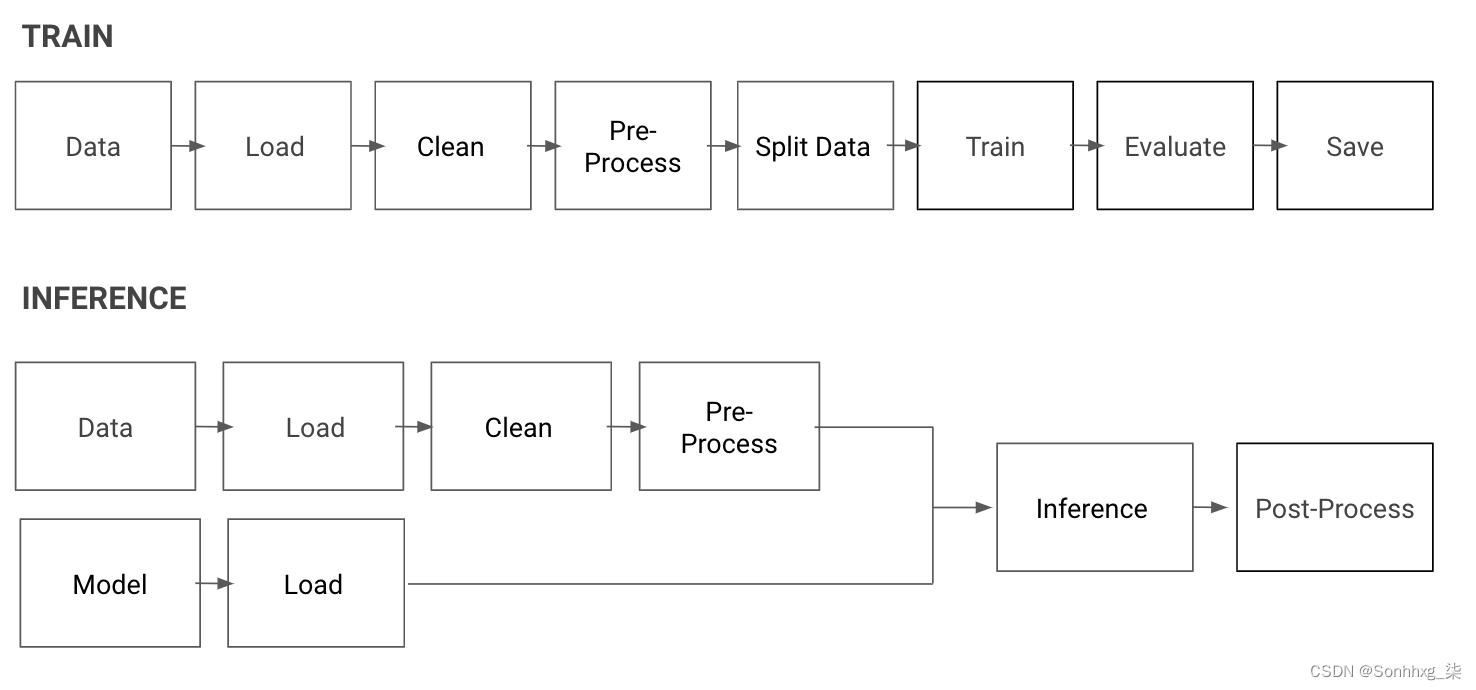
知识点:Budget Constraint
例题
Question: Budget Constraint
Hurley’s income: $1200, Prices: PF = $4 per fish, PM = $1 per mango
A. If Hurley spends all his income on fish, how many fish does he buy?
B. If Hurley spends all his income on mangos, how many mangos does he buy?
C. If Hurley buys 100 fish, how many mangos can he buy?
D. Plot each of the bundles from parts A – C on a graph that measures fish on the horizontal axis and mangos on the vertical, connect the dots.
E. Show what happens to Hurley’s budget constraint if:
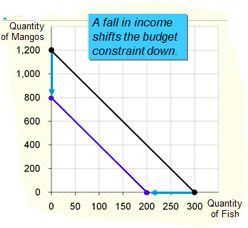
1. His income falls to $800.
2. The price of mangos rises to PM = $2 per mango
解析
A. $1200/$4 = 300 fish
B. $1200/$1 = 1200 mangos
C. 100 fish cost $400, $800 left buys 800 mangos
D.
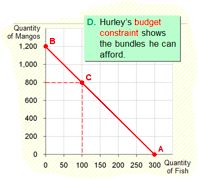
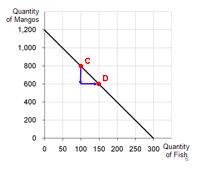
From C to D, “rise” = –200 mangos
“run” = +50 fish
Slope = – 4
Hurley must give up 4 mangos to get one fish.
The slope of the budget constraint equals
· the rate at which Hurley can trade mangos for fish
· the opportunity cost of fish in terms of mangos
· the relative price of fish
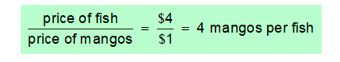
E. 1 Now, Hurley can buy $800/$4= 200 fish or $800/$1 = 800 mangos or any combination in between.
2 Hurley can still buy 300 fish.
But now he can only buy $1200/$2 = 600 mangos.
Notice: slope is smaller, relative price of fish is now only 2 mangos.
下面我们为大家准备了一道同类型的题目,请大家一起来试试解答。
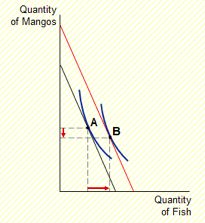
Question: Inferior vs. normal goods
· An increase in income increases the quantity demanded of normal goods and reduces the quantity demanded of inferior goods.
· Suppose fish is a normal good but mangos are an inferior good.
· Use a diagram to show the effects of an increase in income on Hurley’s optimal bundle of fish and mangos.
(答案见下方)
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
正确答案:
If mangos are inferior, the new optimum will contain fewer mangos.