写的【Insert】和【Erase】做一个测试
- 首先先看下查找结点吧
- 首先是插入的复用版,将【Insert】放到尾插和头插中复用
- 接着就是【直接万用板】,直接使用【Insert】
- 然后来看一下删除【Erase】
- 首先是【直接复用版】
- 然后是【直接万用版】,像删哪个删哪个
可以看出,直接万用版比较灵活,就是需要去查找位置,直接复用版只能进行头插和尾插,比较方便,无需查找位置。看自己喜好使用
🍒打印【Print】
- 可以看到,我上面在测试的的时候使用到了很多Print()语句,接下来我们来看看Print该如何去实现
- 很简单,和单链表一样的思路,【cur】指针代替遍历即可
/*打印*/
void DListPrint(DList* phead)
{
DList* cur = phead->next;
while (cur != phead)
{
printf("%d ", cur->data);
cur = cur->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
🍒判空【Empty】
- 再来看一下如何判空,也就是一个结点都没有的时候,即只有头结点,那也就是我们初始化时的逻辑,头结点的【next】指向它自己
bool DListEmpty(DList* phead)
{
return phead->next == phead;
}
🍒求解链表大小【Size】
- 对于求解链表的大小,其实是求内部有多少个结点,那此时有同学就选择直接return【phead->data】,大家觉得这个对吗,其实是不对的,直接去用头结点的【data】值表示的话,除非题目说明这个数据的类型就是整型,否则的话其实是不准确的,因为这个链表中的每一个数据结构不一样时一个数,放到很多现实中的场景中它就有可能是一个人、一条信息了,所以这个data的类型,也就是
typedef int DLDataType;
- 可能是【char】【double】之类的,我们根本不能确定,所以应该去一个个地遍历这些结点,才能去求出这个链表长度
/*求解链表的大小*/
size_t DListSize(DList* phead)
{
size_t sz = 0;
DList* cur = phead->next;
while (cur != phead)
{
sz++;
cur = cur->next;
}
return sz;
}
🍒释放【Destroy】
- 最后的舞台📷,当然是留给【Destroy】了,有初始化,怎么能没有销毁呢,要做到有始有终
/*释放链表*/
void DListDestroy(DList* phead)
{
DList* cur = phead->next;
while (cur != phead)
{
DList* nextNode = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = nextNode; //迭代
}
free(phead); //链表释放完后释放头结点
}
🌳OJ题目实训
【LeetCode】138 - 复制带随机指针的链表
链接
🌳整体代码展示
- 这里给出源码,供需要的小伙伴使用
DList.h
#pragma once
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#include <assert.h>
typedef int DLDataType;
typedef struct DLinkList {
DLDataType data;
struct DLinkList* prev;
struct DLinkList* next;
}DList;
DList* DListBugNode(DLDataType x);
DList* DlistInit();
void DListPushBack(DList* phead, DLDataType x);
void DListPopBack(DList* phead);
void DListPushFront(DList* phead, DLDataType x);
void DListPopFront(DList* phead);
void DListInsert1(DList* pos, DLDataType x);
void DListInsert2(DList* phead, DList* pos, DLDataType x);
void DListErase1(DList* pos);
void DListErase2(DList* phead, DList* pos);
void DListPrint(DList* phead);
DList* DListFind(DList* phead, DLDataType x);
bool DListEmpty(DList* phead);
size_t DListSize(DList* phead);
void DListDestroy(DList* phead);
DList.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
/*
* 带头双向循环链表
*/
#include "DList.h";
/*开辟一个结点空间*/
DList* DListBugNode(DLDataType x)
{
DList* newnode = (DList*)malloc(sizeof(DList));
if (newnode == NULL) {
perror("fail malloc");
exit(-1);
}
newnode->data = x;
newnode->prev = NULL;
newnode->next = NULL;
return newnode;
}
/*初始化结点*/
DList* DlistInit()
{
DList* phead = DListBugNode(-1);
phead->prev = phead;
phead->next = phead;
return phead;
}
/*尾插*/
void DListPushBack(DList* phead, DLDataType x)
{
//assert(phead);
//DList* newnode = DListBugNode(x);
1、首先需要找到尾指针
//DList* tail = phead->prev;
2、修改指针域进行插入
//tail->next = newnode;
//newnode->prev = tail;
//newnode->next = phead;
//phead->prev = newnode;
DListInsert1(phead, x);
}
/*尾删*/
void DListPopBack(DList* phead)
{
//assert(phead);
1.先找到尾指针
//DList* tail = phead->prev;
2.保存待删结点的上一个结点
//DList* pre = tail->prev;
3.修改指针域进行删除
//pre->next = phead;
//phead->prev = pre;
//free(tail);
DListErase1(phead->prev);
}
/*头插*/
void DListPushFront(DList* phead, DLDataType x)
{
//assert(phead);
//DList* newnode = DListBugNode(x);
//需要考虑顺序
//newnode->next = phead->next;
//phead->next->prev = newnode;
//
//phead->next = newnode;
//newnode->prev = phead;
//可以先保存头结点的下一结点
//DList* first = phead->next;
无需考虑顺序
//phead->next = newnode;
//newnode->prev = phead;
//newnode->next = first;
//first->prev = newnode;
DListInsert1(phead->next, x);
}
/*头删*/
void DListPopFront(DList* phead)
{
//assert(phead);
//DList* cur = phead->next;
//DList* nextNode = cur->next;
//phead->next = nextNode;
//nextNode->prev = phead;
//free(cur);
DListErase1(phead->next);
}
/*查找*/
DList* DListFind(DList* phead, DLDataType x)
{
DList* cur = phead->next;
while (cur != phead)
{
if (cur->data == x)
return cur;
cur = cur->next;
}
}
/*插入 - 复用版*/
void DListInsert1(DList* pos, DLDataType x)
{
assert(pos);
DList* pre = pos->prev;
DList* newnode = DListBugNode(x);
pre->next = newnode;
newnode->prev = pre;
newnode->next = pos;
pos->prev = newnode;
}
/*插入 - 万能版*/
void DListInsert2(DList* phead, DList* pos, DLDataType x)
{
if (pos == phead->next)
DListPushFront(phead, x);
else if (pos == phead)
DListPushBack(phead, x);
else
{
DList* pre = pos->prev;
DList* newnode = DListBugNode(x);
pre->next = newnode;
newnode->prev = pre;
newnode->next = pos;
pos->prev = newnode;
}
}
/*删除 - 复用版*/
void DListErase1(DList* pos)
{
assert(pos);
DList* pre = pos->prev;
DList* nextNode = pos->next;
free(pos);
pre->next = nextNode;
nextNode->prev = pre;
}
/*删除 - 万能版*/
void DListErase2(DList* phead, DList* pos)
{
assert(pos);
if (pos == phead->next)
DListPopFront(phead);
else if (pos == phead->prev)
DListPopBack(phead);
else
{
DList* pre = pos->prev;
DList* nextNode = pos->next;
free(pos);
pre->next = nextNode;
nextNode->prev = pre;
}
}
/*打印*/
void DListPrint(DList* phead)
{
DList* cur = phead->next;
while (cur != phead)
{
printf("%d ", cur->data);
cur = cur->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
/*判空*/
bool DListEmpty(DList* phead)
{
return phead->next == phead;
}
/*求解链表的大小*/
size_t DListSize(DList* phead)
{
size_t sz = 0;
DList* cur = phead->next;
while (cur != phead)
{
sz++;
cur = cur->next;
}
return sz;
}
/*释放链表*/
void DListDestroy(DList* phead)
{
DList* cur = phead->next;
while (cur != phead)
{
DList* nextNode = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = nextNode; //迭代
}
free(phead); //链表释放完后释放头结点
}
test.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include "DList.h"
/*头插、尾插、头删、尾删*/
void DListTest1()
{
DList* phead = DlistInit();
DListPushBack(phead, 1);
DListPushBack(phead, 2);
DListPushBack(phead, 3);
DListPushBack(phead, 4);
DListPushBack(phead, 5);
DListPrint(phead);
DListPopBack(phead);
DListPrint(phead);
DListPushFront(phead, 9);
DListPushFront(phead, 11);
DListPrint(phead);
DListPopFront(phead);
DListPopFront(phead);
DListPopFront(phead);
DListPopFront(phead);
DListPopFront(phead);
//DListPopFront(phead);
DListPrint(phead); //此时头结点的prev和next相同,都指向自己
DListDestroy(phead);
}
/*查找结点*/
void DListTest2()
{
DList* phead = DlistInit();
DListPushBack(phead, 1);
DListPushBack(phead, 2);
DListPushBack(phead, 3);
DListPushBack(phead, 4);
DListPushBack(phead, 5);
DListPrint(phead);
DList* pos = DListFind(phead, 3);
if (pos)
{
pos->data *= 10;
}
DListPrint(phead);
DListDestroy(phead);
}
/*Insert插入 - 直接复用版*/
void DListTest3()
{
DList* phead = DlistInit();
DListPushFront(phead, 1);
DListPushFront(phead, 2);
DListPushFront(phead, 3);
DListPushFront(phead, 4);
DListPushFront(phead, 5);
DListPrint(phead);
DListPushBack(phead, 6);
DListPushBack(phead, 7);
DListPushBack(phead, 8);
DListPushBack(phead, 9);
DListPushBack(phead, 10);
DListPrint(phead);
DListDestroy(phead);
}
/*Insert插入 - 直接万用版*/
void DListTest4()
{
DList* phead = DlistInit();
DListPushBack(phead, 1);
DListPushBack(phead, 2);
DListPushBack(phead, 3);
DListPushBack(phead, 4);
DListPushBack(phead, 5);
DListPrint(phead);
DList* pos = DListFind(phead, 3); //中间结点
if (pos)
{
DListInsert2(phead, pos, 9);
}
DListPrint(phead);
pos = DListFind(phead, 1); //首结点 - 头插
if (pos)
{
DListInsert2(phead, pos, 99);
}
DListPrint(phead);
pos = DListFind(phead, -1); //链表头结点 - 尾插
if (pos)
{
DListInsert2(phead, pos, 999);
}
DListPrint(phead);
DListDestroy(phead);
}
/*Erase删除 - 直接复用版*/
void DListTest5()
{
DList* phead = DlistInit();
DListPushFront(phead, 1);
DListPushFront(phead, 2);
DListPushFront(phead, 3);
DListPushFront(phead, 4);
DListPushFront(phead, 5);
DListPushBack(phead, 6);
DListPushBack(phead, 7);
DListPushBack(phead, 8);
DListPushBack(phead, 9);
DListPushBack(phead, 10);
DListPrint(phead);
DListPopFront(phead);
DListPopBack(phead);
DListPrint(phead);
DListPopFront(phead);
DListPopBack(phead);
DListPrint(phead);
DListPopFront(phead);
DListPopBack(phead);
DListPrint(phead);
DListPopFront(phead);
DListPopBack(phead);
DListPrint(phead);
DListDestroy(phead);
}
/*Erase删除 - 直接万用版*/
void DListTest6()
{
DList* phead = DlistInit();
DListPushBack(phead, 1);
DListPushBack(phead, 2);
DListPushBack(phead, 3);
DListPushBack(phead, 4);
DListPushBack(phead, 5);
DListPrint(phead);
DList* pos = DListFind(phead, 2);
if (pos)
DListErase2(phead, pos);
DListPrint(phead);
pos = DListFind(phead, 5);
if (pos)
DListErase2(phead, pos);
DListPrint(phead);
pos = DListFind(phead, 1);
if (pos)
DListErase2(phead, pos);
DListPrint(phead);
DListDestroy(phead);
}
/*头删复用Erase*/
void DListTest7()
{
DList* phead = DlistInit();
DListPushBack(phead, 1);
DListPushBack(phead, 2);
DListPushBack(phead, 3);
DListPushBack(phead, 4);
DListPushBack(phead, 5);
DListPrint(phead);
DListPopFront(phead);
DListPrint(phead);
DListPopFront(phead);
DListPrint(phead);
DListPopFront(phead);
DListPrint(phead);
DListPopFront(phead);
DListPrint(phead);
DListPopFront(phead);
DListPrint(phead);
DListDestroy(phead);
}
/*。。。*/
void DListTest8()
{
DList* phead = DlistInit();
bool ret = DListEmpty(phead);
if (ret)
printf("链表为空\n");
else
printf("链表不为空\n");
DListPushBack(phead, 1);
DListPushBack(phead, 2);
DListPushBack(phead, 3);
DListPushBack(phead, 4);
DListPushBack(phead, 5);
DListPrint(phead);
ret = DListEmpty(phead);
if (ret)
printf("链表为空\n");
else
printf("链表不为空\n");
size_t sz = DListSize(phead);
printf("当前链表大小为:%d\n", sz);
DListDestroy(phead);
}
int main(void)
{
//DListTest1();
//DListTest2();
//DListTest3();
//DListTest4();
//DListTest5();
//DListTest6();
//DListTest7();
DListTest8();
return 0;
}
🌳总结与提炼
- 好,最后我们来总结一下本所讲解的内容,在本文中,我们认识了一个很复杂的结构,叫做【带头双向循环链表】,虽然这个结构看起来很复杂,但是在我们实现其接口算法的时候就可以感觉到虽然其结构复杂,但是具体的代码实现却并不复杂,只要画个图清楚了思路,那只需要修改一下指针的指向即可
- 其实这个就像是做题一样,题目给到我们的信息越多,那你所拥有的就越多,可以帮助你解出问题,但是当题目给给到你一句话的时候,让你去求一个未知的东西,那就需要你自己去想象然后去实现一些东西,就会感觉到很难,所以有点的时候不要被很长的题目给吓到了,要细心阅读,从中筛选出有用的信息,去解决问题
OK,以上就是本文所要介绍的所有内容,非常感谢您的观看,如有疑问请于评论区留言或者私信我都可以🍀